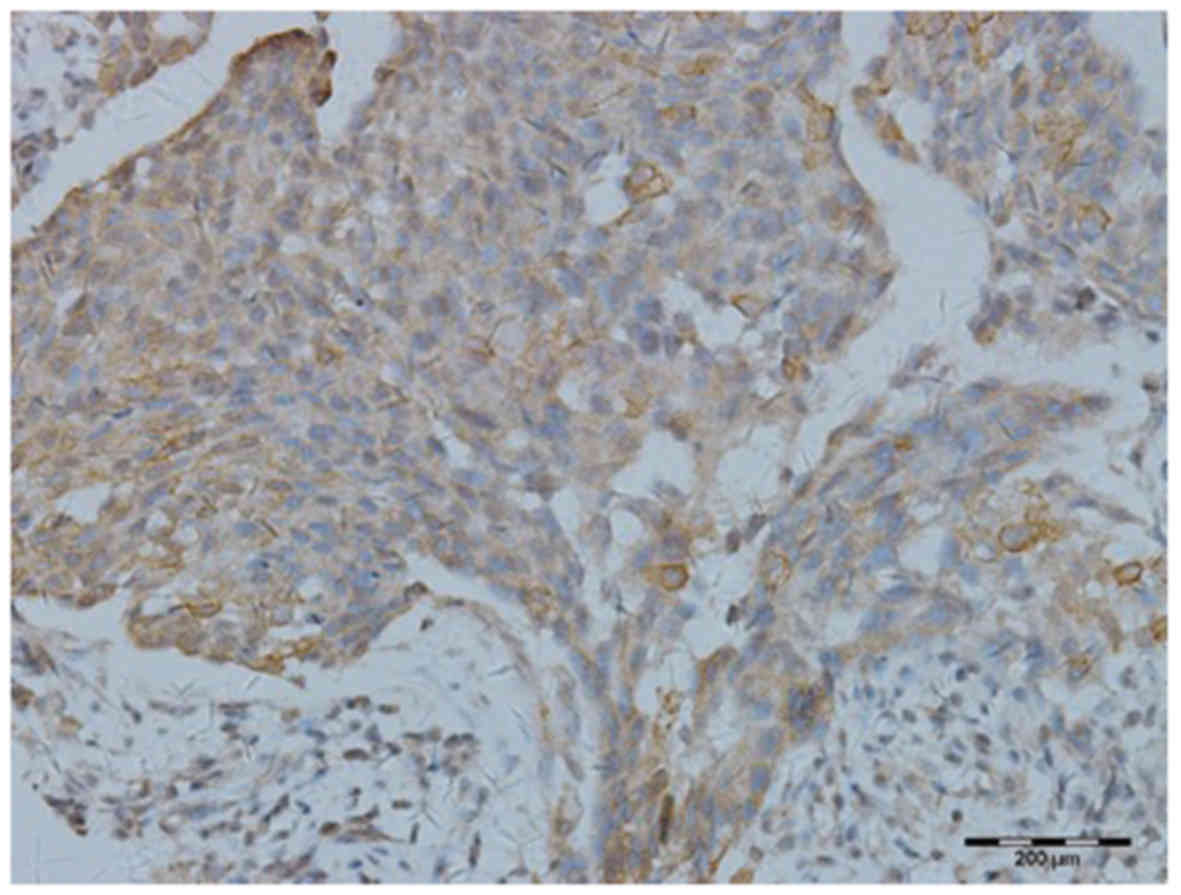
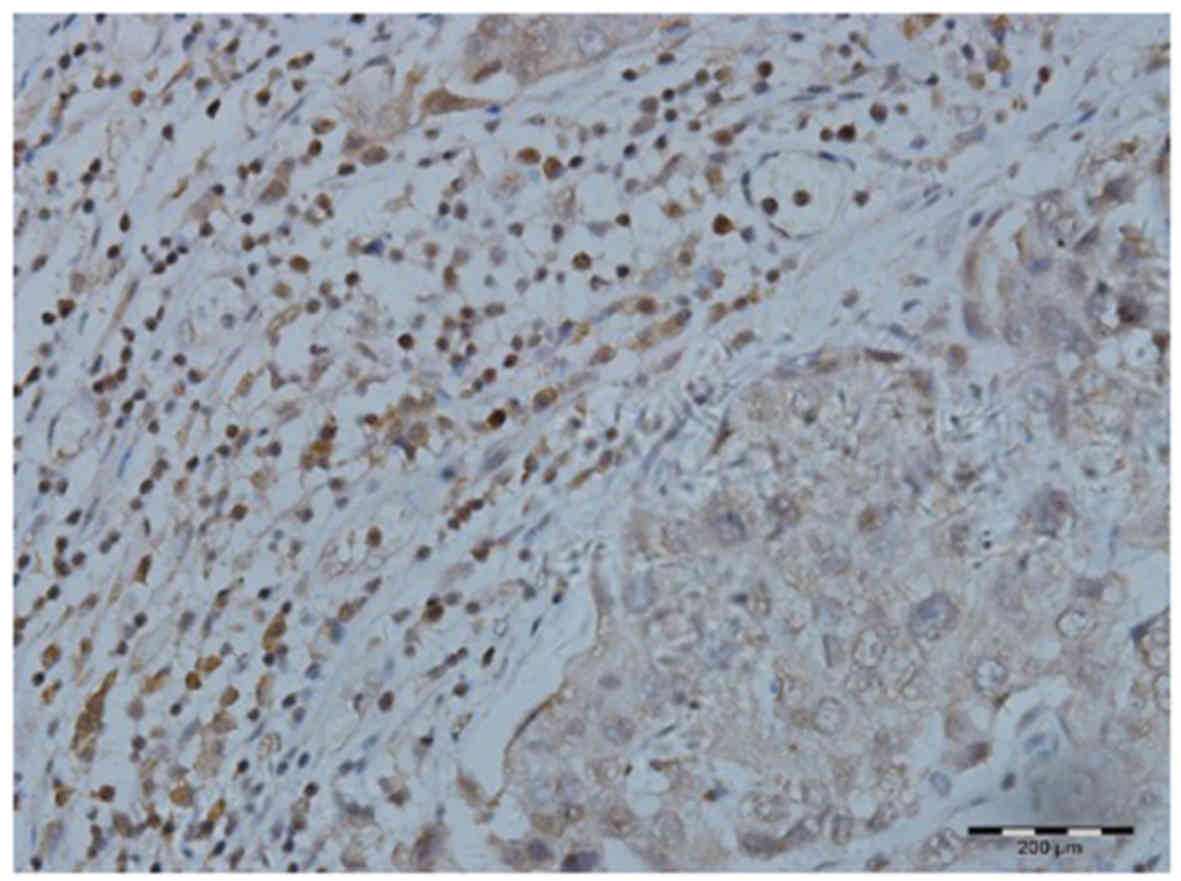
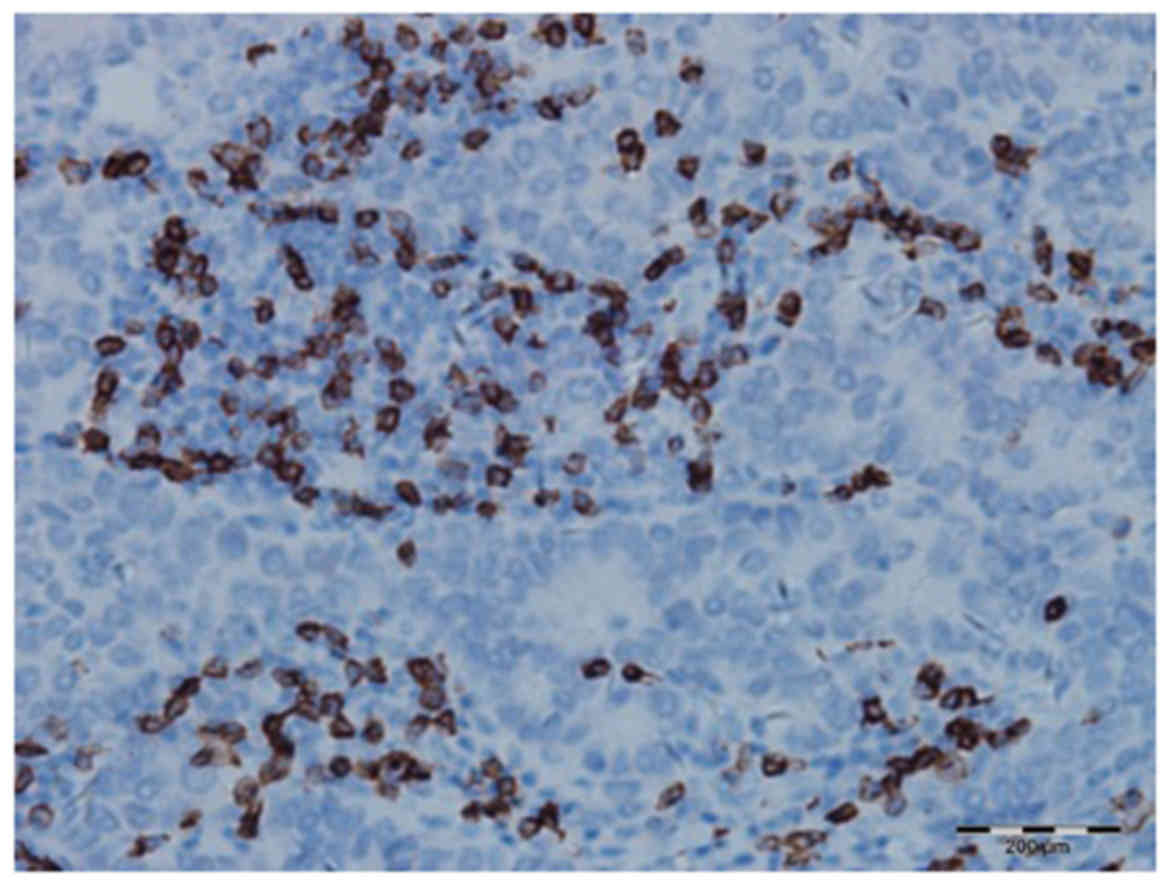
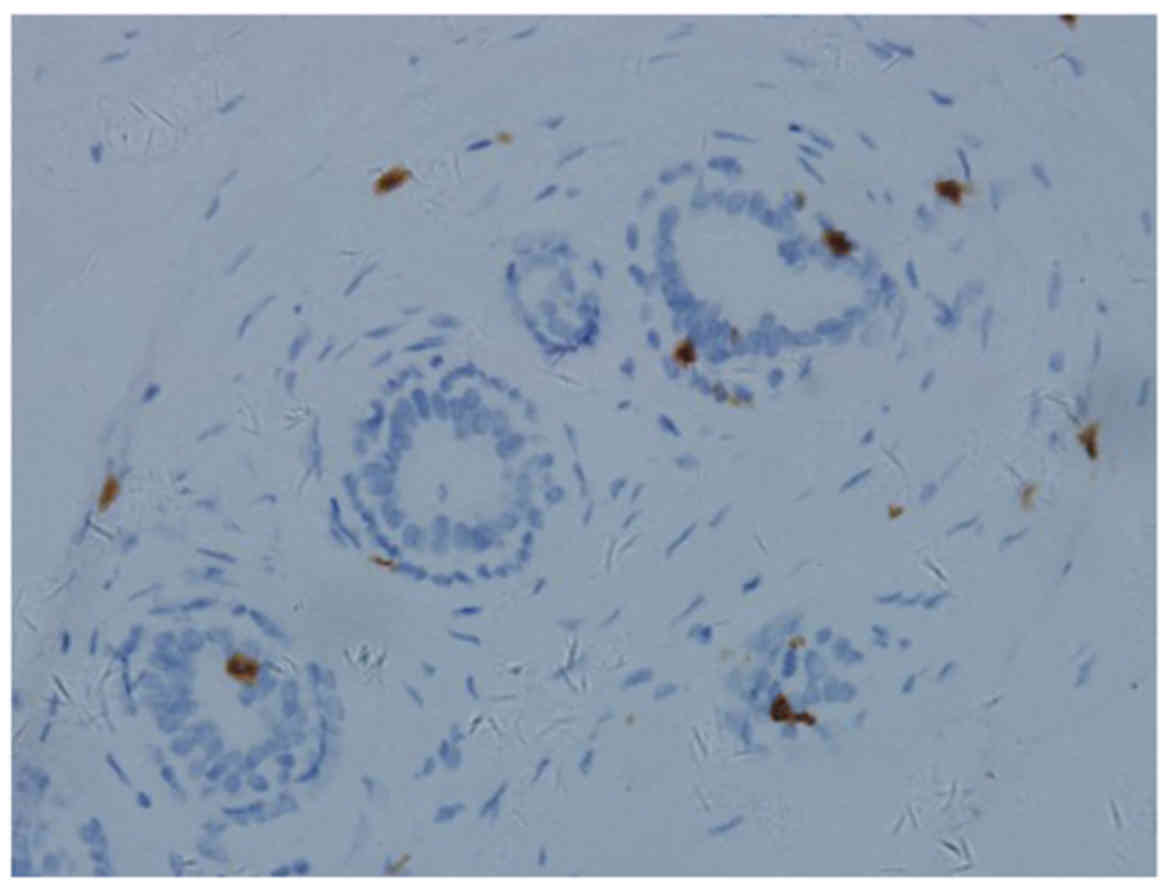
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eccles SA, Aboagye EO, Ali S, Anderson AS,
Armes J, Berditchevski F, Blaydes JP, Brennan K, Brown NJ, Bryant
HE, et al: Critical research gaps and translational priorities for
the successful prevention and treatment of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 15:R922013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McIntire JJ, Umetsu SE, Akbari O, Potter
M, Kuchroo VK, Barsh GS, Freeman GJ, Umetsu DT and DeKruyff RH:
Identification of Tapr (an airway hyperreactivity regulatory locus)
and the linked Tim gene family. Nat Immunol. 2:1109–1116. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McIntire JJ, Umetsu DT and DeKruyff RH:
TIM-1, a novel allergy and asthma susceptibility gene. Springer
Semin Immunopathol. 25:335–348. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hastings WD, Anderson DE, Kassam N,
Koguchi K, Greenfield EA, Kent SC, Zheng XX, Strom TB, Hafler DA
and Kuchroo VK: TIM-3 is expressed on activated human CD4+ T cells
and regulates Th1 and Th17 cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 39:2492–2501.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anderson AC, Anderson DE, Bregoli L,
Hastings WD, Kassam N, Lei C, Chandwaskar R, Karman J, Su EW,
Hirashima M, et al: Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune
receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science.
318:1141–1143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khademi M, Illés Z, Gielen AW, Marta M,
Takazawa N, Baecher-Allan C, Brundin L, Hannerz J, Martin C, Harris
RA, et al: T Cell Ig- and mucin-domain-containing molecule-3
(TIM-3) and TIM-1 molecules are differentially expressed on human
Th1 and Th2 cells and in cerebrospinal fluid-derived mononuclear
cells in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 172:7169–7176. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakae S, Iikura M, Suto H, Akiba H, Umetsu
DT, Dekruyff RH, Saito H and Galli SJ: TIM-1 and TIM-3 enhancement
of Th2 cytokine production by mast cells. Blood. 110:2565–2568.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anderson AC: Tim-3, a negative regulator
of anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 24:213–216. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Anderson AC, Anderson DE, Bregoli L,
Hastings WD, Kassam N, Lei C, Chandwaskar R, Karman J, Su EW,
Hirashima M, et al: Promotion of tissue inflammation by the immune
receptor Tim-3 expressed on innate immune cells. Science.
318:1141–1143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ngiow SF, Teng MW and Smyth MJ: Prospects
for TIM3-targeted antitumor immunotherapy. Cancer Res.
71:6567–6571. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wiener Z, Kohalmi B, Pocza P, Jeager J,
Tolgyesi G, Toth S, Gorbe E, Papp Z and Falus A: TIM-3 is expressed
in melanoma cells and is upregulated in TGF-beta stimulated mast
cells. J Invest Dermatol. 127:906–914. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhuang X, Zhang X, Xia X, Zhang C, Liang
X, Gao L, Zhang X and Ma C: Ectopic expression of TIM-3 in lung
cancers: A potential independent prognostic factor for patients
with NSCLC. Am J Clin Pathol. 137:978–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yan J, Zhang Y, Zhang JP, Liang J, Li L
and Zheng L: Tim-3 expression defines regulatory T cells in human
tumors. PLoS One. 8:e580062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao Y, Zhou X, Huang X, Li Q, Gao L, Jiang
L, Huang M and Zhou J: Tim-3 expression in cervical cancer promotes
tumor metastasis. PLoS One. 8:e538342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang J, Jin MS, Kong F, Cao D, Ma HX, Jia
Z, Wang YP, Suo J and Cao X: Decreased galectin-9 and increased
Tim-3 expression are related to poor prognosis in gastric cancer.
PLoS One. 8:e817992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang ZZ, Grote DM, Ziesmer SC, Niki T,
Hirashima M, Novak AJ, Witzig TE and Ansell SM: IL-12 upregulates
TIM-3 expression and induces T cell exhaustion in patients with
follicular B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Invest.
122:1271–1282. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakuishi K, Apetoh L, Sullivan JM, Blazar
BR, Kuchroo VK and Anderson AC: Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways
to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. J Exp
Med. 207:2187–2194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sánchez-Fueyo A, Tian J, Picarella D,
Domenig C, Zheng XX, Sabatos CA, Manlongat N, Bender O, Kamradt T,
Kuchroo VK, et al: Tim-3 inhibits T helper type 1-mediated auto-
and alloimmune responses and promotes immunological tolerance. Nat
Immunol. 4:1093–1101. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sabatos CA, Chakravarti S, Cha E, Schubart
A, Sánchez-Fueyo A, Zheng XX, Coyle AJ, Strom TB, Freeman GJ and
Kuchroo VK: Interaction of Tim-3 and Tim-3 ligand regulates T
helper type 1 responses and induction of peripheral tolerance. Nat
Immunol. 4:1102–1110. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Simmons WJ, Koneru M, Mohindru M, Thomas
R, Cutro S, Singh P, Dekruyff RH, Inghirami G, Coyle AJ, Kim BS and
Ponzio NM: Tim-3+ T-bet+ tumor-specific Th1 cells colocalize with
and inhibit development and growth of murine neoplasms. J Immunol.
174:1405–1415. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu WK, Lu XX, Yang S, Xu GP, Lan F, Chen
SX, Ni W, Xiong WN and Xiong SD: Expression of the Th1-specific
cell-surface protein Tim-3 increases in a murine model of atopic
asthma. J Asthma. 46:872–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou Q, Munger ME, Veenstra RG, Weigel BJ,
Hirashima M, Munn DH, Murphy WJ, Azuma M, Anderson AC, Kuchroo VK
and Blazar BR: Coexpression of Tim-3 and PD-1 identifies a CD8+
T-cell exhaustion phenotype in mice with disseminated acute
myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 117:4501–4510. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takamura S, Tsuji-Kawahara S, Yagita H,
Akiba H, Sakamoto M, Chikaishi T, Kato M and Miyazawa M: Premature
terminal exhaustion of Friend virus-specific effector CD8+ T cells
by rapid induction of multiple inhibitory receptors. J Immunol.
184:4696–4707. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao X, Zhu Y, Li G, Huang H, Zhang G, Wang
F, Sun J, Yang Q, Zhang X and Lu B: TIM-3 expression characterizes
regulatory T cells in tumor tissues and is associated with lung
cancer progression. PLoS One. 7:e306762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu J, Liu C, Qian S and Hou H: The
expression of Tim-3 in peripheral blood of ovarian cancer. DNA Cell
Biol. 32:648–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Han S, Feng S, Xu L, Shi W, Wang X, Wang
H, Yu C, Dong T, Xu M and Liang G: Tim-3 on peripheral
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is involved in the development of
glioma. DNA Cell Biol. 33:245–250. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Benallaoua M, Guillaume
P, Luescher IF, Sander C, Kirkwood JM, Kuchroo V and Zarour HM:
Upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor
antigen-specific CD8+T cell dysfunction in melanoma patients. J Exp
Med. 207:2175–2186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|