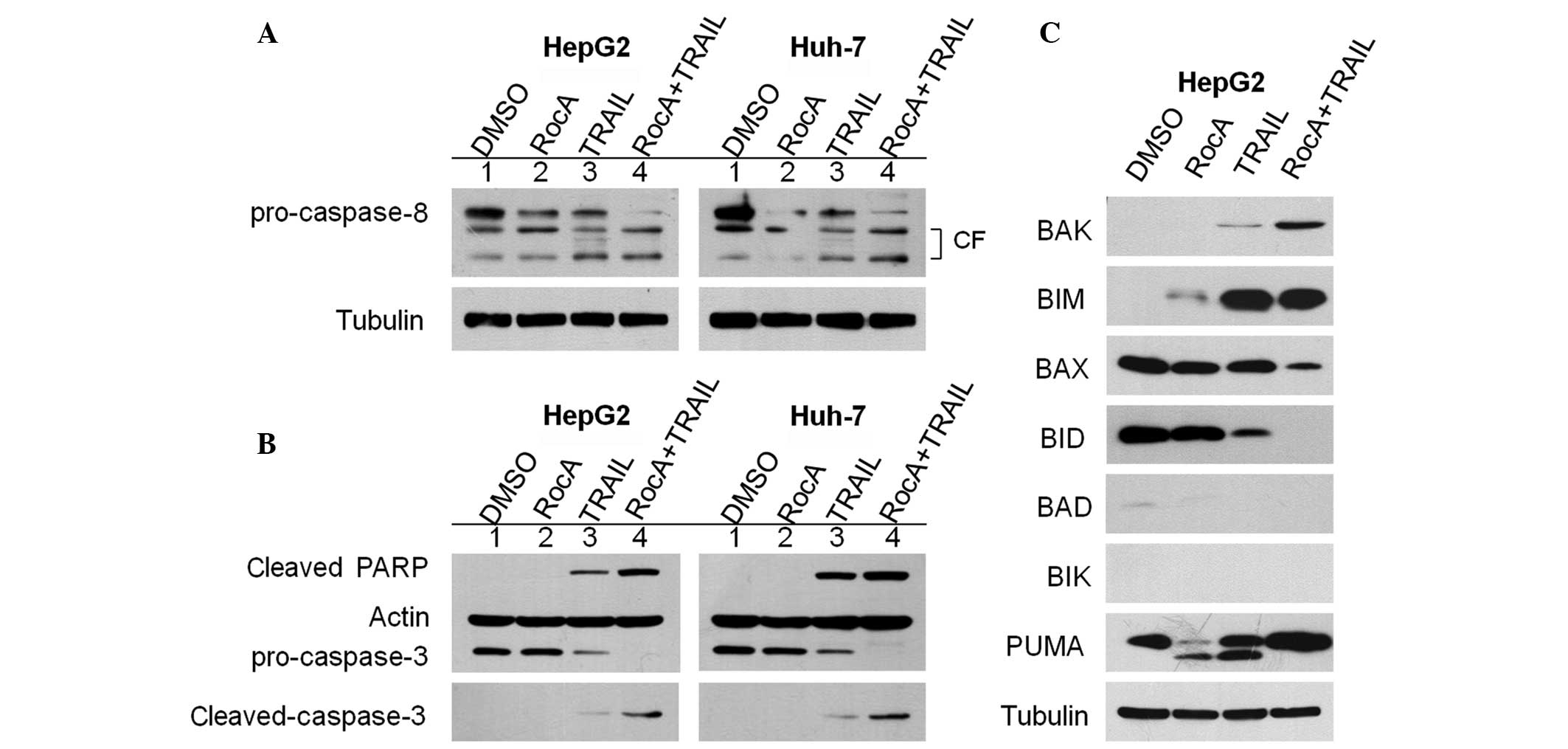
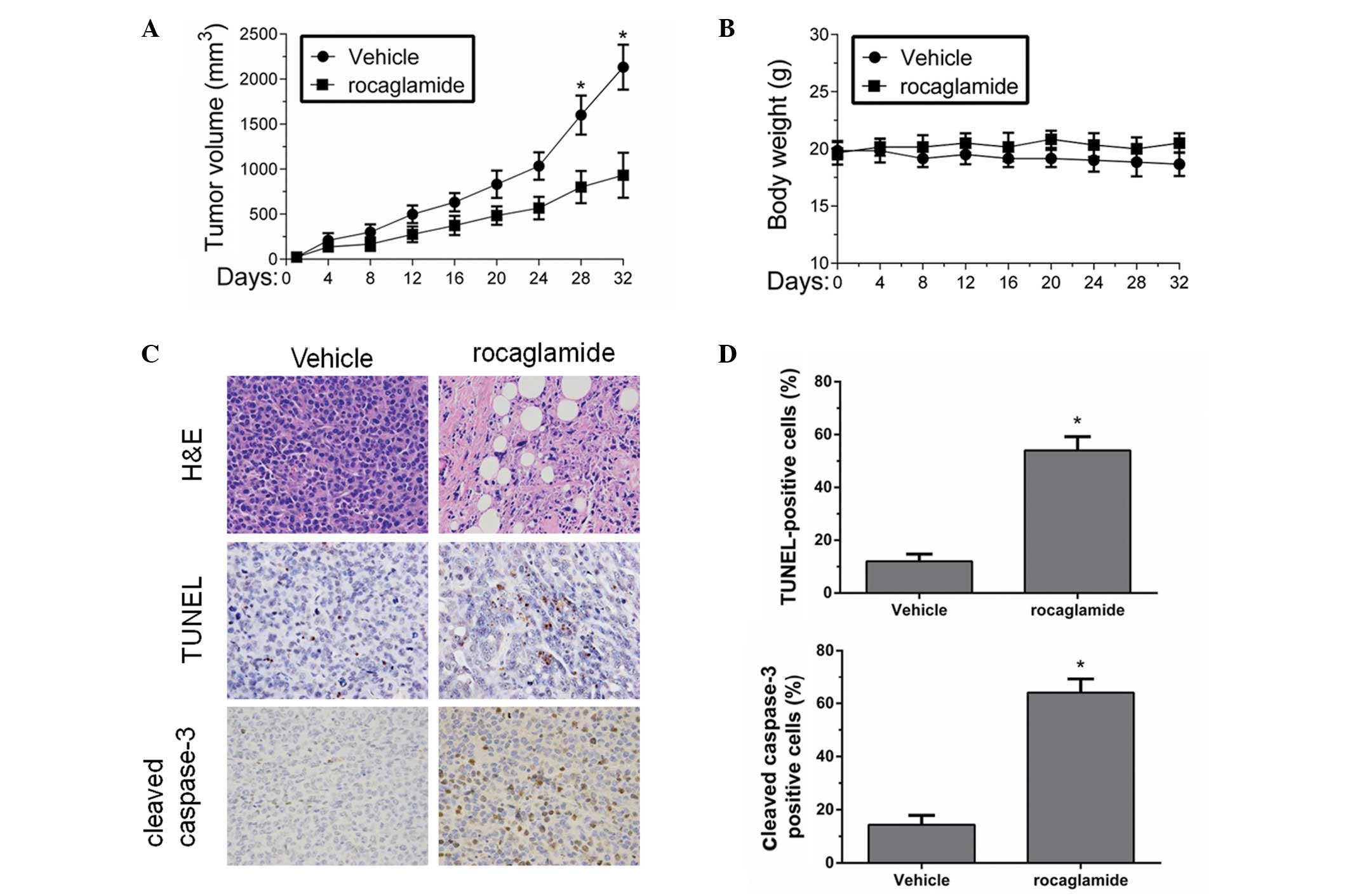
|
1
|
Arzumanyan A, Reis HM and Feitelson MA:
Pathogenic mechanisms in HBV- and HCV-associated hepathocellular
carcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:123–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang K and Lin B: Inhibitor of apoptosis
proteins (IAPs) as regulatory factors of hepatic apoptosis. Cell
Signal. 25:1970–1980. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kischkel FC, Lawrence DA, Chuntharapai A,
Schow P, Kim KJ and Ashkenazi A: Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment
of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5.
Immunity. 12:611–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reed JC: Apoptosis-targeted therapies for
cancer. Cancer Cell. 3:17–22. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hall MA and Cleveland JL: Clearing the
TRAIL for cancer therapy. Cancer Cell. 12:4–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herr I, Schemmer P and Büchler MW: On the
TRAIL to therapeutic intervention in liver disease. Hepatology.
46:266–274. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dickens LS, Boyd RS, Jukes-Jones R, Hughes
MA, Robinson GL, Fairall L, Schwabe JW, Cain K and Macfarlane M: A
death effector domain chain DISC model reveals a crucial role for
caspase-8 chain assembly in mediating apoptotic cell death. Mol
Cell. 47:291–305. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Zhu H, Teraishi F, Davis JJ, Guo
W, Fan Z and Fang B: Accelerated degradation of caspase-8 protein
correlates with TRAIL resistance in a DLD1 human colon cancer line.
Neoplasia. 7:594–602. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haag C, Stadel D, Zhou S, Bachem MG,
Möller P, Debatin KM and Fulda S: Identification of c-FLIP(L) and
c-FLIP(S) as critical regulators of death receptor-induced
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Gut. 60:225–237. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du X, Bao G, He X, Zhao H, Yu F, Qiao Q,
Lu J and Ma Q: Expression and biological significance of c-FLIP in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:242009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lai LJ and Ho TC: Pigment
epithelial-derived factor inhibits c-FLIP expression and assists
ciglitazone-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 31:1173–1180. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim S, Salim AA, Swanson SM and Kinghorn
AD: Potential of cyclopenta[b]benzofurans from Aglaia
species in cancer chemotherapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
6:319–345. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Lucas DM, Edwards RB, Lozanski G, West DA,
Shin JD, Vargo MA, Davis ME, Rozewski DM, Johnson AJ, Su BN, et al:
The novel plant-derived agent silvestrol has B-cell selective
activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic
leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 113:4656–4666. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giaisi M, Köhler R, Fulda S, Krammer PH
and Li-Weber M: Rocaglamide and a XIAP inhibitor cooperatively
sensitize TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Int J
Cancer. 131:1003–1008. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Luan Z, He Y, Alattar M, Chen Z and He F:
Targeting the prohibitin scaffold-CRAF kinase interaction in
RAS-ERK-driven pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer.
13:382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kunzi-Rapp K, Genze F, Küfer R, Reich E,
Hautmann RE and Gschwend JE: Chorioallantoic membrane assay:
vascularized 3-dimensional cell culture system for human prostate
cancer cells as an animal substitute model. J Urol. 166:1502–1507.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen Q, Lou W, Shen J, Ma L, Yang Z, Liu
L, Luo J and Qian C: Potent antitumor activity in experimental
hepatocellular carcinoma by adenovirus-mediated coexpression of
TRAIL and shRNA against COX-2. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3696–3705. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jin Z, Li Y, Pitti R, Lawrence D, Pham VC,
Lill JR and Ashkenazi A: Cullin3-based polyubiquitination and
p62-dependent aggregation of caspase-8 mediate extrinsic apoptosis
signaling. Cell. 137:721–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Häcker S, Dittrich A, Mohr A, Schweitzer
T, Rutkowski S, Krauss J, Debatin KM and Fulda S: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors cooperate with IFN-gamma to restore
caspase-8 expression and overcome TRAIL resistance in cancers with
silencing of caspase-8. Oncogene. 28:3097–3110. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Unterkircher T, Cristofanon S, Vellanki
SH, Nonnenmacher L, Karpel-Massler G, Wirtz CR, Debatin KM and
Fulda S: Bortezomib primes glioblastoma, including glioblastoma
stem cells, for TRAIL by increasing tBid stability and
mitochondrial apoptosis. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4019–4030. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sadlish H, Galicia-Vazquez G, Paris CG,
Aust T, Bhullar B, Chang L, Helliwell SB, Hoepfner D, Knapp B,
Riedl R, Roggo S, Schuierer S, Studer C, Porco JA Jr, Pelletier J
and Movva NR: Evidence for a functionally relevant rocaglamide
binding site on the eIF4A-RNA complex. ACS Chem Biol. 8:1519–1527.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, Schneider P,
Hofmann K, Steiner V, Bodmer JL, Schröter M, Burns K, Mattmann C,
Rimoldi D, French LE and Tschopp J: Inhibition of death receptors
signals by cellular FLIP. Nature. 338:190–195. 1997.
|
|
23
|
Kim JY, Kim EH, Park SS, Lim JH, Kwon TK
and Choi KS: Quercetin sensitizes human hepatoma cells to
TRAIL-induced apoptosis via Sp1-mediated DR5 up-regulation and
proteasome-mediated c-FLIPS down-regulation. J Cell Biochem.
105:1386–1398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bao Q and Shi Y: Apoptosome: a platform
for the activation of initiator caspases. Cell Death Differ.
14:56–65. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang G and Wang X, Yu H, Wei S, Williams
N, Holmes DL, Halfmann R, Naidoo J, Wang L, Li L, Chen S, Harran P,
Lei X and Wang X: Small-molecule activation of the TRAIL receptor
DR5 in human cancer cells. Nat Chem Biol. 9:84–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Takeda K, Wiltrout
RH, Sedger LM, Kayagaki N, Yagita H and Okumura K: Tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) contributes to
interferon gamma-dependent natural killer cell protection from
tumor metastasis. J Exp Med. 193:661–670. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hayakawa Y, Screpanti V, Yagita H,
Grandien A, Ljunggren HG, Smyth MJ and Chambers BJ: NK cell TRAIL
eliminates immature dendritic cells in vivo and limits dendritic
cell vaccination efficacy. J Immunol. 172:123–129. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Villanueva A, Hernandez-Gea V and Llovet
JM: Medical therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical view
of the evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 10:34–42. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nojiri K, Sugimoto K, Shiraki K, Tameda M,
Inagaki Y, Ogura S, Kasai C, Kusagawa S, Yoneda M, Yamamoto N,
Takei Y, Nobori T and Ito M: Sorafenib and TRAIL have synergistic
effect on hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:101–108.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Schattenberg JM, Schuchmann M and Galle
PR: Cell death and hepatocarcinogenesis: Dysregulation of apoptosis
signaling pathways. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:213–219. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Z, Zhou X and Li J, Liu X, Chen Z,
Shen G, Guan T, Ye N, Wei X, Huang N, Yang L, Wei Y and Li J:
Suppression of hepatoma tumor growth by systemic administration of
the phytotoxin gelonin driven by the survivin promoter. Neoplasma.
60:469–479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kelley SK and Ashkenazi A: Targeting death
receptors in cancer with Apo2L/TRAIL. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
4:333–339. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sayers TJ, Brooks AD, Koh CY, Ma W, Seki
N, Raziuddin A, Blazar BR, Zhang X, Elliott PJ and Murphy WJ: The
proteasome inhibitor PS-341 sensitizes neoplastic cells to
TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by reducing levels of c-FLIP. Blood.
102:303–310. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ganten TM, Haas TL, Sykora J, Stahl H,
Sprick MR, Fas SC, Krueger A, Weigand MA, Grosse-Wilde A, Stremmel
W, Krammer PH and Walczak H: Enhanced caspase-8 recruitment to and
activation at the DISC is critical for sensitization of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptotic by
chemotherapeutic drugs. Cell Death Differ. 11(Suppl 1): S86–S96.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Qi L, Bellail AC, Rossi MR, Zhang Z, Pang
H, Hunter S, Cohen C, Moreno CS, Olson JJ, Li S and Hao C:
Heterogeneity of primary glioblastoma cells in the expression of
caspase-8 and the response to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis.
16:1150–1164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaminskyy VO, Surova OV, Vaculova A and
Zhivotovsky B: Combined inhibition of DNA methyltransferase and
histone deacetylase restores caspase-8 expression and sensitizes
SCLC cells to TRAIL. Carcinogenesis. 32:1450–1458. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Yim H, Choi JH, Kim ST, Jin Y and
Lee SK: ATM kinase promotes both caspase-8 and caspase-9 activation
during TNF-α-induced apoptosis of HeLa cells. FEBS Lett.
588:929–935. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Feoktistova M, Geserick P, Kellert B,
Dimitrova DP, Langlais C, Hupe M, Cain K, MacFarlane M, Häcker G
and Leverkus M: cIAPs block Ripoptosome formation, a RIP1/caspase-8
containing intracellular cell death complex differentially
regulated by cFLIP isoforms. Mol Cell. 43:449–463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Safa AR, Day TW and Wu CH: Cellular
FLICE-like inhibitory protein (c-FLIP): a novel target for cancer
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:37–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kataoka T: The caspase-8 modulator c-FLIP.
Crit Rev Immunol. 25:31–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheung HH, Mahoney DJ, Lacasse EC and
Korneluk RG: Down-regulation of c-FLIP enhances death of cancer
cells by smac mimetic compound. Cancer Res. 69:7729–7738. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shirley S and Micheau O: Targeting c-FLIP
in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:141–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|