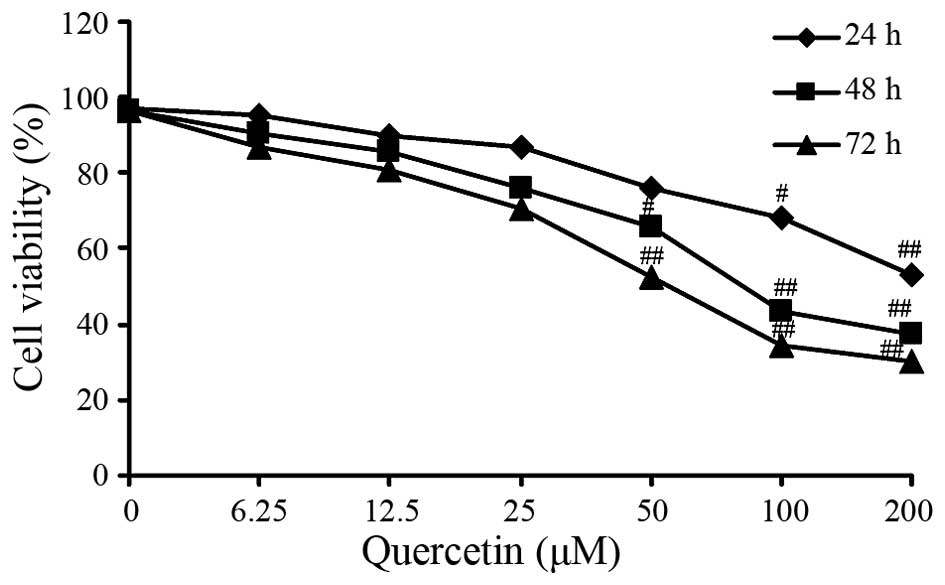
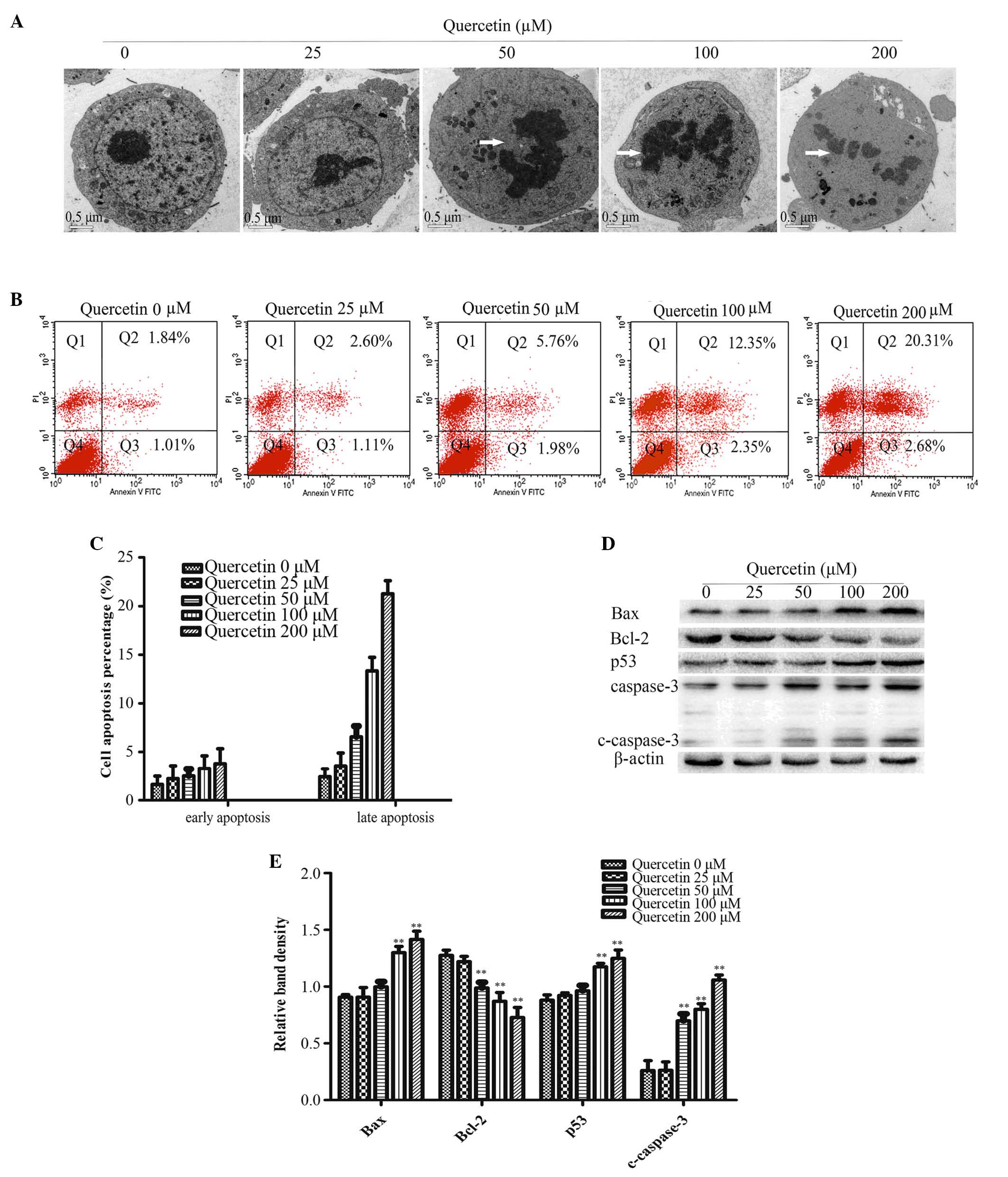
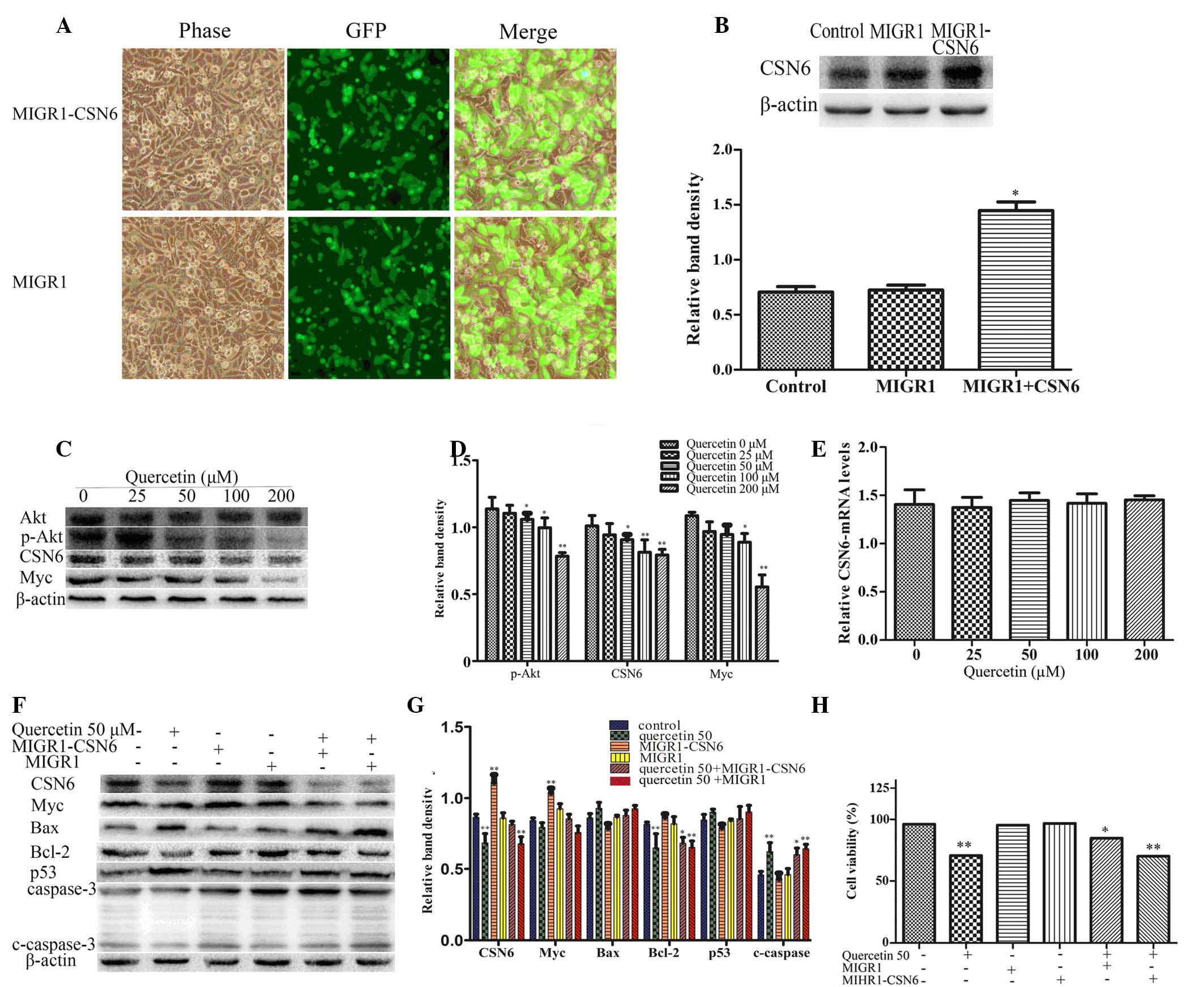
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hirpara KV, Aggarwal P, Mukherjee AJ,
Joshi N and Burman AC: Quercetin and its derivatives: Synthesis,
pharmacological uses with special emphasis on anti-tumor properties
and prodrug with enhanced bio-availability. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 9:138–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tan WF, Lin LP, Li MH, Zhang YX, Tong YG,
Xiao D and Ding J: Quercetin, a dietary-derived flavonoid,
possesses antiangiogenic potential. Eur J Pharmacol. 459:255–262.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prasad S, Phromnoi K, Yadav VR, Chaturvedi
MM and Aggarwal BB: Targeting inflammatory pathways by flavonoids
for prevention and treatment of cancer. Planta Med. 76:1044–1063.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Murakami A, Ashida H and Terao J:
Multitargeted cancer prevention by quercetin. Cancer Lett.
269:315–325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kawahara T, Kawaguchi-Ihara N, Okuhashi Y,
Itoh M, Nara N and Tohda S: Cyclopamine and quercetin suppress the
growth of leukemia and lymphoma cells. Anticancer Res.
29:4629–4632. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luo H, Jiang BH, King SM and Chen YC:
Inhibition of cell growth and VEGF expression in ovarian cancer
cells by flavonoids. Nutr Cancer. 60:800–809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vidya PR, Senthil MR, Maitreyi S,
Ramalingam K, Karunagaran D and Nagini S: The flavonoid quercetin
induces cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in
human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells through p53 induction and
NF-kappaB inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 649:84–91. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suolinna EM, Buchsbaum RN and Racker E:
The effect of flavonoids on aerobic glycolysis and growth of tumor
cells. Cancer Res. 35:1865–1872. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gibellini L, Pinti M, Nasi M, Montagna JP,
De Biasi S, Roat E, Bertoncelli L, Cooper EL and Cossarizza A:
Quercetin and cancer chemoprevention. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2011:5913562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walker EH, Pacold ME, Perisic O, Stephens
L, Hawkins PT, Wymann MP and Williams RL: Structural determinants
of phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibition by wortmannin, LY294002,
quercetin, myricetin and staurosporine. Mol Cell. 6:909–919. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Triantafyllou A, Mylonis I, Simos G,
Bonanou S and Tsakalof A: Flavonoids induce HIF-1alpha but impair
its nuclear accumulation and activity. Free Radic Biol Med.
44:657–670. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deng XW, Dubiel W, Wei N, Hofmann K and
Mundt K: Unified nomenclature for the COP9 signalosome and its
subunits: An essential regulator of development. Trends Genet.
16:2892000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao RY, Yeung SC, Chen J, Iwakuma T, Su
CH, Chen B, Qu C, Zhang F, Chen YT, Lin YL, et al: Subunit 6 of the
COP9 signalosome promotes tumorigenesis in mice through
stabilization of MDM2 and is upregulated in human cancers. J Clin
Invest. 121:851–865. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Choi HH, Gully C, Su CH, Velazquez-Torres
G, Chou PC, Tseng C, Zhao R, Phan L, Shaiken T, Chen J, et al: COP9
signalosome subunit 6 stabilizes COP1, which functions as an E3
ubiquitin ligase for 14-3-3sigma. Oncogene. 30:4791–4801. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee MH, Zhao R, Phan L and Yeung SC: Roles
of COP9 signalosome in cancer. Cell cycle. 10:3057–3066. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH
and Weissman AM: Mdm2 is a ring finger-dependent ubiquitin protein
ligase for itself and p53. J Biol Chem. 275:8945–8951. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inuzuka H, Fukushima H, Shaik S and Wei W:
Novel insights into the molecular mechanisms governing Mdm2
ubiquitination and destruction. Oncotarget. 1:685–690. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xue Y, Chen J, Choi HH, Phan L, Chou PC,
Zhao R, Yang H, Santiago J, Liu M, Yeung GE, et al: HER2-Akt
signaling in regulating COP9 signalsome subunit 6 and p53. Cell
cycle. 11:4181–4190. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Shin JH, Zhao R, Phan L, Wang H,
Xue Y, Post SM, Ho Choi H, Chen JS, Wang E, et al: CSN6 drives
carcinogenesis by positively regulating Myc stability. Nat Commun.
5:53842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sikora K, Chan S, Evan G, Gabra H, Markham
N, Stewart J and Watson J: c-myc oncogene expression in colorectal
cancer. Cancer. 59:1289–1295. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferlay J, Autier P, Boniol M, Heanue M,
Colombet M and Boyle P: Estimates of the cancer incidence and
mortality in Europe in 2006. Ann Oncol. 18:581–592. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harborne JB and Williams CA: Advances in
flavonoid research since 1992. Phytochemistry. 55:481–504. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hirpara KV, Aggarwal P, Mukherjee AJ,
Joshi N and Burman AC: Quercetin and its derivatives: Synthesis,
pharmacological uses with special emphasis on anti-tumor properties
and prodrug with enhanced bio-availability. Anti-Cancer Agents Med
Chem. 9:138–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao D, Beiring B and Glorius F:
Ruthenium-NHC-catalyzed asymmetric hydrogenation of flavones and
chromones: General access to enantiomerically enriched flavanones,
flavanols, chromanones and chromanols. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl.
52:8454–8458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas S, Quinn BA, Das SK, Dash R, Emdad
L, Dasgupta S, Wang XY, Dent P, Reed JC, Pellecchia M, et al:
Targeting the Bcl-2 family for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 17:61–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Veeriah S, Kautenburger T, Habermann N,
Sauer J, Dietrich H, Will F and Pool-Zobel BL: Apple flavonoids
inhibit growth of HT29 human colon cancer cells and modulate
expression of genes involved in the biotransformation of
xenobiotics. Mol Carcinog. 45:164–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim HJ, Kim SK, Kim BS, Lee SH, Park YS,
Park BK, Kim SJ, Kim J, Choi C, Kim JS, et al: Apoptotic effect of
quercetin on HT-29 colon cancer cells via the AMPK signaling
pathway. J Agric. Food Chem. 58:8643–8650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jin Q, Feng L, Behrens C, Bekele BN,
Wistuba II, Hong WK and Lee HY: Implication of AMP-activated
protein kinase and Akt-regulated survivin in lung cancer
chemopreventive activities of deguelin. Cancer Res. 67:11630–11639.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Su RY, Chao Y, Chen TY, Huang DY and Lin
WW: 5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside sensitizes TRAIL-and
TNF(alpha)-induced cytotoxicity in colon cancer cells through
AMP-activated protein kinase signaling. Mol Cancer Ther.
6:1562–1571. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hwang JT, Ha J, Park IJ, Lee SK, Baik HW,
Kim YM and Park OJ: Apoptotic effect of EGCG in HT-29 colon cancer
cells via AMPK signal pathway. Cancer Lett. 247:115–121. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eriksson A, Kalushkova A, Jarvius M,
Hilhorst R, Rickardson L, Kultima HG, de Wijn R, Hovestad L,
Fryknäs M, Öberg F, et al: AKN-028 induces cell cycle arrest,
downregulation of Myc associated genes and dose dependent reduction
of tyrosine kinase activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Biochem
Pharmacol. 87:284–291. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu ZY, Sun J, Zhu XF, Yang D and Zeng YX:
ApoG2 induces cell cycle arrest of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
by suppressing the c-Myc signaling pathway. J Transl Med. 7:742009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang K, Liu R, Li J, Mao J, Lei Y, Wu J,
Zeng J, Zhang T, Wu H, Chen L, et al: Quercetin induces protective
autophagy in gastric cancer cells: Involvement of Akt-mTOR-and
hypoxia-induced factor 1α-mediated signaling. Autophagy. 7:966–978.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moll UM and Petrenko O: The MDM2-p53
interaction. Mol Cancer Research. 1:1001–1008. 2003.
|
|
37
|
Mayo LD and Dormer DB: The PTEN, Mdm2, p53
tumor suppressor-oncoprotein network. Trends Biochem Sci.
27:462–467. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maurya AK and Vinayak M: Quercetin
regresses dalton's lymphoma growth via suppression of PI3K/AKT
signaling leading to upregulation of p53 and decrease in energy
metabolism. Nutr Cancer. 67:354–363. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Zou Y, Spohn B and
Hung MC: HER-2/neu induces p53 ubiquitination via Akt-mediated MDM2
phosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol. 3:973–982. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|