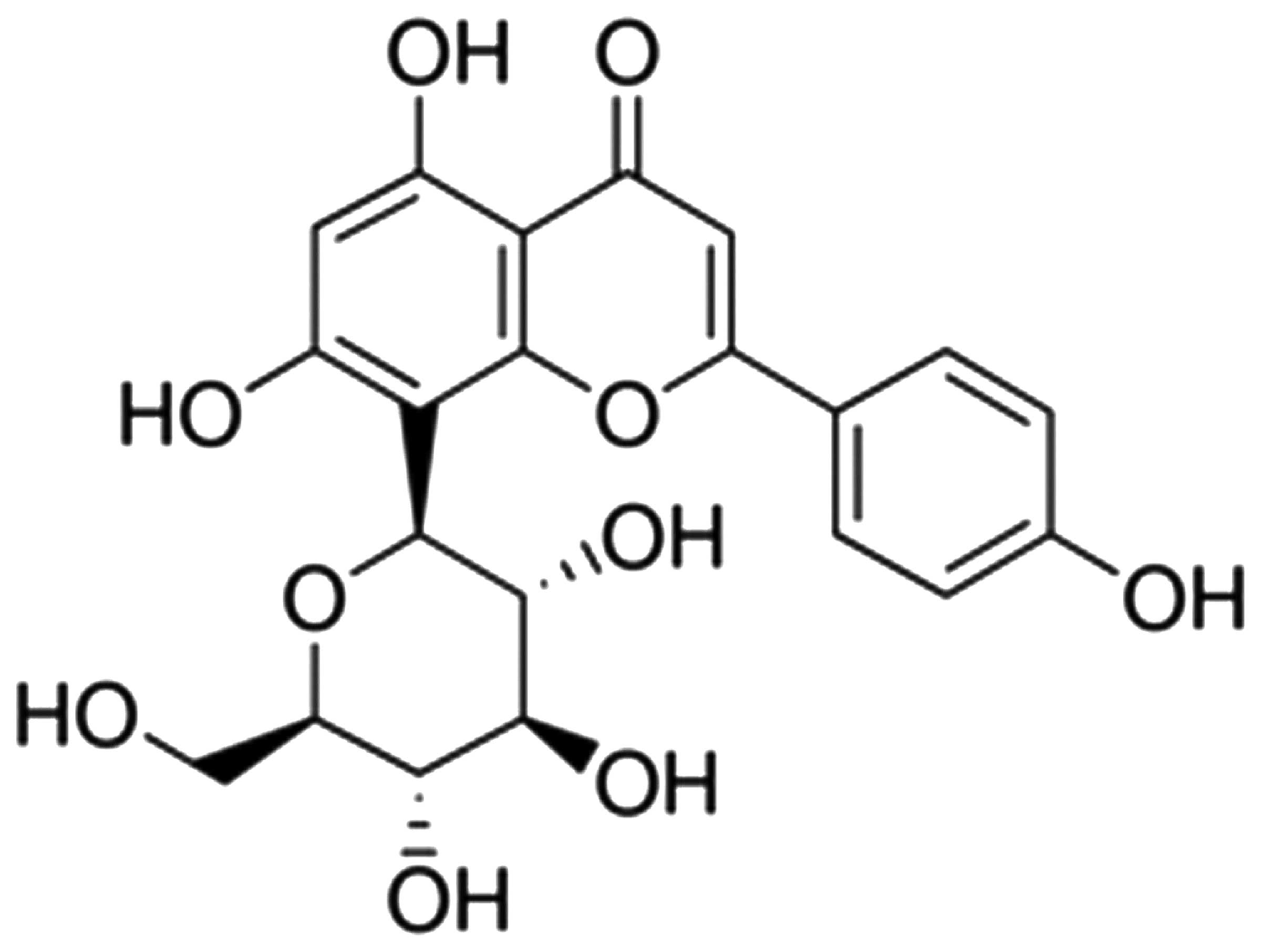
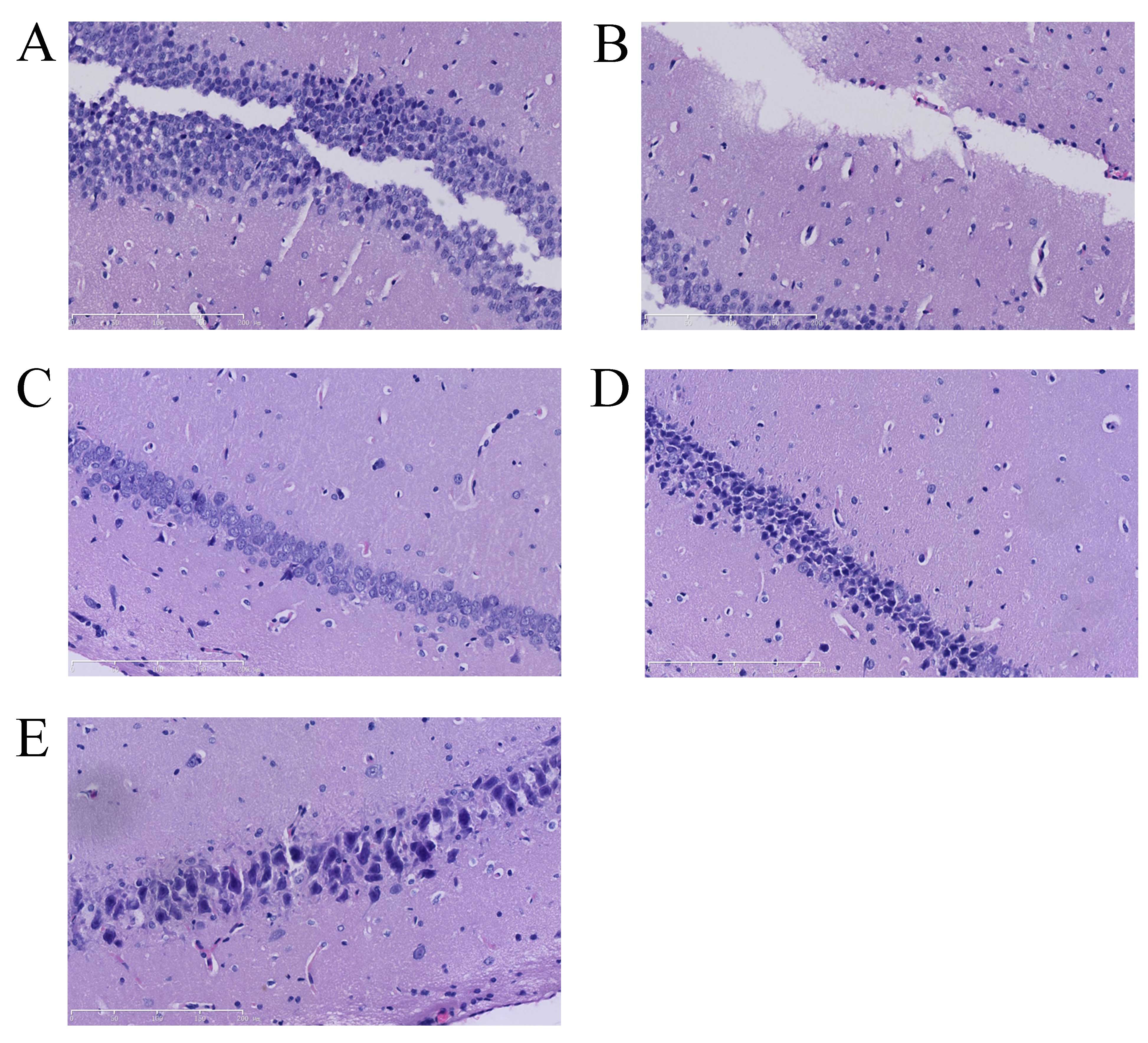
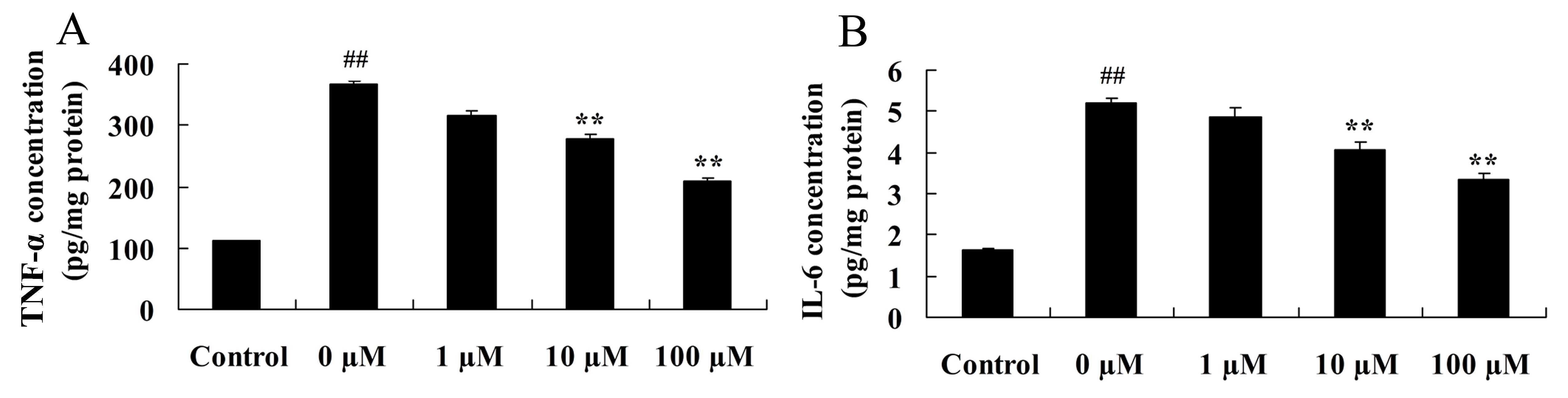
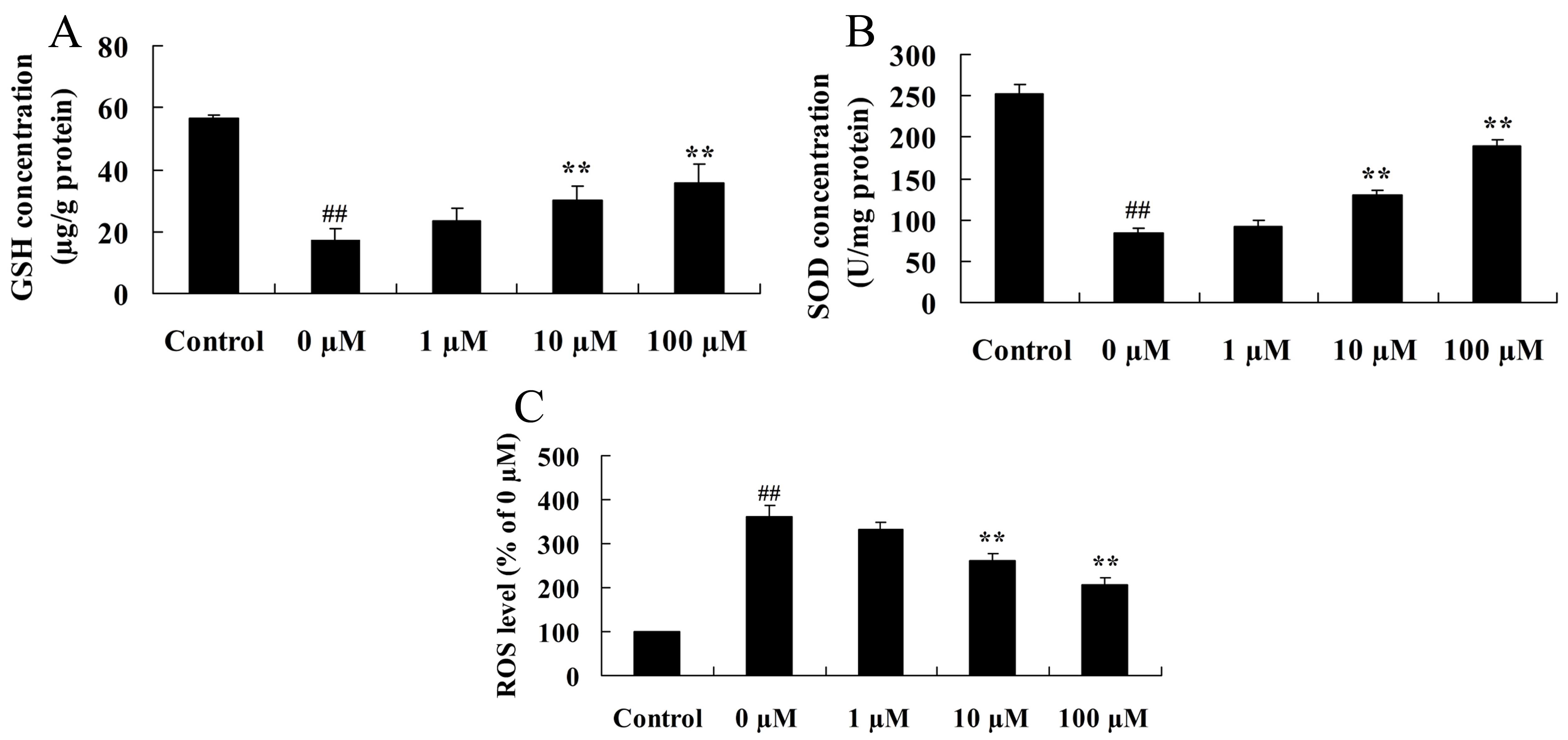
|
1
|
Qu X, Xu C, Wang H, Xu J, Liu W, Wang Y,
Jia X, Xie Z, Xu Z, Ji C, et al: Hippocampal glutamate level and
glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST) are up-regulated in senior
rat associated with isoflurane-induced spatial learning/memory
impairment. Neurochem Res. 38:59–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tanaka K, Kehl F, Gu W, Krolikowski JG,
Pagel PS, Warltier DC and Kersten JR: Isoflurane-induced
preconditioning is attenuated by diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 282:H2018–H2023. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Benveniste H and Makaryus R: Are we moving
closer to noninvasive imaging and monitoring of neonatal
anesthesia-induced neurotoxicity? Anesthesiology. 125:22–24. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stary CM, Sun X and Giffard RG: Astrocytes
protect against isoflurane neurotoxicity by buffering
pro-brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Anesthesiology. 123:810–819.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
An J, Stadnicka A, Kwok WM and Bosnjak ZJ:
Contribution of reactive oxygen species to isoflurane-induced
sensitization of cardiac sarcolemmal adenosine
triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel to pinacidil.
Anesthesiology. 100:575–580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mazoit JX, Roulleau P and Baujard C:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the neonatal rhesus macaque
brain: Isoflurane or ischemia-reperfusion? Anesthesiology.
113:1245–1246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang J and Jiang H: Effect of the inhaled
anesthetics isoflurane, sevoflurane and desflurane on the
neuropathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (review). Mol Med Rep.
12:3–12. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wei H: The role of calcium dysregulation
in anesthetic-mediated neurotoxicity. Anesth Analg. 113:972–974.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pan C, Xu Z, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Zhang J,
McAuliffe S, Yue Y, Li T and Xie Z: The potential dual effects of
anesthetic isoflurane on hypoxia-induced caspase-3 activation and
increases in β-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme
levels. Anesth Analg. 113:145–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Kirby CO and Olney
JW: Isoflurane and propofol block neurotoxicity caused by MK-801 in
the rat posterior cingulate/retrosplenial cortex. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 17:168–174. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bickler PE, Warren DE, Clark JP, Gabatto
P, Gregersen M and Brosnan H: Anesthetic protection of neurons
injured by hypothermia and rewarming: Roles of intracellular
Ca2+ and excitotoxicity. Anesthesiology. 117:280–292.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hara M, Zhou ZY and Hemmings HC Jr:
α2-adrenergic receptor and isoflurane modulation of presynaptic
Ca2+ influx and exocytosis in hippocampal neurons.
Anesthesiology. 125:535–546. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bickler PE, Zhan X and Fahlman CS:
Isoflurane preconditions hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose
deprivation: Role of intracellular Ca2+ and
mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Anesthesiology.
103:532–539. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gemes G, Oyster KD, Pan B, Wu HE, Bangaru
ML, Tang Q and Hogan QH: Painful nerve injury increases plasma
membrane Ca2+-ATPase activity in axotomized sensory
neurons. Mol Pain. 8:462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sanchez JC, Lopez-Zapata DF and Wilkins
RJ: TRPV4 channels activity in bovine articular chondrocytes:
Regulation by obesity-associated mediators. Cell Calcium.
56:493–503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jang Y, Jung J, Kim H, Oh J, Jeon JH, Jung
S, Kim KT, Cho H, Yang DJ, Kim SM, et al: Axonal
neuropathy-associated TRPV4 regulates neurotrophic factor-derived
axonal growth. J Biol Chem. 287:6014–6024. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ciurtin C, Majeed Y, Naylor J, Sukumar P,
English AA, Emery P and Beech DJ: TRPM3 channel stimulated by
pregnenolone sulphate in synovial fibroblasts and negatively
coupled to hyaluronan. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 11:1112010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heckel E, Boselli F, Roth S, Krudewig A,
Belting HG, Charvin G and Vermot J: Oscillatory flow modulates
mechanosensitive klf2a expression through trpv4 and trpp2 during
heart valve development. Curr Biol. 25:1354–1361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nemethova M, Talian I, Danielisova V,
Tkacikova S, Bonova P, Bober P, Matiasova M, Sabo J and Burda J:
Delayed bradykinin postconditioning modulates intrinsic
neuroprotective enzyme expression in the rat CA1 region after
cerebral ischemia: A proteomic study. Metab Brain Dis. Jul
8–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu W, Guo Q, Hu X, Peng L and Zhou B:
Induction of DJ-1 protects neuronal cells from isoflurane induced
neurotoxicity. Metab Brain Dis. 30:703–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang HC, Chang P, Lu SY, Zheng BW and
Jiang ZF: Protection of curcumin against amyloid-β-induced cell
damage and death involves the prevention from NMDA
receptor-mediated intracellular Ca elevation. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 35:450–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Min JW, Hu JJ, He M, Sanchez RM, Huang WX,
Liu YQ, Bsoul NB, Han S, Yin J, Liu WH, et al: Vitexin reduces
hypoxia-ischemia neonatal brain injury by the inhibition of
HIF-1alpha in a rat pup model. Neuropharmacology. 99:38–50. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang ZB, Tan B, Li TB, Lou Z, Jiang JL,
Zhou YJ, Yang J, Luo XJ and Peng J: Protective effect of vitexin
compound B-1 against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in
differentiated PC12 cells via NADPH oxidase inhibition. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 387:861–871. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Edwards JE, Brown PN, Talent N, Dickinson
TA and Shipley PR: A review of the chemistry of the genus
Crataegus. Phytochemistry. 79:5–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Zhen Y, Wu X, Jiang Q, Li X, Chen
Z, Zhang G and Dong L: Vitexin protects brain against
ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating mitogen-activated
protein kinase and apoptosis signaling in mice. Phytomedicine.
22:379–384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang B, Dong Y, Zhang G, Moir RD, Xia W,
Yue Y, Tian M, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Tanzi RE and Xie Z: The
inhalation anesthetic desflurane induces caspase activation and
increases amyloid beta-protein levels under hypoxic conditions. J
Biol Chem. 283:11866–11875. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luo X, Yang L, Chen X and Li S: Tau
hyperphosphorylation: A downstream effector of isoflurane-induced
neuroinflammation in aged rodents. Med Hypotheses. 82:94–96. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Beckmann N, Doelemeyer A, Zurbruegg S,
Bigot K, Theil D, Frieauff W, Kolly C, Moulin P, Neddermann D,
Kreutzer R, et al: Longitudinal noninvasive magnetic resonance
imaging of brain microhemorrhages in BACE inhibitor-treated APP
transgenic mice. Neurobiol Aging. 45:50–60. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C, Zhang N, Hu Y and Wang H: NR2B
overexpression leads to the enhancement of specific protein
phosphorylation in the brain. Brain Res. 1588:127–134. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su JY and Vo AC: Role of PKC in
isoflurane-induced biphasic contraction in skinned pulmonary
arterial strips. Anesthesiology. 96:155–161. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vahle-Hinz C, Detsch O, Siemers M and
Kochs E: Contributions of GABAergic and glutamatergic mechanisms to
isoflurane-induced suppression of thalamic somatosensory
information transfer. Exp Brain Res. 176:159–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong L, Fan Y, Shao X and Chen Z: Vitexin
protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in
Langendorff-perfused rat hearts by attenuating inflammatory
response and apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:3211–3216. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Borghi SM, Carvalho TT, Staurengo-Ferrari
L, Hohmann MS, Pinge-Filho P, Casagrande R and Verri WA Jr: Vitexin
inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative
stress and cytokines. J Nat Prod. 76:1141–1149. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ding W, Li Z, Shen X, Martin J, King SB,
Sivakumaran V, Paolocci N and Gao WD: Reversal of
isoflurane-induced depression of myocardial contraction by nitroxyl
via myofilament sensitization to Ca2+. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 339:825–831. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Li K and Yao S: Effect of
inhalational anesthetics on cytotoxicity and intracellular calcium
differently in rat pheochromocytoma cells (PC12). J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 28:104–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xie Z, Dong Y, Maeda U, Moir R, Inouye SK,
Culley DJ, Crosby G and Tanzi RE: Isoflurane-induced apoptosis: A
potential pathogenic link between delirium and dementia. J Gerontol
A Biol Sci Med Sci. 61:1300–1306. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Harraz OF and Altier C: STIM1-mediated
bidirectional regulation of Ca(2+) entry through voltage-gated
calcium channels (VGCC) and calcium-release activated channels
(CRAC). Front Cell Neurosci. 8:432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shan H, Messi ML, Zheng Z, Wang ZM and
Delbono O: Preservation of motor neuron Ca2+ channel
sensitivity to insulin-like growth factor-1 in brain motor cortex
from senescent rat. J Physiol. 553:49–63. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sturek M: Ca2+ regulatory
mechanisms of exercise protection against coronary artery disease
in metabolic syndrome and diabetes. J Appl Physiol (1985).
111:573–586. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng Y, Wang B, Du F, Li H, Wang S, Hu C,
Zhu C and Yu X: The involvement of PI3K-mediated and L-VGCC-gated
transient Ca2+ influx in 17β-estradiol-mediated
protection of retinal cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis with
Ca2+ overload. PLoS One. 8:e772182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hogan-Cann AD and Anderson CM:
Physiological roles of non-neuronal NMDA receptors. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 37:750–767. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang XN, Li JM, Yang Q, Feng B, Liu SB,
Xu ZH, Guo YY and Zhao MG: Anti-apoptotic effects of hyperoside via
inhibition of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors. Pharmacol Rep.
62:949–955. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li XB, Guo HL, Shi TY, Yang L, Wang M,
Zhang K, Guo YY, Wu YM, Liu SB and Zhao MG: Neuroprotective effects
of a novel translocator protein (18 kDa) ligand, ZBD-2, against
focal cerebral ischemia and NMDA-induced neurotoxicity. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 42:1068–1074. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cho SI, Park UJ, Chung JM and Gwag BJ:
Neu2000, an NR2B-selective, moderate NMDA receptor antagonist and
potent spin trapping molecule for stroke. Drug News Perspect.
23:549–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang L, Yang ZM, Zhang N, Tian Z, Liu SB
and Zhao MG: Neuroprotective effects of vitexin by inhibition of
NMDA receptors in primary cultures of mouse cerebral cortical
neurons. Mol Cell Biochem. 386:251–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|