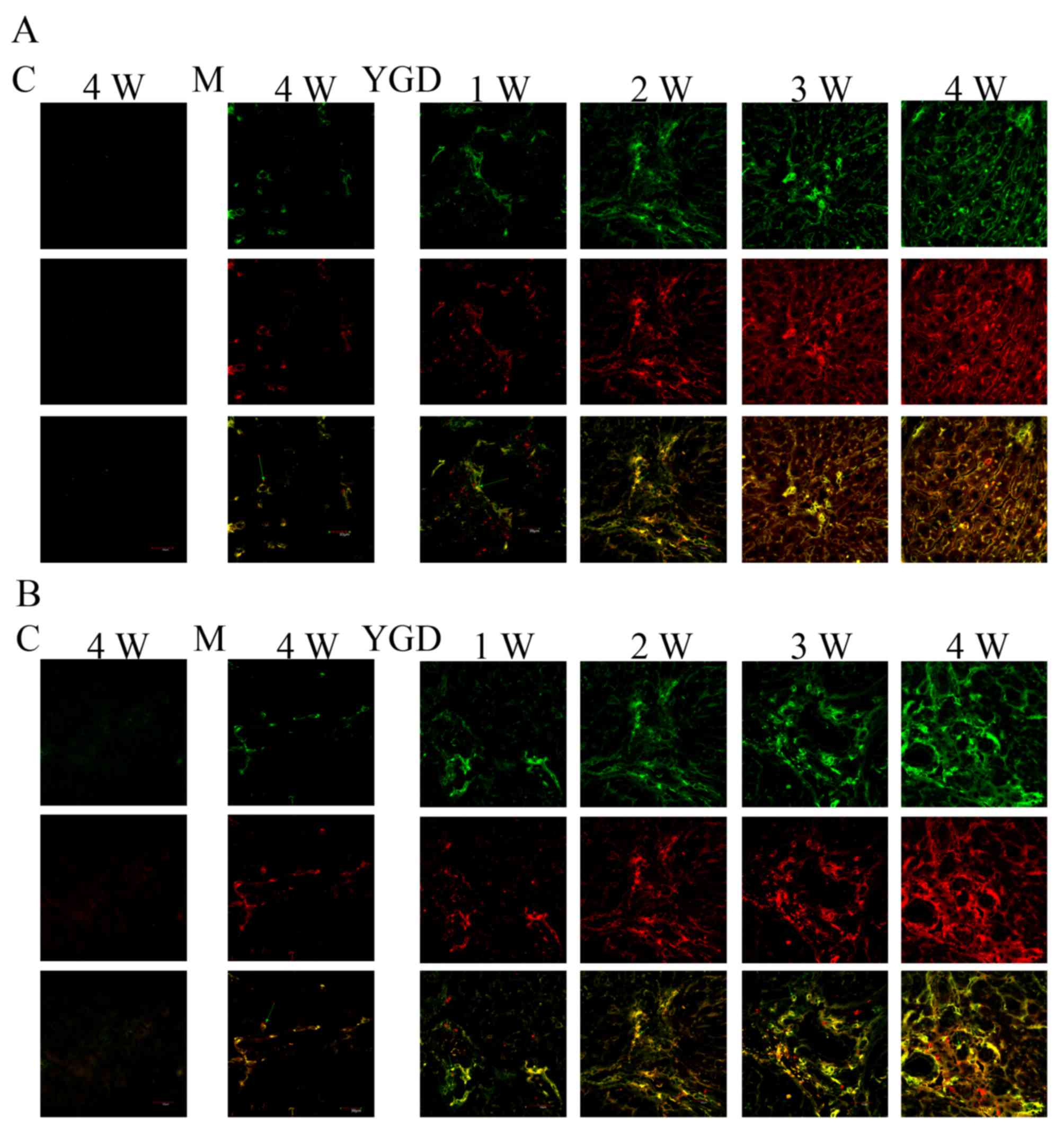
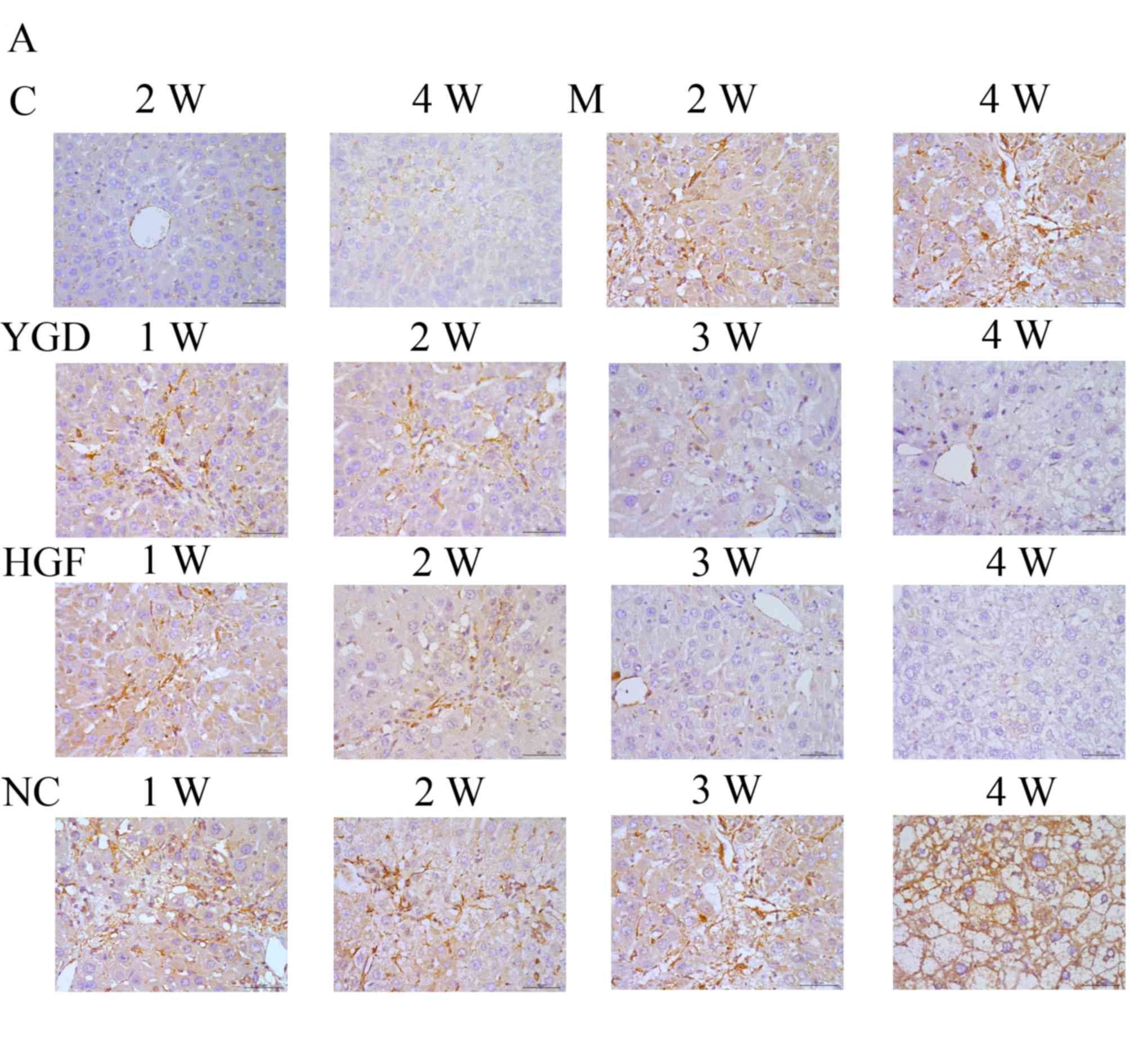
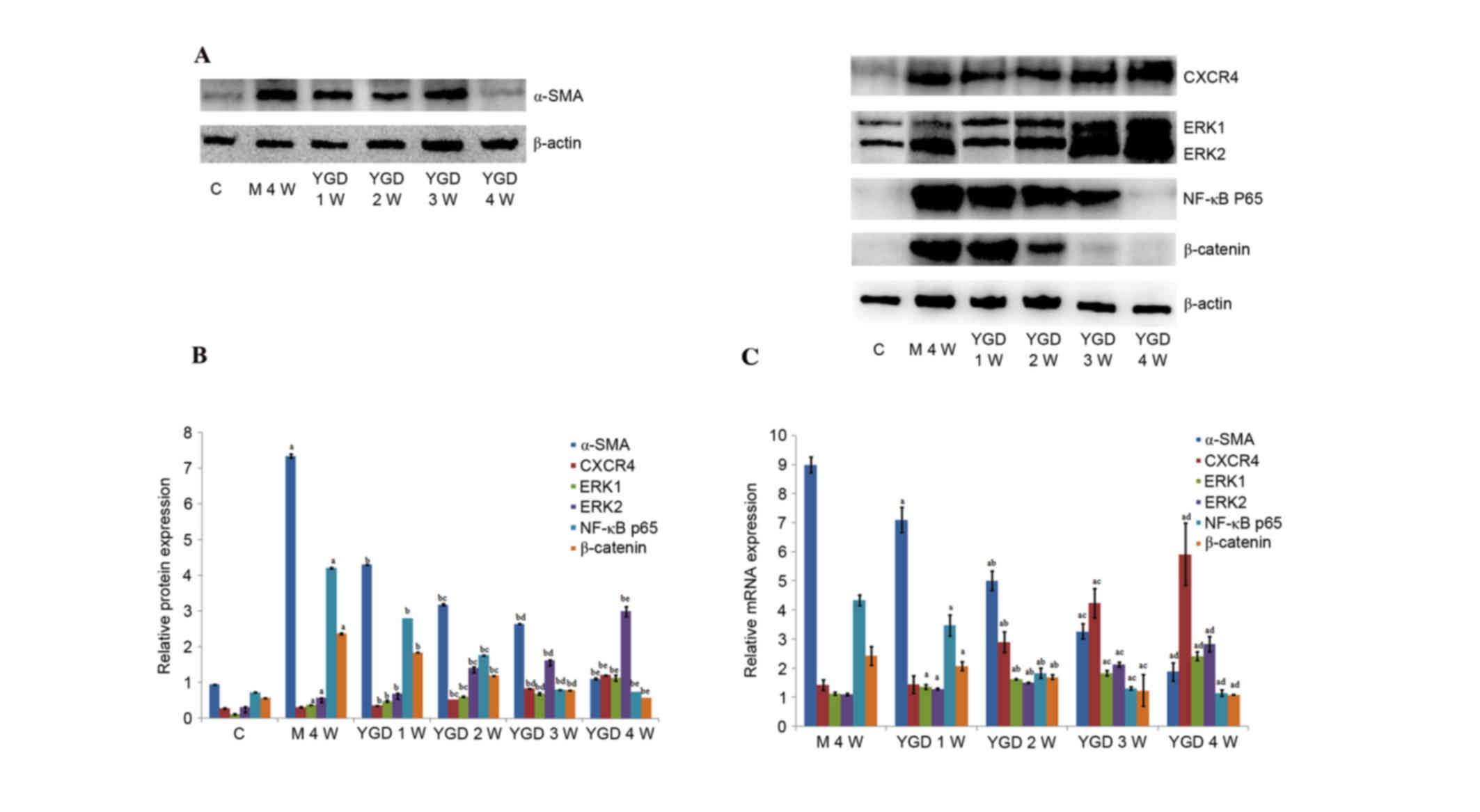
|
1
|
Wu XB and Tao R: Hepatocyte
differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. HepatobiliaryPancreat
Dis Int. 11:360–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pilat N, Unger L and Berlakovich GA:
Implication for bone marrow stem cells in hepatocyte regeneration
after orthotopic liver transplantation. Int J Hepatol.
2013:3106122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang L, Ping L, Yongping M, et al: Study
on TCM recipe and syndrome of dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats. J Trad Chin Med. 47:929–932. 2006.
|
|
4
|
Min L, Zhiying C and Guobin W: Investigate
Yiguanjian treatment the liver-kidney yin deficiency syndrome of
posthepatitic cirrhosis. TCM Research. 22:3–4. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Ying Z and Ping Z: Effect of YGJ on
proliferation and differenciation of hepatic oval cells in rat
cirrhosis by DMN. Journal of Dalian Medical University. 33:11–16.
2011.
|
|
6
|
Jenkins SA, Crandison A, Baxter JN, Day
DW, Taylor I and Shields R: A dimethyl nitrosamine-induced model of
cirrhosis and portal hypertension in the rat. J Hepatol. 1:489–499.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Mills AG,
Gorn V, Singer MJ and Reed MW: Quantitative reverse
transcription-polymerase chain reaction to study Mrna decay:
Comparison of endpoint and real-timemethods. Anal Biochem.
285:194–204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jézéquel AM, Mancini R, Rinaldesi ML,
Ballardini G, Fallani M, Bianchi F and Orlandi F:
Dimethylnitrosamine-induced cirrhosis. Evidence for an
immunological mechanism. J Hepatol. 8:42–52. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim KS, Yang HJ, Lee JY, Na YC, Kwon SY,
Kim YC, Lee JH and Jang HJ: Effects of β-sitosterol derived from
Artemisia capillaris on the activated human hepatic stellate cells
and dimethylnitrisamine-induced mouse liver fibrosis. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 14:3632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nishibe Y, Kaneko H, Suzuki H, Abe T,
Matsuura Y and Takaku H: Baculovirus-mediated interferon alleviates
dimethyl nitrosamine-induced liver cirrhosis symptomsin a murine
model. Gene Ther. 15:990–997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen P, Li J, Huo Y, Lu J, Wan L, Yang Q,
Huang J, Gan R and Guo C: Adenovirus-mediated expression of orphan
nuclear receptor NR4A2 targeting hepatic stellate cell attenuates
liver fibrosis in rats. Sci Rep. 6:335932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bell LN, Cai L, Johnstone BH, Traktuev DO,
March KL and Considine RV: A central role for hepatocyte growth
factor in adipose tissue angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 294:E336–E344. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inagaki Y, Higashi K, Kushida M, Hong YY,
Nakao S, Higashiyama R, Moro T, Itoh J, Mikami T, Kimura T, et al:
Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses profibrogenic signal
transduction via nuclear export of Smad3 with galectin-7.
Gastroenterology. 134:1180–1190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oh SH, Miyazaki M, Kouchi H, Inoue Y,
Sakaguchi M, Tsuji T, Shima N, Higashio K and Namba M: Hepatocyte
growth factor induces differentiation of adult rat bone marrow
cells into a hepatocyte lineage in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 279:500–504. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Okumoto K, Saito T, Hattori E, Ito JI,
Adachi T, Takeda T, Sugahara K, Watanabe H, Saito K, Togashi H and
Kawata S: Diffferentiation of bone marrow cells into cells that
express liver-specific genes in vitro: Implication of the Notch
signals in differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:691–695. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van de Kamp J, Jahnen-Dechent W, Rath B,
Knuechel R and Neuss S: Hepatocyte growth factor-loaded
biomaterials for mesenchymal stem cell recruitment. Stem Cells Int.
2013:8920652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim WH, Matsumoto K, Bessho K and Nakamura
T: Growth inhibition and apoptosis in liver myofibroblasts promoted
by hepatocyte growth factor leads to resolution from liver
cirrhosis. Am J Pathol. 166:1017–1028. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tian DD, Wang W, Wang HN, Sze SC and Zhang
ZJ: Pharmacokinetic evaluation of clozapine in concomitant use of
Radix Rehmanniae, fructus schisandrae, radix bupleuri, or fructus
gardeniae in rats. Molecules. 21:E6962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu YY, Zhao Y, Song YN, Dong S, Wei B,
Chen QL, Hu YY and Su SB: Serum cytokine profiling analysis for
zheng differentiation in chronic hepatitis B. Chin Med. 10:242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ping J, Chen HY, Yang Z, Yang C and Xu LM:
Effect of yiguan decoction on differentiation of bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocyte-like cells: An experimental
research. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 34:348–354. 2014.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Anzalone R, Lo Iacono M, Corrao S, Magno
F, Loria T, Cappello F, Zummo G, Farina F and La Rocca G: New
energing potentials for human Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem
cells: Immunological features and hepatocyte-like differentiative
capacity. Stem Cells Dev. 19:423–438. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haridass D, Narain N and Ott M: Hepatocyte
transplantation: Waiting for stem cells. CurrOpin Organ Transplant.
13:627–632. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Facciorusso A, Antonino M, Del Prete V,
Neve V, Scavo MP and Barone M: Are hematopoietic stem cells
involved in hepatocarcinogenesis? Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr.
3:199–206. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kucia M, Ratajczak J, Reca R,
Janowska-Wieczorek A and Ratajczak MZ: Tissue-specific muscle,
neural and liver stem/progenitor cells reside in the bone marrow,
respond to an SDF-1 gradient and are mobilized into peripheral
blood during stress and tissue injury. Blood Cells Mol Dis.
32:52–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun L, Fan X, Zhang L, Shi G, Aili M, Lu
X, Jiang T and Zhang Y: Bone mesenchymal cell transplantation via
four routes for the treatment of acute liver failure in rats. Int J
Mol Med. 34:987–996. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Delgado-Martín C, Escribano C, Pablos JL,
Riol-Blanco L and Rodríguez-Fernández JL: Chemokine CXCL12 uses
CXCR4 and a signaling core formed by bifunctional AKT,
extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and mammalian
target of rapamycin complex 1(m TORC1) proteins to control
chemotaxis and survival simultaneously in mature dendritic cells. J
Biol Chem. 286:37222–37236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luedde T and Schwabe RF: NF-κB in the
liver-linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:108–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang J, Liu F, Lee M, Wu B, Ting K, Zara
JN, Soo C, Al Hezaimi K, Zou W, Chen X, et al: NF-κB inhibits
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by promoting
β-catenin degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:9469–9474. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pandey AC, Semon JA, Kaushal D, O'Sullivan
RP, Glowacki J, Gimble JM and Bunnell BA: MicroRNA profiling
reveals age-dependent differential expression of nuclear factor κB
and mitogen-activated protein kinase in adipose and bone
marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther.
2:492011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ke Z, Zhou F, Wang L, Chen S, Liu F, Fan
X, Tang F, Liu D and Zhao G: Down-regulation of Wnt signaling could
promote bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate
into hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 367:342–348. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|