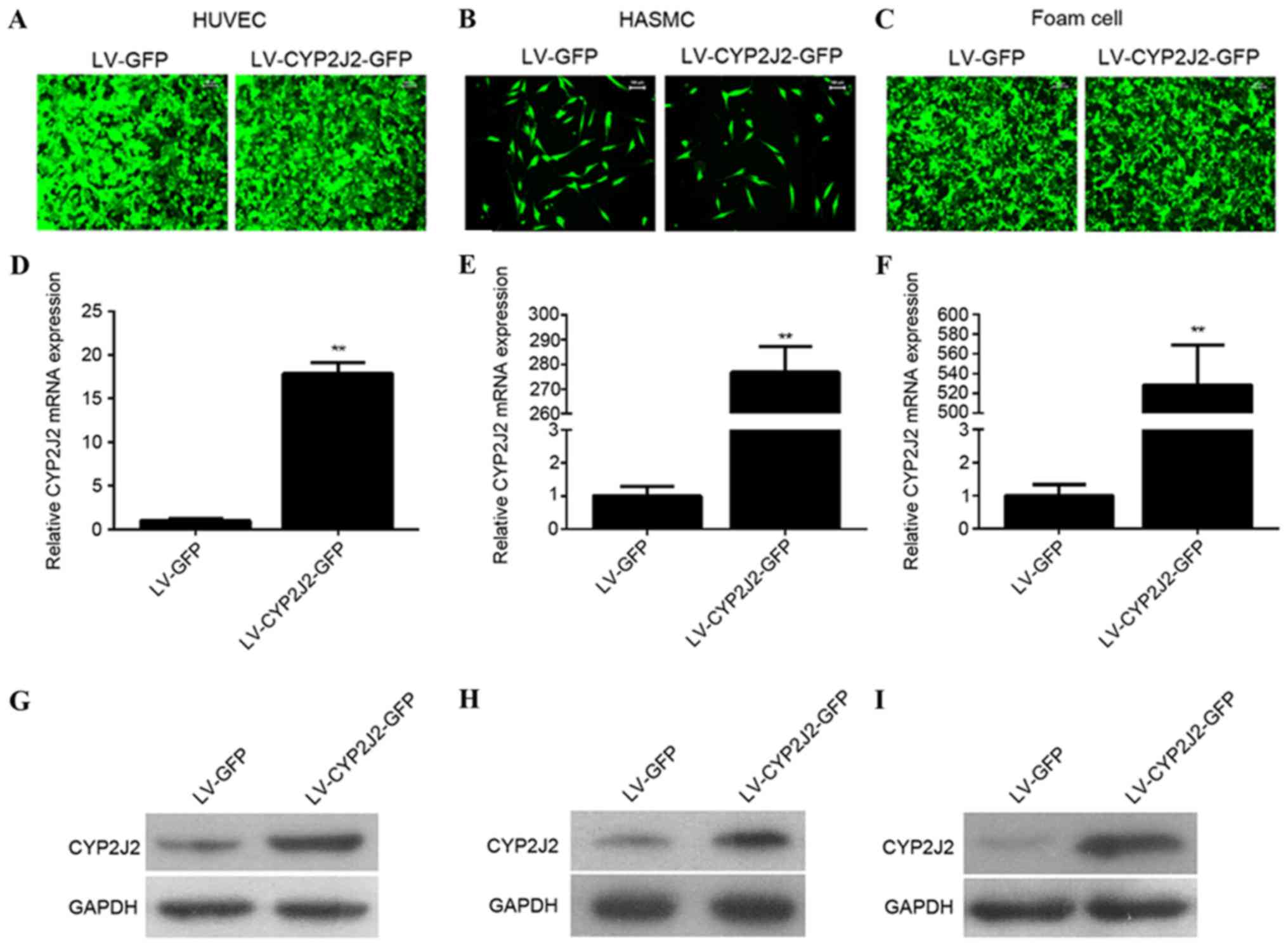
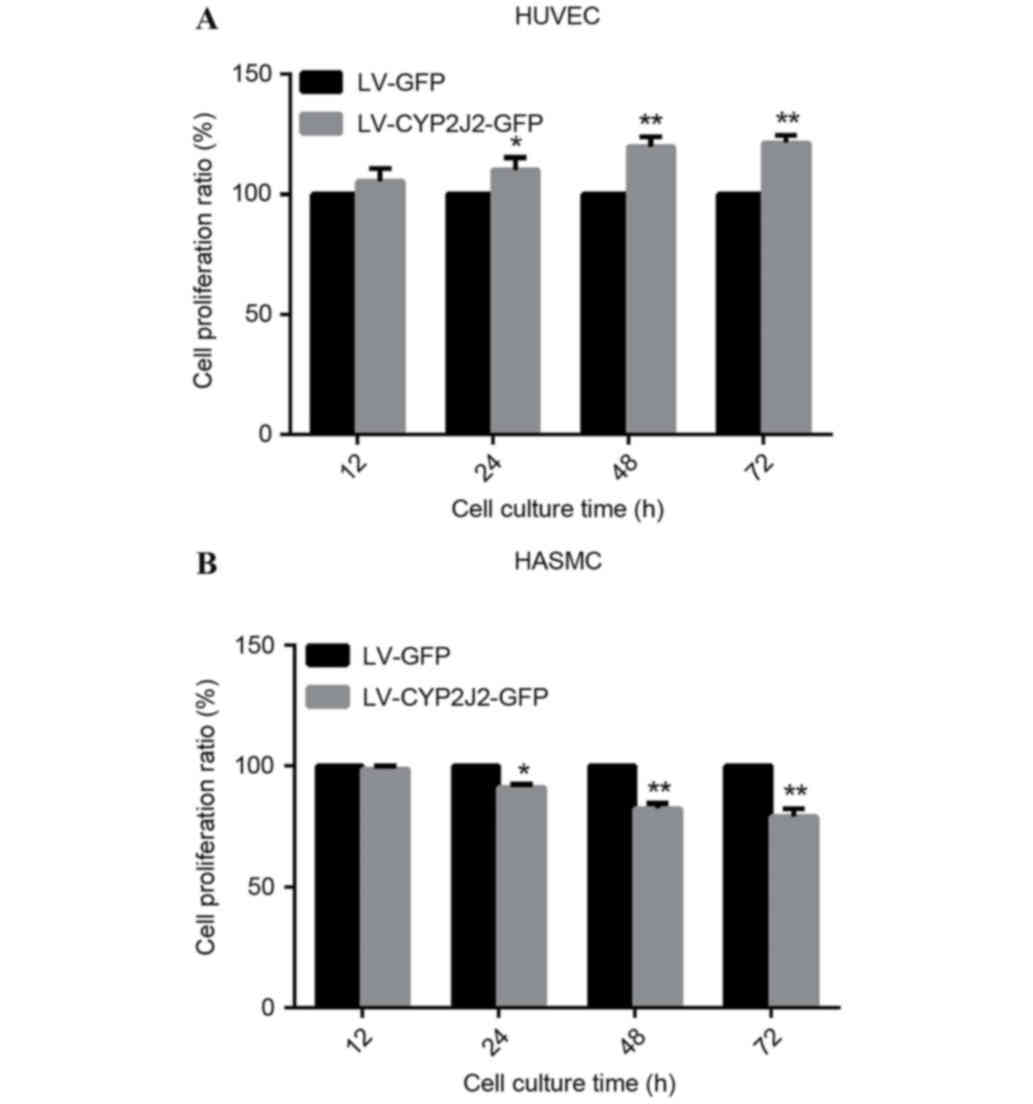
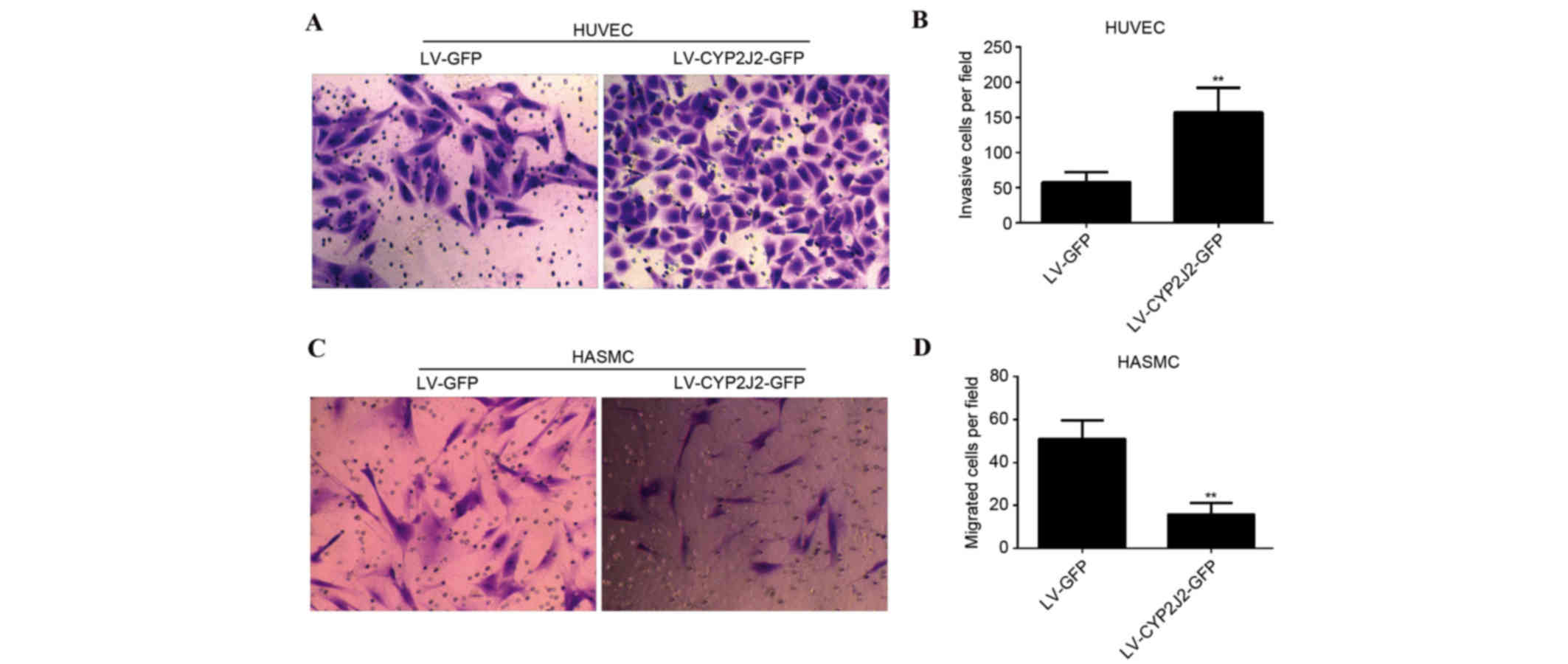
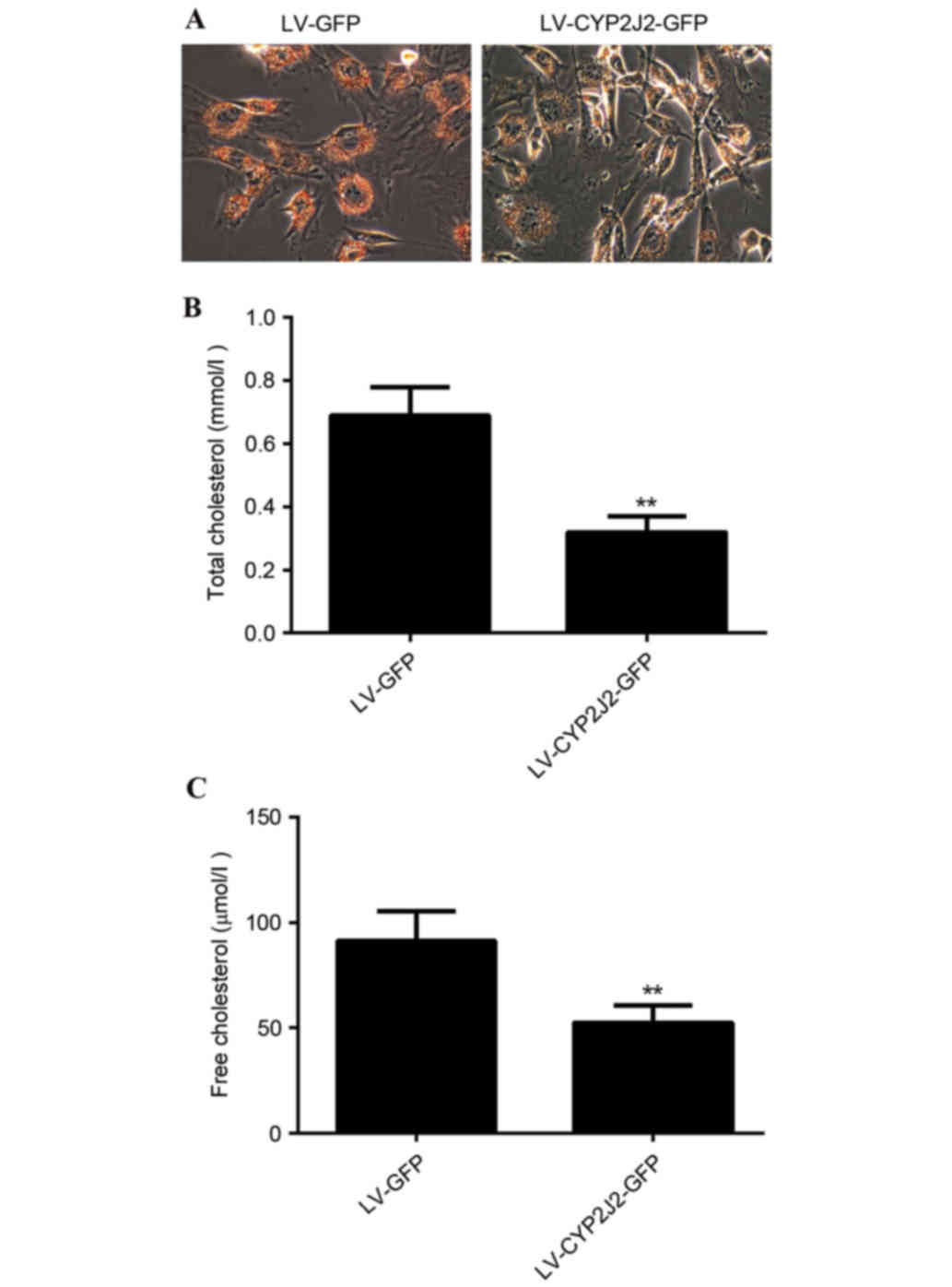
|
1
|
Negi S and Anand A: Atherosclerotic
coronary heart disease-epidemiology, classification and management.
Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 10:257–261. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weber C and Noels H: Atherosclerosis:
Current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med.
17:1410–1422. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z and Xu H: Anti-inflammatory and
immunomodulatory mechanism of tanshinone IIA for atherosclerosis.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:2679762014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Athirakul K, Bradbury JA, Graves JP,
DeGraff LM, Ma J, Zhao Y, Couse JF, Quigley R, Harder DR, Zhao X,
et al: Increased blood pressure in mice lacking cytochrome P450
2J5. FASEB J. 22:4096–4108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bodiga S, Zhang R, Jacobs DE, Larsen BT,
Tampo A, Manthati VL, Kwok WM, Zeldin DC, Falck JR, Gutterman DD,
et al: Protective actions of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid: Dual
targeting of cardiovascular PI3K and KATP channels. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 46:978–988. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee CR, Imig JD, Edin ML, Foley J, DeGraff
LM, Bradbury JA, Graves JP, Lih FB, Clark J, Myers P, et al:
Endothelial expression of human cytochrome P450 epoxygenases lowers
blood pressure and attenuates hypertension-induced renal injury in
mice. FASEB J. 24:3770–3781. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, Yang B, Spiecker M,
Ley K, Zeldin DC and Liao JK: Anti-inflammatory properties of
cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science.
285:1276–1279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Node K, Ruan XL, Dai J, Yang SX, Graham L,
Zeldin DC and Liao JK: Activation of Galpha s mediates induction of
tissue-type plasminogen activator gene transcription by
epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. J Biol Chem. 276:15983–15989. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Wei X, Xiao X, Hui R, Card JW,
Carey MA, Wang DW and Zeldin DC: Arachidonic acid epoxygenase
metabolites stimulate endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis via
mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 314:522–532.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao B, Li X, Yan J, Yu X, Yang G, Xiao X,
Voltz JW, Zeldin DC and Wang DW: Overexpression of cytochrome P450
epoxygenases prevents development of hypertension in spontaneously
hypertensive rats by enhancing atrial natriuretic peptide. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:784–794. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu X, Zhang XA and Wang DW: The roles of
CYP450 epoxygenases and metabolites, epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, in
cardiovascular and malignant diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
63:597–609. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang S, Lin L, Chen JX, Lee CR, Seubert
JM, Wang Y, Wang H, Chao ZR, Tao DD, Gong JP, et al: Cytochrome
P-450 epoxygenases protect endothelial cells from apoptosis induced
by tumor necrosis factor-alpha via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling
pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H142–H151. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zufferey R, Dull T, Mandel RJ, Bukovsky A,
Quiroz D, Naldini L and Trono D: Self-inactivating lentivirus
vector for safe and efficient in vivo gene delivery. J Virol.
72:9873–9880. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dull T, Zufferey R, Kelly M, Mandel RJ,
Nguyen M, Trono D and Naldini L: A third-generation lentivirus
vector with a conditional packaging system. J Virol. 72:8463–8471.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Zhao JH, Ma PJ, Su LL, Tao SB and Ji
SB: Association of CYP2J2 gene polymorphisms with ischemic stroke.
Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:8163–8167. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kumar AS Arun, Kumar SS, Umamaheswaran G,
Kesavan R, Balachandar J and Adithan C: Association of CYP2C8,
CYP2C9 and CYP2J2 gene polymorphisms with myocardial infarction in
South Indian population. Pharmacol Rep. 67:97–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee CR, North KE, Bray MS, Couper DJ,
Heiss G and Zeldin DC: CYP2J2 and CYP2C8 polymorphisms and coronary
heart disease risk: The atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC)
study. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 17:349–358. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang S, Chen G, Li N, Dai M, Chen C, Wang
P, Tang H, Hoopes SL, Zeldin DC, Wang DW and Xu X: CYP2J2
overexpression ameliorates hyperlipidemia via increased fatty acid
oxidation mediated by the AMPK pathway. Obesity (Silver Spring).
23:1401–1413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang L, Ni L, Duan Q, Wang X, Chen C, Chen
S, Chaugai S, Zeldin DC, Tang JR and Wang DW: CYP epoxygenase 2J2
prevents cardiac fibrosis by suppression of transmission of
pro-inflammation from cardiomyocytes to macrophages. Prostaglandins
Other Lipid Mediat. 116–117, 64–75. 2015.
|
|
21
|
Westphal C, Spallek B, Konkel A, Marko L,
Qadri F, DeGraff LM, Schubert C, Bradbury JA, Regitz-Zagrosek V,
Falck JR, et al: CYP2J2 overexpression protects against arrhythmia
susceptibility in cardiac hypertrophy. PLoS One. 8:e734902013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Spiecker M, Darius H, Hankeln T, Soufi M,
Sattler AM, Schaefer JR, Node K, Börgel J, Mügge A, Lindpaintner K,
et al: Risk of coronary artery disease associated with polymorphism
of the cytochrome P450 epoxygenase CYP2J2. Circulation.
110:2132–2136. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu Q, Fu Z, Ma Y, Yang H, Huang D, Xie X,
Liu F, Zheng Y and Cha E: A novel polymorphism of the CYP2J2 gene
is associated with coronary artery disease in Uygur population in
China. Clin Biochem. 46:1047–1054. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Doran AC, Meller N and McNamara CA: Role
of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of
atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:812–819. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ross R: The pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis: A perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 362:801–809.
1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lu Q, Qiu TQ and Yang H: Ligustilide
inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation. Eur J
Pharmacol. 542:136–140. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eun SY, Ko YS, Park SW, Chang KC and Kim
HJ: IL-1β enhances vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration via P2Y2 receptor-mediated RAGE expression and HMGB1
release. Vascul Pharmacol. 72:108–117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu XH, Fu YC, Zhang DW, Yin K and Tang CK:
Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 424:245–252. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|