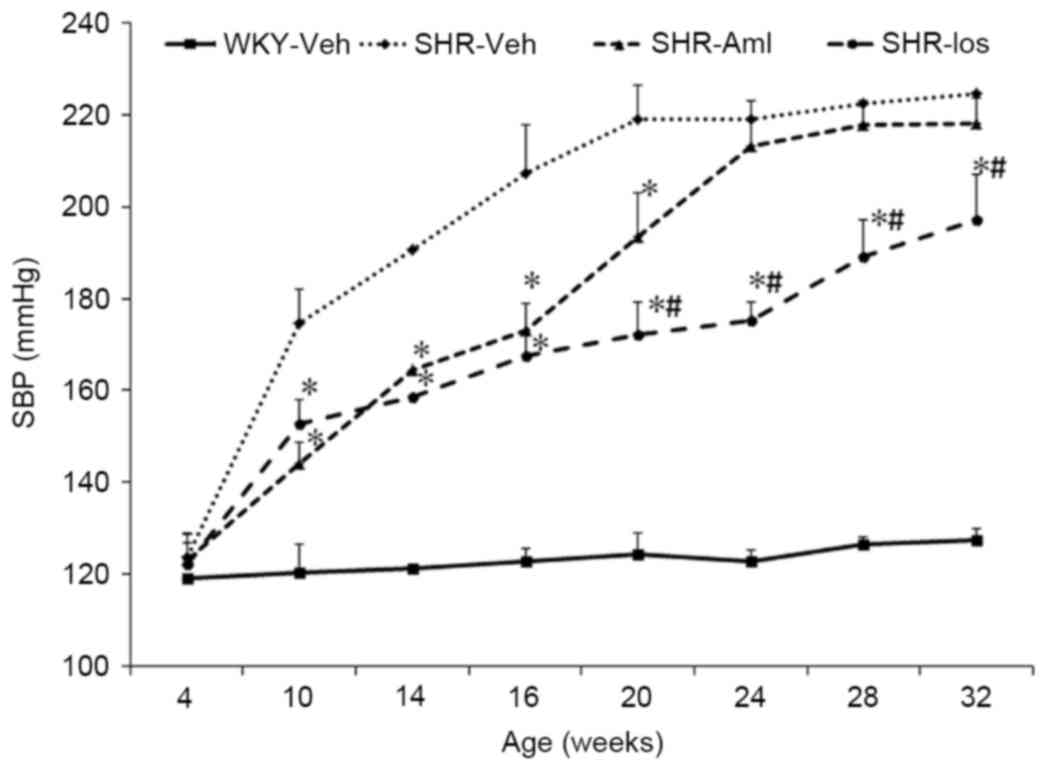
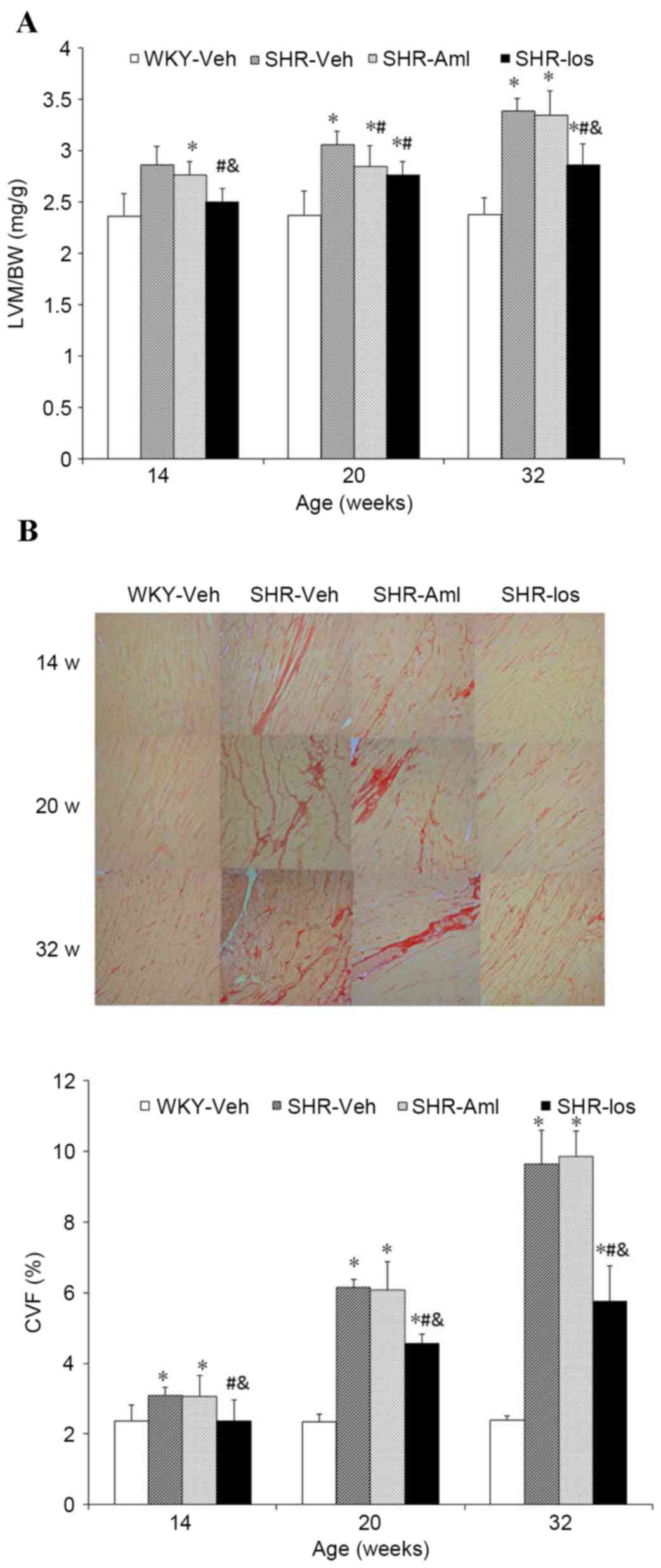
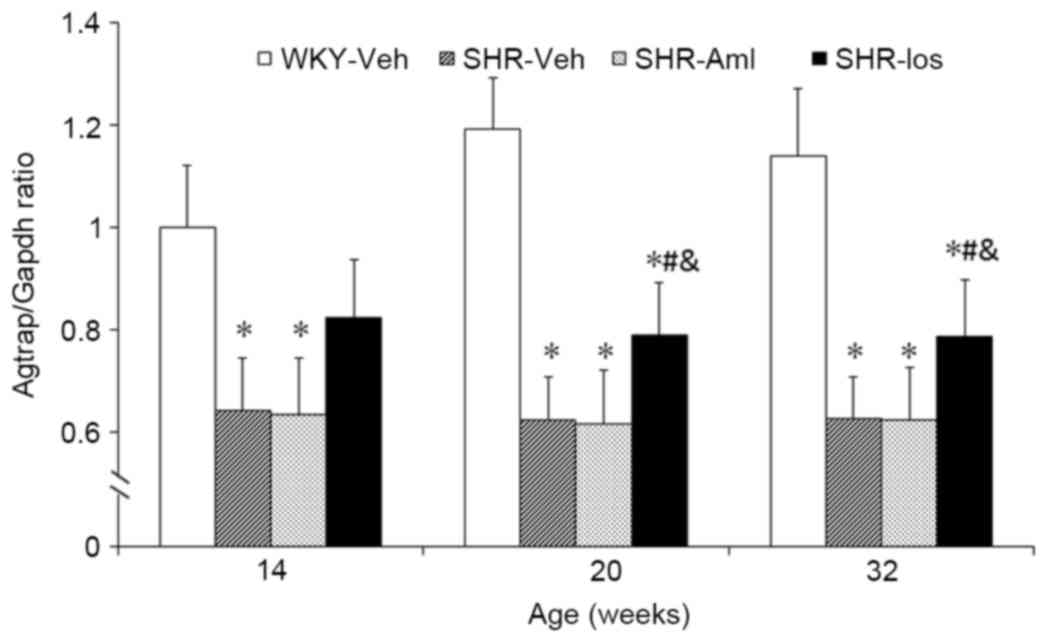
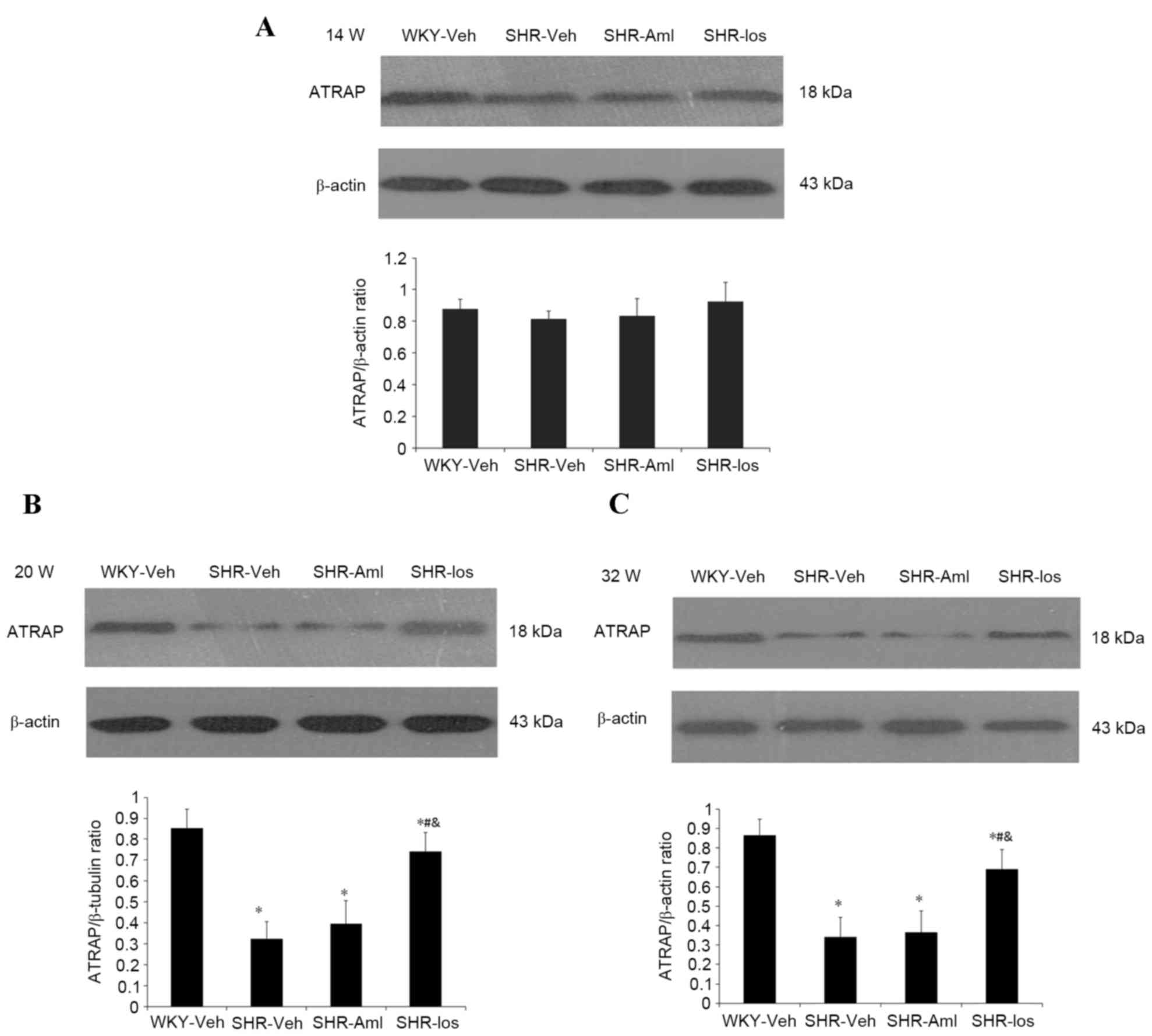
|
1
|
Taylor J: 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the
management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J. 34:2108–2109.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chatterjee S, Bavishi C, Sardar P, Agarwal
V, Krishnamoorthy P, Grodzicki T and Messerli FH: Meta-analysis of
left ventricular hypertrophy and sustained arrhythmias. Am J
Cardiol. 114:1049–1052. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB
and Castelli WP: Prognostic implications of echocardiographically
determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N
Engl J Med. 322:1561–1566. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Okin PM, Devereux RB, Nieminen MS, Jern S,
Oikarinen L, Viitasalo M, Toivonen L, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S,
Snapinn S, et al: Electrocardiographic strain pattern and
prediction of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in
hypertensive patients. Hypertension. 44:48–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang S, Xue H, Zou Y, Sun K, Fu C, Wang H
and Hui R: Left ventricular hypertrophy, abnormal ventricular
geometry and relative wall thickness are associated with increased
risk of stroke in hypertensive patients among the Han Chinese.
Hypertens Res. 37:870–874. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Charytan D: Is left ventricular
hypertrophy a modifiable risk factor in end-stage renal disease.
Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 23:578–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng F, Lin J, Lin L and Tang H: Transient
prehypertensive treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats: A
comparison of losartan and amlodipine regarding long-term blood
pressure, cardiac and renal protection. Int J Mol Med.
30:1376–1386. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Horiuchi M, Iwanami J and Mogi M:
Regulation of angiotensin II receptors beyond the classical
pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). 123:193–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lopez-Ilasaca M, Liu X, Tamura K and Dzau
VJ: The angiotensin II type I receptor-associated protein, ATRAP,
is a transmembrane protein and a modulator of angiotensin II
signaling. Mol Biol Cell. 14:5038–5050. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tanaka Y, Tamura K, Koide Y, Sakai M,
Tsurumi Y, Noda Y, Umemura M, Ishigami T, Uchino K, Kimura K, et
al: The novel angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R)-associated
protein ATRAP downregulates AT1R and ameliorates cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy. FEBS Lett. 579:1579–1586. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wakui H, Dejima T, Tamura K, Uneda K,
Azuma K, Maeda A, Ohsawa M, Kanaoka T, Azushima K and Kobayashi R:
Activation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein
exerts an inhibitory effect on vascular hypertrophy and oxidative
stress in angiotensin II-mediated hypertension. Cardiovasc Res.
100:511–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maeda A, Tamura K, Wakui H, Dejima T,
Ohsawa M, Azushima K, Kanaoka T, Uneda K, Matsuda M, Yamashita A,
et al: Angiotensin receptor-binding protein ATRAP/Agtrap inhibits
metabolic dysfunction with visceral obesity. J Am Heart Assoc.
2:e0003122013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wakui H, Tamura K, Tanaka Y, Matsuda M,
Bai Y, Dejima T, Masuda S, Shigenaga A, Maeda A, Mogi M, et al:
Cardiac-specific activation of angiotensin II type 1
receptor-associated protein completely suppresses cardiac
hypertrophy in chronic angiotensin II-infused mice. Hypertension.
55:1157–1164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shigenaga A, Tamura K, Wakui H, Masuda S,
Azuma K, Tsurumi-Ikeya Y, Ozawa M, Mogi M, Matsuda M, Uchino K, et
al: Effect of olmesartan on tissue expression balance between
angiotensin II receptor and its inhibitory binding molecule.
Hypertension. 52:672–678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baumann M, Sollinger D, Roos M, Lutz J and
Heemann U: Prehypertensive preconditioning improves adult
antihypertensive and cardioprotective treatment. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 332:1121–1126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Widdop RE and Li XC: A simple versatile
method for measuring tail cuff systolic blood pressure in conscious
rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 93:191–194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao J, Xie XL, Xie LD, et al: The
influence of naoxintong on myocardial fibrosis in spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Chin J of Integ Med. 6:188–190. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J,
Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA,
Kuznetsova T, et al: Recommendations for cardiac chamber
quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the
American society of echocardiography and the European association
of cardiovascular imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging.
16:233–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen HF, Xie LD and Xu CS: Role of heat
shock protein 27 phosphorylation in migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 327:1–6. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vasan RS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Kannel WB
and Levy D: Assessment of frequency of progression to hypertension
in non-hypertensive participants in the Framingham Heart Study: A
cohort study. Lancet. 358:1682–1686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vasan RS, Larson MG, Leip EP, Evans JC,
O'Donnell CJ, Kannel WB and Levy D: Impact of high-normal blood
pressure on the risk of cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med.
345:1291–1297. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Julius S, Nesbitt SD, Egan BM, Weber MA,
Michelson EL, Kaciroti N, Black HR, Grimm RH Jr, Messerli FH,
Oparil S, et al: Feasibility of treating prehypertension with an
angiotensin-receptor blocker. N Engl J Med. 354:1685–1697. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lüders S, Schrader J, Berger J, Unger T,
Zidek W, Böhm M, Middeke M, Motz W, Lübcke C, Gansz A, et al: The
PHARAO study: Prevention of hypertension with the
angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramipril in patients with
high-normal blood pressure: A prospective, randomized, controlled
prevention trial of the German Hypertension League. J Hypertens.
26:1487–1496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Racasan S, Braam B, van der Giezen DM,
Goldschmeding R, Boer P, Koomans HA and Joles JA: Perinatal
L-arginine and antioxidant supplements reduce adult blood pressure
in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension. 44:83–88. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harrap SB, Nicolaci JA and Doyle AE:
Persistent effects on blood pressure and renal haemodynamics
following chronic angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition with
perindopril. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 13:753–765. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen DG, Jin XQ and Wang HJ: Mechanisms
responsible for sustained hypotension after captopril treatment. J
Hypertens. 13:1113–1121. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Christensen KL, Jespersen LT and Mulvany
MJ: Development of blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive
rats after withdrawal of long-term treatment related to vascular
structure. J Hypertens. 7:83–90. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li N, Wang HX, Han QY, Li WJ, Zhang YL, Du
J, Xia YL and Li HH: Activation of the cardiac proteasome promotes
angiotension II-induced hypertrophy by down-regulation of ATRAP. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 79:303–314. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vahebi S, Ota A, Li M, Warren CM, De Tombe
PP, Wang Y and Solaro RJ: p38-MAPK induced dephosphorylation of
alpha-tropomyosin is associated with depression of myocardial
sarcomeric tension and ATPase activity. Circ Res. 100:408–415.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ng DC, Ng IH, Yeap YY, Badrian B,
Tsoutsman T, McMullen JR, Semsarian C and Bogoyevitch MA: Opposing
actions of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in regulating
microtubule stabilization during cardiac hypertrophy. J Biol Chem.
286:1576–1587. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Min LJ, Mogi M, Tamura K, Iwanami J,
Sakata A, Fujita T, Tsukuda K, Jing F, Iwai M and Horiuchi M:
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein prevents vascular
smooth muscle cell senescence via inactivation of
calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells pathway. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 47:798–809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiao D, Dasgupta C, Li Y, Huang X and
Zhang L: Perinatal nicotine exposure increases angiotensin II
receptor-mediated vascular contractility in adult offspring. PLoS
one. 9:e1081612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Friso S, Pizzolo F, Choi SW, Guarini P,
Castagna A, Ravagnani V, Carletto A, Pattini P, Corrocher R and
Olivieri O: Epigenetic control of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase 2 gene promoter is related to human hypertension.
Atherosclerosis. 199:323–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho HM, Lee HA, Kim HY, Han HS and Kim IK:
Expression of Na+-K+ −2Cl- cotransporter 1 is epigenetically
regulated during postnatal development of hypertension. Am J
Hypertens. 24:1286–1293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pei F, Wang X, Yue R, Chen C, Huang J,
Huang J, Li X and Zeng C: Differential expression and DNA
methylation of angiotensin type 1A receptors in vascular tissues
during genetic hypertension development. Mol Cell Biochem. 402:1–8.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Watson CJ, Horgan S, Neary R, Glezeva N,
Tea I, Corrigan N, McDonald K, Ledwidge M and Baugh J: Epigenetic
therapy for the treatment of hypertension-induced cardiac
hypertrophy and fibrosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 21:127–137.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Subramaniam D, Thombre R, Dhar A and Anant
S: DNA methyltransferases: A novel target for prevention and
therapy. Front Oncol. 4:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rexhaj E, Bloch J, Jayet PY, Rimoldi SF,
Dessen P, Mathieu C, Tolsa JF, Nicod P, Scherrer U and Sartori C:
Fetal programming of pulmonary vascular dysfunction in mice: Role
of epigenetic mechanisms. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
301:H247–H252. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|