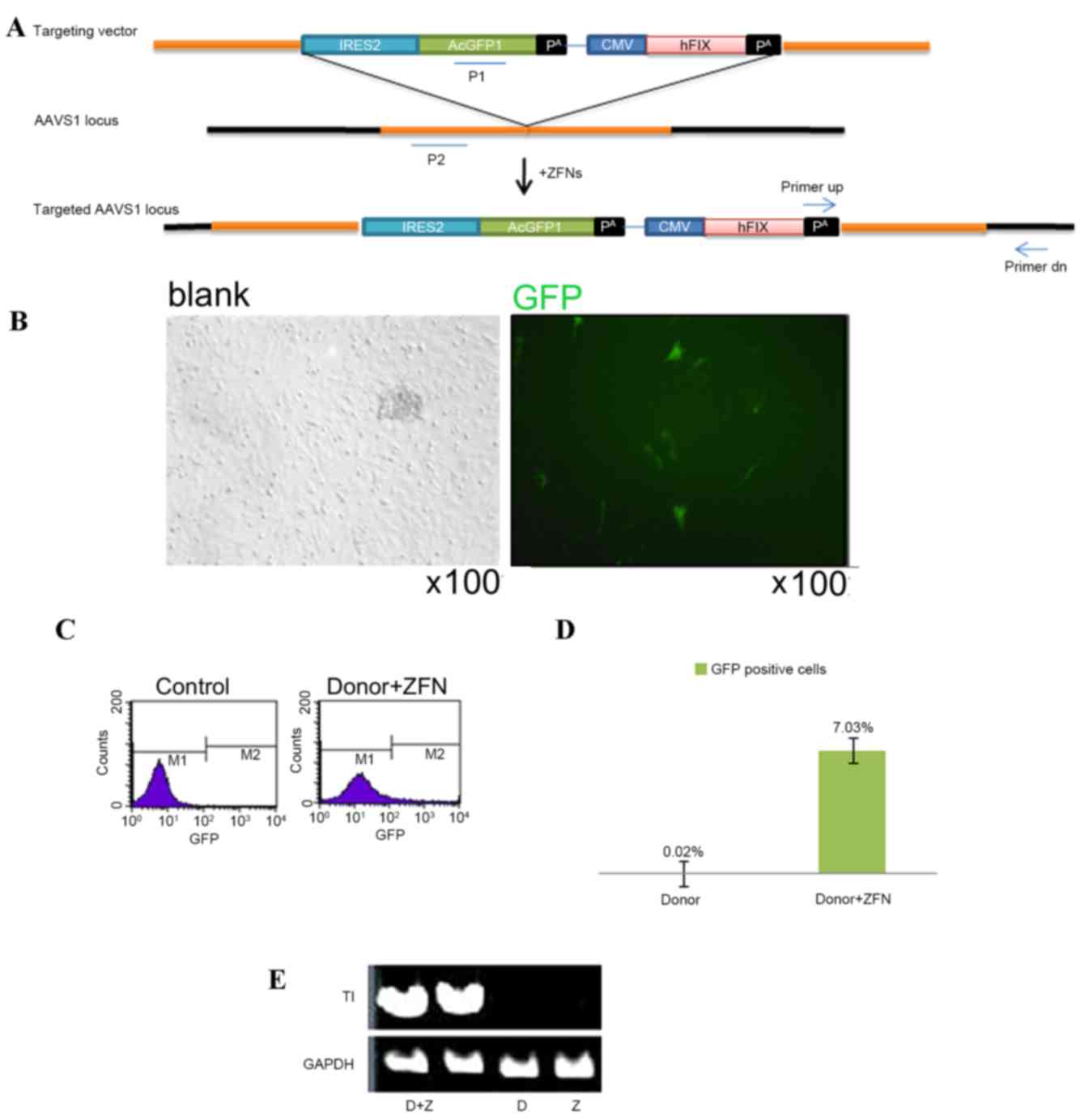
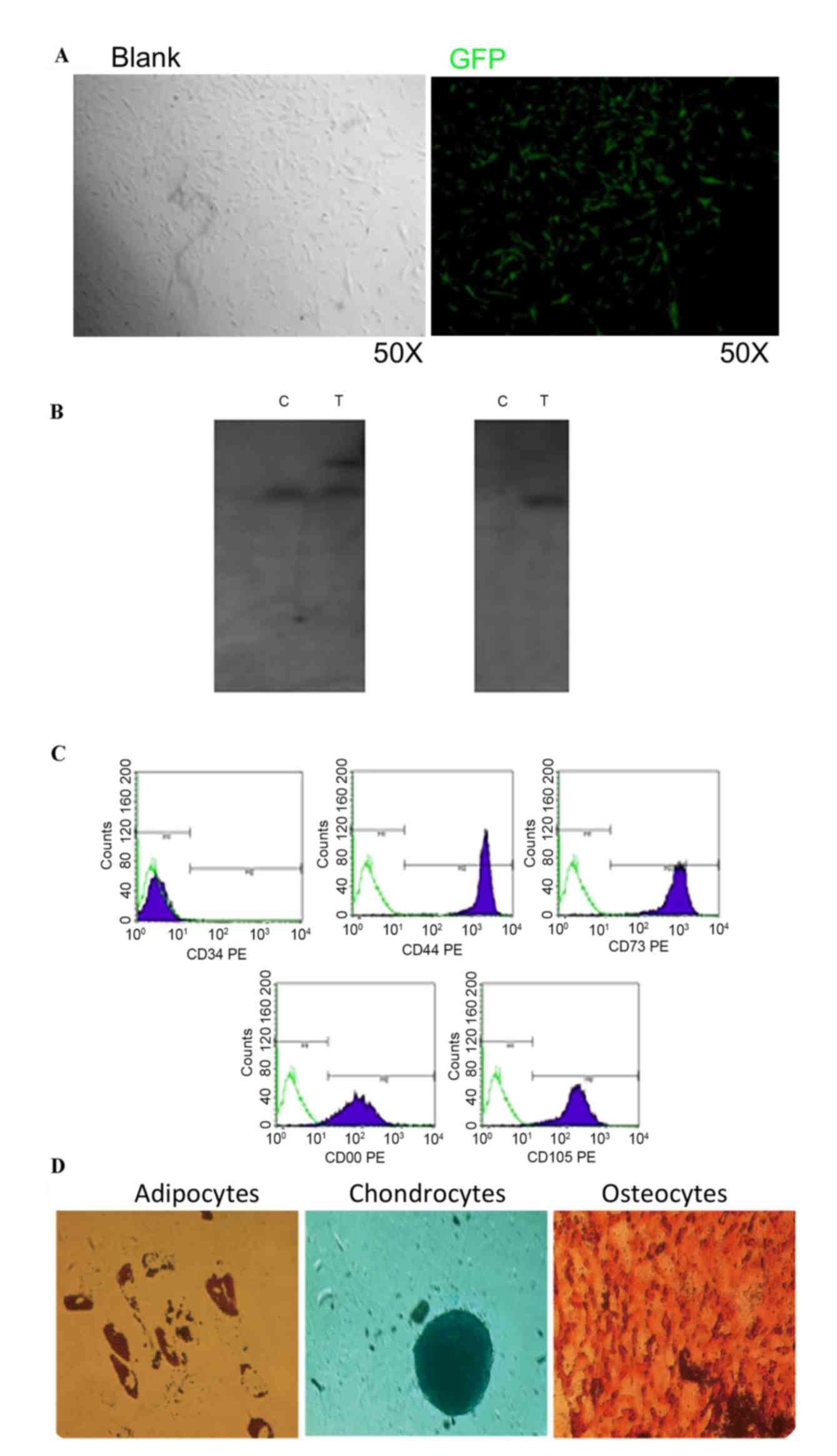
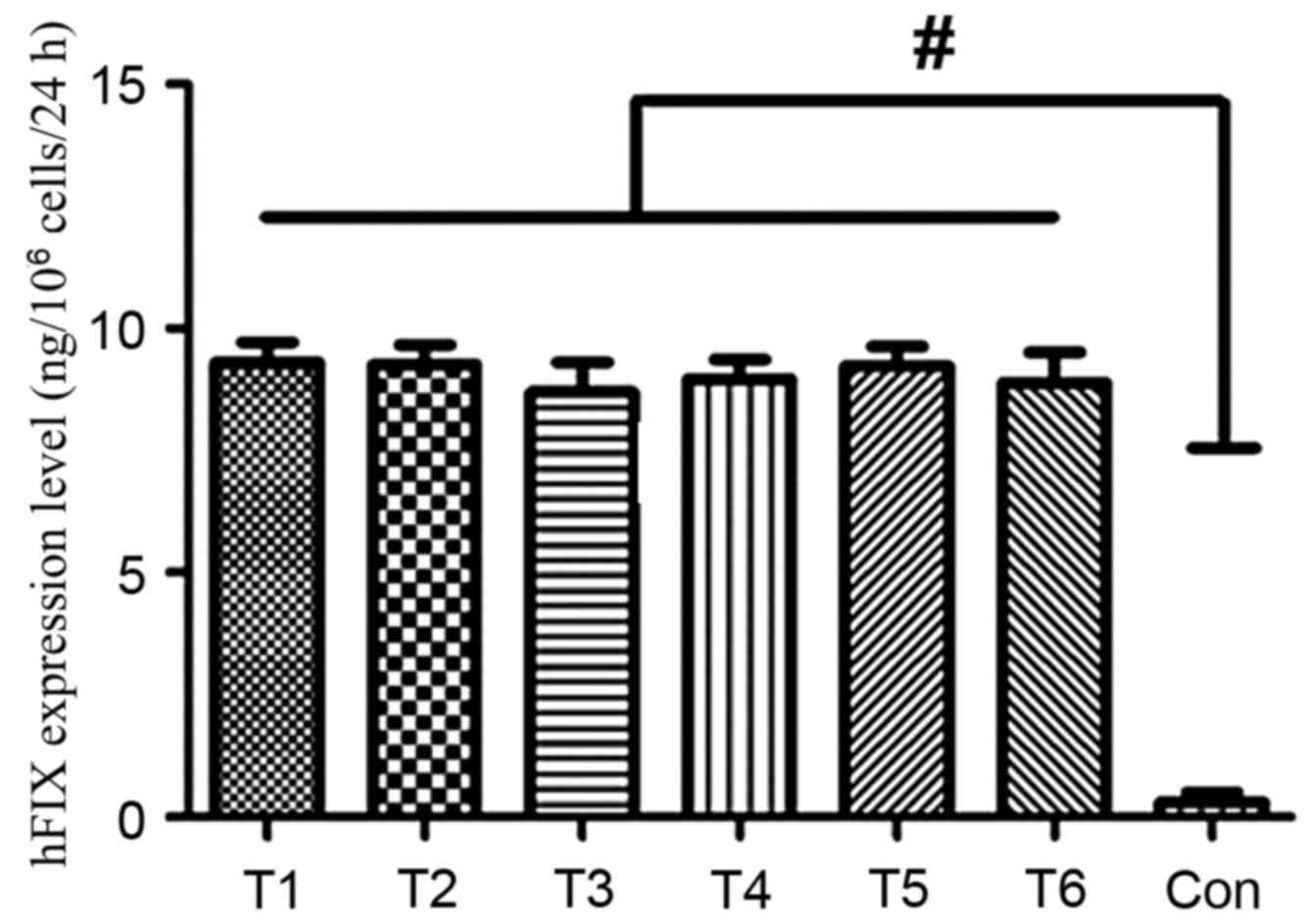
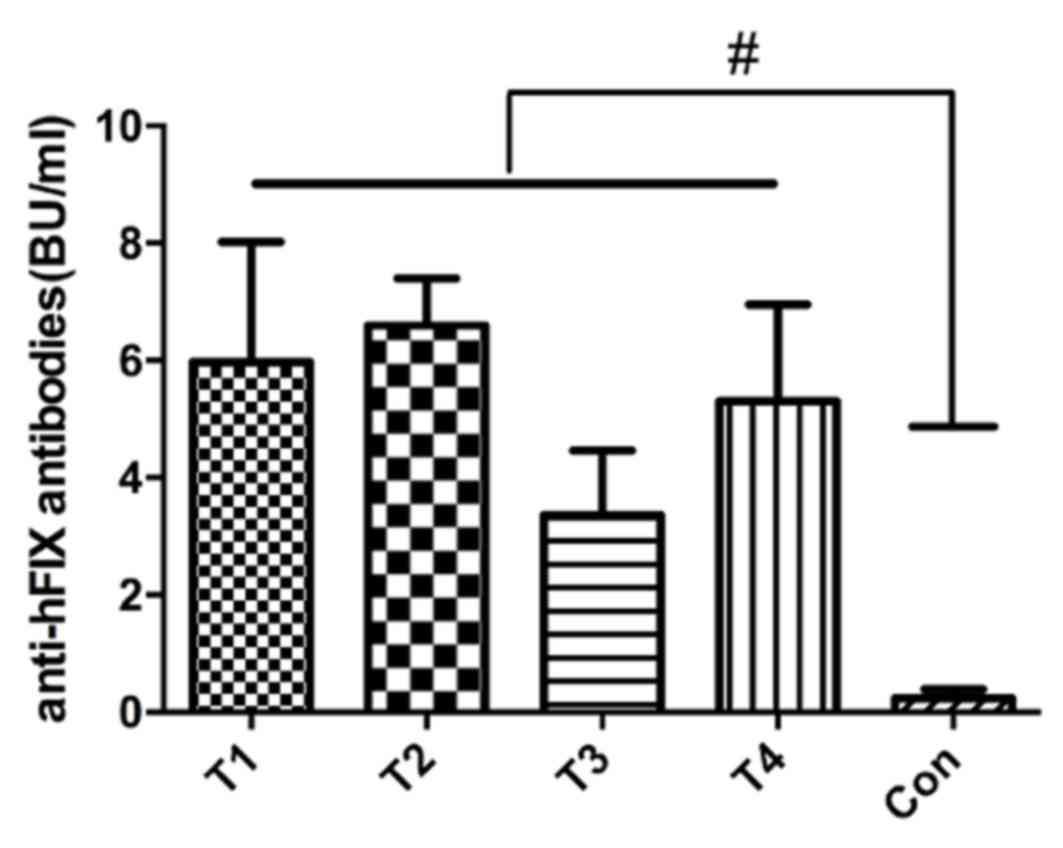
|
1
|
Giannelli F, Choo KH, Rees DJ, Boyd Y,
Rizza CR and Brownlee GG: Gene deletions in patients with
haemophilia B and anti-factor IX antibodies. Nature. 303:181–182.
1983. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Beltrami EM, Williams IT, Shapiro CN and
Chamberland ME: Risk and management of blood-borne infections in
health care workers. Clin Microbiol Rev. 13:385–407. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peters RT, Low SC, Kamphaus GD, Dumont JA,
Amari JV, Lu Q, Zarbis-Papastoitsis G, Reidy TJ, Merricks EP,
Nichols TC and Bitonti AJ: Prolonged activity of factor IX as a
monomeric Fc fusion protein. Blood. 115:2057–2064. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kung SH, Hagstrom JN, Cass D, Tai SJ, Lin
HF, Stafford DW and High KA: Human factor IX corrects the bleeding
diathesis of mice with hemophilia B. Blood. 91:784–790.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
VandenDriessche T, Collen D and Chuah MK:
Viral vector-mediated gene therapy for hemophilia. Curr Gene Ther.
1:301–315. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bittner RE, Schöfer C, Weipoltshammer K,
Ivanova S, Streubel B, Hauser E, Freilinger M, Höger H, Elbe-Bürger
A and Wachtler F: Recruitment of bone-marrow-derived cells by
skeletal and cardiac muscle in adult dystrophic mdx mice. Anat
Embryol (Berl). 199:391–396. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferreira E, Potier E, Logeart-Avramoglou
D, Salomskaite-Davalgiene S, Mir LM and Petite H: Optimization of a
gene electrotransfer method for mesenchymal stem cell transfection.
Gene ther. 15:537–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baksh D, Song L and Tuan RS: Adult
mesenchymal stem cells: Characterization, differentiation, and
application in cell and gene therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 8:301–316.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Benabdallah BF, Allard E, Yao S, Friedman
G, Gregory PD, Eliopoulos N, Fradette J, Spees JL, Haddad E, Holmes
MC and Beauséjour CM: Targeted gene addition to human mesenchymal
stromal cells as a cell-based plasma-soluble protein delivery
platform. Cytotherapy. 12:394–399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kucerova L, Altanerova V, Matuskova M,
Tyciakova S and Altaner C: Adipose tissue-derived human mesenchymal
stem cells mediated prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Res.
67:6304–6313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ellis J: Silencing and variegation of
gammaretrovirus and lentivirus vectors. Hum Gene Ther.
16:1241–1246. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Von Kalle C, Schmidt
M, McCormack MP, Wulffraat N, Leboulch P, Lim A, Osborne CS,
Pawliuk R, Morillon E, et al: LMO2-associated clonal T cell
proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1.
Science New York, N.Y.: 302. pp. pp415–419. 2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lombardo A, Cesana D, Genovese P, Di
Stefano B, Provasi E, Colombo DF, Neri M, Magnani Z, Cantore A, Lo
Riso P, et al: Site-specific integration and tailoring of cassette
design for sustainable gene transfer. Nat Methods. 8:861–869. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bartsch E, Park AL, Kingdom JC and Ray JG:
Risk threshold for starting low dose aspirin in pregnancy to
prevent preeclampsia: An opportunity at a low cost. PloS one.
10:e01162962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedenstein AJ, Chailakhjan RK and
Lalykina KS: The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer
cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue
Kinet. 3:393–403. 1970.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hockemeyer D, Soldner F, Beard C, Gao Q,
Mitalipova M, DeKelver RC, Katibah GE, Amora R, Boydston EA,
Zeitler B, et al: Efficient targeting of expressed and silent genes
in human ESCs and iPSCs using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat
Biotechnol. 27:851–857. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li SJ, Shi RZ, Bai YP, Hong D, Yang W,
Wang X, Mo L and Zhang GG: Targeted introduction of tissue
plasminogen activator (TPA) at the AAVS1 locus in mesenchymal stem
cells (MSCs) and its stable and effective expression. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 437:74–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doering CB: Retroviral modification of
mesenchymal stem cells for gene therapy of hemophilia. Methods Mol
Biol. 433:203–212. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Van Damme A, Thorrez L, Ma L, Vandenburgh
H, Eyckmans J, Dell'Accio F, De Bari C, Luyten F, Lillicrap D,
Collen D, et al: Efficient lentiviral transduction and improved
engraftment of human bone marrow mesenchymal cells. Stem Cells.
24:896–907. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Coutu DL, Cuerquis J, El Ayoubi R, Forner
KA, Roy R, François M, Griffith M, Lillicrap D, Yousefi AM,
Blostein MD and Galipeau J: Hierarchical scaffold design for
mesenchymal stem cell-based gene therapy of hemophilia B.
Biomaterials. 32:295–305. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sayyar B, Dodd M, Wen J, Ma S,
Marquez-Curtis L, Janowska-Wieczorek A and Hortelano G:
Encapsulation of factor IX-engineered mesenchymal stem cells in
fibrinogen-alginate microcapsules enhances their viability and
transgene secretion. J Tissue Eng. 3:20417314124620182012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chamberlain J, Yamagami T, Colletti E,
Theise ND, Desai J, Frias A, Pixley J, Zanjani ED, Porada CD and
Almeida-Porada G: Efficient generation of human hepatocytes by the
intrahepatic delivery of clonal human mesenchymal stem cells in
fetal sheep. Hepatology. 46:1935–1945. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shi D, Chen G, Lv L, Li L, Wei D, Gu P,
Gao J, Miao Y and Hu W: The effect of lentivirus-mediated TH and
GDNF genetic engineering mesenchymal stem cells on Parkinson's
disease rat model. Neurol Sci. 32:41–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang W, Xu X, Li Z, Lendlein A and Ma N:
Genetic engineering of mesenchymal stem cells by non-viral gene
delivery. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 58:19–48. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee K, Majumdar MK, Buyaner D, Hendricks
JK, Pittenger MF and Mosca JD: Human mesenchymal stem cells
maintain transgene expression during expansion and differentiation.
Mol Ther. 3:857–866. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao S, Sukonnik T, Kean T, Bharadwaj RR,
Pasceri P and Ellis J: Retrovirus silencing, variegation,
extinction, and memory are controlled by a dynamic interplay of
multiple epigenetic modifications. Mol Ther. 10:27–36. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liew CG, Draper JS, Walsh J, Moore H and
Andrews PW: Transient and stable transgene expression in human
embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 25:1521–1528. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ogata T, Kozuka T and Kanda T:
Identification of an insulator in AAVS1, a preferred region for
integration of adeno-associated virus DNA. J Virol. 77:9000–9007.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Smith JR, Maguire S, Davis LA, Alexander
M, Yang F, Chandran S, ffrench-Constant C and Pedersen RA: Robust,
persistent transgene expression in human embryonic stem cells is
achieved with AAVS1-targeted integration. Stem Cells. 26:496–504.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sethe S, Scutt A and Stolzing A: Aging of
mesenchymal stem cells. Ageing Res Rev. 5:91–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|