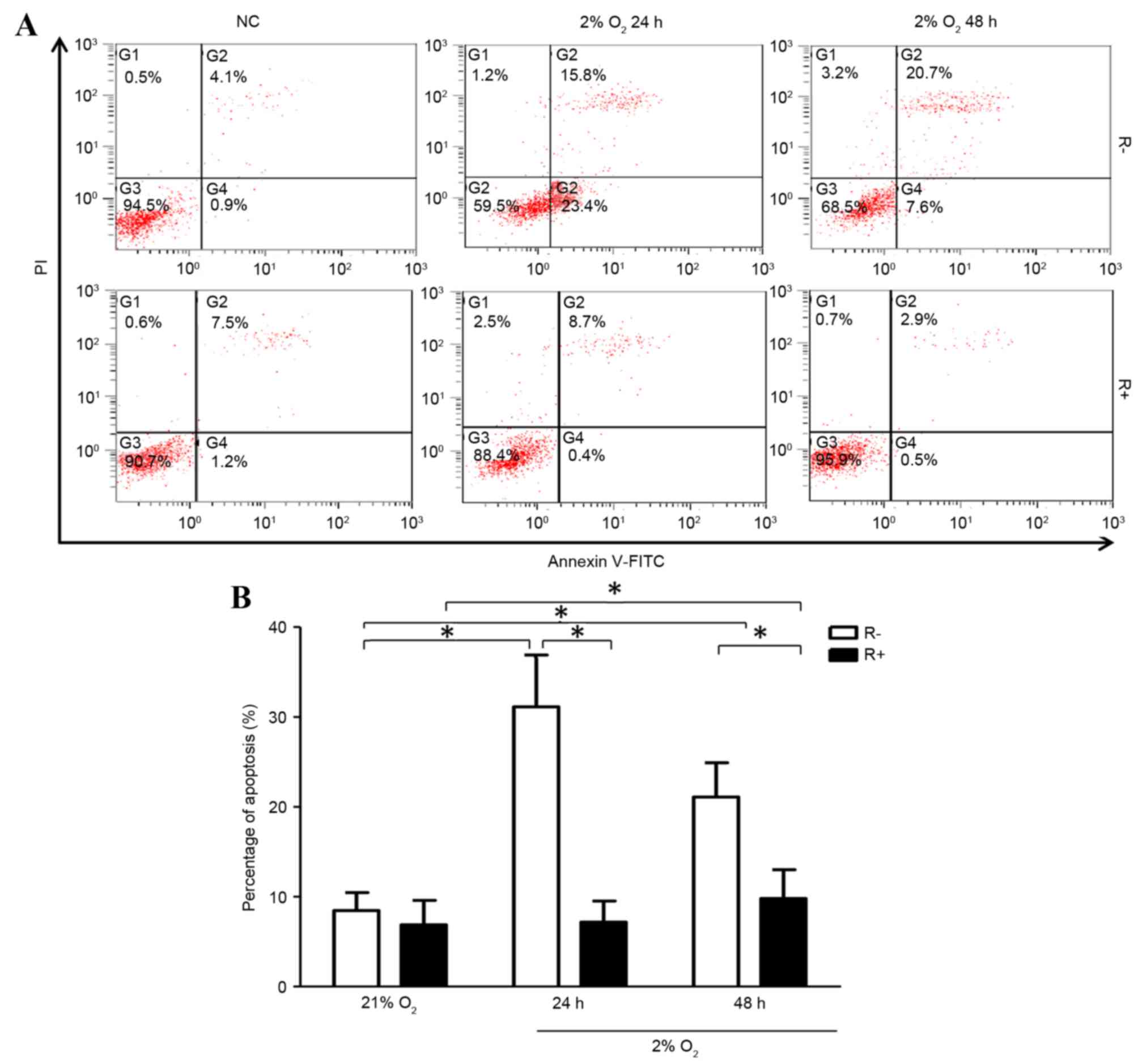
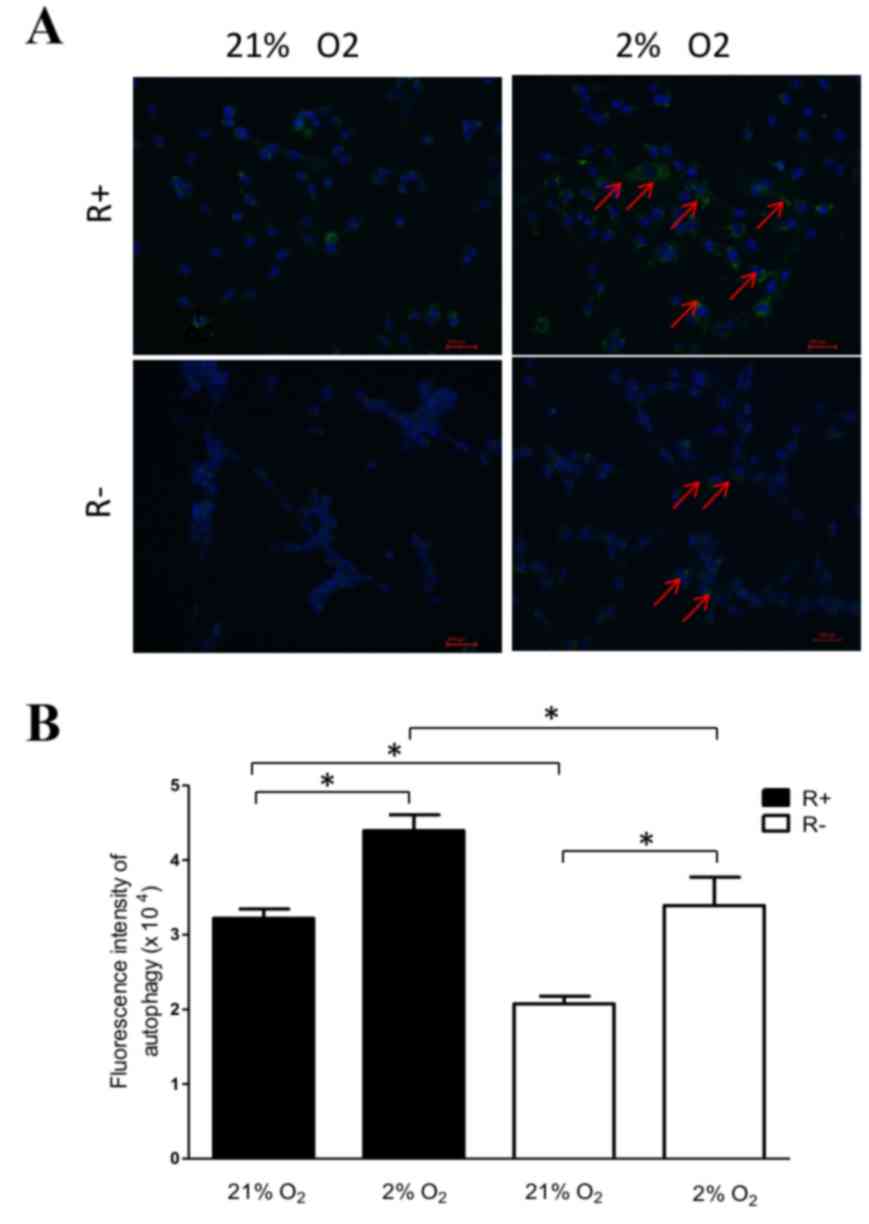
|
1
|
Liu W, D'Ercole JA and Ye P: Blunting type
1 insulin-like growth factor receptor expression exacerbates
neuronal apoptosis following hypoxic/ischemic injury. BMC Neurosci.
12:642011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Du L, Yu Y, Ma H, Lu X, Ma L, Jin Y and
Zhang H: Hypoxia enhances protective effect of placental-derived
mesenchymal stem cells on damaged intestinal epithelial cells by
promoting secretion of insulin-like growth factor-1. Int J Mol Sci.
15:1983–2002. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li HX, Zhou YF, Zhao X, Jiang B and Yang
XJ: GATA-4 protects against hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte injury:
Effects on mitochondrial membrane potential. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 92:669–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Caldwell CC, Tschoep J and Lentsch AB:
Lymphocyte function during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. J
Leukoc Biol. 82:457–464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ildefonso JA and Arias-Diaz J:
Pathophysiology of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cir Esp.
87:202–209. 2010.(In Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vujaskovic Z, Anscher MS, Feng QF, Rabbani
ZN, Amin K, Samulski TS, Dewhirst MW and Haroon ZA:
Radiation-induced hypoxia may perpetuate late normal tissue injury.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 50:851–855. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vujaskovic Z, Marks LB and Anscher MS: The
physical parameters and molecular events associated with
radiation-induced lung toxicity. Semin Radiat Oncol. 10:296–307.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo Y, Liu X, Zheng Q, Wan X, Ouyang S,
Yin Y, Sui X, Liu J and Yang X: Hydrogen sulfide prevents
hypoxia-induced apoptosis via inhibition of an H2O2-activated
calcium signaling pathway in mouse hippocampal neurons. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 425:473–477. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim BM and Chung HW: Hypoxia/reoxygenation
induces apoptosis through a ROS-mediated caspase-8/Bid/Bax pathway
in human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 363:745–750.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng C, Rao W, Zhang L, Wang K, Hui H,
Wang L, Su N, Luo P, Hao YL, Tu Y, et al: Mitofusin 2 ameliorates
hypoxia-induced apoptosis via mitochondrial function and signaling
pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 69:29–40. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuo CY, Chiu YC, Lee AY and Hwang TL:
Mitochondrial Lon protease controls ROS-dependent apoptosis in
cardiomyocyte under hypoxia. Mitochondrion. 23:7–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Laron Z: Insulin-like growth factor 1
(IGF-1): A growth hormone. Mol Pathol. 54:311–316. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chisalita SI and Arnqvist HJ: Insulin-like
growth factor I receptors are more abundant than insulin receptors
in human micro- and macrovascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 286:E896–E901. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang M, Woodard LE, Liang A, Luo J,
Wilson MH, Mitch WE and Cheng J: Protective role of insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor in endothelial cells against unilateral
ureteral obstruction-induced renal fibrosis. Am J Pathol.
185:1234–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Custodio RJ, do Carmo Custodio VI,
Scrideli CA, Milani SL Sader, Cervi MC, Cupo P and Martinelli CE
Jr: Impact of hypoxia on IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-3, ALS and IGFBP-1
regulation and on IGF1R gene expression in children. Growth Horm
IGF Res. 22:186–191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morgan BL and Chao CR: The effects of
hypoxia on growth cones in the ovine fetal brain. J Matern Fetal
Neonatal Med. 16:55–59. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Heck S, Lezoualc'h F, Engert S and Behl C:
Insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated neuroprotection against
oxidative stress is associated with activation of nuclear factor
kappaB. J Biol Chem. 274:9828–9835. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baregamian N, Song J, Jeschke MG, Evers BM
and Chung DH: IGF-1 protects intestinal epithelial cells from
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J Surg Res. 136:31–37. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maldonado C, Cea P, Adasme T, Collao A,
Díaz-Araya G, Chiong M and Lavandero S: IGF-1 protects cardiac
myocytes from hyperosmotic stress-induced apoptosis via CREB.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:1112–1118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu D, Watanabe H, Shibuya H and Miura M:
Redundancy of radioresistant signaling pathways originating from
insulin-like growth factor I receptor. J Biol Chem. 278:6702–6709.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu D, Shibuya H and Miura M: Roles of the
insulin-like growth factor I receptor C-terminus in cellular
radioresistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 311:174–178. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martin M, Lefaix J and Delanian S:
TGF-beta1 and radiation fibrosis: A master switch and a specific
therapeutic target? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 47:277–290. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murphy MP: How mitochondria produce
reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. 417:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lopez-Lopez C, LeRoith D and Torres-Aleman
I: Insulin-like growth factor I is required for vessel remodeling
in the adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:9833–9838. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Conti E, Carrozza C, Capoluongo E, Volpe
M, Crea F, Zuppi C and Andreotti F: Insulin-like growth factor-1 as
a vascular protective factor. Circulation. 110:2260–2265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Adams MM, Forbes M Elizabeth, Linville M
Constance, Riddle DR, Sonntag WE and Brunso-Bechtold JK: Stability
of local brain levels of insulin-like growth factor-I in two
well-characterized models of decreased plasma IGF-I. Growth
Factors. 27:181–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Carro E, Spuch C, Trejo JL, Antequera D
and Torres-Aleman I: Choroid plexus megalin is involved in
neuroprotection by serum insulin-like growth factor I. J Neurosci.
25:10884–10893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Avivar-valderas A, Bobrovnikova-Marjon E,
Diehl J Alan, Bardeesy N, Debnath J and Aguirre-Ghiso JA:
Regulation of autophagy during ECM detachment is linked to a
selective inhi- bition of mTORC1 by PERK. Oncogene. 32:4932–4940.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu B, Wen X and Cheng Y: Survival or
death: Disequilibrating the oncogenic and tumor suppressive
autophagy in cancer. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rouschop KM, Ramaekers CH, Schaaf MB,
Keulers TG, Savelkouls KG, Lambin P, Koritzinsky M and Wouters BG:
Autophagy is required during cycling hypoxia to lower production of
reactive oxygen species. Radiother Oncol. 92:411–416. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Farombi EO: Genotoxicity of chloroquine in
rat liver cells: Protective role of free radical scavengers. Cell
Biol Toxicol. 22:159–167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun Y, Xing X, Liu Q, Wang Z, Xin Y, Zhang
P, Hu C and Liu Y: Hypoxia-induced autophagy reduces
radiosensitivity by the HIF-1α/miR-210/Bcl-2 pathway in colon
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:750–756. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Q, Sun Y, Lv Y, Le Z, Xin Y, Zhang P
and Liu Y: TERT alleviates irradiation-induced late rectal injury
by reducing hypoxia-induced ROS levels through the activation of
NF-κB and autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 38:785–793. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shao X, Lai D, Zhang L and Xu H: Induction
of autophagy and apoptosis via PI3K/AKT/TOR pathways by
azadirachtin a in spodoptera litura cells. Sci Rep. 6:354822016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan XJ, Wang Y, Wang L and Zhu M:
Salidroside induces apoptosis and autophagy in human colorectal
cancer cells through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Oncol
Rep. 36:3559–3567. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Opgaard O Saetrum and Wang PH: IGF-I is a
matter of heart. Growth Horm IGF Res. 15:89–94. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Troncoso R, Vicencio JM, Parra V,
Nemchenko A, Kawashima Y, Del Campo A, Toro B, Battiprolu PK,
Aranguiz P, Chiong M, et al: Energy-preserving effects of IGF-1
antagonize starvation-induced cardiac autophagy. Cardiovasc Res.
93:320–329. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bitto A, Lerner C, Torres C, Roell M,
Malaguti M, Perez V, Lorenzini A, Hrelia S, Ikeno Y, Matzko ME, et
al: Long-term IGF-I exposure decreases autophagy and cell
viability. PLoS One. 5:e125922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jia G, Cheng G, Gangahar DM and Agrawal
DK: Insulin-like growth factor-1 and TNF-alpha regulate autophagy
through c-jun N-terminal kinase and Akt pathways in human
atherosclerotic vascular smooth cells. Immunol Cell Biol.
84:448–454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Aki T, Yamaguchi K, Fujimiya T and
Mizukami Y: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase accelerates autophagic cell
death during glucose deprivation in the rat cardiomyocyte-derived
cell line H9c2. Oncogene. 22:8529–8535. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Renna M, Bento CF, Fleming A, Menzies FM,
Siddiqi FH, Ravikumar B, Puri M, Garcia-Arencibia M, Sadiq O,
Corrochano S, et al: IGF-1 receptor antagonism inhibits autophagy.
Hum Mol Genet. 22:4528–4544. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bains M, Florez-McClure ML and Heidenreich
KA: Insulin-like growth factor-I prevents the accumulation of
autophagic vesicles and cell death in Purkinje neurons by
increasing the rate of autophagosome-to-lysosome fusion and
degradation. J Biol Chem. 284:20398–20407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|