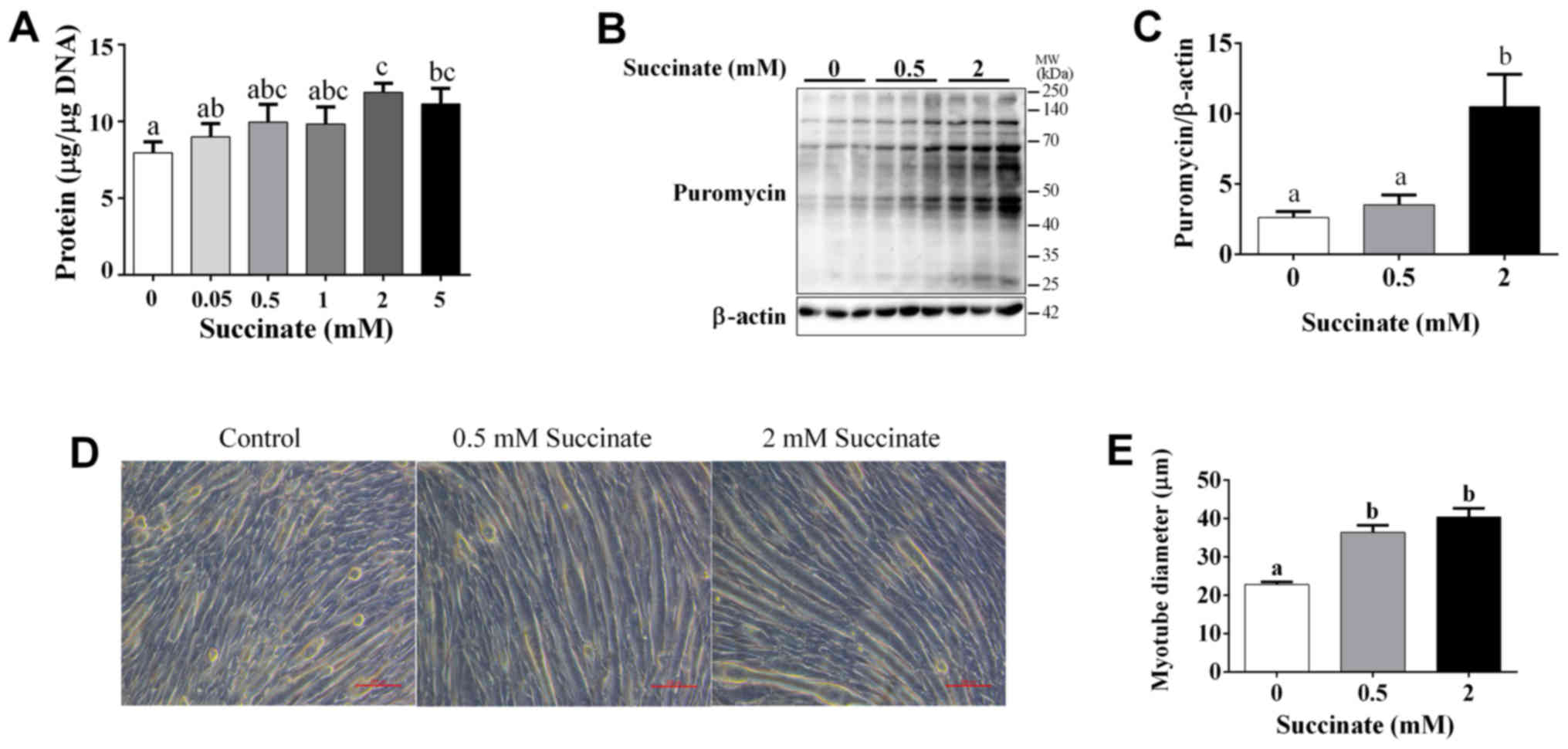
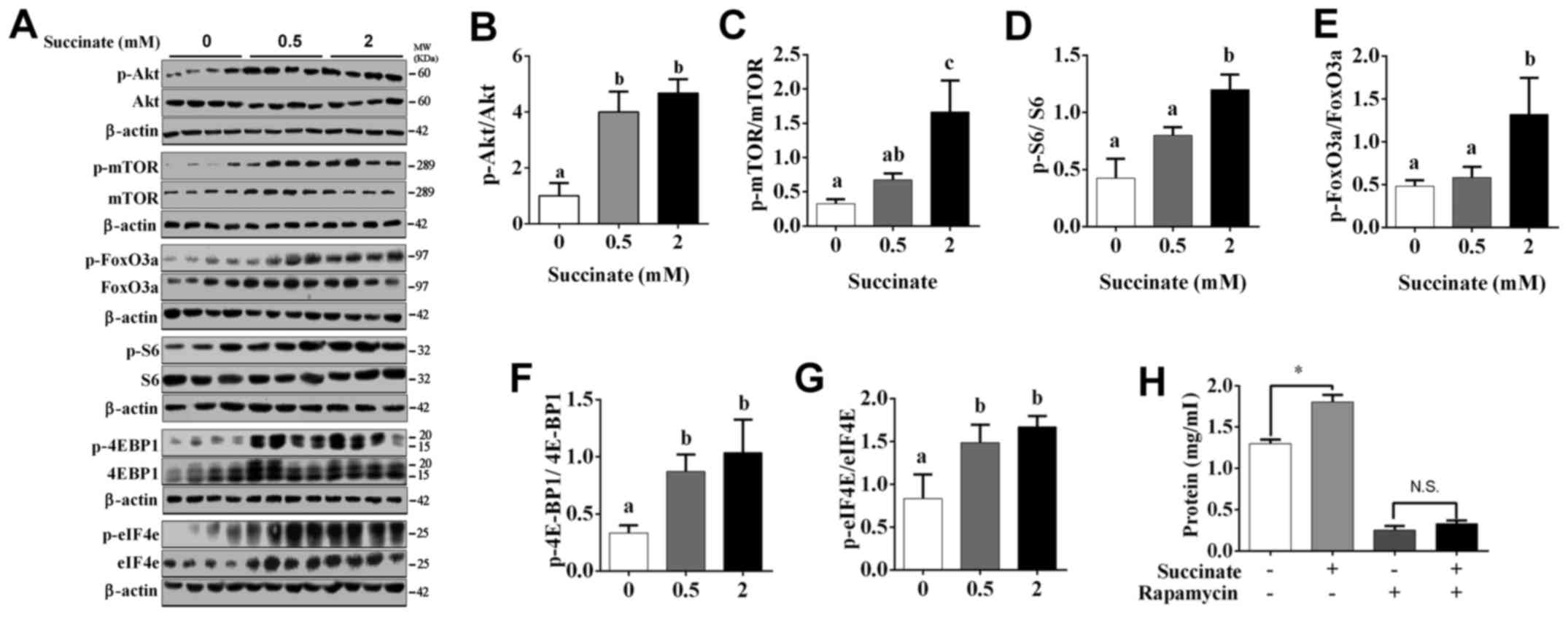
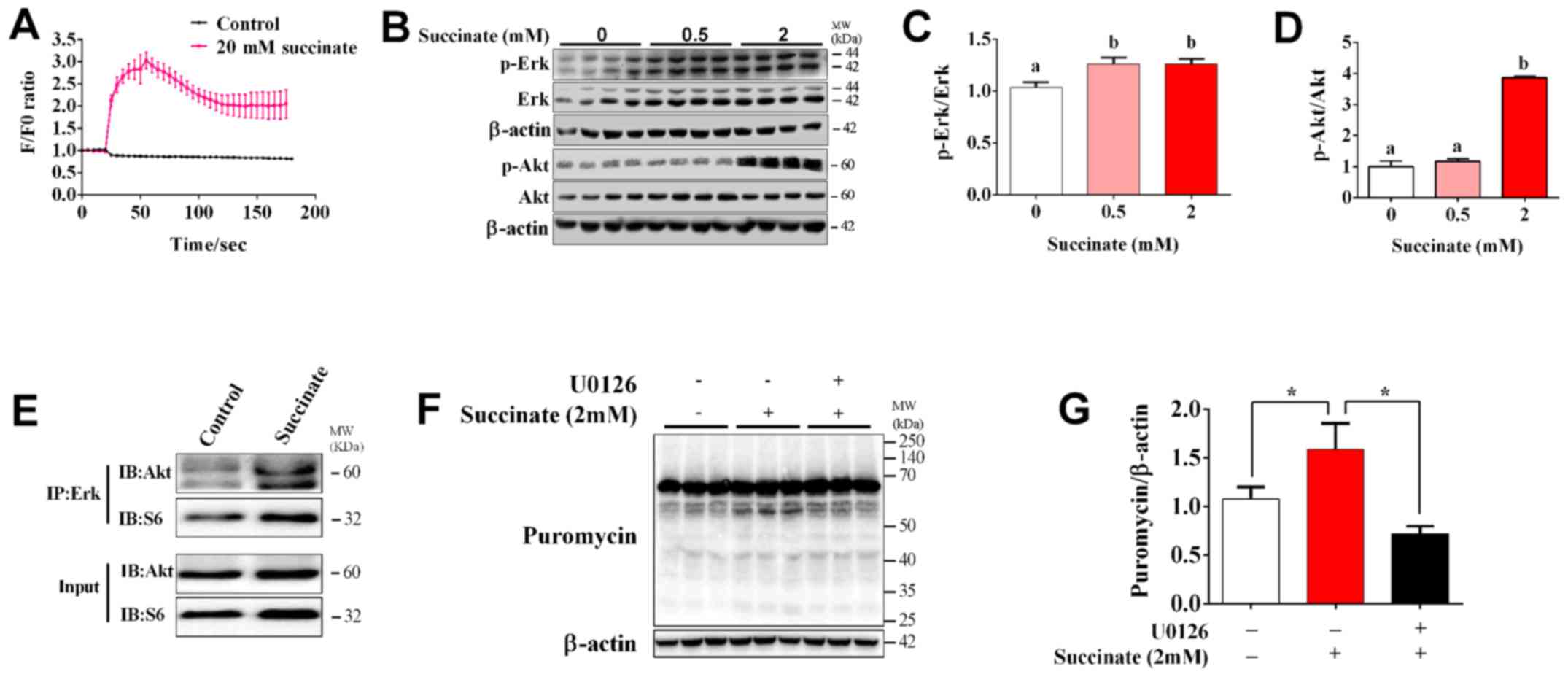
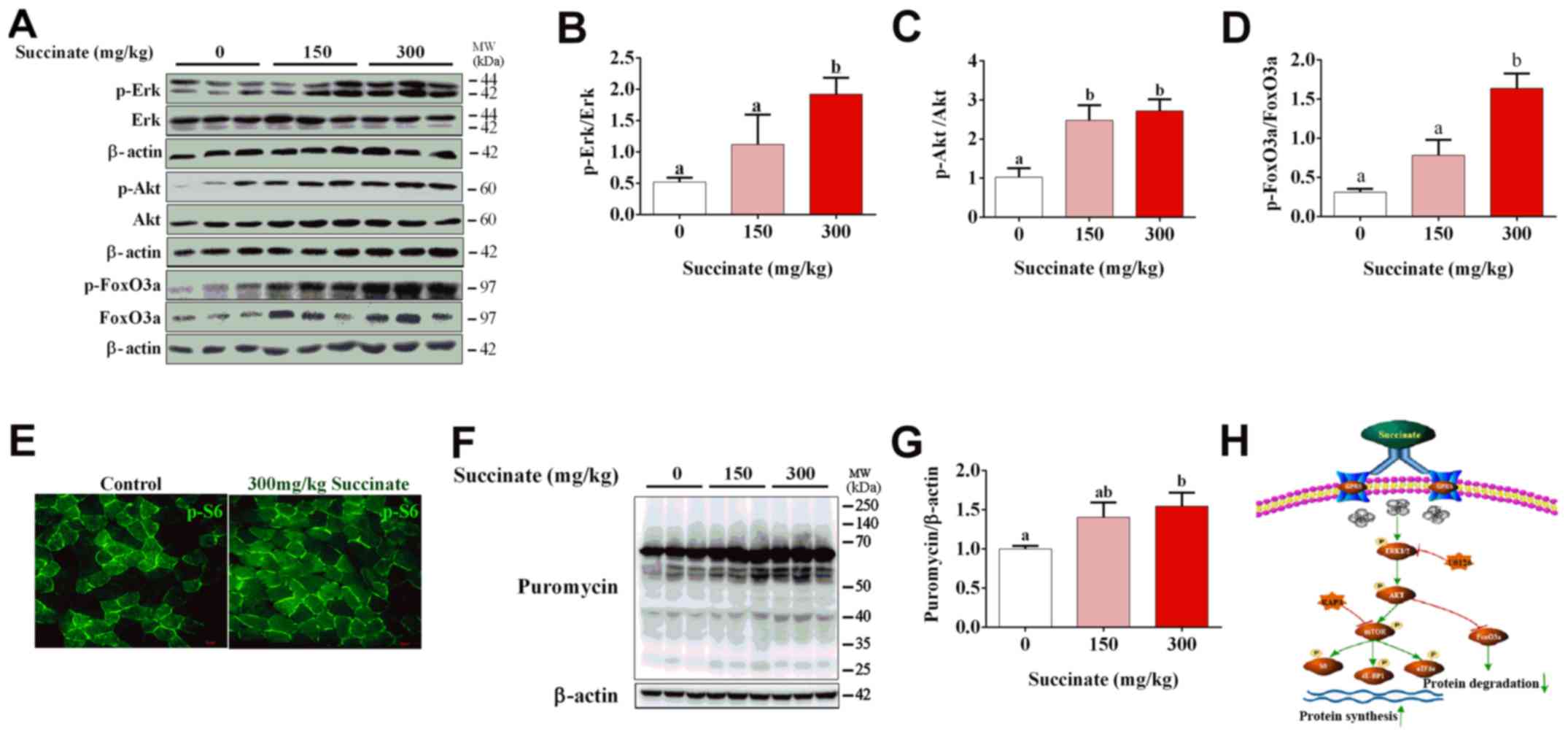
|
1
|
Fanzani A, Conraads VM, Penna F and
Martinet W: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of skeletal muscle
atrophy: An update. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 3:163–179. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sandri M: Signaling in muscle atrophy and
hypertrophy. Physiology (Bethesda). 23:160–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cai X, Zhu C, Xu Y, Jing Y, Yuan Y, Wang
L, Wang S, Zhu X, Gao P, Zhang Y, et al: Alpha-ketoglutarate
promotes skeletal muscle hypertrophy and protein synthesis through
Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Sci Rep. 6:268022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Egerman MA and Glass DJ: Signaling
pathways controlling skeletal muscle mass. Crit Rev Biochem Mol
Biol. 49:59–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brooks NE and Myburgh KH: Skeletal muscle
wasting with disuse atrophy is multi-dimensional: The response and
interaction of myonuclei, satellite cells and signaling pathways.
Front Physiol. 5:992014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fuentes EN, Einarsdottir IE, Paredes R,
Hidalgo C, Valdes JA, Björnsson BT and Molina A: The TORC1/P70S6K
and TORC1/4EBP1 signaling pathways have a stronger contribution on
skeletal muscle growth than MAPK/ERK in an early vertebrate:
Differential involvement of the IGF system and atrogenes. Gen Comp
Endocrinol. 210:96–106. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schiaffino S, Dyar KA, Ciciliot S, Blaauw
B and Sandri M: Mechanisms regulating skeletal muscle growth and
atrophy. FEBS J. 280:4294–4314. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White JP, Gao S, Puppa MJ, Sato S, Welle
SL and Carson JA: Testosterone regulation of Akt/mTORC1/FoxO3a
signaling in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 365:174–186.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Crossland H, Constantin-Teodosiu D,
Gardiner SM, Constantin D and Greenhaff PL: A potential role for
Akt/FOXO signalling in both protein loss and the impairment of
muscle carbohydrate oxidation during sepsis in rodent skeletal
muscle. J Physiol. 586:5589–5600. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu Z, Long W, Fryburg DA and Barrett EJ:
The regulation of body and skeletal muscle protein metabolism by
hormones and amino acids. J Nutr. 136 1 Suppl:212S–217S.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suryawan A and Davis TA: Regulation of
protein degradation pathways by amino acids and insulin in skeletal
muscle of neonatal pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 5:82014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sugden PH and Fuller SJ: Regulation of
protein turnover in skeletal and cardiac muscle. Biochem J.
273:21–37. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suryawan A and Davis TA: Regulation of
protein synthesis by amino acids in muscle of neonates. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1445–1460. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van Schaardenburgh M, Wohlwend M, Rognmo Ø
and Mattsson EJ: Mitochondrial respiration after one session of
calf raise exercise in patients with peripheral vascular disease
and healthy older adults. PLoS One. 11:e01650382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsai HH, Chang SC, Chou CH, Weng TP, Hsu
CC and Wang JS: Exercise training alleviates hypoxia-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction in the lymphocytes of sedentary males.
Sci Rep. 6:351702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tretter L, Patocs A and Chinopoulos C:
Succinate, an intermediate in metabolism, signal transduction, ROS,
hypoxia, and tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1857:1086–1101.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sundström L, Greasley PJ, Engberg S,
Wallander M and Ryberg E: Succinate receptor GPR91, a Gα(i) coupled
receptor that increases intracellular calcium concentrations
through PLCβ. FEBS Lett. 587:2399–2404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aguiar CJ, Andrade VL, Gomes ER, Alves MN,
Ladeira MS, Pinheiro AC, Gomes DA, Almeida AP, Goes AM, Resende RR,
et al: Succinate modulates Ca(2+) transient and cardiomyocyte
viability through PKA-dependent pathway. Cell Calcium. 47:37–46.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Espinosa A, Leiva A, Peña M, Müller M,
Debandi A, Hidalgo C, Carrasco MA and Jaimovich E: Myotube
depolarization generates reactive oxygen species through NAD(P)H
oxidase; ROS-elicited Ca2+ stimulates ERK, CREB, early
genes. J Cell Physiol. 209:379–388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
May C, Weigl L, Karel A and Hohenegger M:
Extracellular ATP activates ERK1/ERK2 via a metabotropic P2Y1
receptor in a Ca2+ independent manner in differentiated
human skeletal muscle cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1497–1509. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishida H, Ikegami A, Kaneko C, Kakuma H,
Nishi H, Tanaka N, Aoyama M, Usami M and Okimura Y: Dexamethasone
and BCAA failed to modulate muscle mass and mTOR signaling in
GH-deficient rats. PLoS One. 10:e01288052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang Q, He L, Hou Y, Chen J, Duan Y, Deng
D, Wu G, Yin Y and Yao K: Alpha-ketoglutarate enhances milk protein
synthesis by porcine mammary epithelial cells. Amino Acids.
48:2179–2188. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duan Y, Li F, Li Y, Tang Y, Kong X, Feng
Z, Anthony TG, Watford M, Hou Y, Wu G and Yin Y: The role of
leucine and its metabolites in protein and energy metabolism. Amino
Acids. 48:41–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gilissen J, Jouret F, Pirotte B and Hanson
J: Insight into SUCNR1 (GPR91) structure and function. Pharmacol
Ther. 159:56–65. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He W, Miao FJ, Lin DC, Schwandner RT, Wang
Z, Gao J, Chen JL, Tian H and Ling L: Citric acid cycle
intermediates as ligands for orphan G-protein-coupled receptors.
Nature. 429:188–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Littlewood-Evans A, Sarret S, Apfel V,
Loesle P, Dawson J, Zhang J, Muller A, Tigani B, Kneuer R, Patel S,
et al: Sarret GPR91 senses extracellular succinate released from
inflammatory macrophages and exacerbates rheumatoid arthritis. J
Exp Med. 213:1655–1662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Castro Fonseca M, Aguiar CJ, da Rocha
Franco JA, Gingold RN and Leite MF: GPR91: Expanding the frontiers
of Krebs cycle intermediates. Cell Commun Signal. 14:32016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ato S, Makanae Y, Kido K and Fujita S:
Contraction mode itself does not determine the level of mTORC1
activity in rat skeletal muscle. Physiol Rep. 4(pii): e129762016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Agergaard J, Bülow J, Jensen JK,
Reitelseder S, Drummond MJ, Schjerling P, Scheike T, Serena A and
Holm L: Light-load resistance exercise increases muscle protein
synthesis and hypertrophy signaling in elderly men. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 312:E326–E338. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Osterweil EK, Krueger DD, Reinhold K and
Bear MF: Hypersensitivity to mGluR5 and ERK1/2 leads to excessive
protein synthesis in the hippocampus of a mouse model of fragile X
syndrome. J Neurosci. 30:15616–15627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Quan-Jun Y, Yan H, Yong-Long H, Li-Li W,
Jie L, Jin-Lu H, Jin L, Peng-Guo C, Run G and Cheng G: Selumetinib
attenuate skeletal muscle wasting in murine cachexia model through
ERK inhibition and AKT activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:334–343.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hegedũs L, Garay T, Molnár E, Varga K,
Bilecz Á, Török S, Padányi R, Pászty K, Wolf M, Grusch M, et al:
The plasma membrane Ca2+ pump PMCA4b inhibits the
migratory and metastatic activity of BRAF mutant melanoma cells.
Int J Cancer. 140:2758–2770. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aguiar CJ, Rocha-Franco JA, Sousa PA,
Santos AK, Ladeira M, Rocha-Resende C, Ladeira LO, Resende RR,
Botoni FA, Melo M Barrouin, et al: Succinate causes pathological
cardiomyocyte hypertrophy through GPR91 activation. Cell Commun
Signal. 12:782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|