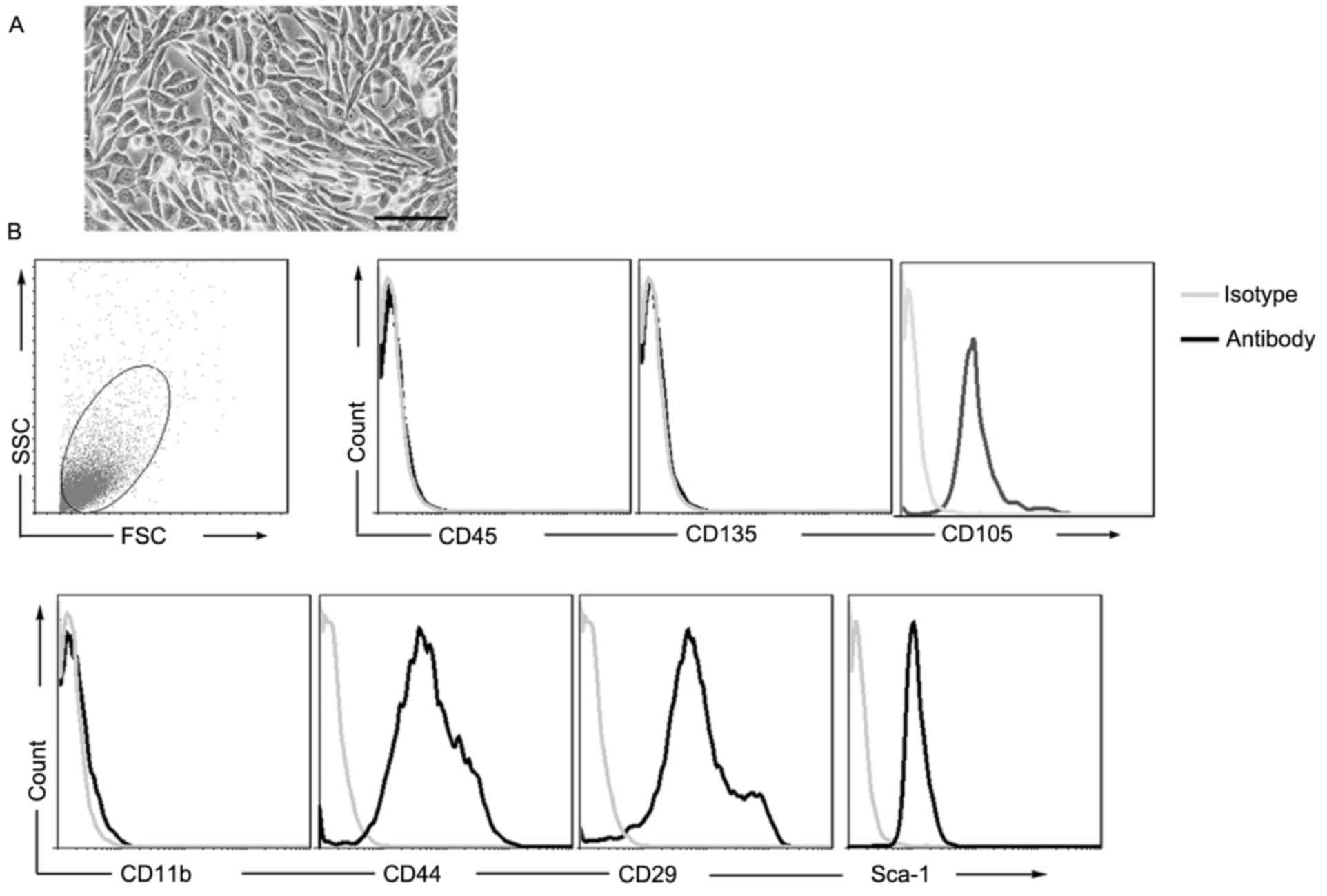
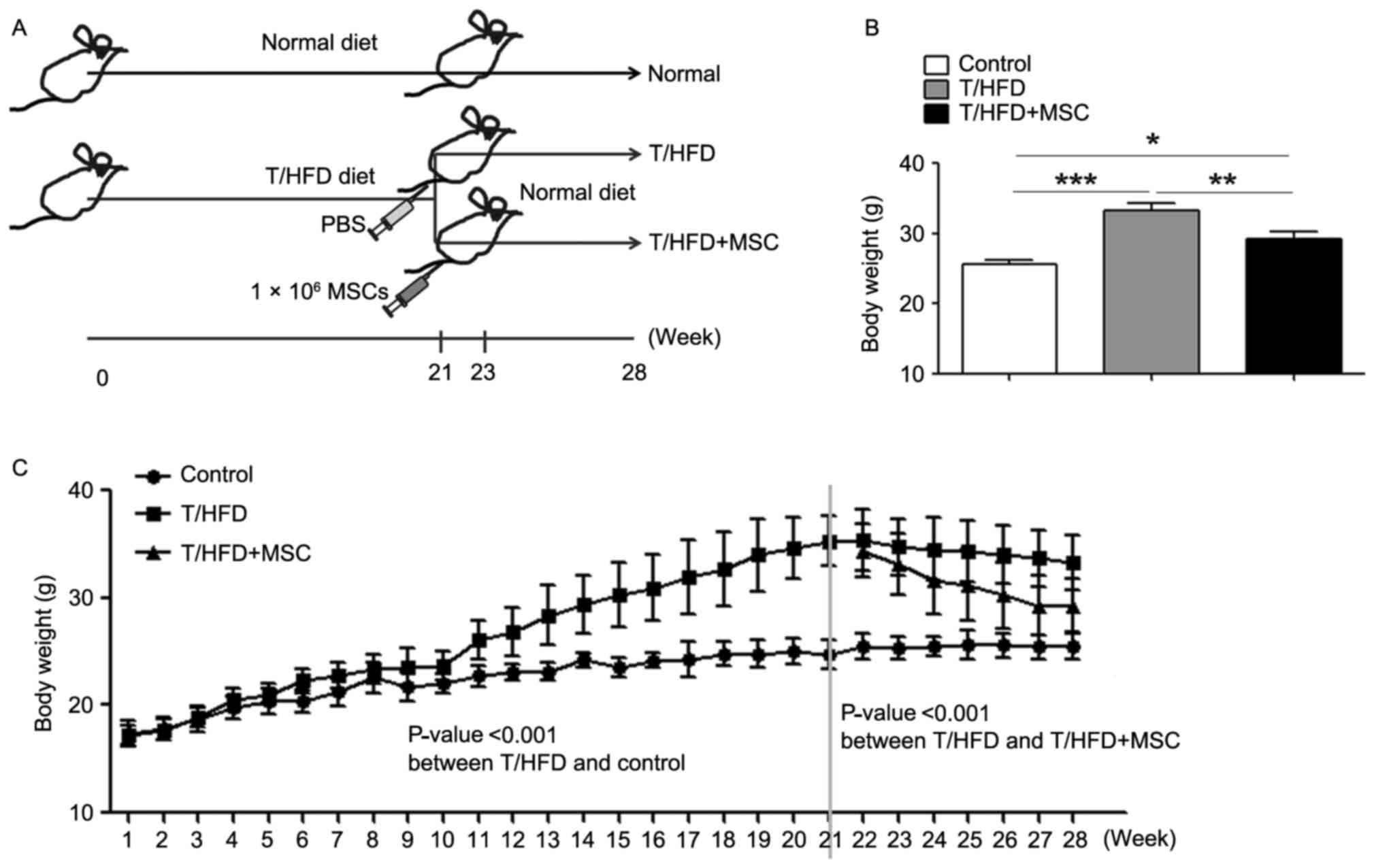
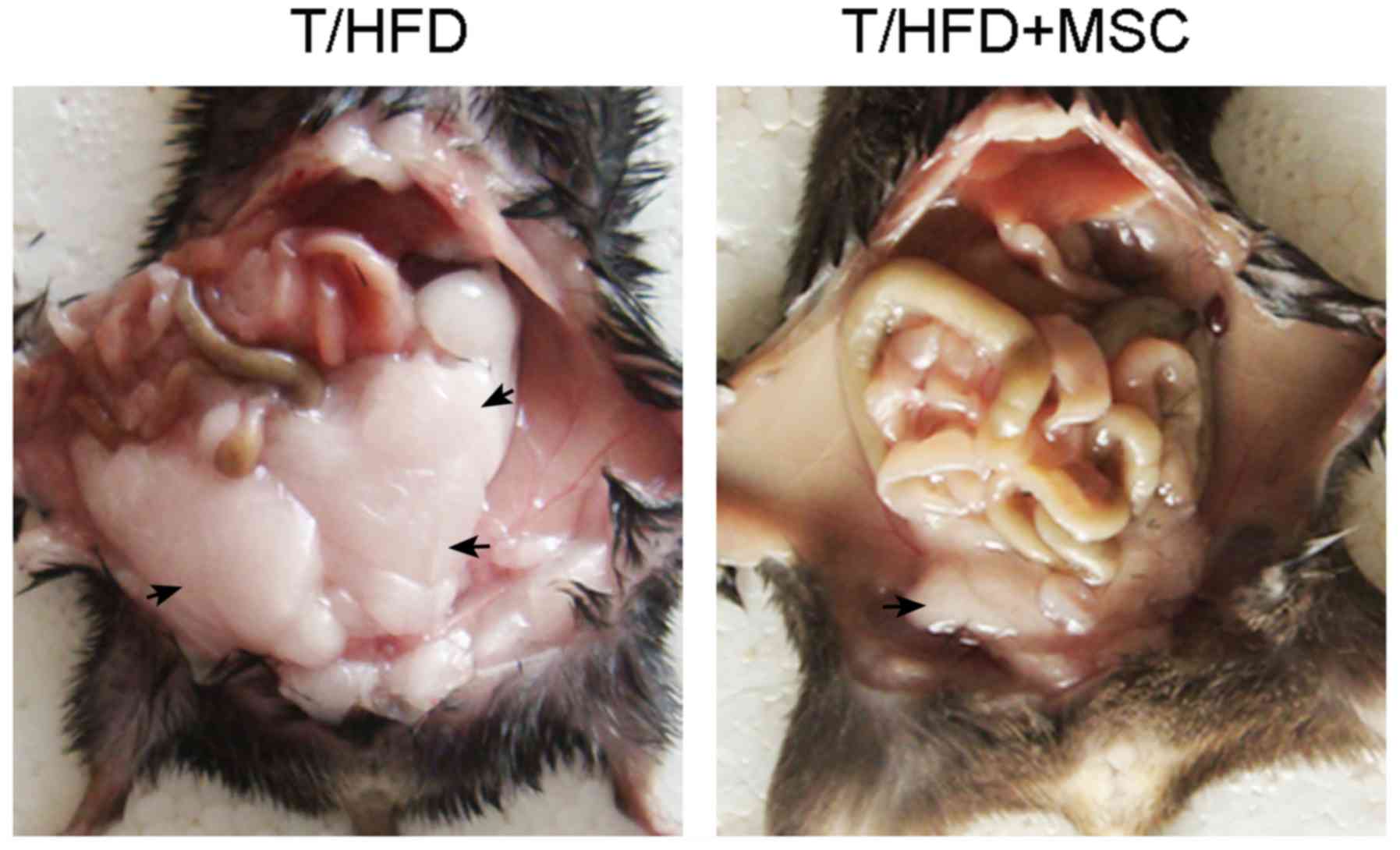
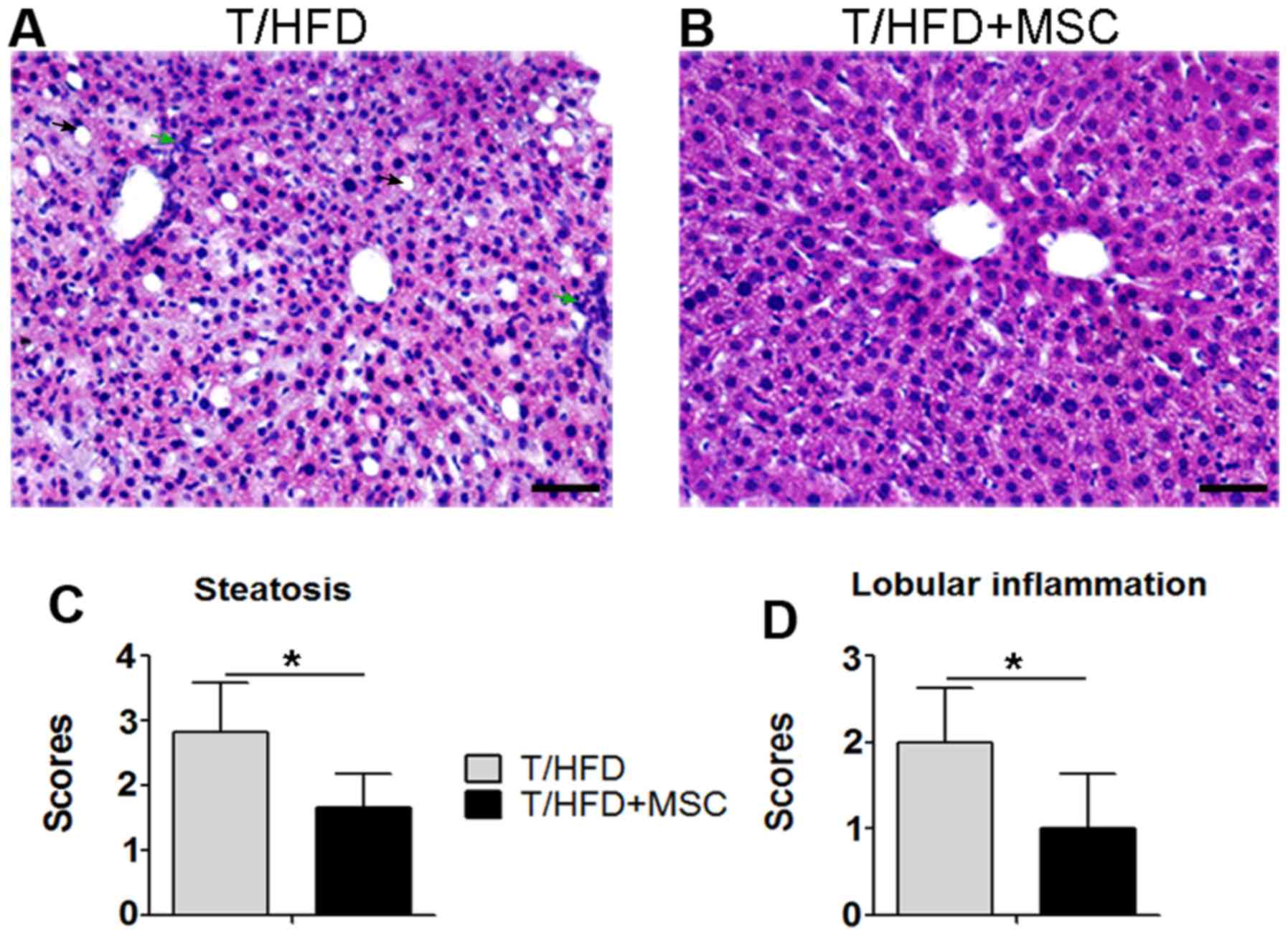
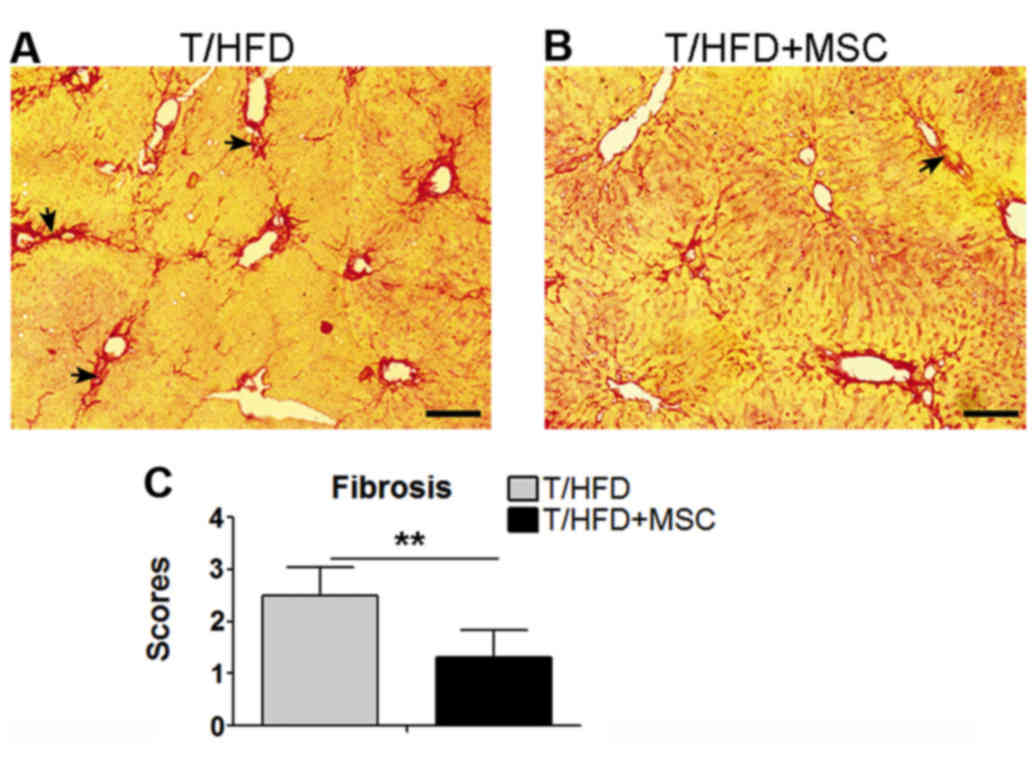
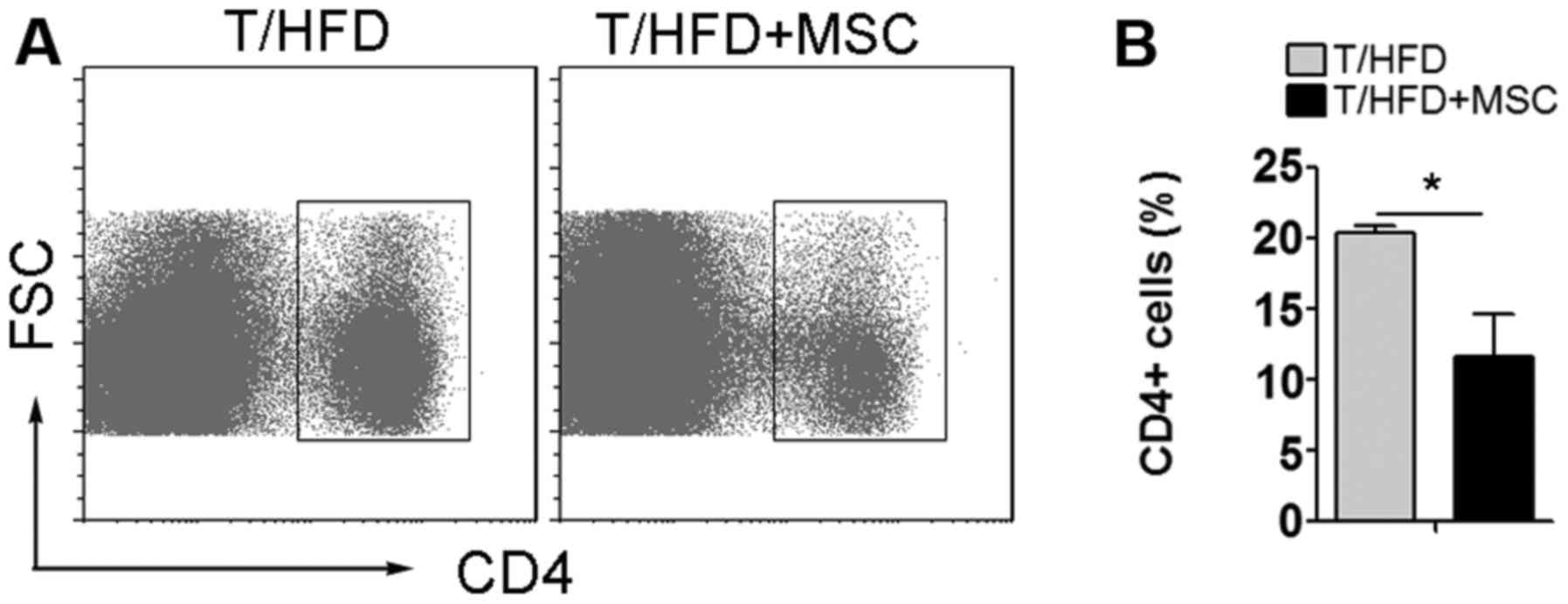
|
1
|
Lieber CS, Leo MA, Mak KM, Xu Y, Cao Q,
Ren C, Ponomarenko A and DeCarli LM: Model of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Am J Clin Nutr. 79:502–509. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Kit BK and Ogden
CL: Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body
mass index among US adults, 1999–2010. Jama. 307:491–497. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ahmed M: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
in 2015. World J Hepatol. 7:1450–1459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wong VW: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
in Asia: A story of growth. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:18–23.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fan J: Steatohepatitis studies in China.
World Chi J Digestology. 9:6–10. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Fan JG and Farrell GC: Epidemiology of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in China. J Hepatol. 50:204–210.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang HJ, Zhuang H and Liu XE: Advances in
the epidemiological study of fatty liver. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing
Xue Za Zhi. 25:630–632. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Huang B, Cheng
X, Wang D, La Gahu Z, Xue Z, Da Y, Li D, et al: Adiponectin-derived
active peptide ADP355 exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic
activities in thioacetamide-induced liver injury. Sci Rep.
6:194452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uccelli A, Moretta L and Pistoia V:
Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
8:726–736. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ding DC, Shyu WC and Lin SZ: Mesenchymal
stem cells. Cell Transplant. 20:5–14. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Huang B, Li G and Jiang XH: Fate
determination in mesenchymal stem cells: A perspective from
histone-modifying enzymes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ke C, Biao H, Qianqian L, Yunwei S and
Xiaohua J: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for inflammatory bowel
diseases: Promise and challenge. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
10:499–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rankin S: Mesenchymal stem cells. Thorax.
67:565–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sato Y, Araki H, Kato J, Nakamura K,
Kawano Y, Kobune M, Sato T, Miyanishi K, Takayama T, Takahashi M,
et al: Human mesenchymal stem cells xenografted directly to rat
liver are differentiated into human hepatocytes without fusion.
Blood. 106:756–763. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fang B, Shi M, Liao L, Yang S, Liu Y and
Zhao RC: Systemic infusion of FLK1(+) mesenchymal stem cells
ameliorate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice.
Transplantation. 78:83–88. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aurich I, Mueller LP, Aurich H,
Luetzkendorf J, Tisljar K, Dollinger MM, Schormann W, Walldorf J,
Hengstler JG, Fleig WE and Christ B: Functional integration of
hepatocytes derived from human mesenchymal stem cells into mouse
livers. Gut. 56:405–415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parekkadan B, Van Poll D, Suganuma K,
Carter EA, Berthiaume F, Tilles AW and Yarmush ML: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived molecules reverse fulminant hepatic failure. PLoS One.
2:e9412007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kuo TK, Hung SP, Chuang CH, Chen CT, Shih
YR, Fang SC, Yang VW and Lee OK: Stem cell therapy for liver
disease: Parameters governing the success of using bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells. Gastroenterology. 134:2111–2121, e1-e3.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang B, Cheng X, Wang H, Huang W, La Ga
Hu Z, Wang D, Zhang K, Zhang H, Xue Z, Da Y, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells and their secreted molecules predominantly ameliorate
fulminant hepatic failure and chronic liver fibrosis in mice
respectively. J Transl Med. 14:452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu XJ, Wang BW, Zhang C, Xia MZ, Chen YH,
Hu CQ, Wang H, Chen X and Xu DX: Vitamin d deficiency attenuates
high-fat diet-induced hyperinsulinemia and hepatic lipid
accumulation in male mice. Endocrinology. 156:2103–2113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu H, Guo ZK, Jiang XX, Li H, Wang XY,
Yao HY, Zhang Y and Mao N: A protocol for isolation and culture of
mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protoc.
5:550–560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja J and Kulagina
NN: Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse
hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 4:267–274. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Phinney DG, Kopen G, Isaacson RL and
Prockop DJ: Plastic adherent stromal cells from the bone marrow of
commonly used strains of inbred mice: Variations in yield, growth,
and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 72:570–585. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meier RP, Müller YD, Morel P,
Gonelle-Gispert C and Bühler LH: Transplantation of mesenchymal
stem cells for the treatment of liver diseases, is there enough
evidence? Stem Cell Res. 11:1348–1364. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M,
Milanesi M, Longoni PD, Matteucci P, Grisanti S and Gianni AM:
Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation
induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood.
99:3838–3843. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zappia E, Casazza S, Pedemonte E,
Benvenuto F, Bonanni I, Gerdoni E, Giunti D, Ceravolo A, Cazzanti
F, Frassoni F, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate
experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis inducing T-cell anergy.
Blood. 106:1755–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Augello A, Tasso R, Negrini SM, Cancedda R
and Pennesi G: Cell therapy using allogeneic bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells prevents tissue damage in collagen-induced
arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 56:1175–1186. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J, Gócza E, Vas
V, Monostori E and Uher F: Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with
bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes. Stem Cells. 26:244–253.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|