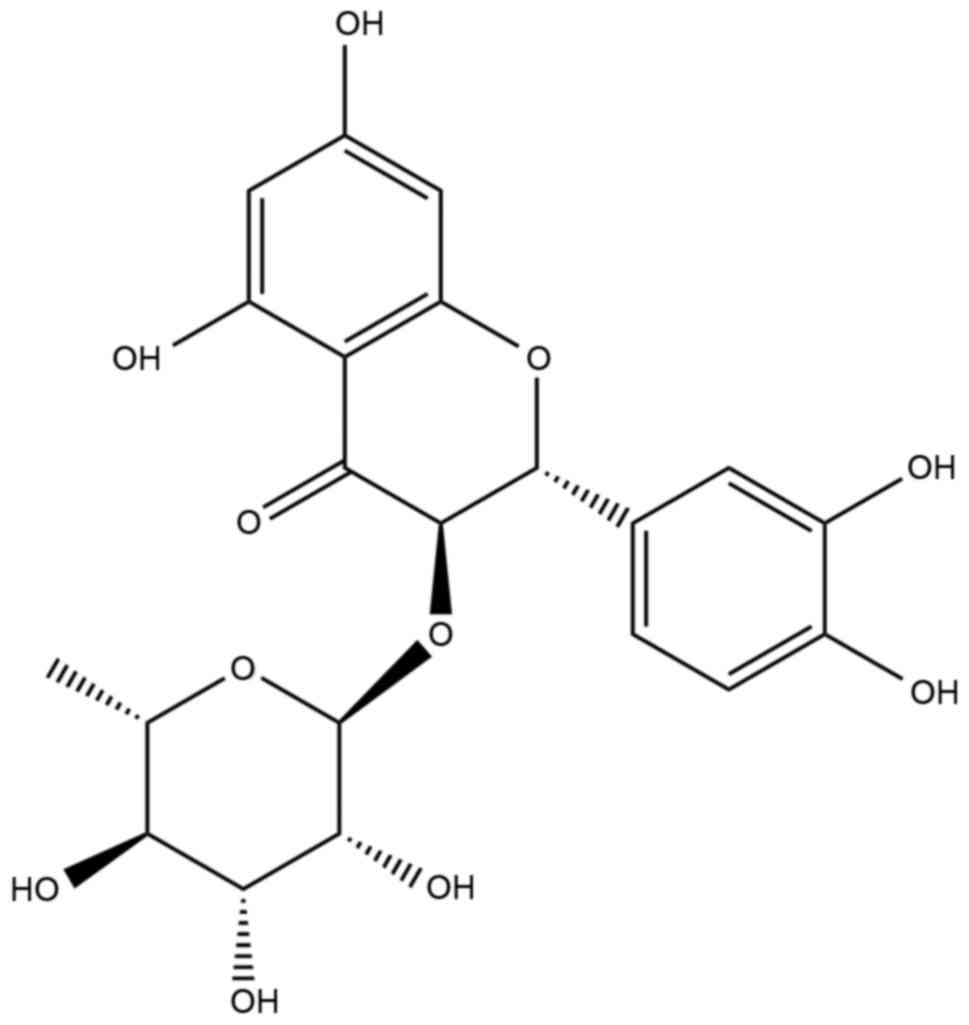
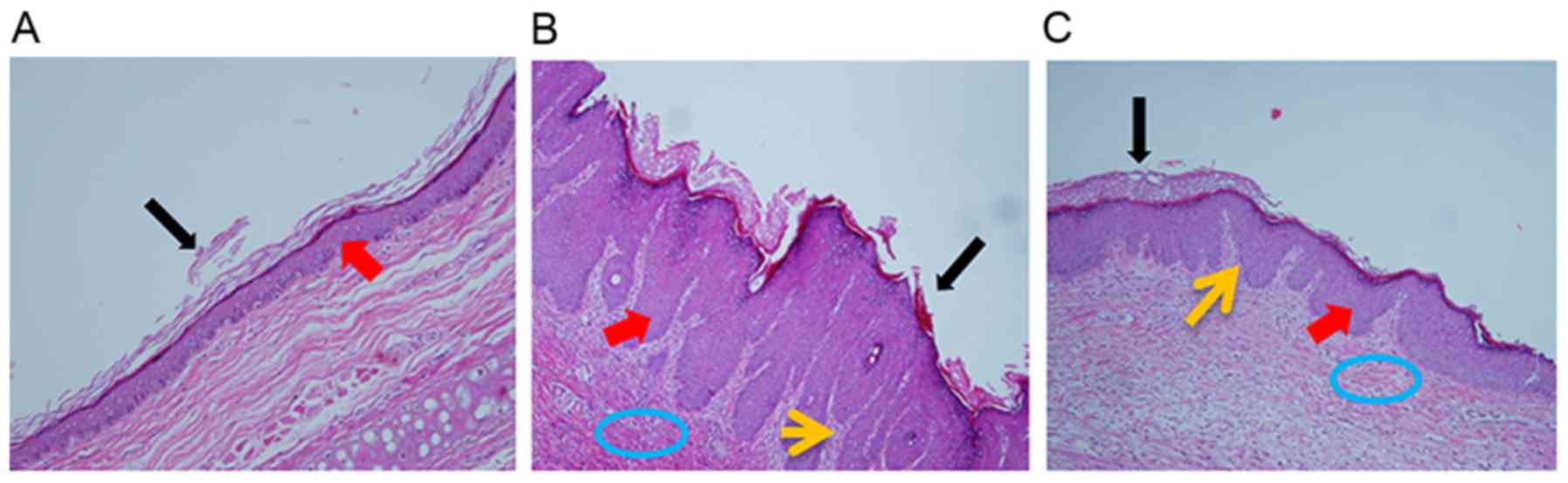
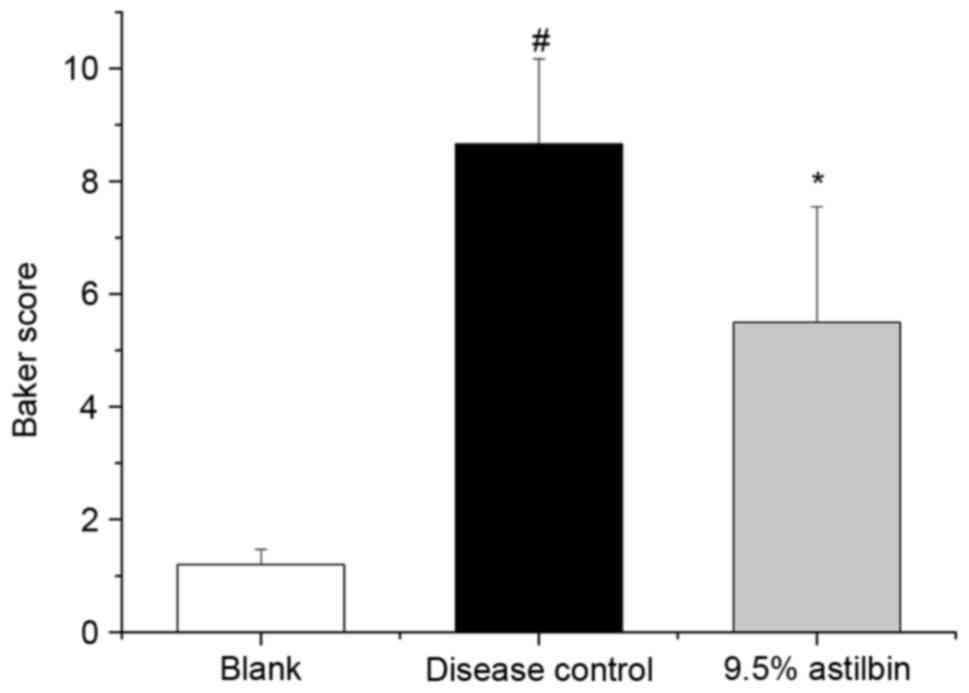
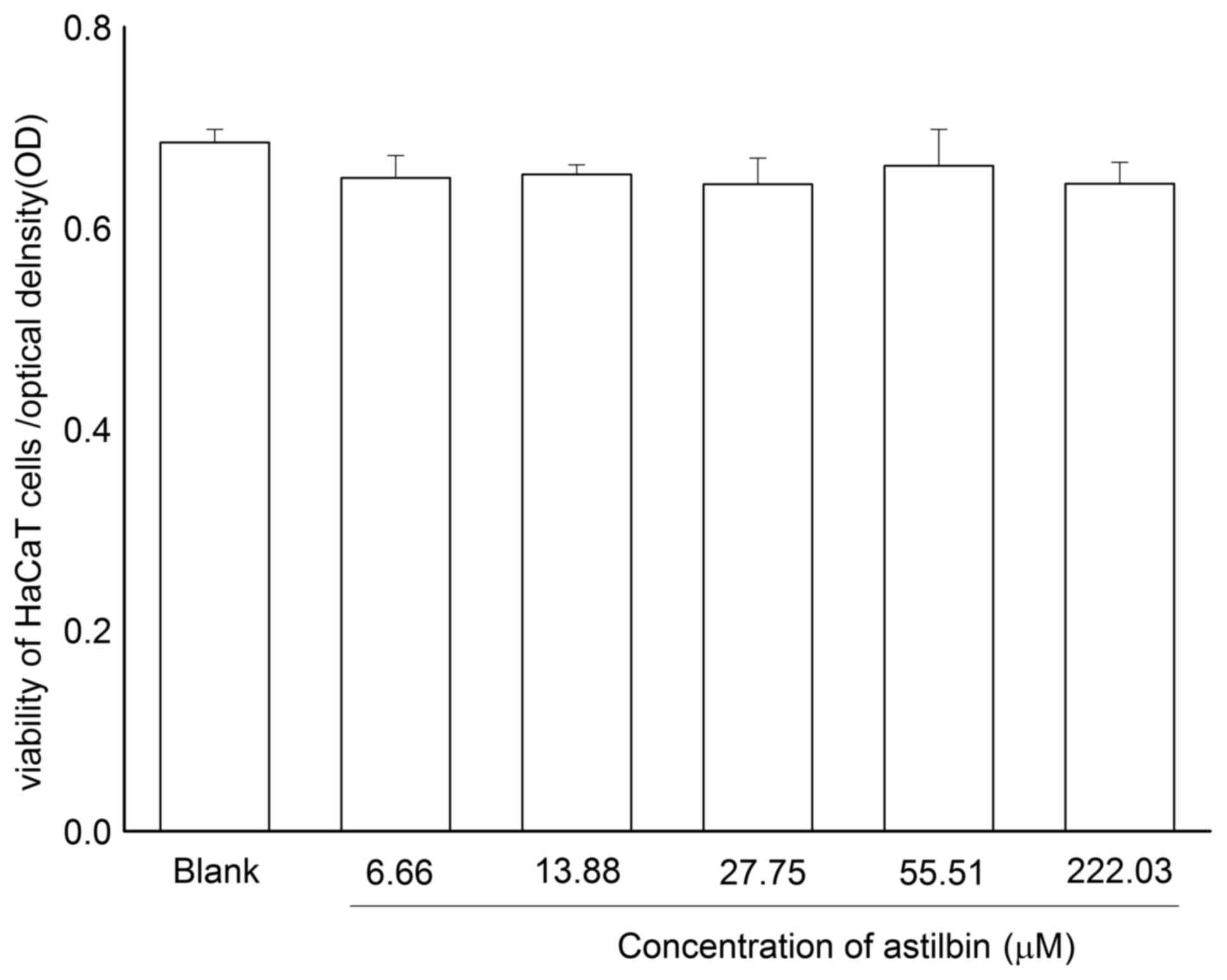
|
1
|
Abe R, Yamagishi S, Fujita Y, Hoshina D,
Sasaki M, Nakamura K, Matsui T, Shimizu T, Bucala R and Shimizu H:
Topical application of anti-angiogenic peptides based on pigment
epithelium-derived factor can improve psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci.
57:1–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Richards HL, Fortune DG, O'Sullivan TM,
Main CJ and Griffiths CE: Patients with psoriasis and their
compliance with medication. J Am Acad Dermatol. 41:581–583. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen T, Li J, Cao J, Xu Q, Komatsu K and
Namba T: A new flavanone isolated from Rhizoma Smilacis glabrae and
the structural requirements of its derivatives for preventing
immunological hepatocyte damage. Planta Med. 65:56–59. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo J, Xu Q and Chen T: Quantitative
determination of astilbin in rabbit plasma by liquid
chromatography. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life.
805:357–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Huang H, Cheng Z, Shi H, Xin W, Wang TT
and Yu LL: Isolation and chacterization of two flavonoids,
engeletin and astilbin from the leaves of Engelhardia roxburghiana
and their potential anti-inflammatory properties. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:4562–4569. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bezerra GP, Góis RW, de Brito TS, de Lima
FJ, Bandeira MA, Romero NR, Magalhães PJ and Santiago GM:
Phytochemical study guided by the myorelaxant activity of the crude
extract, fractions and constituent from stem bark of Hymeana
courbaril L. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:62–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi HW, Lu XM, Fang F, Wang J and Xu Q:
Astilbin inhibits the adhesion of T lymphocytes via decreasing
TNF-alpha and its associated MMP-9 activity and CD44 expression.
Int Immunopharmacol. 18:1467–1474. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li GS, Jiang WL, Yue XD, Qu GW, Tian JW,
Wu J and Fu FH: Effect of astilbin on experimental diabetic
nephropathy in vivo and in vitro. Planta Med. 75:1470–1475. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fei M, Wu X and Xu Q: Astilbin inhibits
contact hypersensitivity through negative cytokine regulation
distinct from cyclosporine A. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
116:1350–1356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zou S, Shen X, Tang Y, Fu Z, Zheng Q and
Wang Q: Astilbin suppresses acute heart allograft rejection by
inhibiting maturation and function of dendritic cells in mice.
Transplant Proc. 42:pp. 3798–3802. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo L, Liu W, Lu T, Guo W, Gao J, Luo Q,
Wu X, Sun Y, Wu X, Shen Y and Xu Q: Decrease of functional
activated T and B cells and treatment of glomerulonephitis in
Lupus-prone mice using a natural flavonid astilbin. PLoS One.
10:e01240022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gaylarde PM, Brock AP and Sarkany I:
Psoriasiform changes in guinea-pig skin from propranolol. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 3:157–160. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baker BS, Brent L, Valdimarsson H, Powles
AV, al-Imara L, Walker M and Fry L: Is epidermal cell proliferation
in psoriatic skin-grafts on nude-mice driven by T-cell derived
cytokines. Br J Dermatol. 12:105–110. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Diao H, Kang Z, Han F and Jiang W:
Astilbin protects diabetic rat heart against ischemia-reperfusion
injury via blockade of HMGB1-dependent NF-κB signaling pathway.
Food Chem Toxicol. 63:104–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fei MJ, Wu XF and Xu Q: Astilbin inhibits
contact hypersensitivity through negative cytokine regulation
distinct from cyclosporin A. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 116:1350–1356.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding Y, Liang Y, Deng B, Qiao A, Wu K,
Xiao W and Gong W: Induction of TGF-β and IL-10 production in
dendritic cells using astilbin to inhibit dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:529–534.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Puig L: Cardiovascular risk and psoriasis:
The role of biologic therapy. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 103:853–862.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, Van
Voorhees AS, Leonardi CL, Gordon KB, Lebwohl M, Koo JY, Elmets CA,
Korman NJ, et al: Guidelines of care for the management of
psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis-section 1. Overview of psoriasis
and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with
biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 58:826–850. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pietrzak AT, Zalewska A, Chodorowska G,
Krasowska D, Michalak-Stoma A, Nockowski P, Osemlak P, Paszkowski T
and Roliński JM: Cytokines and anticytokines in psoriasis. Clin
Chim Acta. 394:7–21. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin J, Sundararaj KP, Samuvel DJ, Zhang X,
Li Y, Lu Z, Lopes-Virella MF and Huang Y: Different signaling
mechanisms regulating IL-6 expression by LPS between gingival
fibroblasts and mononuclear cells: Seeking the common target. Clin
Immunol. 143:188–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grossman RM, Krueger J, Yourish D,
Granelli-Piperno A, Murphy DP, May LT, Kupper TS, Sehgal PB and
Gottlieb AB: Interleukin 6 is expressed in high levels in psoriatic
skin and stimulates proliferation of cultured human keratinocytes.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 86:pp. 6367–6371. 1989; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo L, Liu W, Lu T, Guo W, Gao J, Luo Q,
Wu X, Sun Y, Wu X, Shen Y and Xu Q: Decrease of functional
activated T and B cells and treatment of glomerulonephitis in
lupus-prone mice using a natural flavonoid astilbin. PLoS One.
10:e01240022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang H, Cheng Z, Shi H, Xin W, Wang TT
and Yu L: Isolation and characterization of two flavonoids,
engeletin and astilbin, from the leaves of engelhardia roxburghiana
and their potential anti-inflammatory properties. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:4562–4569. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Song SH, Shen XY, Liu F, Tang Y, Wang ZM
and Fu ZR: Protective effects of astilbin on renal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao.
7:753–757. 2009.(In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hao JQ: Targeting Interleukin-22 in
psoriasis. Inflammation. 37:94–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwakura Y, Nakae S, Saijo S and Ishigame
H: The roles of IL-17A in inflammatory immune responses and host
defense against pathogens. Immunol Rev. 226:57–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grygorczuk S, Świerzbińska R, Moniuszko A,
Kondrusik M, Zajkowska J, Czupryna P, Dunaj J and Pancewicz S:
Synthesis of Th17 cytokines in the culture of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells stimulated with Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato.
Ann Agric Environ Med. 23:242–247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim SR, Kim HJ, Kim DI, Lee KB, Park HJ,
Jeong JS, Cho SH and Lee YC: Blockade of interplay between IL-17A
and endoplasmic reticulum stress attenuates LPS-induced lung
injury. Theranostics. 5:1343–1362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waggoner SA and Liebhaber SA: Regulation
of alpha-globin mRNA stability. Exp Biol Med. 228:387–395. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pesole G, Gissi C, Grillo G, Licciulli F,
Liuni S and Saccone C: Analysis of oligonucleotide AUG start codon
context in eukariotic mRNAs. Gene. 261:85–91. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bachmair A, Finley D and Varshavsky A: In
vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal
residue. Science. 234:179–186. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mavropoulos A, Rigopoulou EI, Liaskos C,
Bogdanos DP and Sakkas LI: The role of p38 MAPK in the
aetiopathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2013:5697512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Johansen C, Kragballe K, Westergaard M,
Henningsen J, Kristiansen K and Iversen L: The mitogen-activated
protein kinases p38 and ERK1/2 are increased in lesional psoriatic
skin. Br J Dermatol. 152:37–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zou S, Shen X, Tang Y, Fu Z, Zheng Q and
Wang Q: Astilbin suppresses acute heart allograft rejection by
inhibiting maturation and function of dendritic cells in mice.
Transplant Proc. 42:pp. 3798–3802. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|