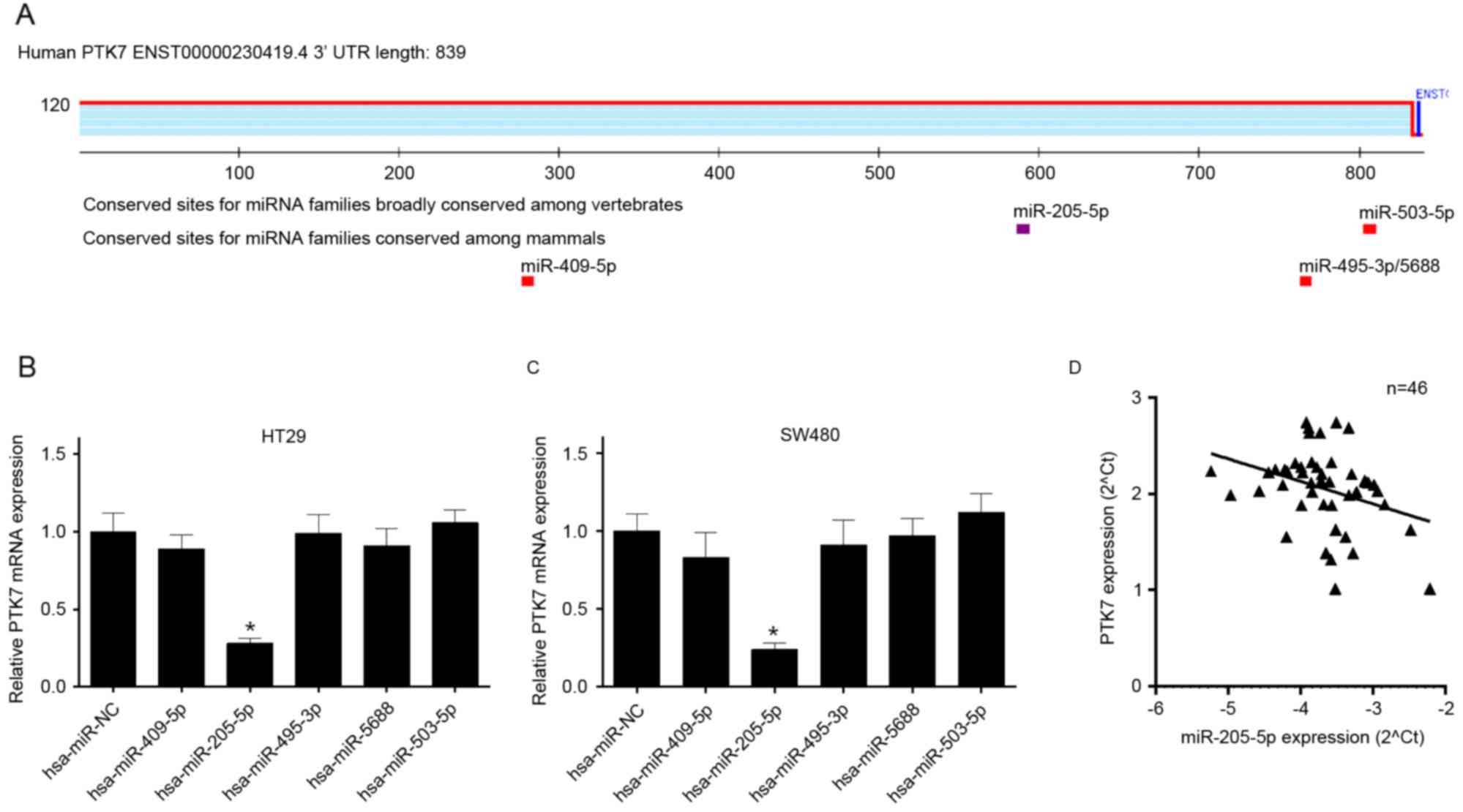
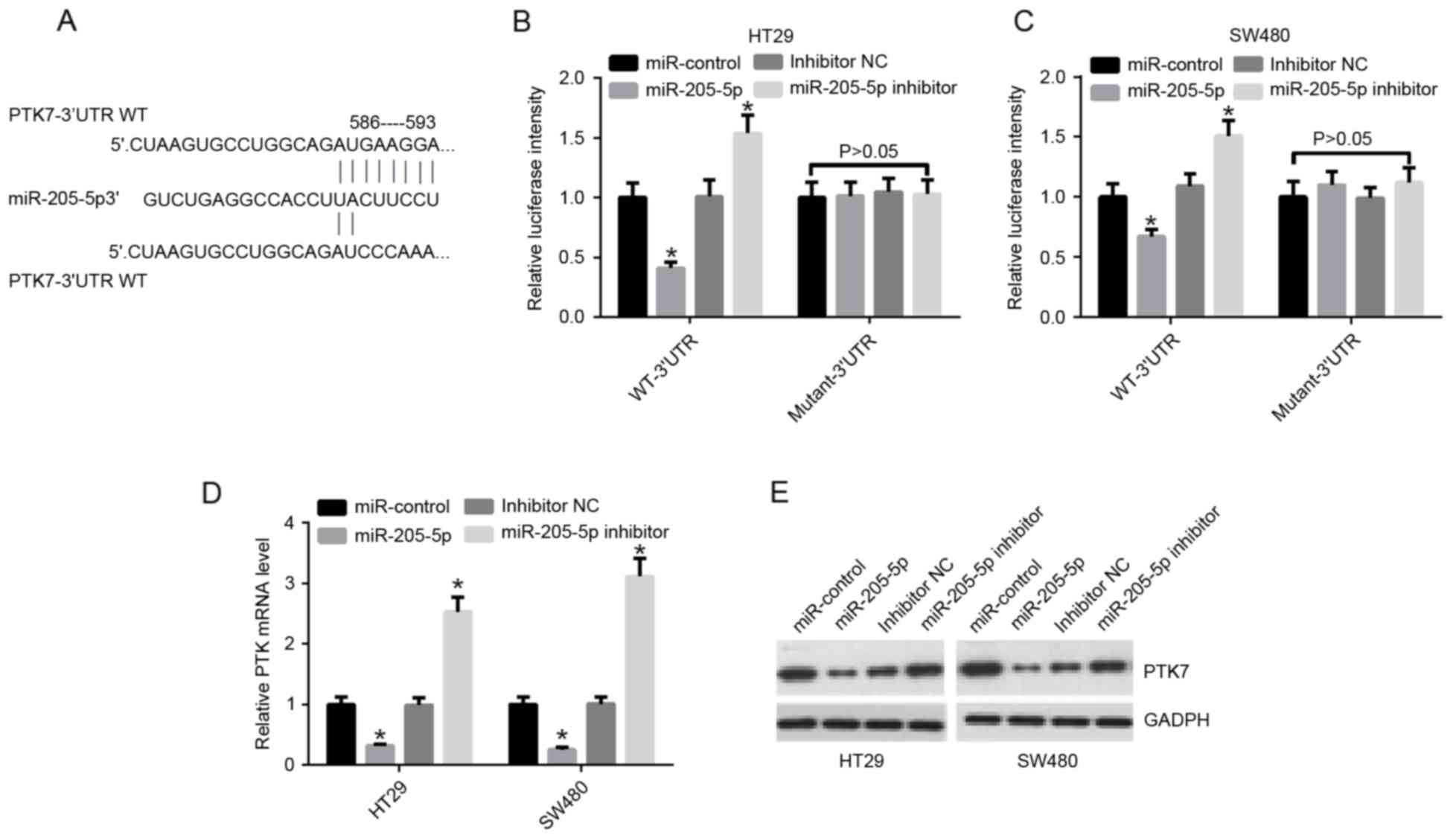
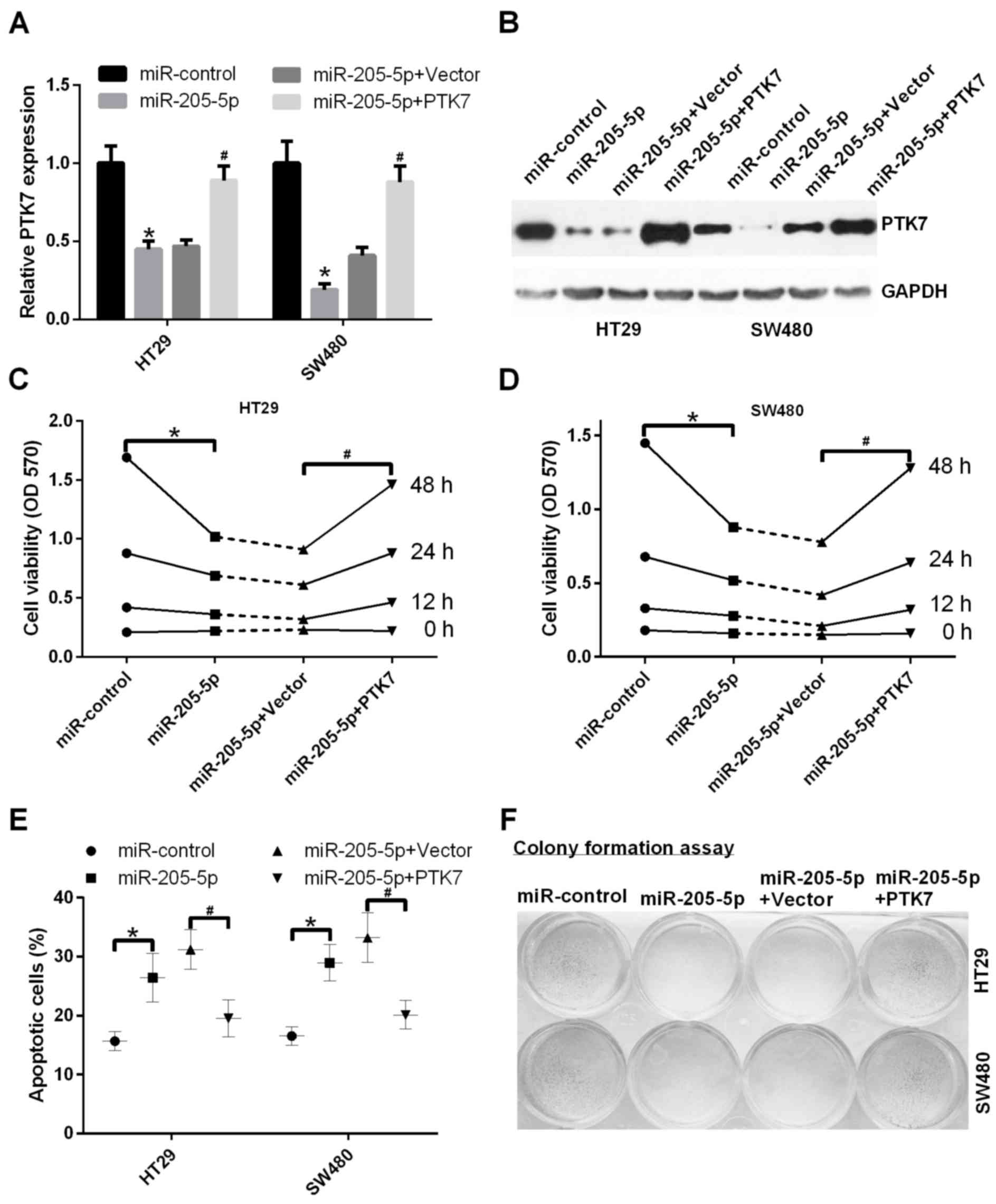
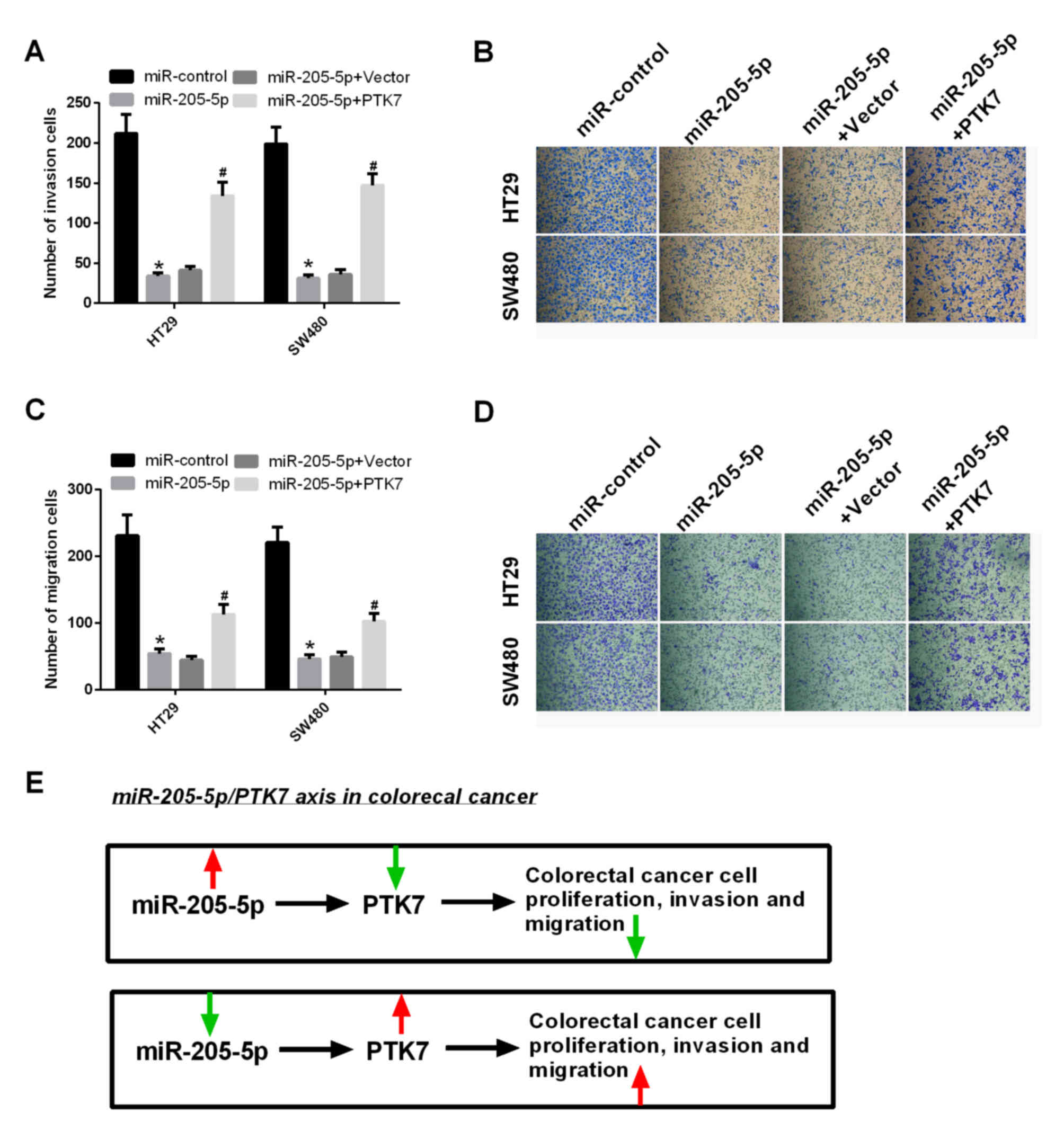
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haggar FA and Boushey RP: Colorectal
cancer epidemiology: Incidence, mortality, survival, and risk
factors. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 22:191–197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Khair G, Monson JR and Greenman J:
Epithelial molecular markers in the peripheral blood of patients
with colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 50:1188–1203. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Farazi TA, Hoell JI, Morozov P and Tuschl
T: MicroRNAs in human cancerMicroRNA Cancer Regulation. Springer;
New York, NY: pp. 1–20. 2013, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Djuranovic S, Nahvi A and Green R: A
parsimonious model for gene regulation by miRNAs. Science.
331:550–553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs en
route to the clinic: Progress in validating and targeting microRNAs
for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:849–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zaman MS, Maher DM, Khan S, Jaggi M and
Chauhan SC: Current status and implications of microRNAs in ovarian
cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Ovarian Res. 5:442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Di Leva G and Croce CM: The role of
microRNAs in the tumorigenesis of ovarian cancer. Front Oncol.
3:1532013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Valeri N, Braconi C, Gasparini P, Murgia
C, Lampis A, Paulus-Hock V, Hart JR, Ueno L, Grivennikov SI, Lovat
F, et al: MicroRNA-135b promotes cancer progression by acting as a
downstream effector of oncogenic pathways in colon cancer. Cancer
Cell. 25:469–483. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bu P, Chen KY, Chen JH, Wang L, Walters J,
Shin YJ, Goerger JP, Sun J, Witherspoon M, Rakhilin N, et al: A
microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets Notch in colon
cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 12:602–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Q, Zou C, Zou C, Han Z, Xiao H, Wei H,
Wang W, Zhang L, Zhang X, Tang Q, et al: MicroRNA-25 functions as a
potential tumor suppressor in colon cancer by targeting Smad7.
Cancer Lett. 335:168–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Y, Kanwar SS, Patel BB, Oh PS, Nautiyal
J, Sarkar FH and Majumdar AP: MicroRNA-21 induces stemness by
downregulating transforming growth factor beta receptor 2 (TGFβR2)
in colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 33:68–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park SK, Lee HS and Lee ST:
Characterization of the human full-length PTK7 cDNA encoding a
receptor protein tyrosine kinase-like molecule closely related to
chick KLG. J Biochem. 119:235–239. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee ST, Strunk KM and Spritz RA: A survey
of protein tyrosine kinase mRNAs expressed in normal human
melanocytes. Oncogene. 8:3403–3410. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shnitsar I and Borchers A: PTK7 recruits
dsh to regulate neural crest migration. Development. 135:4015–4024.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu X, Borchers AG, Jolicoeur C, Rayburn H,
Baker JC and Tessier-Lavigne M: PTK7/CCK-4 is a novel regulator of
planar cell polarity in vertebrates. Nature. 430:93–98. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Puppo F, Thomé V, Lhoumeau AC, Cibois M,
Gangar A, Lembo F, Belotti E, Marchetto S, Lécine P, Prébet T, et
al: Protein tyrosine kinase 7 has a conserved role in Wnt/β-catenin
canonical signalling. EMBO Rep. 12:43–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saha S, Bardelli A, Buckhaults P,
Velculescu VE, Rago C, St Croix B, Romans KE, Choti MA, Lengauer C,
Kinzler KW and Vogelstein B: A phosphatase associated with
metastasis of colorectal cancer. Science. 294:1343–1346. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Endoh H, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Konishi H,
Osada H, Tajima K, Kuwano H, Takahashi T and Mitsudomi T:
Prognostic model of pulmonary adenocarcinoma by expression
profiling of eight genes as determined by quantitative real-time
reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Oncol.
22:811–819. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gorringe KL, Boussioutas A and Bowtell DD:
Melbourne Gastric Cancer Group, Peter Mac Micro ArrayFacility:
Novel regions of chromosomal amplification at 6p21, 5p13, and 12q14
in gastric cancer identified by array comparative genomic
hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 42:247–259. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Müller-Tidow C, Schwäble J, Steffen B,
Tidow N, Brandt B, Becker K, Schulze-Bahr E, Halfter H, Vogt U,
Metzger R, et al: High-throughput analysis of genome-wide receptor
tyrosine kinase expression in human cancers identifies potential
novel drug targets. Clinical Cancer Res. 10:1241–1249. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gobble RM, Qin LX, Brill ER, Angeles CV,
Ugras S, O'Connor RB, Moraco NH, Decarolis PL, Antonescu C and
Singer S: Expression profiling of liposarcoma yields a multigene
predictor of patient outcome and identifies genes that contribute
to liposarcomagenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2697–2705. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin WS, Maeng YS, Jung JW, Min JK, Kwon
YG and Lee ST: Soluble PTK7 inhibits tube formation, migration, and
invasion of endothelial cells and angiogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 371:793–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Nicholson AG,
Yatabe Y, Austin JHM, Beasley MB, Chirieac LR, Dacic S, Duhig E,
Flieder DB, et al: The 2015 World health organization
classification of lung tumors: Impact of Genetic, clinical and
radiologic advances since the 2004 Classification. J Thorac Oncol.
10:1243–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang L, Lai YK, Zhang J, Wang H, Lin MC,
He ML and Kung HF: Targeting S100P inhibits colon cancer growth and
metastasis by Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and proteomic
analysis. Mol Med. 17:709–716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mossie K, Jallal B, Alves F, Sures I,
Plowman GD and Ullrich A: Colon carcinoma kinase-4 defines a new
subclass of the receptor tyrosine kinase family. Oncogene.
11:2179–2184. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shin WS, Kwon J, Lee HW, Kang MC, Na HW,
Lee ST and Park JH: Oncogenic role of protein tyrosine kinase 7 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:1120–1126.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lin Y, Zhang LH, Wang XH, Xing XF, Cheng
XJ, Dong B, Hu Y, Du H, Li YA, Zhu YB, et al: PTK7 as a novel
marker for favorable gastric cancer patient survival. J Surg Oncol.
106:880–886. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Na HW, Shin WS, Ludwig A and Lee ST: The
cytosolic domain of PTK7, generated from sequential cleavage by
ADAM17 and γ-secretase, enhances cell proliferation and migration
in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:25001–25009. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kim JH, Kwon J, Lee HW, Kang MC, Yoon HJ,
Lee ST and Park JH: Protein tyrosine kinase 7 plays a tumor
suppressor role by inhibiting ERK and AKT phosphorylation in lung
cancer. Oncol Reports. 31:2708–2712. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Meng L, Sefah K, O'Donoghue MB, Zhu G,
Shangguan D, Noorali A, Chen Y, Zhou L and Tan W: Silencing of PTK7
in colon cancer cells: Caspase-10-dependent apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway. PLoS One. 5:e140182010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang J, Paris PL, Chen J, Ngo V, Yao H,
Frazier ML, Killary AM, Liu CG, Liang H, Mathy C, et al: Next
generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid microRNAs from low
grade-benign and high grade-invasive lesions. Cancer Lett.
356:404–409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stahlhut C and Slack FJ: MicroRNAs and the
cancer phenotype: Profiling, signatures and clinical implications.
Genome Med. 5:1112013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA,
Leupold JH, Colburn NH, Post S and Allgayer H: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21)
post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor suppressor Pdcd4 and
stimulates invasion, intravasation and metastasis in colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He X, Dong Y, Wu CW, Zhao Z, Ng SS, Chan
FK, Sung JJ and Yu J: MicroRNA-218 inhibits cell cycle progression
and promotes apoptosis in colon cancer by downregulating BMI1
polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol Med. 18:1491–1498. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Gopalan V, Smith RA and Lam AK:
Downregulation of microRNA-498 in colorectal cancers and its
cellular effects. Exp Cell Res. 330:423–428. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva
G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et
al: A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Roldo C, Missiaglia E, Hagan JP, Falconi
M, Capelli P, Bersani S, Calin GA, Volinia S, Liu CG, Scarpa A and
Croce CM: MicroRNA expression abnormalities in pancreatic endocrine
and acinar tumors are associated with distinctive pathologic
features and clinical behavior. J Clin Oncol. 24:4677–4684. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|