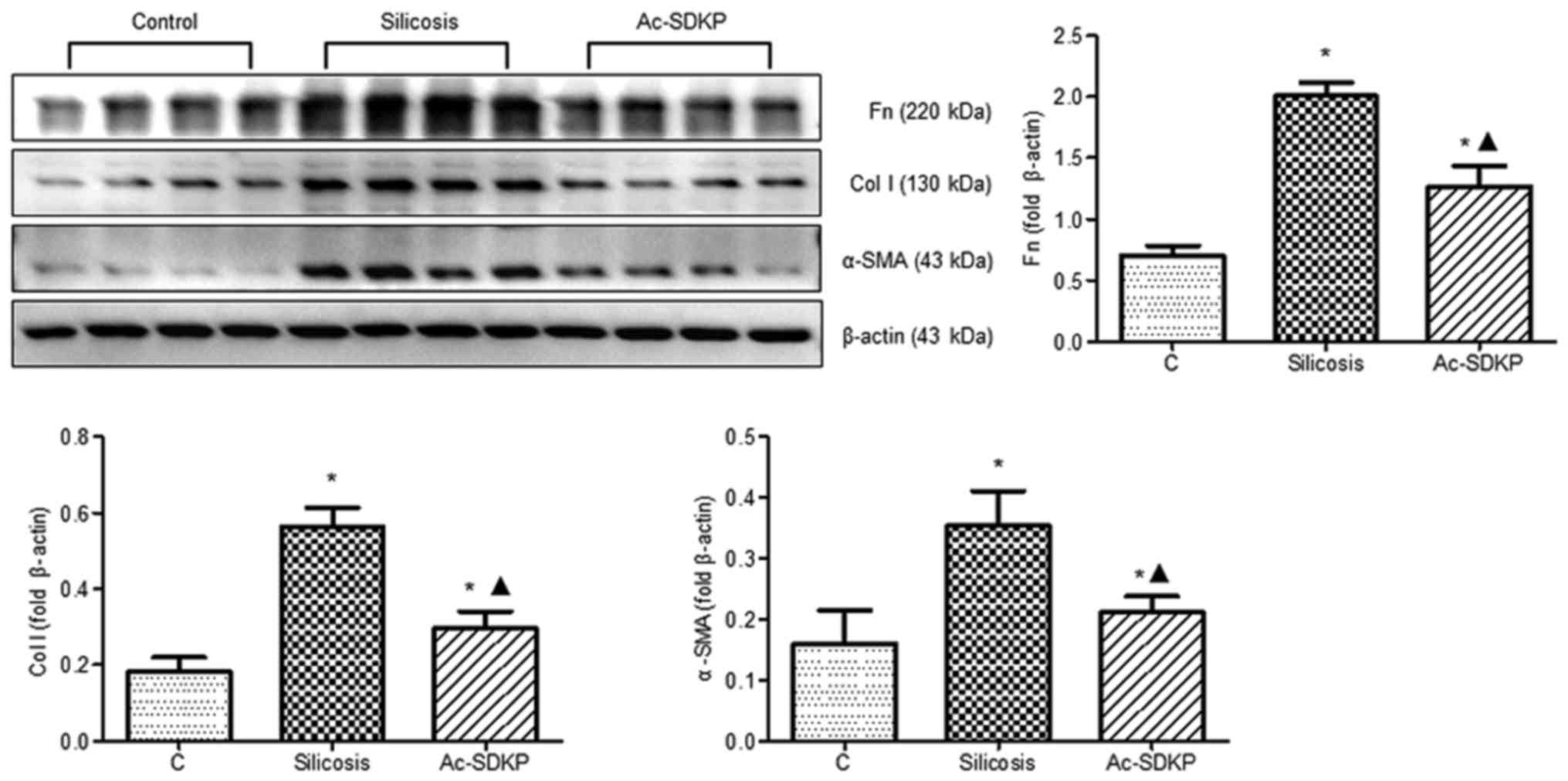
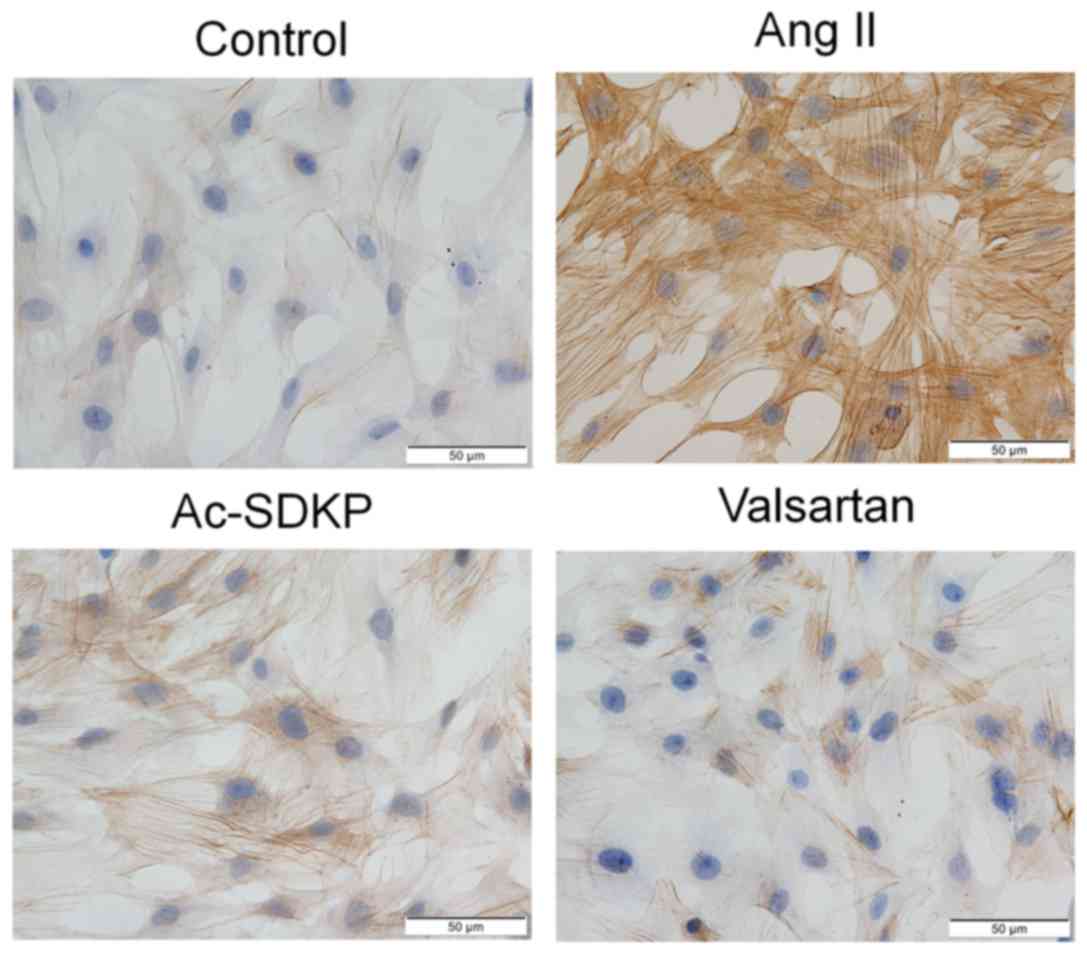
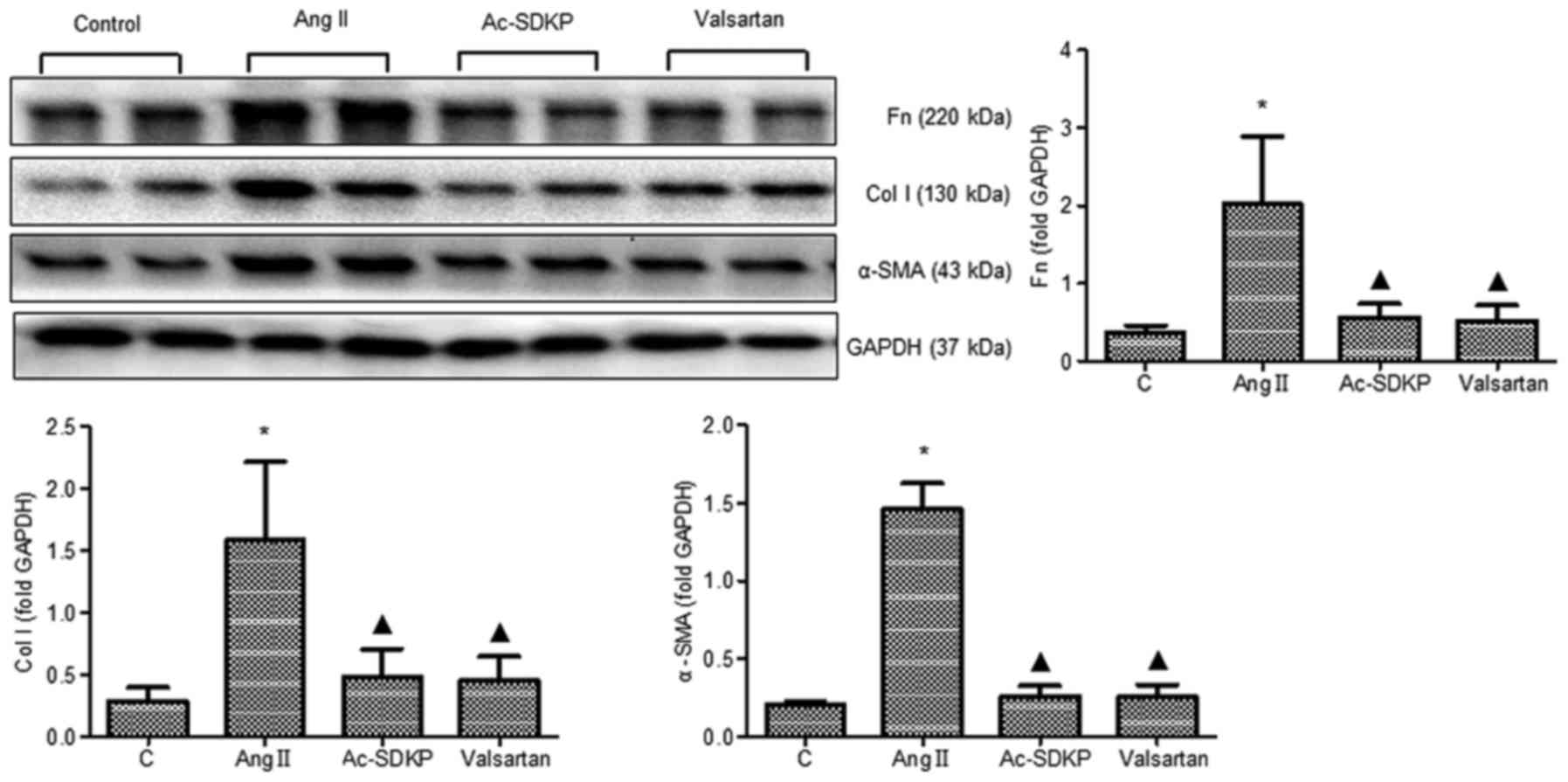
|
1
|
Rimal B, Greenberg AK and Rom WN: Basic
pathogenetic mechanisms in silicosis: Current understanding. Curr
Opin Pulm Med. 11:169–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cavasin MA, Rhaleb NE, Yang XP and
Carretero OA: Prolyl oligopeptidase is involved in release of the
antifibrotic peptide Ac-SDKP. Hypertension. 43:1140–1145. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mnguni AT, Engel ME, Borkum MS and Mayosi
BM: The effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE-I)
on human N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (Ac-SDKP) levels: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 10:e01433382015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kumar N, Nakagawa P, Janic B, Romero CA,
Worou ME, Monu SR, Peterson EL, Shaw J, Valeriote F, Ongeri EM, et
al: The anti-inflammatory peptide Ac-SDKP is released from
thymosin-β4 by renal meprin-α and prolyl oligopeptidase. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 310:F1026–F1034. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Meng Y, Yu CH, Li W, Li T, Luo W, Huang S,
Wu PS, Cai SX and Li X: Angiotensin-converting enzyme
2/angiotensin-(1–7)/Mas axis protects against lung fibrosis by
inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
50:723–736. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ntsekhe M, Matthews K, Wolske J, Badri M,
Wilkinson KA, Wilkinson RJ, Sturrock ED and Mayosi BM: Scientific
letter: Ac-SDKP (N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline) and
Galectin-3 levels in tuberculous pericardial effusion: Implications
for pathogenesis and prevention of pericardial constriction. Heart.
98:1326–1328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Chen L, Chen B, Meliton A, Liu SQ,
Shi Y, Liu T, Deb DK, Solway J and Li YC: Chronic activation of the
renin-angiotensin system induces lung fibrosis. Sci Rep.
5:155612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murphy AM, Wong AL and Bezuhly M:
Modulation of angiotensin II signaling in the prevention of
fibrosis. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 8:72015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei L, Alhenc-Gelas F, Corvol P and
Clauser E: The two homologous domains of human angiotensin
I-converting enzyme are both catalytically active. J Biol Chem.
266:9002–9008. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Masuyer G, Schwager SL, Sturrock ED, Isaac
RE and Acharya KR: Molecular recognition and regulation of human
angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) activity by natural
inhibitory peptides. Sci Rep. 2:7172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stawski L, Han R, Bujor AM and Trojanowska
M: Angiotensin II induces skin fibrosis: A novel mouse model of
dermal fibrosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R1942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cavin S, Maric D and Diviani D: A-kinase
anchoring protein-Lbc promotes pro-fibrotic signaling in cardiac
fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:335–345. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong MH, Chapin OC and Johnson MD:
LPS-stimulated cytokine production in type I cells is modulated by
the renin-angiotensin system. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
46:641–650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uhal BD, Kim JK, Li X and Molina-Molina M:
Angiotensin-TGF-beta 1 crosstalk in human idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Autocrine mechanisms in myofibroblasts and macrophages.
Curr Pharm Des. 13:1247–1256. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Masuyer G, Douglas RG, Sturrock ED and
Acharya KR: Structural basis of Ac-SDKP hydrolysis by Angiotensin-I
converting enzyme. Sci Rep. 5:137422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Xu H, Geng Y, Xu D, Zhang L, Yang
Y, Wei Z, Zhang B, Li S, Gao X, et al: Dibutyryl-cAMP attenuates
pulmonary fibrosis by blocking myofibroblast differentiation via
PKA/CREB/CBP signaling in rats with silicosis. Respir Res.
18:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu H, Yang F, Sun Y, Yuan Y, Cheng H, Wei
Z, Li S, Cheng T, Brann D and Wang R: A new antifibrotic target of
Ac-SDKP: Inhibition of myofibroblast differentiation in rat lung
with silicosis. PLoS One. 7:e403012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li S, Gao X, Xu D, Wang X, Liu Y, Zhang L,
Deng H, Wei Z, Tian J, Xu H and Yang F: Inhibition effect of
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline on myofibroblast
differentiation by regulating acetylated tubulin α in silicotic rat
model. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 33:816–821.
2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng Y, Li T, Zhou GS, Chen Y, Yu CH, Pang
MX, Li W, Li Y, Zhang WY and Li X: The angiotensin-converting
enzyme 2/angiotensin (1–7)/Mas axis protects against lung
fibroblast migration and lung fibrosis by inhibiting the
NOX4-derived ROS-mediated RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 22:241–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Morimoto Y, Nagatomo H, Hirohashi M, Oyabu
T, Ogami A, Yamato H, Kuroda K, Obata Y, Higashi T and Tanaka I:
Expression of clara cell secretory protein in the lungs of rats
exposed to crystalline silica in vivo. J Occup Health. 47:504–509.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong H, Jing W, Yabo Y, Xiaokang Y, Wan W,
Min M, Wenyang W, Zhaoquan C, Yingru X and Rongbo Z: Establishment
of rat model of silicotuberculosis and its pathological
characteristic. Pathog Glob Health. 108:312–316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang
H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, et al: Interactions
between β-catenin and transforming growth factor-β signaling
pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are
dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response
element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem.
287:7026–7038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hashimoto N, Phan SH, Imaizumi K, Matsuo
M, Nakashima H, Kawabe T, Shimokata K and Hasegawa Y:
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:161–172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marriott S, Baskir RS, Gaskill C, Menon S,
Carrier EJ, Williams J, Talati M, Helm K, Alford CE, Kropski JA, et
al: ABCG2pos lung mesenchymal stem cells are a novel pericyte
subpopulation that contributes to fibrotic remodeling. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 307:C684–C698. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zolak JS, Jagirdar R, Surolia R, Karki S,
Oliva O, Hock T, Guroji P, Ding Q, Liu RM, Bolisetty S, et al:
Pleural mesothelial cell differentiation and invasion in fibrogenic
lung injury. Am J Pathol. 182:1239–1247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tumelty KE, Smith BD, Nugent MA and Layne
MD: Aortic carboxypeptidase-like protein (ACLP) enhances lung
myofibroblast differentiation through transforming growth factor β
receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem.
289:2526–2536. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Specks U, Martin WJ II and Rohrbach MS:
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid angiotensin-converting enzyme in
interstitial lung diseases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 141:117–123. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Molina-Molina M, Abdul-Hafez A,
Ramirez J, Serrano-Mollar A, Xaubet A and Uhal BD: Extravascular
sources of lung angiotensin peptide synthesis in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
291:L887–L895. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bai J, Zhang N, Hua Y, Wang B, Ling L,
Ferro A and Xu B: Metformin inhibits angiotensin II-induced
differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. PLoS
One. 8:e721202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo X, Yan F, Li J, Zhang C and Bu P:
SIRT3 attenuates AngII-induced cardiac fibrosis by inhibiting
myofibroblasts transdifferentiation via STAT3-NFATc2 pathway. Am J
Transl Res. 9:3258–3269. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peng H, Carretero OA, Peterson EL and
Rhaleb NE: Ac-SDKP inhibits transforming growth
factor-beta1-induced differentiation of human cardiac fibroblasts
into myofibroblasts. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H1357–H1364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pokharel S, Rasoul S, Roks AJ, van Leeuwen
RE, van Luyn MJ, Deelman LE, Smits JF, Carretero O, van Gilst WH
and Pinto YM: N-acetyl-Ser-Asp-Lys-Pro inhibits phosphorylation of
Smad2 in cardiac fibroblasts. Hypertension. 40:155–161. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kanasaki K, Koya D, Sugimoto T, Isono M,
Kashiwagi A and Haneda M: N-Acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline
inhibits TGF-beta-mediated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
expression via inhibition of Smad pathway in human mesangial cells.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:863–872. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin CX, Rhaleb NE, Yang XP, Liao TD,
D'Ambrosio MA and Carretero OA: Prevention of aortic fibrosis by
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline in angiotensin II-induced
hypertension. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1253–H1261.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamazaki KG, Gonzalez E and Zambon AC:
Crosstalk between the renin-angiotensin system and the advance
glycation end product axis in the heart: Role of the cardiac
fibroblast. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 5:805–813. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Samarakoon R, Overstreet JM and Higgins
PJ: TGF-β signaling in tissue fibrosis: Redox controls, target
genes and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Signal. 25:264–268. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rosenkranz S: TGF-beta1 and angiotensin
networking in cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc Res. 63:423–432. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Craig VJ, Zhang L, Hagood JS and Owen CA:
Matrix metalloproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 53:585–600. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Yoshii J, Ikenaka
Y, Noguchi R, Nakatani T, Tsujinoue H, Yanase K, Namisaki T, Imazu
H and Fukui H: Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 attenuates
spontaneous liver fibrosis resolution in the transgenic mouse.
Hepatology. 36:850–860. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|