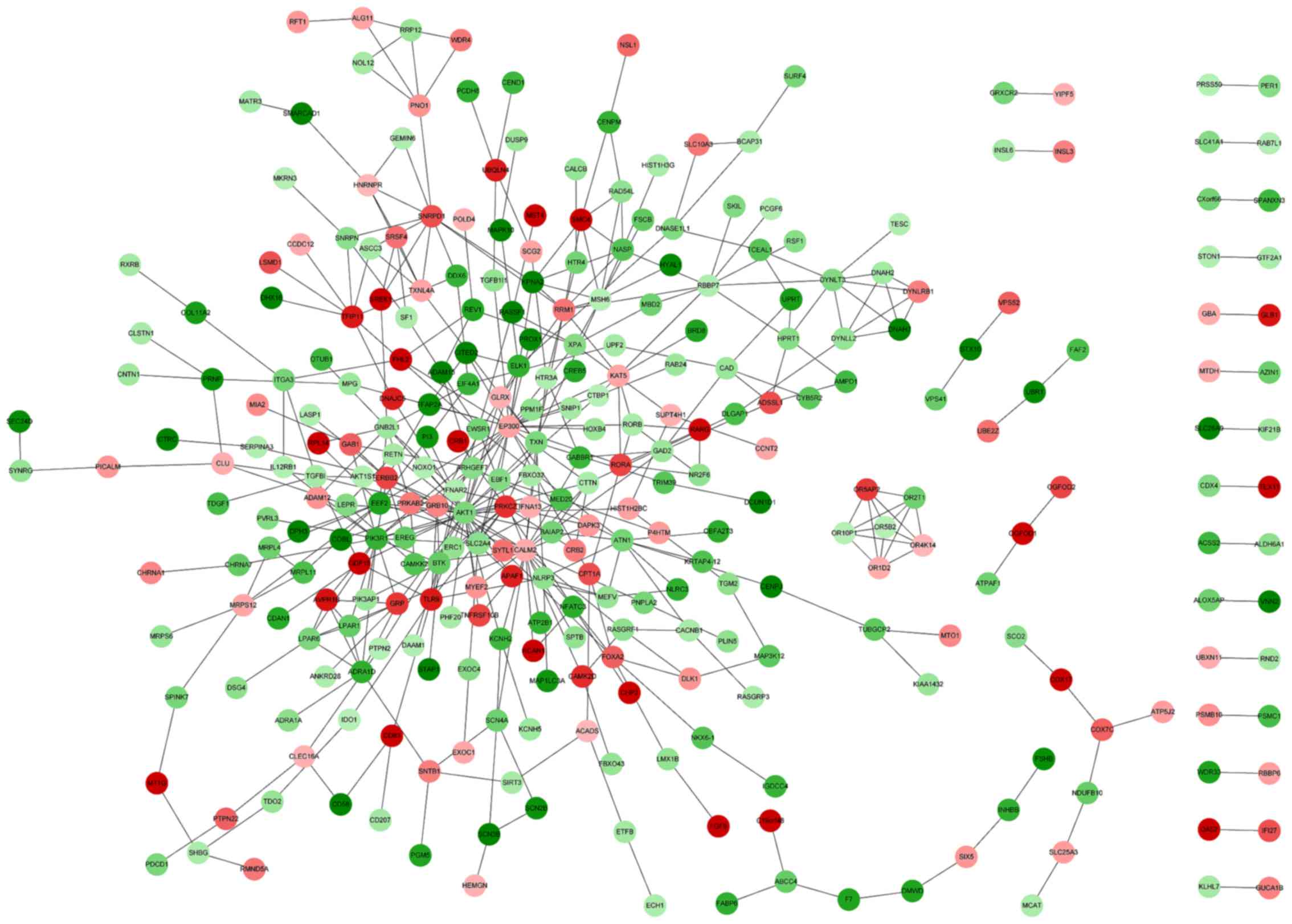
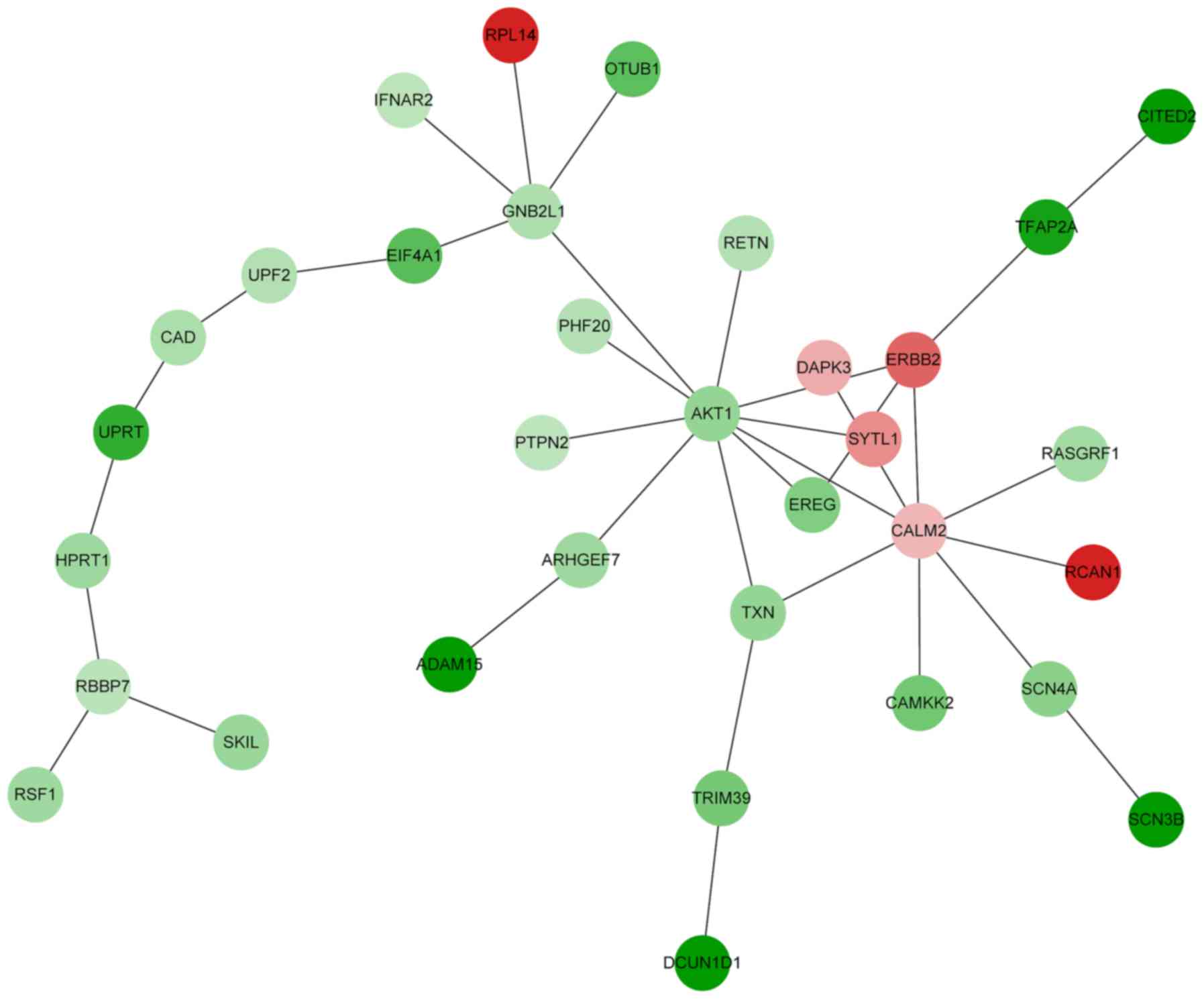
|
1
|
Böckelman C, Hagström J, Mäkinen L,
Keski-Säntti H, Häyry V, Lundin J, Atula T, Ristimäki A and Haglund
C: High CIP2A immunoreactivity is an independent prognostic
indicator in early-stage tongue cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:1890–1895.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sano D and Myers JN: Metastasis of
squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:645–662. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gosselin BJ: Malignant Tumors of the
Mobile Tongue. Medscape. Jun;2011.http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/847428-overviewAccessed
April 3, 2015.
|
|
4
|
Liang XH, Lewis J, Foote R, Smith D and
Kademani D: Prevalence and significance of human papillomavirus in
oral tongue cancer: The Mayo Clinic experience. J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 66:1875–1880. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Z, Wang H and Li Q: Tongue tumor
detection in medical hyperspectral images. Sensors. 12:162–174.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garavello W, Spreafico R and Gaini RM:
Oral tongue cancer in young patients: A matched analysis. Oral
Oncol. 43:894–897. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moore SR, Johnson NW, Pierce AM and Wilson
DF: The epidemiology of tongue cancer: a review of global
incidence. Oral Dis. 6:75–84. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sebastian P, Babu JM, Prathibha R,
Hariharan R and Pillai MR: Anterior tongue cancer with no history
of tobacco and alcohol use may be a distinct molecular and clinical
entity. J Oral Pathol Med. 43:593–599. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie X, Clausen OP, De Angelis P and Boysen
M: The prognostic value of spontaneous apoptosis, Bax, Bcl-2, and
p53 in oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Cancer.
86:913–920. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seo J and Hoffman EP: Probe set
algorithms: Is there a rational best bet? BMC Bioinformatics.
7:3952006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wettenhall JM and Smyth GK: limmaGUI: A
graphical user interface for linear modeling of microarray data.
Bioinformatics. 20:3705–3706. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . Gene ontology
consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D1049–D1056. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M, Tanabe M
and Hirakawa M: KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular
networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:D355–D360. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
ENCODE Project Consortium, . An integrated
encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature.
489:57–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen JS, Hung WS, Chan HH, Tsai SJ and Sun
HS: In silico identification of oncogenic potential of fyn-related
kinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. Bioinformatics. 29:420–427.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beisser D, Klau GW, Dandekar T, Müller T
and Dittrich MT: BioNet An R-Package for the functional analysis of
biological networks. Bioinformatics. 26:1129–1130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ogryzko VV, Schiltz RL, Russanova V,
Howard BH and Nakatani Y: The transcriptional coactivators p300 and
CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell. 87:953–959. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kalkhoven E: CBP and p300: HATs for
different occasions. Biochem Pharmacol. 68:1145–1155. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lahtz C and Pfeifer GP: Epigenetic changes
of DNA repair genes in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 3:51–58. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hasan S, Hassa PO, Imhof R and Hottiger
MO: Transcription coactivator p300 binds PCNA and may have a role
in DNA repair synthesis. Nature. 410:387–391. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Moldovan GL, Pfander B and Jentsch S:
PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 129:665–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Debes JD, Sebo TJ, Lohse CM, Murphy LM,
Haugen DA and Tindall DJ: p300 in prostate cancer proliferation and
progression. Cancer Res. 63:7638–7640. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ionov Y, Matsui S and Cowell JK: A role
for p300/CREB binding protein genes in promoting cancer progression
in colon cancer cell lines with microsatellite instability. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:1273–1278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ju X, Katiyar S, Wang C, Liu M, Jiao X, Li
S, Zhou J, Turner J, Lisanti MP, Russell RG, et al: Akt1 governs
breast cancer progression in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:7438–7443. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Freeman-Cook KD, Autry C, Borzillo G,
Gordon D, BarbacciTobin E, Bernardo V, Briere D, Clark T, Corbett
M, Jakubczak J, et al: Design of selective, ATP-competitive
inhibitors of Akt. J Med Chem. 53:4615–4622. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pfisterer K, Fusi A, Klinghammer K,
Knödler M, Nonnenmacher A and Keilholz U: PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR
polymorphisms: association with clinical outcome in patients with
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma receiving cetuximab-docetax.
Head Neck. 37:471–478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amornphimoltham P, Patel V, Molinolo A and
Gutkind JS: Head and Neck Cancer and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling
Network: Novel Molecular Targeted Therapies. Signaling Pathways in
Squamous Cancer. pp407–pp429. 2010.
|
|
31
|
Kong L, Schäfer G, Bu H, Zhang Y, Zhang Y
and Klocker H: Lamin A/C protein is overexpressed in
tissue-invading prostate cancer and promotes prostate cancer cell
growth, migration and invasion through the PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway.
Carcinogenesis. 33:751–759. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Castaneda CA, CortesFunes H, Gomez HL and
Ciruelos EM: The phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase/AKT signaling
pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:751–759. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eide PW, Cekaite L, Danielsen SA,
Eilertsen IA, Kjenseth A, Fykerud TA, Ågesen TH, Bruun J, Rivedal
E, Lothe RA and Leithe E: NEDD4 is overexpressed in colorectal
cancer and promotes colonic cell growth independently of the
PI3K/PTEN/AKT pathway. Cell Signal. 25:12–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weber SM, Bornstein S, Li Y, Malkoski SP,
Wang D, Rustgi AK, KuleszMartin MF, Wang XJ and Lu SL:
Tobacco-specific carcinogen nitrosamine
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone induces AKT
activation in head and neck epithelia. Int J Oncol. 39:1193–1198.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
West KA, Brognard J, Clark AS, Linnoila
IR, Yang X, Swain SM, Harris C, Belinsky S and Dennis PA: Rapid Akt
activation by nicotine and a tobacco carcinogen modulates the
phenotype of normal human airway epithelial cells. J Clin Invest.
111:81–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Massarelli E, Liu DD, Lee JJ, ElNaggar AK,
Lo Muzio L, Staibano S, De Placido S, Myers JN and
Papadimitrakopoulou VA: Akt activation correlates with adverse
outcome in tongue cancer. Cancer. 104:2430–2436. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Amornphimoltham P, Sriuranpong V, Patel V,
Benavides F, Conti CJ, Sauk J, Sausville EA, Molinolo AA and
Gutkind JS: Persistent activation of the Akt pathway in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: A potential target for UCN-01. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:4029–4037. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Altomare DA, Wang HQ, Skele KL, De Rienzo
A, Klein-Szanto AJ, Godwin AK and Testa JR: AKT and mTOR
phosphorylation is frequently detected in ovarian cancer and can be
targeted to disrupt ovarian tumor cell growth. Oncogene.
23:5853–5857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lundstrom TS and Sobel JD: Antibiotics for
gram-positive bacterial infections: Vancomycin,
quinupristin-dalfopristin, linezolid, and daptomycin. Infect Dis
Clin North Am. 18651–668. (x)2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hardy KM, Booth BW, Hendrix MJ, Salomon DS
and Strizzi L: ErbB/EGF signaling and EMT in mammary development
and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:191–199.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sosa MS, LopezHaber C, Yang C, Wang H,
Lemmon MA, Busillo JM, Luo J, Benovic JL, KleinSzanto A, Yagi H, et
al: Identification of the Rac-GEF P-Rex1 as an essential mediator
of ErbB signaling in breast cancer. Mol Cell. 40:877–892. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Silva SD, Perez DE, Alves FA, Nishimoto
IN, Pinto CA, Kowalski LP and Graner E: ErbB2 and fatty acid
synthase (FAS) expression in 102 squamous cell carcinomas of the
tongue: Correlation with clinical outcomes. Oral Oncol. 44:484–490.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lu Z, Jiang G, BlumeJensen P and Hunter T:
Epidermal growth factor-induced tumor cell invasion and metastasis
initiated by dephosphorylation and downregulation of focal adhesion
kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4016–4031. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Uribe P and Gonzalez S: Epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin:
Molecular bases for EGFR-targeted therapy. Pathol Res Pract.
207:337–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nickerson NK, Gilmore JL, Allen KT, Riese
DJ II, Nephew KP and Foley J: EGFR-Ligand signaling in breast
cancer metastasis: Recurring developmental themes. 2011.
|