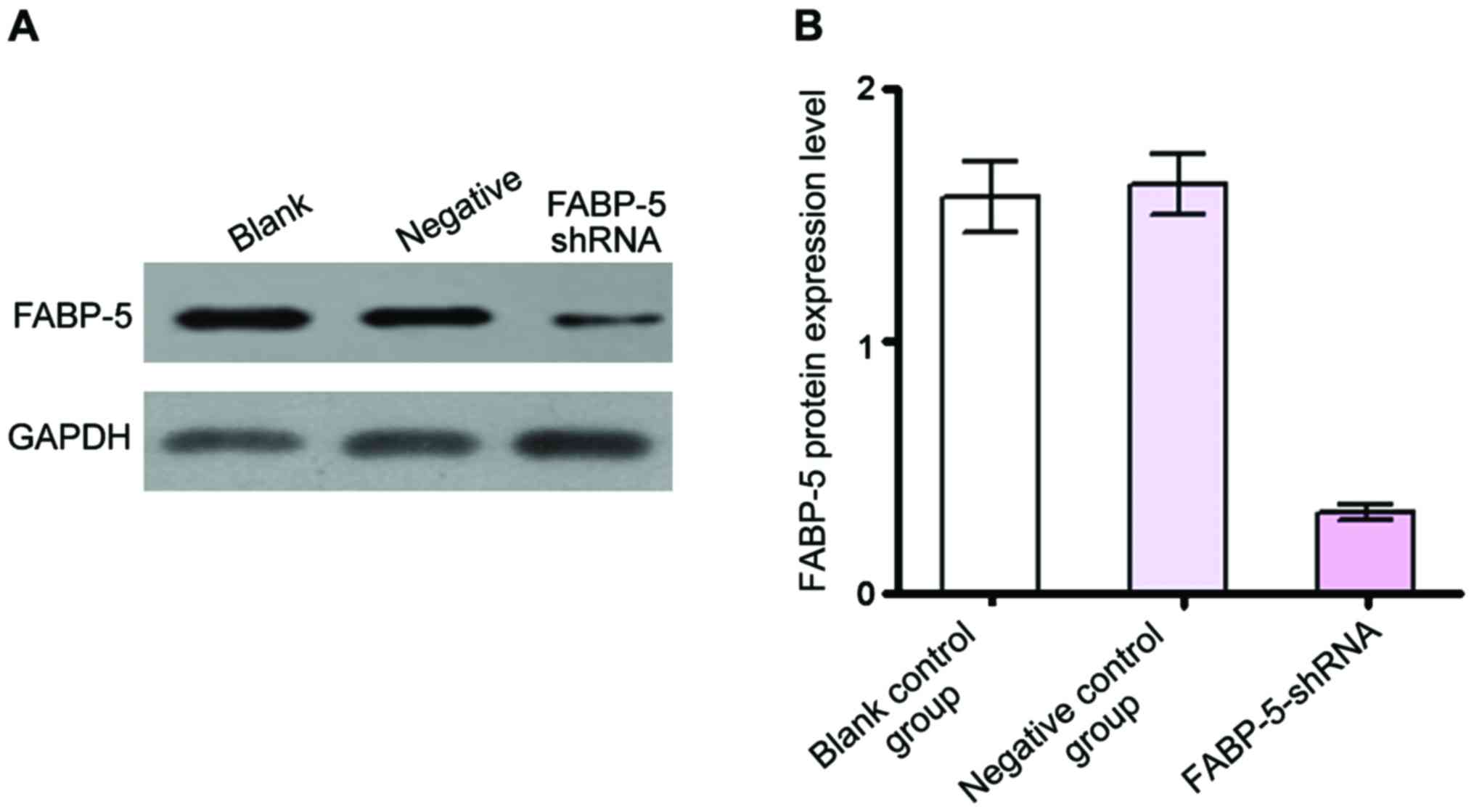
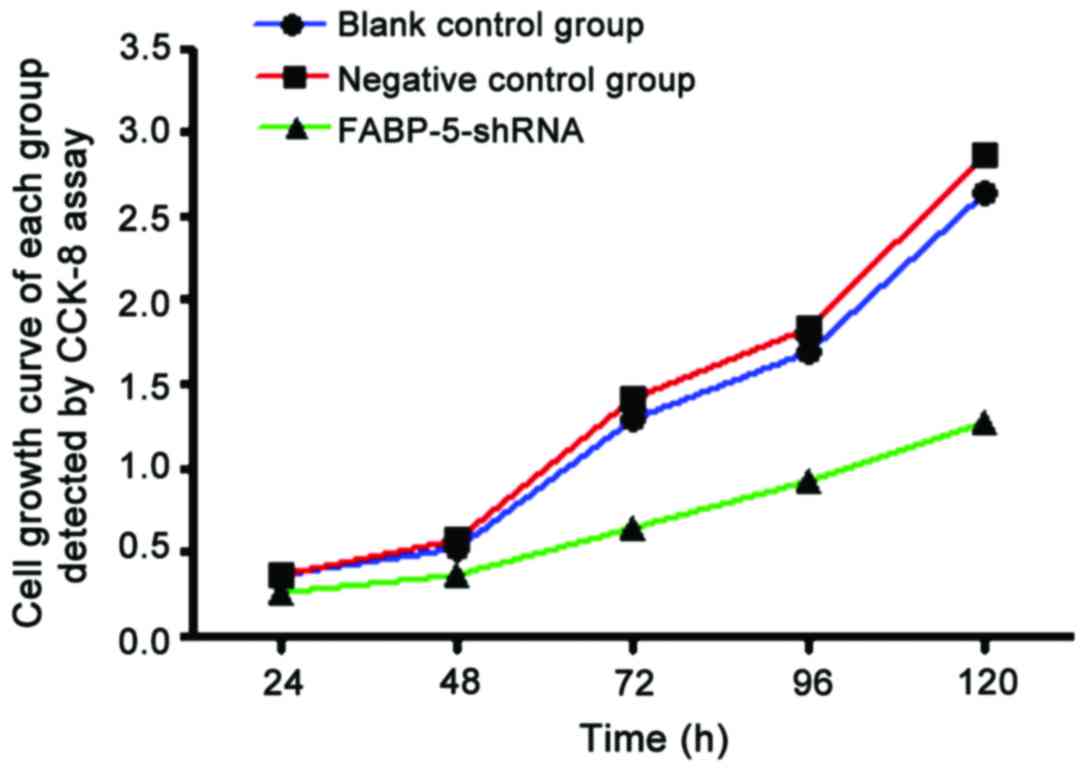
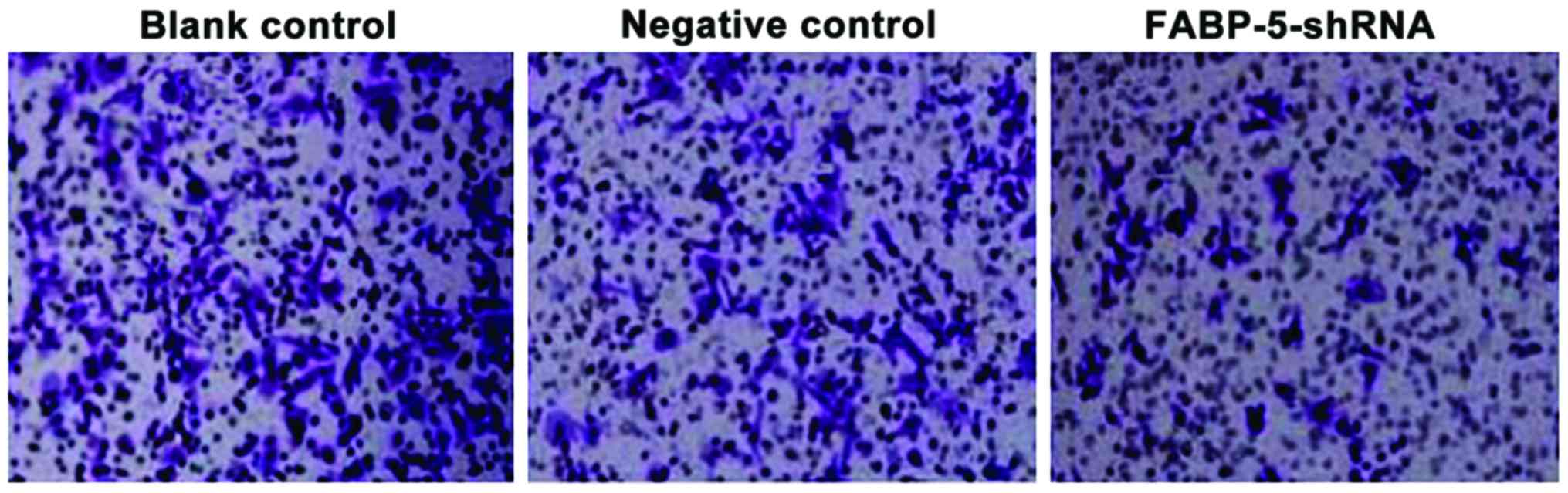
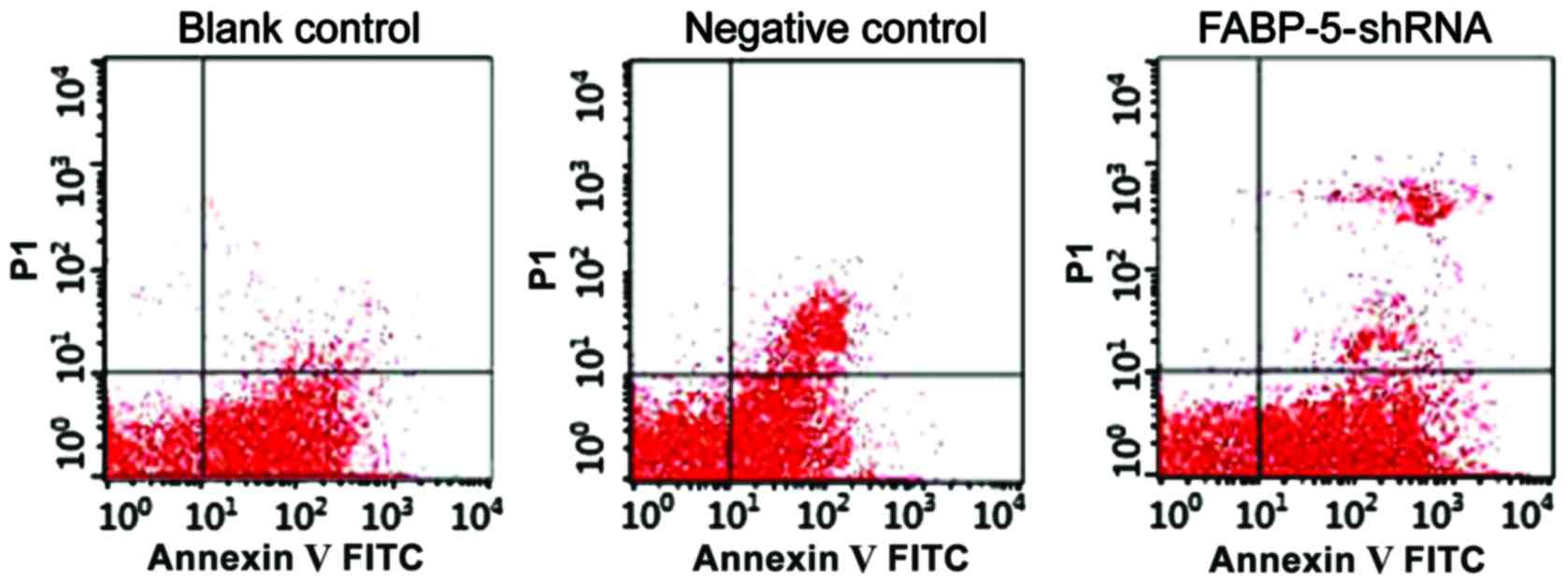
|
1
|
Zhu YL, Yang L, Sui ZQ, Liu L and Du JF:
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of Borrmann type IV
gastric cancer. J BUON. 21:1471–1475. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yildiz B, Etiz D, Dal P, Junushova B,
Pasaoglu O, Yilmaz E, Erkasap S and Dincer M: Tumor deposits:
Prognostic significance in gastric cancer patients. J BUON.
21:1476–1481. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Veerkamp JH, Maatman RG and Prinsen CF:
Fatty acid-binding proteins: Structural and functional diversity.
Biochem Soc Trans. 20:801–805. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Münz M, Zeidler R and Gires O: The
tumour-associated antigen EpCAM upregulates the fatty acid binding
protein E-FABP. Cancer Lett. 225:151–157. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uma RS, Naresh KN, D'Cruz AK, Mulherkar R
and Borges AM: Metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the oral
tongue is associated with down-regulation of epidermal fatty acid
binding protein (E-FABP). Oral Oncol. 43:27–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu RZ, Graham K, Glubrecht DD, Germain
DR, Mackey JR and Godbout R: Association of FABP5 expression with
poor survival in triple-negative breast cancer: implication for
retinoic acid therapy. Am J Pathol. 178:997–1008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith S, Witkowski A and Joshi AK:
Structural and functional organization of the animal fatty acid
synthase. Prog Lipid Res. 42:289–317. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chmurzyńska A: The multigene family of
fatty acid-binding proteins (FABPs): Function, structure and
polymorphism. J Appl Genet. 47:39–48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thumser AE, Moore JB and Plant NJ: Fatty
acid binding proteins: Tissue-specific functions in health and
disease. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 17:124–129. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zimmerman AW, van Moerkerk HT and Veerkamp
JH: Ligand specificity and conformational stability of human fatty
acid-binding proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 33:865–876. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawamura T, Kanno R, Fujii H and Suzuki T:
Expression of liver-type fatty-acid-binding protein, fatty acid
synthase and vascular endothelial growth factor in human lung
carcinoma. Pathobiology. 72:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lawrie LC, Dundas SR, Curran S and Murray
GI: Liver fatty acid binding protein expression in colorectal
neoplasia. Br J Cancer. 90:1955–1960. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hammamieh R, Chakraborty N, Barmada M, Das
R and Jett M: Expression patterns of fatty acid binding proteins in
breast cancer cells. J Exp Ther Oncol. 5:133–143. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tölle A, Suhail S, Jung M, Jung K and
Stephan C: Fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs) in prostate, bladder
and kidney cancer cell lines and the use of IL-FABP as survival
predictor in patients with renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
11:3022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hashimoto T, Kusakabe T, Watanabe K,
Sugino T, Fukuda T, Nashimoto A, Honma K, Sato Y, Kimura H, Fujii
H, et al: Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein is highly expressed
in intestinal metaplasia and in a subset of carcinomas of the
stomach without association with the fatty acid synthase status in
the carcinoma. Pathobiology. 71:115–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Armstrong EH, Goswami D, Griffin PR, Noy N
and Ortlund EA: Structural basis for ligand regulation of the fatty
acid-binding protein 5, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
β/δ (FABP5-PPARβ/δ) signaling pathway. J Biol Chem.
289:14941–14954. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Levi L, Lobo G, Doud MK, von Lintig J,
Seachrist D, Tochtrop GP and Noy N: Genetic ablation of the fatty
acid-binding protein FABP5 suppresses HER2-induced mammary
tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 73:4770–4780. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harris FT, Rahman SM, Hassanein M, Qian J,
Hoeksema MD, Chen H, Eisenberg R, Chaurand P, Caprioli RM, Shiota
M, et al: Acyl-coenzyme A-binding protein regulates Beta-oxidation
required for growth and survival of non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 7:748–757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Q, Wang S, Xu H and Zhang S:
Expressions and significances of CRABPII and E-FABP in non-small
cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 16:12–19. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Celis JE, Rasmussen HH, Vorum H, Madsen P,
Honoré B, Wolf H and Orntoft TF: Bladder squamous cell carcinomas
express psoriasin and externalize it to the urine. J Urol.
155:2105–2112. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adamson J, Morgan EA, Beesley C, Mei Y,
Foster CS, Fujii H, Rudland PS, Smith PH and Ke Y: High-level
expression of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein in prostatic
carcinomas and its effect on tumorigenicity. Oncogene.
22:2739–2749. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morgan EA, Forootan SS, Adamson J, Foster
CS, Fujii H, Igarashi M, Beesley C, Smith PH and Ke Y: Expression
of cutaneous fatty acid-binding protein (C-FABP) in prostate
cancer: Potential prognostic marker and target for
tumourigenicity-suppression. Int J Oncol. 32:767–775.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jeong CY, Hah YS, Cho BI, Lee SM, Joo YT,
Jung EJ, Jeong SH, Lee YJ, Choi SK, Ha WS, et al: Fatty
acid-binding protein 5 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in
human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 28:1283–1292.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fang LY, Wong TY, Chiang WF and Chen YL:
Fatty-acid-binding protein 5 promotes cell proliferation and
invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med.
39:342–348. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rauch J, Ahlemann M, Schaffrik M, Mack B,
Ertongur S, Andratschke M, Zeidler R, Lang S and Gires O: Allogenic
antibody-mediated identification of head and neck cancer antigens.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 323:156–162. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z, Huang C, Bai S, Pan X, Zhou R, Wei Y
and Zhao X: Prognostic evaluation of epidermal fatty acid-binding
protein and calcyphosine, two proteins implicated in endometrial
cancer using a proteomic approach. Int J Cancer. 123:2377–2383.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brouard MC, Saurat JH, Ghanem G and
Siegenthaler G: Urinary excretion of epidermal-type fatty
acid-binding protein and S100A7 protein in patients with cutaneous
melanoma. Melanoma Res. 12:627–631. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ogawa R, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M,
Mitsui A, Mori Y, Mori R, Tomoda K, Katada T, Harada K, et al:
Identification of candidate genes involved in the radiosensitivity
of esophageal cancer cells by microarray analysis. Dis Esophagus.
21:288–297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|