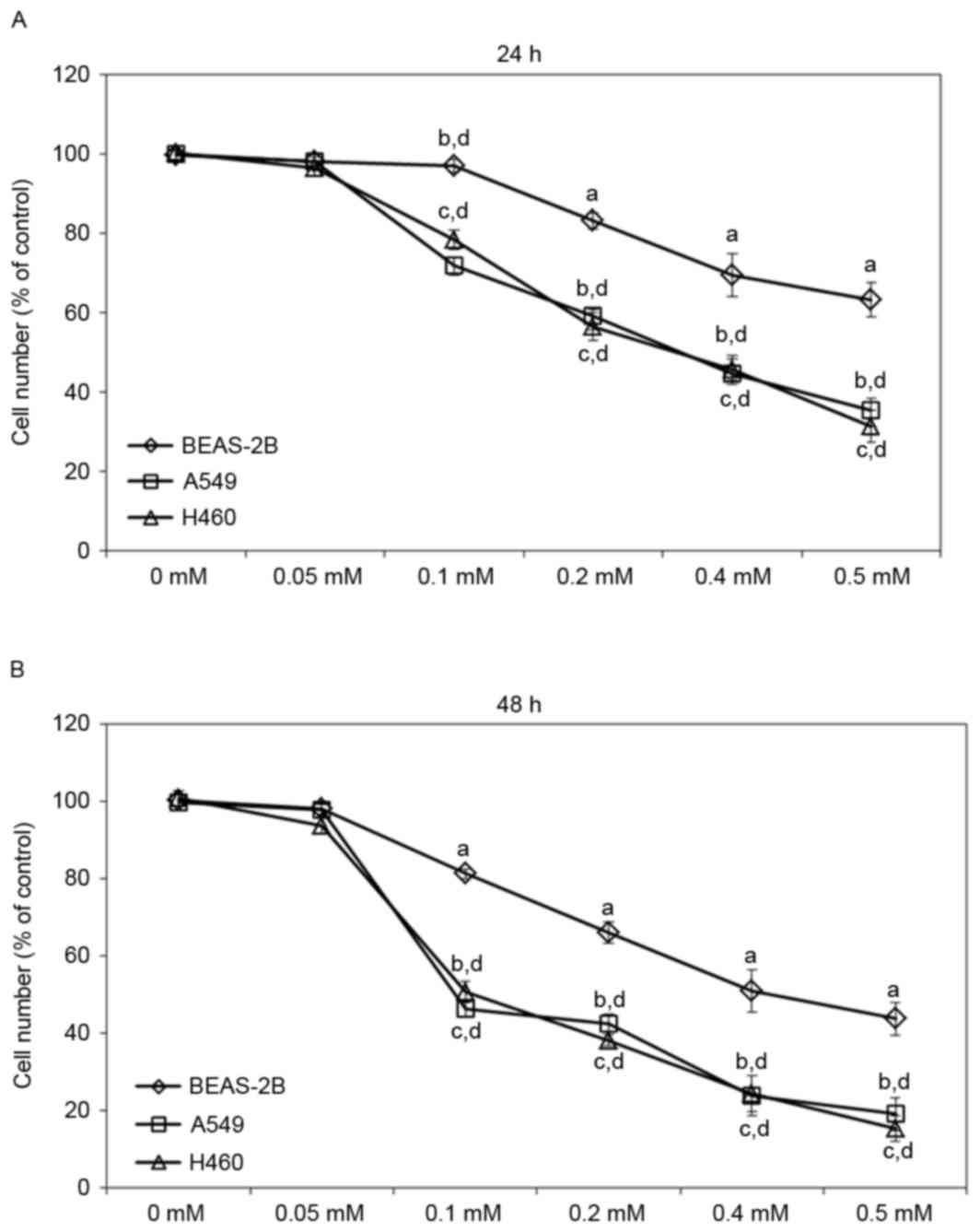
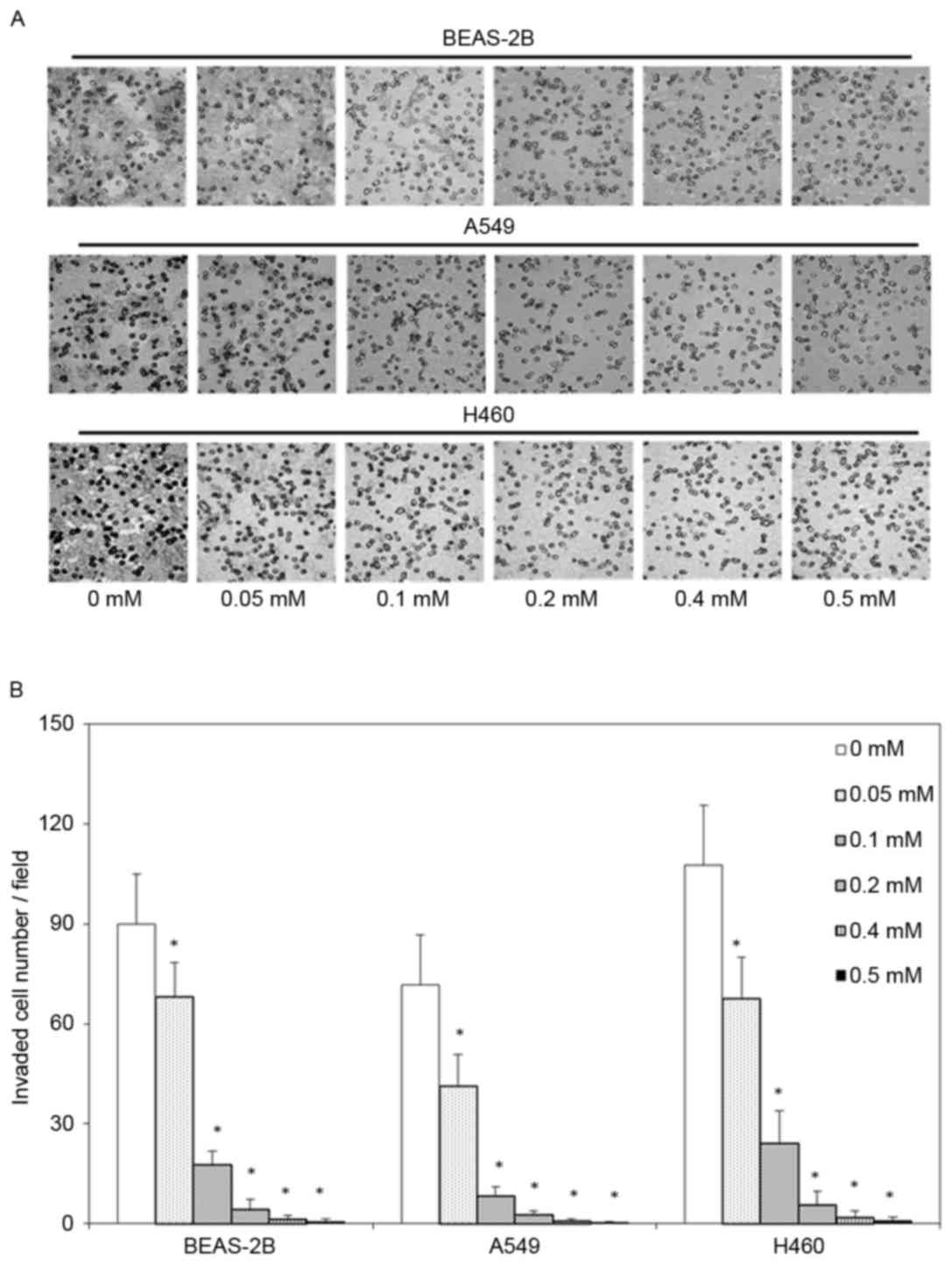
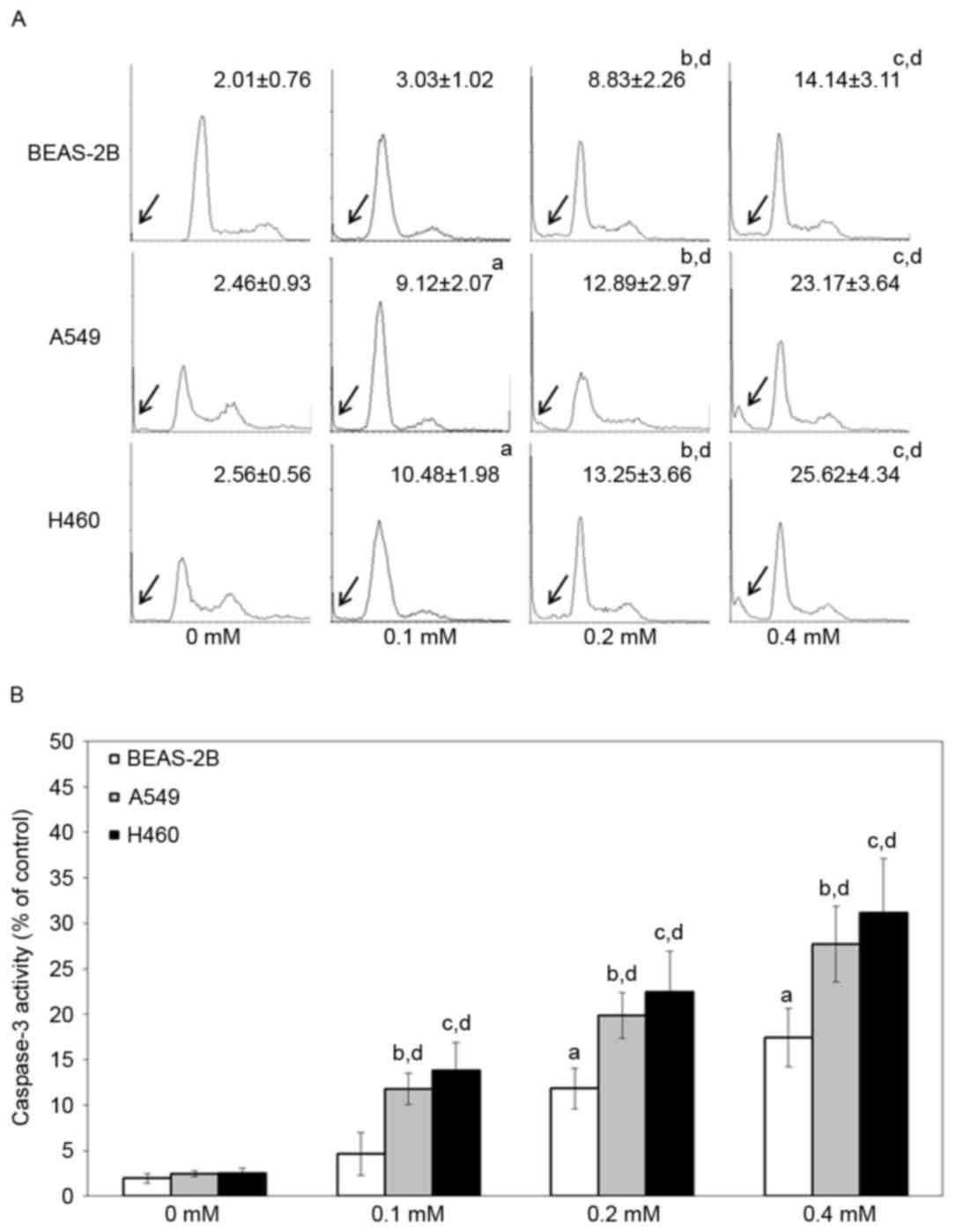
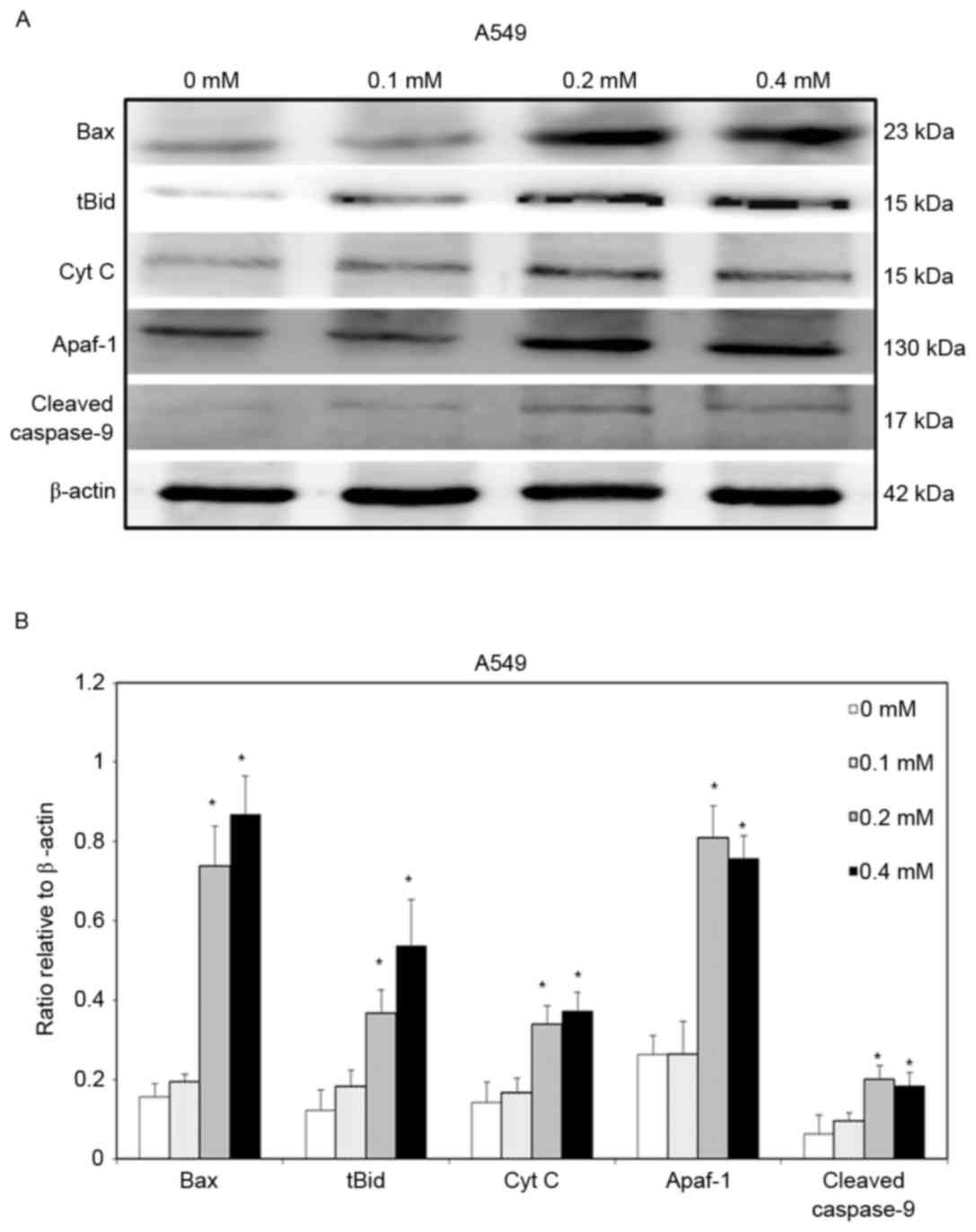
|
1
|
Islami F, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global
trends of lung cancer mortality and smoking prevalence. Transl Lung
Cancer Res. 4:327–338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petersen I and Warth A: Lung cancer:
Developments, concepts, and specific aspects of the new WHO
classification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:895–904. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
American Cancer Society: Lung Cancer
(Non-Small Cell), . American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging
(AJCC-2010). Atlanta, GA: 2013
|
|
6
|
Jones GR: Cancer therapy: Phenothiazines
in an unexpected role. Tumori. 71:563–569. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Toh S, Rodríguez LA and Hernández-Díaz S:
Use of antidepressants and risk of lung cancer. Cancer Causes
Control. 18:1055–1064. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dodd S, Berk M, Kelin K, Zhang Q, Eriksson
E, Deberdt W and Craig Nelson J: Application of the Gradient
Boosted method in randomised clinical trials: Participant variables
that contribute to depression treatment efficacy of duloxetine,
SSRIs or placebo. J Affect Disord. 168:284–293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Stepulak A, Rzeski W, Sifringer M, Brocke
K, Gratopp A, Kupisz K, Turski L and Ikonomidou C: Fluoxetine
inhibits the extracellular signal regulated kinase pathway and
suppresses growth of cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1685–1693.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burke WJ: Escitalopram. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 11:1477–1486. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kirino E: Escitalopram for the management
of major depressive disorder: A review of its efficacy, safety and
patient acceptability. Patient Prefer Adherence. 6:853–861. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chiu CC, Shi YF, Yang JJ, Hsiao YC, Tzang
BS and Hsu TC: Effects of human parvovirus B19 and bocavirus VP1
unique region on tight junction of human airway epithelial A549
cells. PLoS One. 9:e1079702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Binamé F, Pawlak G, Roux P and Hibner U:
What makes cells move: Requirements and obstacles for spontaneous
cell motility. Mol Biosyst. 6:648–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahai E: Mechanisms of cancer cell
invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:87–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liotta LA, Rao CN and Wewer UM:
Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane.
Ann Rev Biochem. 55:1037–1057. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gabbert H: Mechanisms of tumor invasion:
Evidence from in vivo observations. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
4:293–309. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guan X: Cancer metastases: Challenges and
opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B. 5:402–418. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wells A, Grahovac J, Wheeler S, Ma B and
Lauffenburger D: Targeting tumor cell motility as a strategy
against invasion and metastasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 34:283–289.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seyfried TN and Huysentruyt LC: On the
origin of cancer metastasis. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:43–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Los M, Burek CJ, Stroh C, Benedyk K, Hug H
and Mackiewicz A: Anticancer drugs of tomorrow: Apoptotic pathways
as target for drug design. Drug Discov Today. 8:67–77. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu J, Zhao BB, Shen Y, Chen W, Ma YD and
Shen YM: A novel p-terphenyl derivative inducing cell-cycle arrest
and apoptosis in MDA-MB-435 cells through topoisomerase inhibition.
Eur J Med Chem. 68:192–202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: Tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Locksley RM, Killeen N and Lenardo MJ: The
TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: Integrating mammalian biology.
Cell. 104:487–501. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hill MM, Adrain C, Duriez PJ, Creagh EM
and Martin SJ: Analysis of the composition, assembly kinetics and
activity of native Apaf-1 apoptosomes. EMBO J. 23:2134–2145. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dalton SO, Johansen C, Poulsen AH,
Nørgaard M, Sørensen HT, McLaughlin JK, Mortensen PB and Friis S:
Cancer risk among users of neuroleptic medication: A
population-based cohort study. Br J Cancer. 95:934–939. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mun AR, Lee SJ, Kim GB, Kang HS, Kim JS
and Kim SJ: Fluoxetine-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 33:3691–3697. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kraft SL, Baker NM, Carpenter J and
Bostwick JR: Procarbazine and antidepressants: A retrospective
review of the risk of serotonin toxicity. Psychooncology.
23:108–113. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kannen V, Garcia SB, Silva WA Jr, Gasser
M, Mönch R, Alho EJ, Heinsen H, Scholz CJ, Friedrich M, Heinze KG,
et al: Oncostatic effects of fluoxetine in experimental colon
cancer models. Cell Signal. 27:1781–1788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Andersen J, Kristensen AS, Bang-Andersen B
and Strømgaard K: Recent advances in the understanding of the
interaction of antidepressant drugs with serotonin and
norepinephrine transporters. Chem Commun (Camb). 25:3677–3692.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|