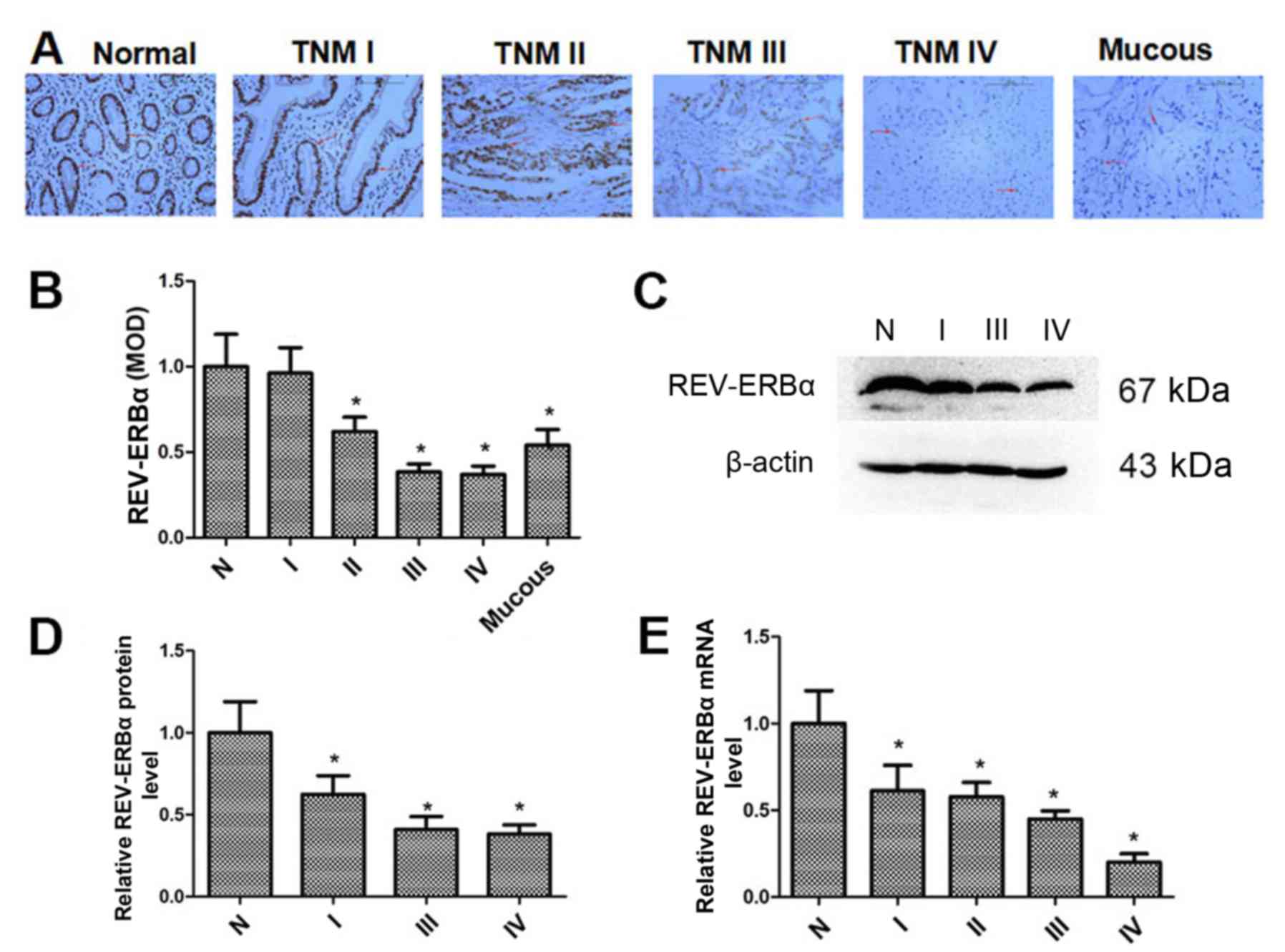
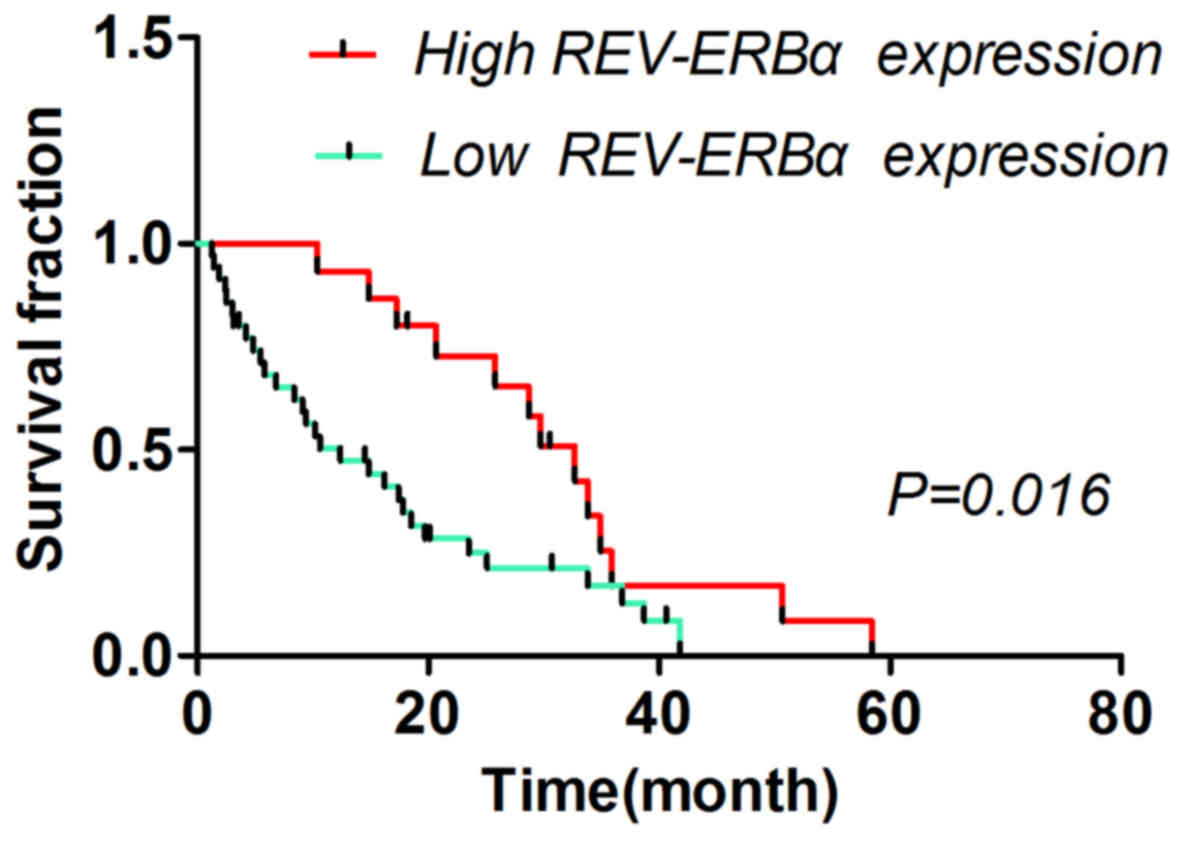
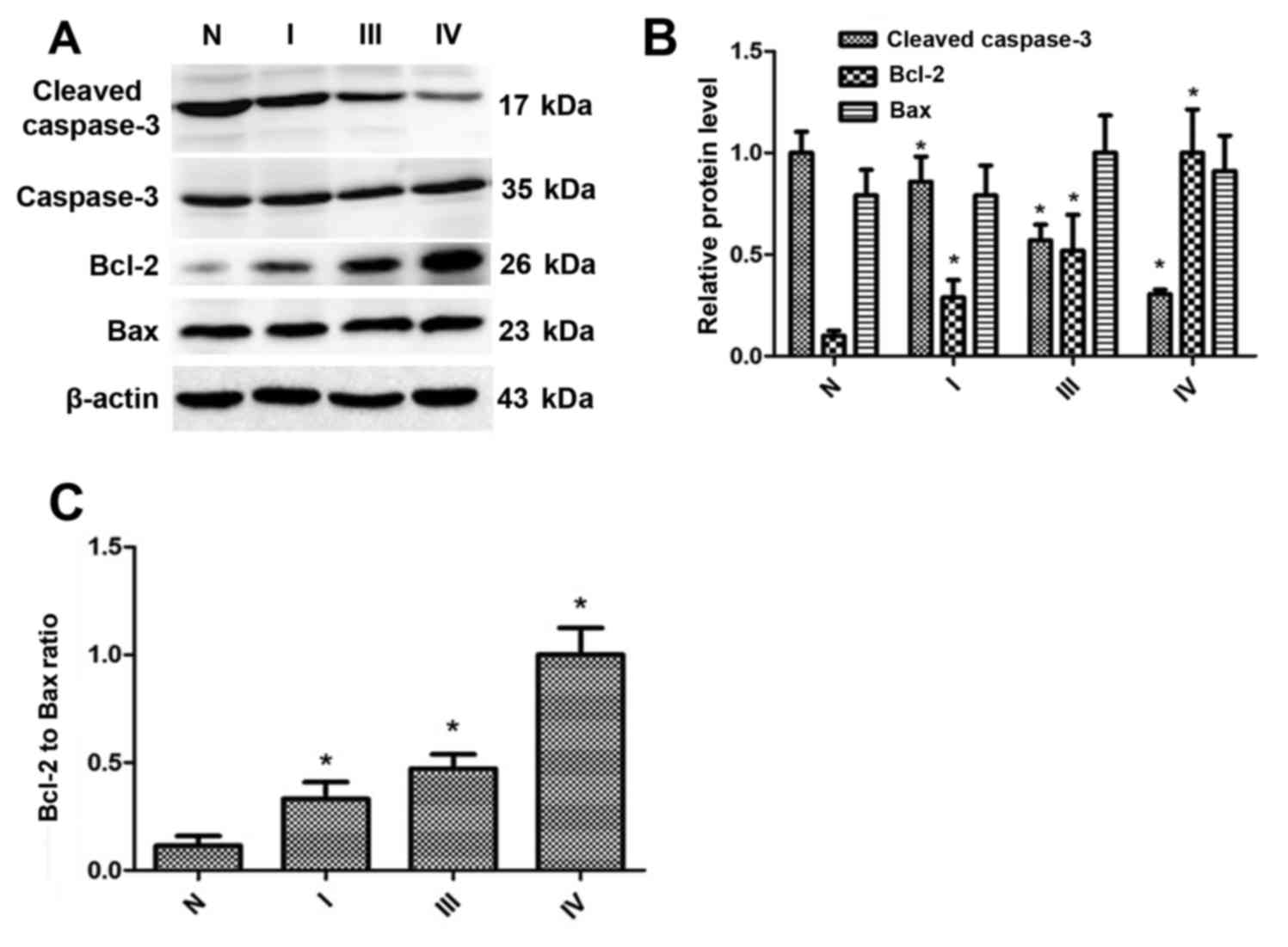
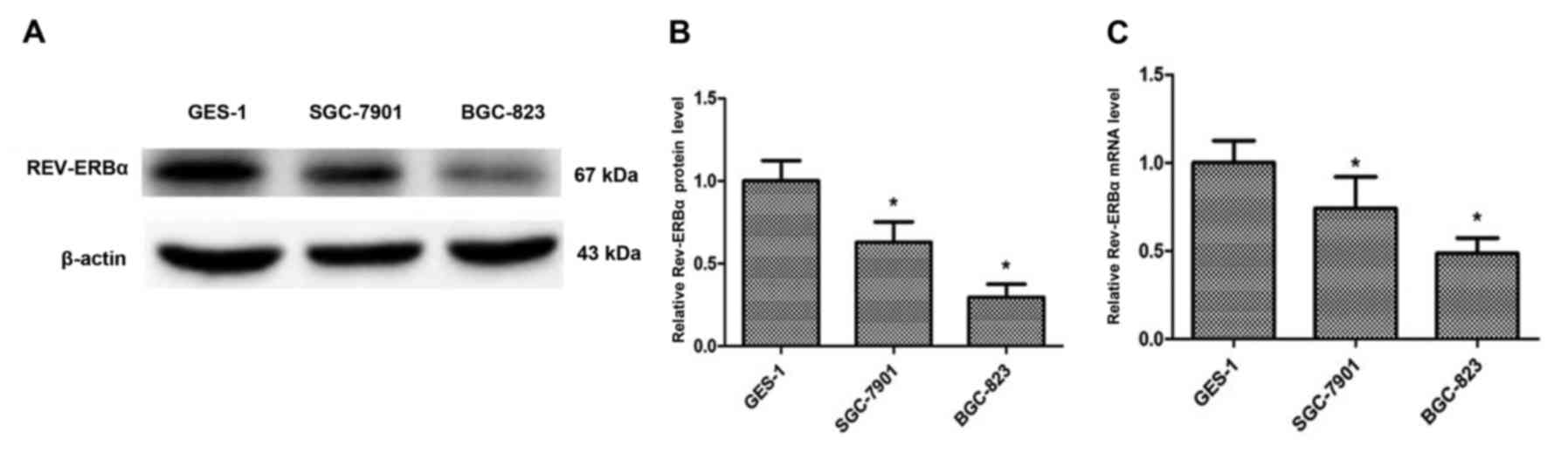
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cho H, Zhao X, Hatori M, Yu RT, Barish GD,
Lam MT, Chong LW, DiTacchio L, Atkins AR, Glass CK, et al:
Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by REV-ERB-α and
REV-ERB-β. Nature. 485:123–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mazzoccoli G, Cai Y, Liu S, Francavilla M,
Giuliani F, Piepoli A, Pazienza V, Vinciguerra M, Yamamoto T and
Takumi T: REV-ERBα and the clock gene machinery in mouse peripheral
tissues: A possible role as a synchronizing hinge. J Biol Regul
Homeost Agents. 26:265–276. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vieira E, Merino B and Quesada I: Role of
the clock gene Rev-erbα in metabolism and in the endocrine
pancreas. Diabetes Obes Metab. 17(Suppl 1): S106–S114. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kourtidis A, Jain R, Carkner RD, Eifert C,
Brosnan MJ and Conklin DS: An RNA interference screen identifies
metabolic regulators NR1D1 and PBP as novel survival factors for
breast cancer cells with the ERBB2 signature. Cancer Res.
70:1783–1792. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ka NL, Na TY, Na H, Lee MH, Park HS, Hwang
S, Kim IY, Seong JK and Lee MO: NR1D1 recruitment to sites of DNA
damage inhibits repair and is associated with chemosensitivity of
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 77:2453–2463. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Z, Xiong F, Wang X, Qi Y, Yu H, Zhu Y
and Zhu H: Nuclear receptor retinoid-related orphan receptor alpha
promotes apoptosis but is reduced in human gastric cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:11105–11113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yuan SQ, Nie RC, Chen YM, Qiu HB, Li XP,
Chen XJ, Xu LP, Yang LF, Sun XW, Li YF, et al: Glasgow Prognostic
Score is superior to ECOG PS as a prognostic factor in patients
with gastric cancer with peritoneal seeding. Oncol Lett.
15:4193–4200. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Si X, Xu A, Meng X, Gao S, Qi Y,
Zhu L, Li T, Li W and Dong L: Activation of STAT3 in human gastric
cancer cells via interleukin (IL)-6-type cytokine signaling
correlates with clinical implications. PLoS One. 8:e757882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) methods. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Dong L, Zhen Y, Wang Y, Qi D, Xu
A, Meng X and Li W: Astragalus extract inhibits proliferation but
enhances apoptosis in gastric cancer. Pak J Pharm Sci.
29:1473–1482. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sitaula S, Zhang J, Ruiz F and Burris TP:
Rev-erb regulation of cholesterologenesis. Biochem Pharmacol.
131:68–77. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Qi Y, Liu H, Wang X, Zhu H and Wang
Z: AMPK activator AICAR promotes 5-FU-induced apoptosis in gastric
cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 411:299–305. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Partch CL, Green CB and Takahashi JS:
Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Trends
Cell Biol. 24:90–99. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marciano DP, Chang MR, Corzo CA, Goswami
D, Lam VQ, Pascal BD and Griffin PR: The therapeutic potential of
nuclear receptor modulators for treatment of metabolic disorders:
PPARγ, RORs, and Rev-erbs. Cell Metab. 19:193–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee J, Lee S, Chung S, Park N, Son GH, An
H, Jang J, Chang DJ, Suh YG and Kim K: Identification of a novel
circadian clock modulator controlling BMAL1 expression through a
ROR/REV-ERB-response element-dependent mechanism. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 469:580–586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mazzoccoli G, de Cata A, Piepoli A and
Vinciguerra M: The circadian clock and the hypoxic response pathway
in kidney cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:1–7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reszka E and Przybek M: Circadian genes in
breast cancer. Adv Clin Chem. 75:53–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Kojetin D and Burris TP:
Anti-proliferative actions of a synthetic REV-ERBα/β agonist in
breast cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 96:315–322. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fu L and Kettner NM: The circadian clock
in cancer development and therapy. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
119:221–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gutierrez-Martinez P, Rossi DJ and Beerman
I: DNA damage and aging around the clock. Trends Mol Med.
22:635–637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chomez P, Neveu I, Mansén A, Kiesler E,
Larsson L, Vennström B and Arenas E: Increased cell death and
delayed development in the cerebellum of mice lacking the
rev-erbA(alpha) orphan receptor. Development. 127:1489–1498.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tao W, Wu J, Zhang Q, Lai SS, Jiang S,
Jiang C, Xu Y, Xue B, Du J and Li CJ: EGR1 regulates hepatic clock
gene amplitude by activating Per1 transcription. Sci Rep.
5:152122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JH and Sancar A: Circadian clock
disruption improves the efficacy of chemotherapy through
p73-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:10668–10672.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bugge A, Feng D, Everett LJ, Briggs ER,
Mullican SE, Wang F, Jager J and Lazar MA: Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ
coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic
function. Genes Dev. 26:657–667. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He Y, Lin F, Chen Y, Tan Z, Bai D and Zhao
Q: Overexpression of the circadian clock gene rev-erbα affects
murine bone mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenesis.
Stem Cells Dev. 24:1194–1204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|