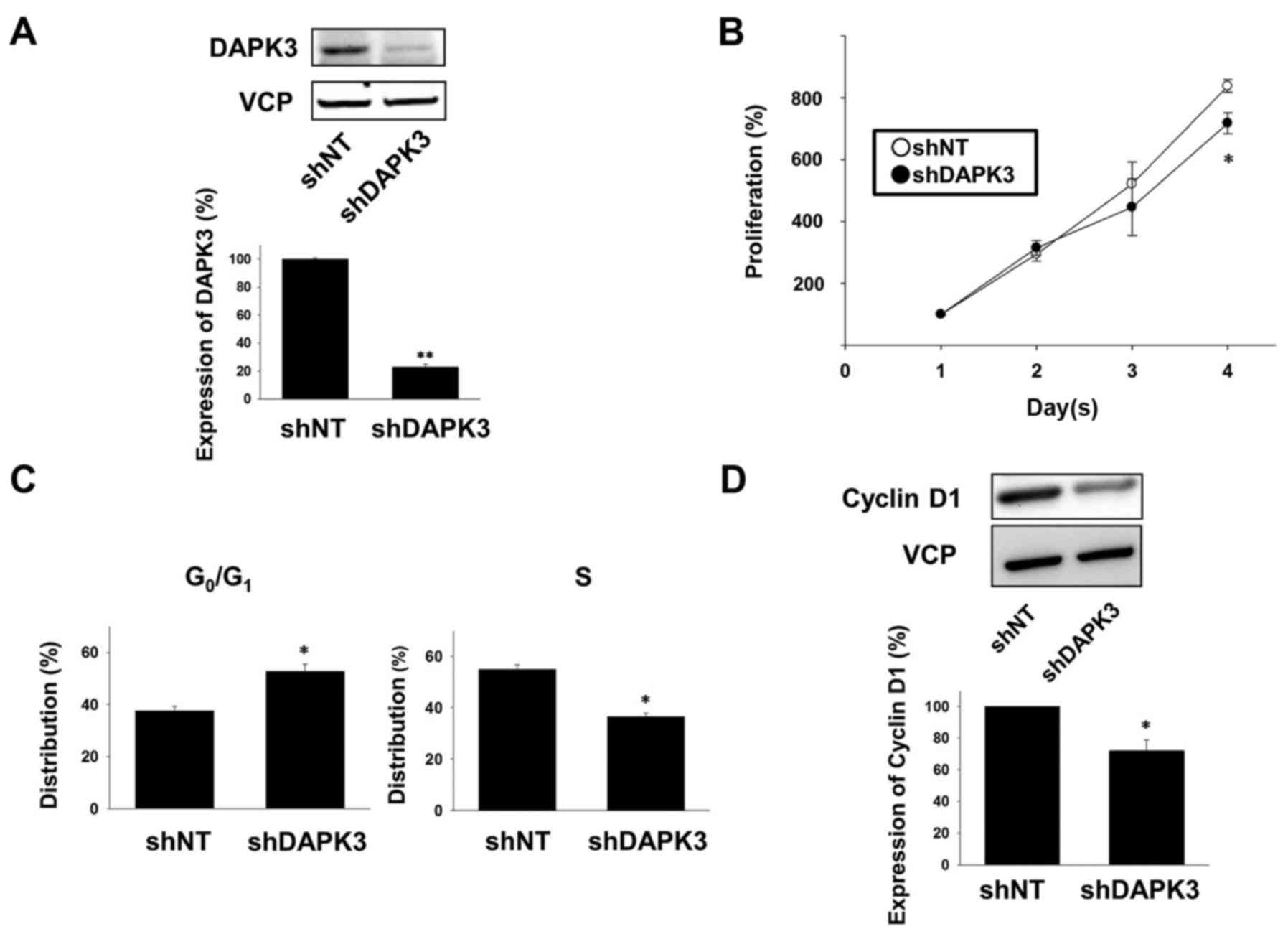
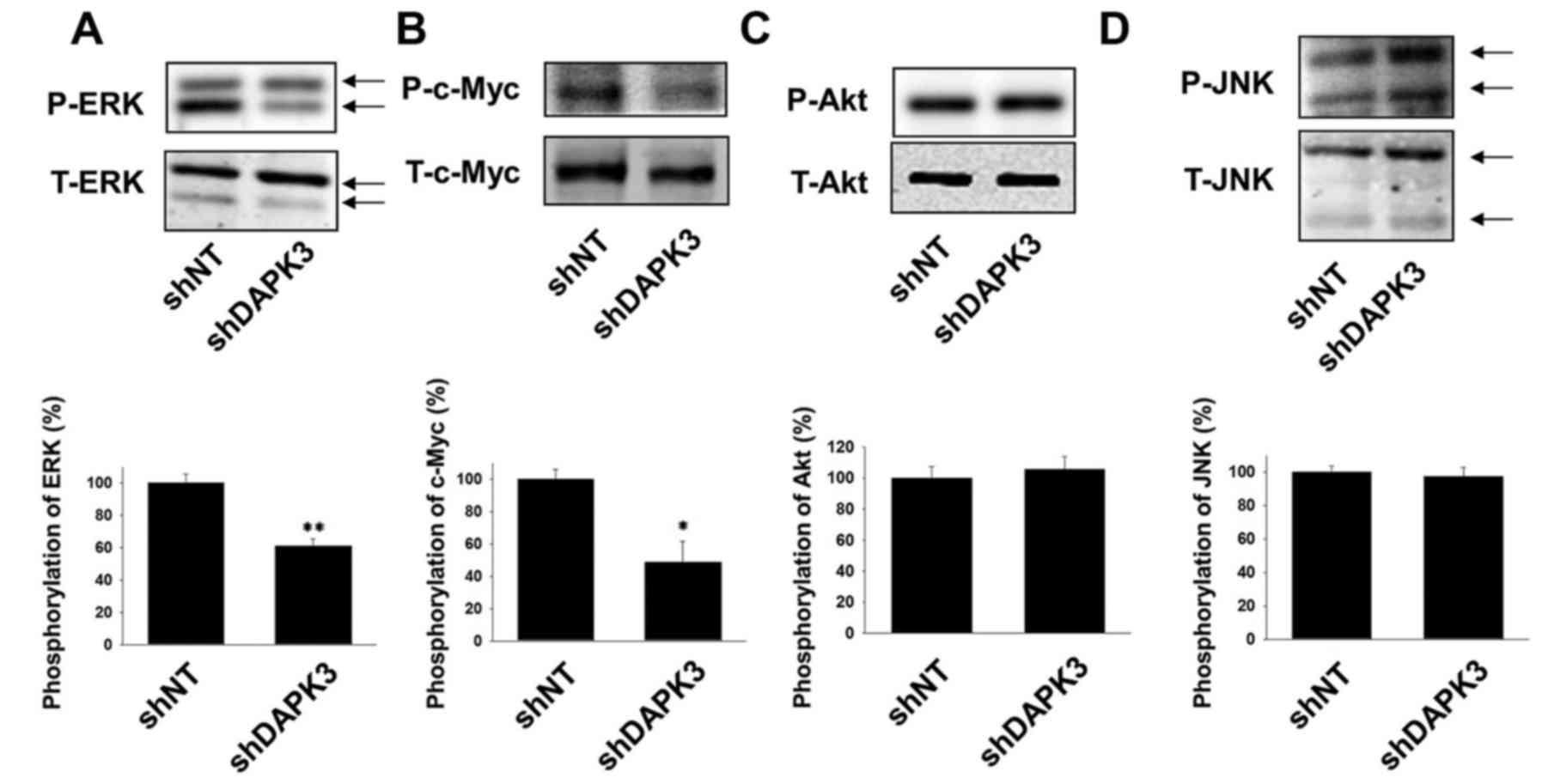
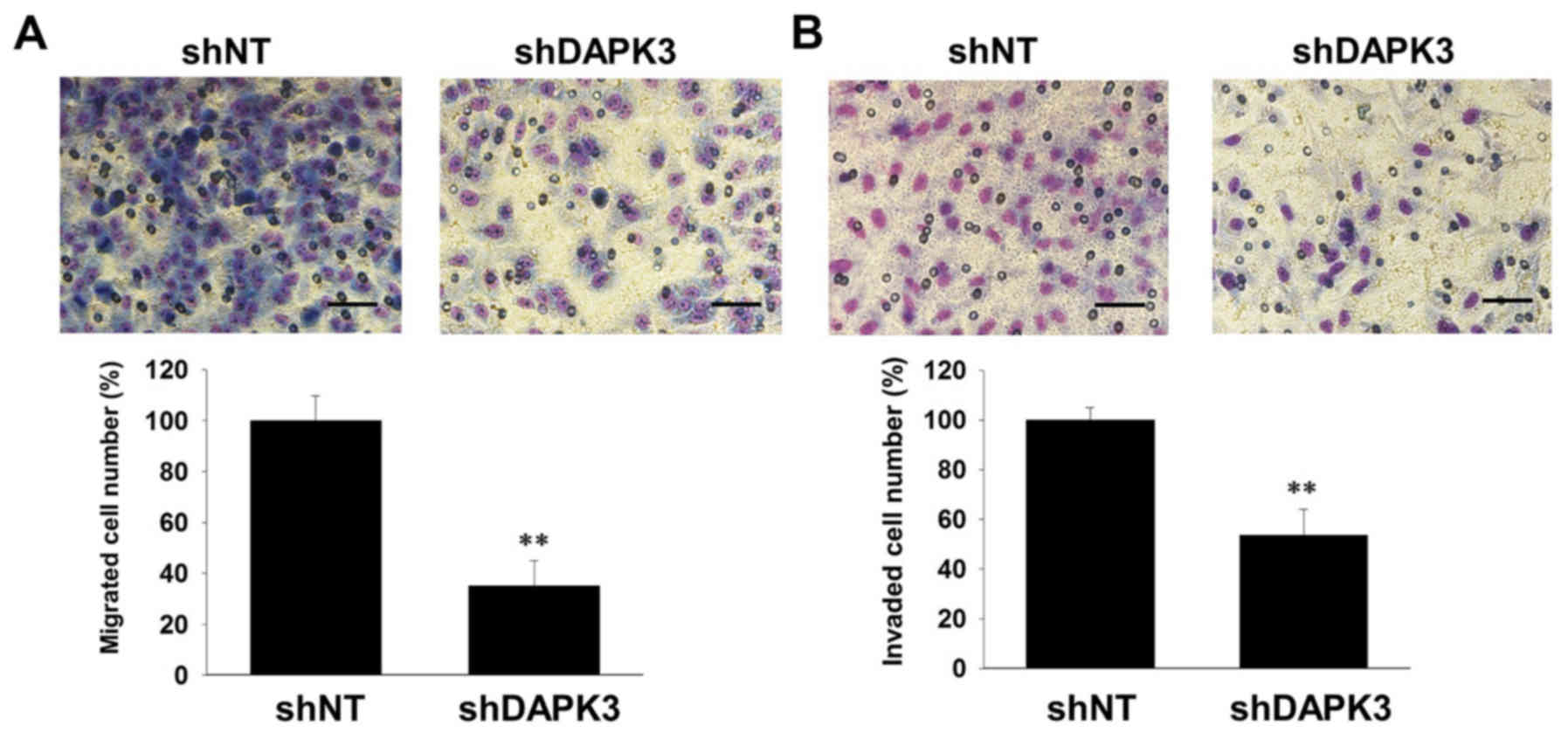
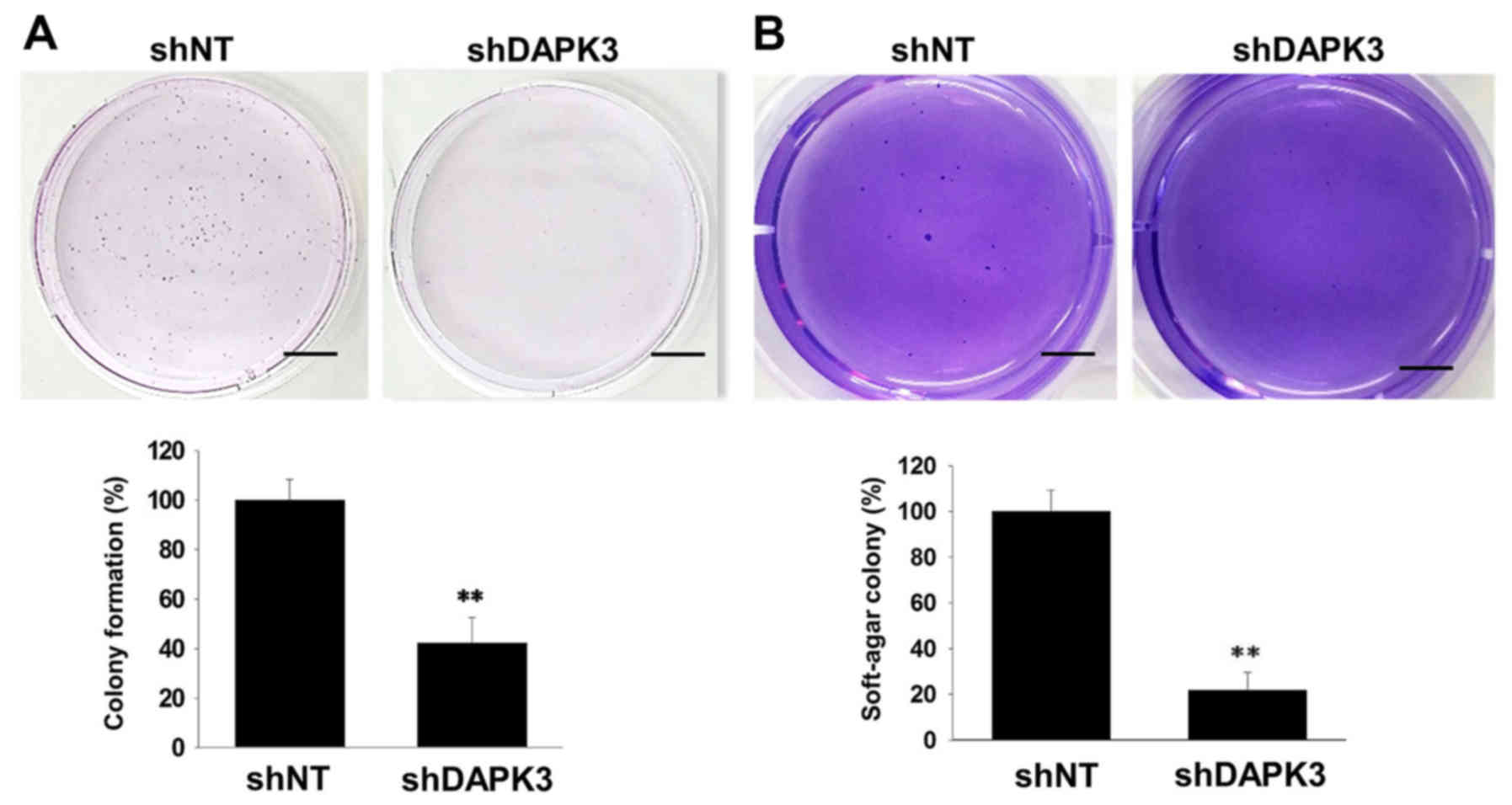
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bialik S and Kimchi A: The
death-associated protein kinases: Structure, function, and beyond.
Annu Rev Biochem. 75:189–210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shani G, Marash L, Gozuacik D, Bialik S,
Teitelbaum L, Shohat G and Kimchi A: Death-associated protein
kinase phosphorylates ZIP kinase, forming a unique kinase hierarchy
to activate its cell death functions. Mol Cell Biol. 24:8611–8626.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tang HW, Wang YB, Wang SL, Wu MH, Lin SY
and Chen GC: Atg1-mediated myosin II activation regulates
autophagosome formation during starvation-induced autophagy. EMBO
J. 30:636–651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mallipeddi R, Wessagowit V, South AP,
Robson AM, Orchard GE, Eady RA and McGrath JA: Reduced expression
of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in
Squamous cell carcinoma complicating recessive dystrophic
epidermolysis bullosa. J Invest Dermatol. 122:1302–1309. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Deng Z, Wang Z, Wang D, Zhang L, Su
Q, Lai Y, Li B, Luo Z, Chen X, et al: Zipper-interacting protein
kinase promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and
metastasis through AKT and NF-kB signaling and is associated with
metastasis and poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 6:8323–8338. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leister P, Felten A, Chasan AI and
Scheidtmann KH: ZIP kinase plays a crucial role in androgen
receptor-mediated transcription. Oncogene. 27:3292–3300. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Togi S, Ikeda O, Kamitani S, Nakasuji M,
Sekine Y, Muromoto R, Nanbo A, Oritani K, Kawai T, Akira S, et al:
Zipper-interacting protein kinase (ZIPK) modulates canonical
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling through interaction with Nemo-like
kinase and T-cell factor 4 (NLK/TCF4). J Biol Chem.
286:19170–19177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brognard J, Zhang YW, Puto LA and Hunter
T: Cancer-associated loss-of-function mutations implicate DAPK3 as
a tumor-suppressing kinase. Cancer Res. 71:3152–3161. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Enjoji S, Yabe R, Fujiwara N, Tsuji S,
Vitek MP, Mizuno T, Nakagawa T, Usui T, Ohama T and Sato K: The
therapeutic effects of SET/I2PP2A inhibitors on canine melanoma. J
Vet Med Sci. 77:1451–1456. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Usui T, Nijima R, Sakatsume T, Otani K,
Kameshima S, Okada M and Yamawaki H: Eukaryotic elongation factor 2
kinase controls proliferation and migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells. Acta Physiol. 213:472–480. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yabe R, Miura A, Usui T, Mudrak I, Ogris
E, Ohama T and Sato K: Protein phosphatase methyl-esterase PME-1
protects protein phosphatase 2A from ubiquitin/proteasome
degradation. PLoS One. 10:e01452262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Usui T, Sakatsume T, Nijima R, Otani K,
Kazama K, Morita T, Kameshima S, Okada M and Yamawaki H:
Death-associated protein kinase 3 mediates vascular structural
remodelling via stimulating smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration. Clin Sci. 127:539–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hunter T and Pines J: Cyclins and cancer.
II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 79:573–582.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Hodgson L and Condeelis
J: Directed cell invasion and migration during metastasis. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 24:277–283. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scheel C and Weinberg RA: Cancer stem
cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Concepts and molecular
links. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:396–403. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kawai T, Matsumoto M, Takeda K, Sanjo H
and Akira S: ZIP kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase which
mediates apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 18:1642–1651. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guin S, Ru Y, Wynes MW, Mishra R, Lu X,
Owens C, Barn AE, Vasu VT, Hirsch FR, Kern JA, et al: Contributions
of KRAS and RAL in non-small-cell lung cancer growth and
progression. J Thorac Oncol. 8:1492–1501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oneyama C, Ikeda J, Okuzaki D, Suzuki K,
Kanou T, Shintani Y, Morii E, Okumura M, Aozasa K and Okada M:
MicroRNA-mediated downregulation of mTOR/FGFR3 controls tumor
growth induced by Src-related oncogenic pathways. Oncogene.
30:3489–3501. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
An S, Yang Y, Ward R, Liu Y, Guo XX and Xu
TR: A-Raf: A new star of the family of raf kinases. Crit Rev
Biochem Mol Biol. 50:520–531. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Endo A, Surks HK, Mochizuki S, Mochizuki N
and Mendelsohn ME: Identification and characterization of
zipper-interacting protein kinase as the unique vascular smooth
muscle myosin phosphatase-associated kinase. J Biol Chem.
279:42055–42061. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsai YT, Chuang MJ, Tang SH, Wu ST, Chen
YC, Sun GH, Hsiao PW, Huang SM, Lee HJ, Yu CP, et al: Novel cancer
therapeutics with allosteric modulation of the mitochondrial
C-Raf-DAPK complex by Raf inhibitor combination therapy. Cancer
Res. 75:3568–3582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ku MJ, Kim JH, Lee J, Cho JY, Chun T and
Lee SY: Maclurin suppresses migration and invasion of human
non-small-cell lung cancer cells via anti-oxidative activity and
inhibition of the Src/FAK-ERK-β-catenin pathway. Mol Cell Biochem.
402:243–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Usui T, Okada M, Hara Y and Yamawaki H:
Death-associated protein kinase 3 mediates vascular inflammation
and development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Hypertension. 60:1031–1039. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marcus AI and Zhou W: LKB1 regulated
pathways in lung cancer invasion and metastasis. J Thorac Oncol.
5:1883–1886. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|