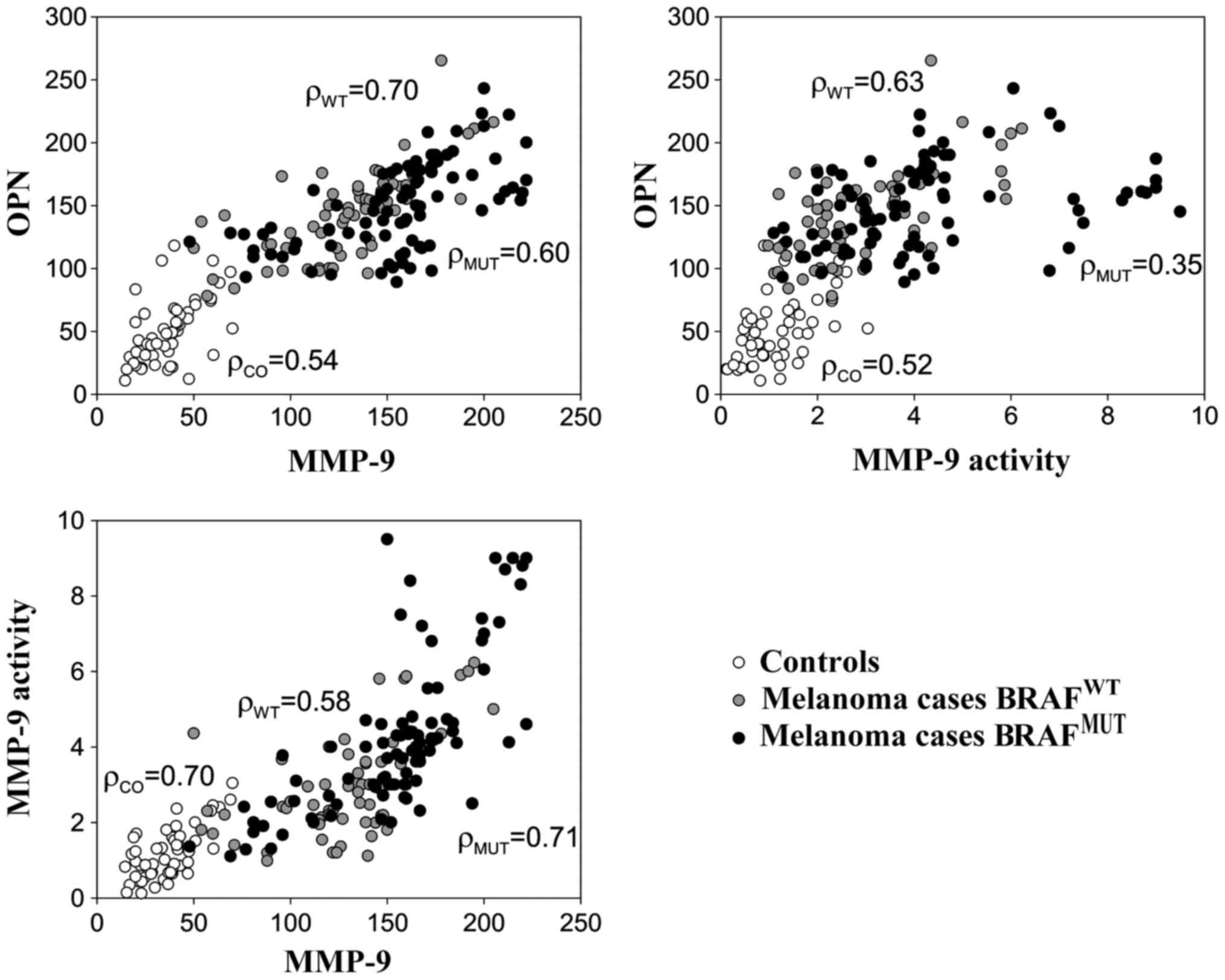
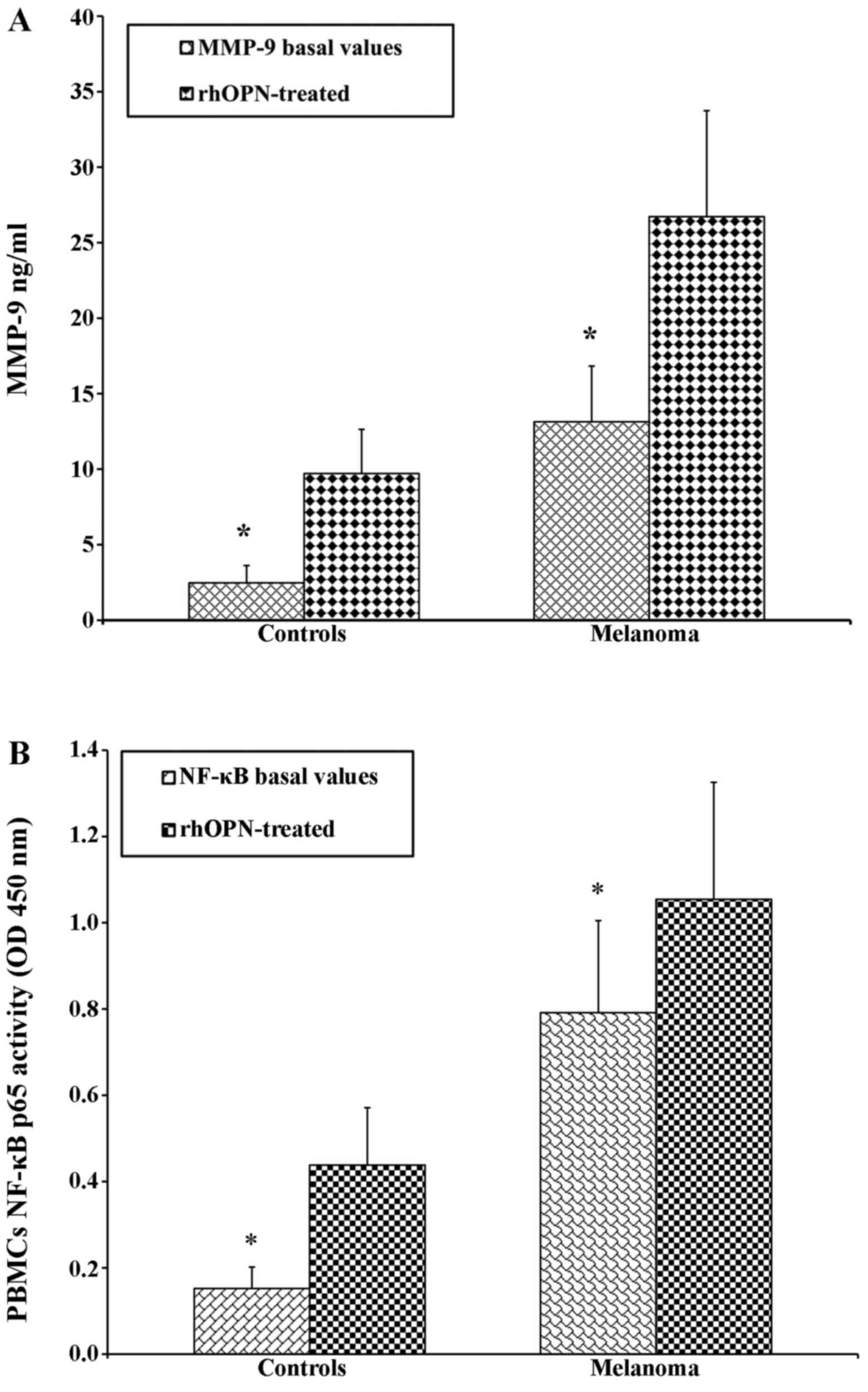
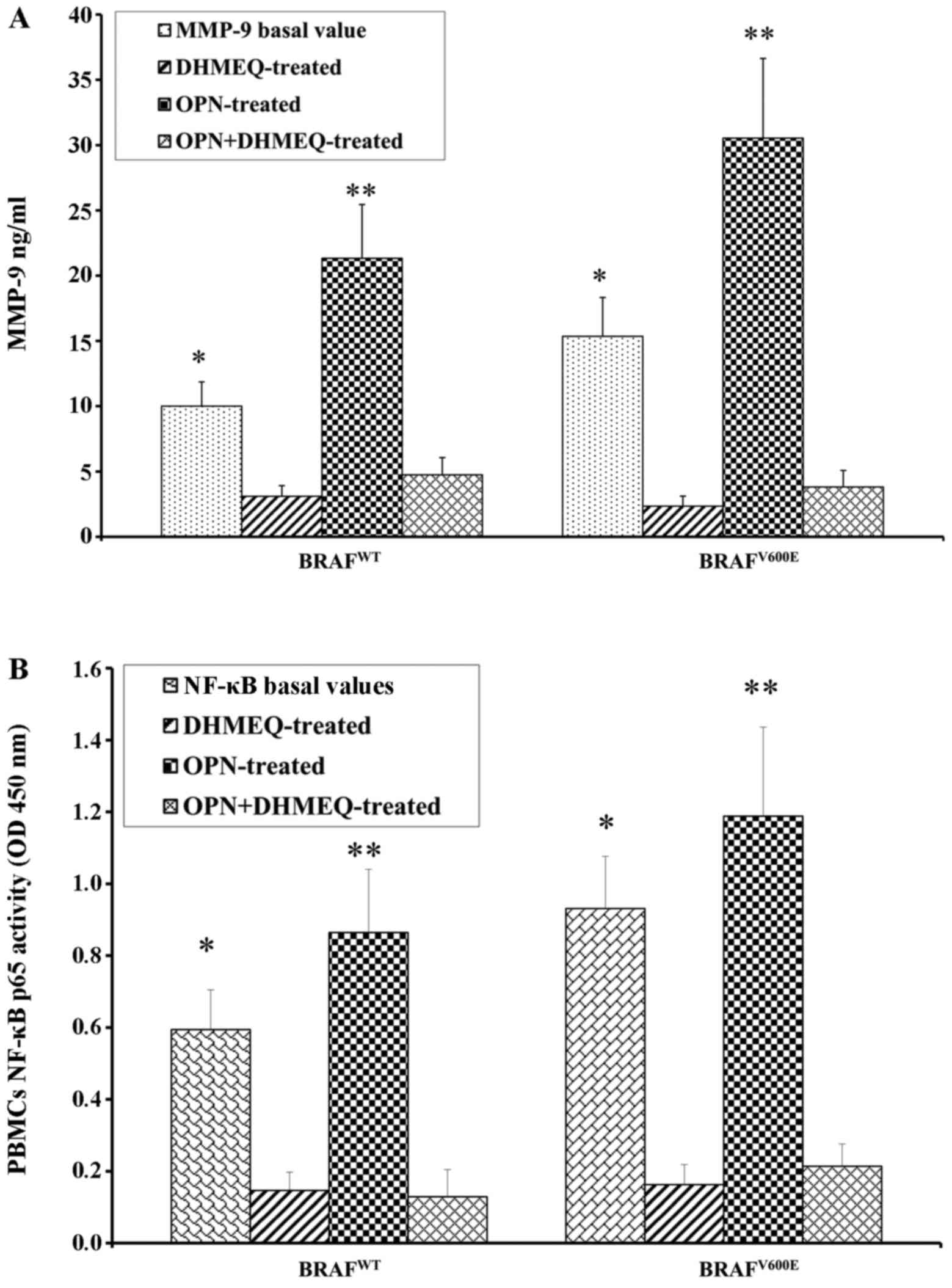
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fava P, Astrua C, Chiarugi A, Crocetti E,
Pimpinelli N, Fargnoli MC, Maurichi A, Rubegni P, Manganoni AM,
Bottoni U, et al: Differences in clinicopathological features and
distribution of risk factors in Italian melanoma patients.
Dermatology. 230:256–262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russo A, Ficili B, Candido S, Pezzino FM,
Guarneri C, Biondi A, Travali S, McCubrey JA, Spandidos DA and
Libra M: Emerging targeted therapies for melanoma treatment
(Review). Int J Oncol. 45:516–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eggermont AM and Schadendorf D: Melanoma
and immunotherapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 23:547–564, ix-x.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Caporali S, Alvino E, Lacal PM, Levati L,
Giurato G, Memoli D, Caprini E, Cappellini GC Antonini and D'Atri
S: Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway overcomes the stimulating
effect of dabrafenib on the invasive behavior of melanoma cells
with acquired resistance to the BRAF inhibitor. Int J Oncol.
49:1164–1174. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Montalto G, Cervello M, Nicoletti F, Fagone P, Malaponte
G, Mazzarino MC, et al: Mutations and deregulation of
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR cascades which alter therapy
response. Oncotarget. 3:954–987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grazia G, Penna I, Perotti V, Anichini A
and Tassi E: Towards combinatorial targeted therapy in melanoma:
From pre-clinical evidence to clinical application (Review). Int J
Oncol. 45:929–949. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Solus JF and Kraft S: Ras, Raf, and MAP
kinase in melanoma. Adv Anat Pathol. 20:217–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Libra M, Malaponte G, Navolanic PM,
Gangemi P, Bevelacqua V, Proietti L, Bruni B, Stivala F, Mazzarino
MC, Travali S, et al: Analysis of BRAF mutation in primary and
metastatic melanoma. Cell Cycle. 4:1382–1384. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Candido S, Rapisarda V, Marconi A,
Malaponte G, Bevelacqua V, Gangemi P, Scalisi A, McCubrey JA,
Maestro R, Spandidos DA, et al: Analysis of the
B-RafV600E mutation in cutaneous melanoma patients with
occupational sun exposure. Oncol Rep. 31:1079–1082. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin K, Baritaki S, Militello L, Malaponte
G, Bevelacqua Y and Bonavida B: The Role of B-RAF Mutations in
Melanoma and the Induction of EMT via Dysregulation of the
NF-κB/Snail/RKIP/PTEN Circuit. Genes Cancer. 1:409–420. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cantwell-Dorris ER, O'Leary JJ and Sheils
OM: BRAFV600E: Implications for carcinogenesis and molecular
therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:385–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mbeunkui F and Johann DJ Jr: Cancer and
the tumor microenvironment: A review of an essential relationship.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:571–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J and Liu J: Tumor stroma as targets
for cancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 137:200–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bevelacqua V, Bevelacqua Y, Candido S,
Skarmoutsou E, Amoroso A, Guarneri C, Strazzanti A, Gangemi P,
Mazzarino MC, D'Amico F, et al: Nectin like-5 overexpression
correlates with the malignant phenotype in cutaneous melanoma.
Oncotarget. 3:882–892. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Whipple CA: Tumor talk: Understanding the
conversation between the tumor and its microenvironment. Cancer
Cell Microenviron. 2:e7732015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Villanueva J and Herlyn M: Melanoma and
the tumor microenvironment. Curr Oncol Rep. 10:439–446. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seftor EA, Brown KM, Chin L, Kirschmann
DA, Wheaton WW, Protopopov A, Feng B, Balagurunathan Y, Trent JM,
Nickoloff BJ, et al: Epigenetic transdifferentiation of normal
melanocytes by a metastatic melanoma microenvironment. Cancer Res.
65:10164–10169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Postovit LM, Seftor EA, Seftor RE and
Hendrix MJ: Influence of the microenvironment on melanoma cell fate
determination and phenotype. Cancer Res. 66:7833–7836. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bauvois B: New facets of matrix
metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers:
Outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1825:29–36. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis.
Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 10:383–392, x. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Falzone L, Salemi R, Travali S, Scalisi A,
McCubrey JA, Candido S and Libra M: MMP-9 overexpression is
associated with intragenic hypermethylation of MMP9 gene in
melanoma. Aging (Albany NY). 8:933–944. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Candido S, Abrams SL, Steelman LS,
Lertpiriyapong K, Fitzgerald TL, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Montalto G,
Cervello M, Polesel J, et al: Roles of NGAL and MMP-9 in the tumor
microenvironment and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:438–448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shellman YG, Makela M and Norris DA:
Induction of secreted matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity in human
melanoma cells by extracellular matrix proteins and cytokines.
Melanoma Res. 16:207–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Rath M and
Niedzwiecki A: In vitro modulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in pediatric
human sarcoma cell lines by cytokines, inducers and inhibitors. Int
J Oncol. 44:27–34. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heo DS, Choi H, Yeom MY, Song BJ and Oh
SJ: Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 predict lymph node
metastasis in breast cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 31:1567–1572.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aalinkeel R, Nair BB, Reynolds JL, Sykes
DE, Mahajan SD, Chadha KC and Schwartz SA: Overexpression of MMP-9
contributes to invasiveness of prostate cancer cell line LNCaP.
Immunol Invest. 40:447–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chou CH, Teng CM, Tzen KY, Chang YC, Chen
JH and Cheng JC: MMP-9 from sublethally irradiated tumor promotes
Lewis lung carcinoma cell invasiveness and pulmonary metastasis.
Oncogene. 31:458–468. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Malaponte G, Polesel J, Candido S, et al:
IL-6-174 G > C and MMP-9-1562 C > T polymorphisms are
associated with increased risk of deep vein thrombosis in cancer
patients. Cytokine. 62:64–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Di Carlo A, Terracciano D, Mariano A and
Macchia V: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 type IV collagenases in serum of patients with
pleural effusions. Int J Oncol. 26:1363–1368. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kato Y, Yamashita T and Ishikawa M:
Relationship between expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
matrix metalloproteinase-9 and invasion ability of cervical cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 9:565–569. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mook OR, Frederiks WM and Van Noorden CJ:
The role of gelatinases in colorectal cancer progression and
metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1705:69–89. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Malaponte G, Zacchia A, Bevelacqua Y,
Marconi A, Perrotta R, Mazzarino MC, Cardile V and Stivala F:
Co-regulated expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and
transforming growth factor-beta in melanoma development and
progression. Oncol Rep. 24:81–87. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nikkola J, Vihinen P, Vuoristo MS,
Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Kähäri VM and Pyrhönen S: High serum levels
of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are
associated with rapid progression in patients with metastatic
melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5158–5166. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen YJ, Wei YY, Chen HT, Fong YC, Hsu CJ,
Tsai CH, Hsu HC, Liu SH and Tang CH: Osteopontin increases
migration and MMP-9 up-regulation via alphavbeta3 integrin, FAK,
ERK, and NF-kappaB-dependent pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells.
J Cell Physiol. 221:98–108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Philip S, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Osteopontin stimulates tumor growth and activation of promatrix
metalloproteinase-2 through nuclear factor-kappa B-mediated
induction of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in murine
melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 276:44926–44935. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Castellano G, Malaponte G, Mazzarino MC,
Figini M, Marchese F, Gangemi P, Travali S, Stivala F, Canevari S
and Libra M: Activation of the osteopontin/matrix
metalloproteinase-9 pathway correlates with prostate cancer
progression. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7470–7480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Malaponte G, Hafsi S, Polesel J,
Castellano G, Spessotto P, Guarneri C, Canevari S, Signorelli SS,
McCubrey JA and Libra M: Tumor microenvironment in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma: Matrixmetalloproteinases activation is mediated by
osteopontin overexpression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:483–489.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wai PY and Kuo PC: Osteopontin: Regulation
in tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:103–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Weber GF: The metastasis gene osteopontin:
A candidate target for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1552:61–85. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
El-Tanani MK, Campbell FC, Kurisetty V,
Jin D, McCann M and Rudland PS: The regulation and role of
osteopontin in malignant transformation and cancer. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 17:463–474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Libra M, Indelicato M, De Re V, Zignego
AL, Chiocchetti A, Malaponte G, Dianzani U, Nicoletti F, Stivala F,
McCubrey JA, et al: Elevated Serum Levels of Osteopontin in
HCV-Associated Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Cancer Biol Ther.
4:1192–1194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Poruk KE, Firpo MA, Scaife CL, Adler DG,
Emerson LL, Boucher KM and Mulvihill SJ: Serum osteopontin and
tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1 as diagnostic and
prognostic biomarkers for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas.
42:193–197. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang YD, Chen H, Liu HQ and Hao M:
Correlation between ovarian neoplasm and serum levels of
osteopontin: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:11799–11808. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cao DX, Li ZJ, Jiang XO, Lum YL, Khin E,
Lee NP, Wu GH and Luk JM: Osteopontin as potential biomarker and
therapeutic target in gastric and liver cancers. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:3923–3930. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lin F, Li Y, Cao J, Fan S, Wen J, Zhu G,
Du H and Liang Y: Overexpression of osteopontin in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its relationships with metastasis, invasion of tumor
cells. Mol Biol Rep. 38:5205–5210. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rangel J, Nosrati M, Torabian S, Shaikh L,
Leong SP, Haqq C, Miller JR III, Sagebiel RW and Kashani-Sabet M:
Osteopontin as a molecular prognostic marker for melanoma. Cancer.
112:144–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sturm RA: Osteopontin in melanocytic
lesions - a first step towards invasion? J Invest Dermatol.
124:xiv–xv. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kiss T, Ecsedi S, Vizkeleti L, Koroknai V,
Emri G, Kovács N, Adany R and Balazs M: The role of osteopontin
expression in melanoma progression. Tumour Biol. 36:7841–7847.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhou Y, Dai DL, Martinka M, Su M, Zhang Y,
Campos EI, Dorocicz I, Tang L, Huntsman D, Nelson C, et al:
Osteopontin expression correlates with melanoma invasion. J Invest
Dermatol. 124:1044–1052. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Matušan-Ilijaš K, Damante G, Fabbro D,
Dorđević G, Hadžisejdić I, Grahovac M, Marić I, Spanjol J, Grahovac
B, Jonjić N, et al: Osteopontin expression correlates with nuclear
factor-κB activation and apoptosis downregulation in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 207:104–110. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Das R, Mahabeleshwar GH and Kundu GC:
Osteopontin stimulates cell motility and nuclear factor
kappaB-mediated secretion of urokinase type plasminogen activator
through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 278:28593–28606. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rangaswami H and Kundu GC: Osteopontin
stimulates melanoma growth and lung metastasis through
NIK/MEKK1-dependent MMP-9 activation pathways. Oncol Rep.
18:909–915. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Nuclear factor-inducing kinase plays a crucial role in
osteopontin-induced MAPK/IkappaBalpha kinase-dependent nuclear
factor kappaB-mediated promatrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. J
Biol Chem. 279:38921–38935. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu J, Liu Q, Wan Y, Zhao Z, Yu H, Luo H
and Tang Z: Osteopontin promotes the progression of gastric cancer
through the NF-κB pathway regulated by the MAPK and PI3K. Int J
Oncol. 45:282–290. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Polesel J, Franceschi S, Talamini R, Negri
E, Barzan L, Montella M, Libra M, Vaccher E, Franchin G, La Vecchia
C and Serraino D: Tobacco smoking, alcohol drinking, and the risk
of different histological types of nasopharyngeal cancer in a
low-risk population. Oral Oncol. 47:541–545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Matsumoto N, Ariga A, To-e S, Nakamura H,
Agata N, Hirano S, Inoue J and Umezawa K: Synthesis of NF-kappaB
activation inhibitors derived from epoxyquinomicin C. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 10:865–869. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez A,
Ramírez B, Valentí V, Moncada R, Silva C, Salvador J and Frühbeck
G: Peripheral mononuclear blood cells contribute to the
obesity-associated inflammatory state independently of glycemic
status: involvement of the novel proinflammatory adipokines
chemerin, chitinase-3-like protein 1, lipocalin-2 and osteopontin.
Genes Nutr. 10:4602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Buommino E, De Filippis A, Gaudiello F,
Balato A, Balato N, Tufano MA and Ayala F: Modification of
osteopontin and MMP-9 levels in patients with psoriasis on
anti-TNF-α therapy. Arch Dermatol Res. 304:481–485. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tímár J, Gyorffy B and Rásó E: Gene
signature of the metastatic potential of cutaneous melanoma: Too
much for too little? Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:371–387. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Brooks SA, Lomax-Browne HJ, Carter TM,
Kinch CE and Hall DM: Molecular interactions in cancer cell
metastasis. Acta Histochem. 112:3–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hu M and Polyak K: Microenvironmental
regulation of cancer development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 18:27–34.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Nuclear factor inducing kinase: A key regulator in osteopontin-
induced MAPK/IkappaB kinase dependent NF-kappaB-mediated promatrix
metalloproteinase-9 activation. Glycoconj J. 23:221–232. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rangaswami H, Bulbule A and Kundu GC:
Osteopontin: Role in cell signaling and cancer progression. Trends
Cell Biol. 16:79–87. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mitra A, Conway C, Walker C, Cook M,
Powell B, Lobo S, Chan M, Kissin M, Layer G, Smallwood J, et al:
Melanoma sentinel node biopsy and prediction models for relapse and
overall survival. Br J Cancer. 103:1229–1236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Vlahopoulos SA, Cen O, Hengen N, Agan J,
Moschovi M, Critselis E, Adamaki M, Bacopoulou F, Copland JA,
Boldogh I, et al: Dynamic aberrant NF-κB spurs tumorigenesis: A new
model encompassing the microenvironment. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 26:389–403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xia Y, Shen S and Verma IM: NF-κB, an
active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:823–830.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
McCubrey JA, Milella M, Tafuri A, Martelli
AM, Lunghi P, Bonati A, Cervello M, Lee JT and Steelman LS:
Targeting the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway with small-molecule inhibitors.
Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 9:614–630. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Gupta SC, Sundaram C, Reuter S and
Aggarwal BB: Inhibiting NF-κB activation by small molecules as a
therapeutic strategy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1799:775–787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Malaponte G, Signorelli SS, Bevelacqua V,
Polesel J, Taborelli M, Guarneri C, Fenga C, Umezawa K and Libra M:
Increased Levels of NF-κB-Dependent Markers in Cancer-Associated
Deep Venous Thrombosis. PLoS One. 10:e01324962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|