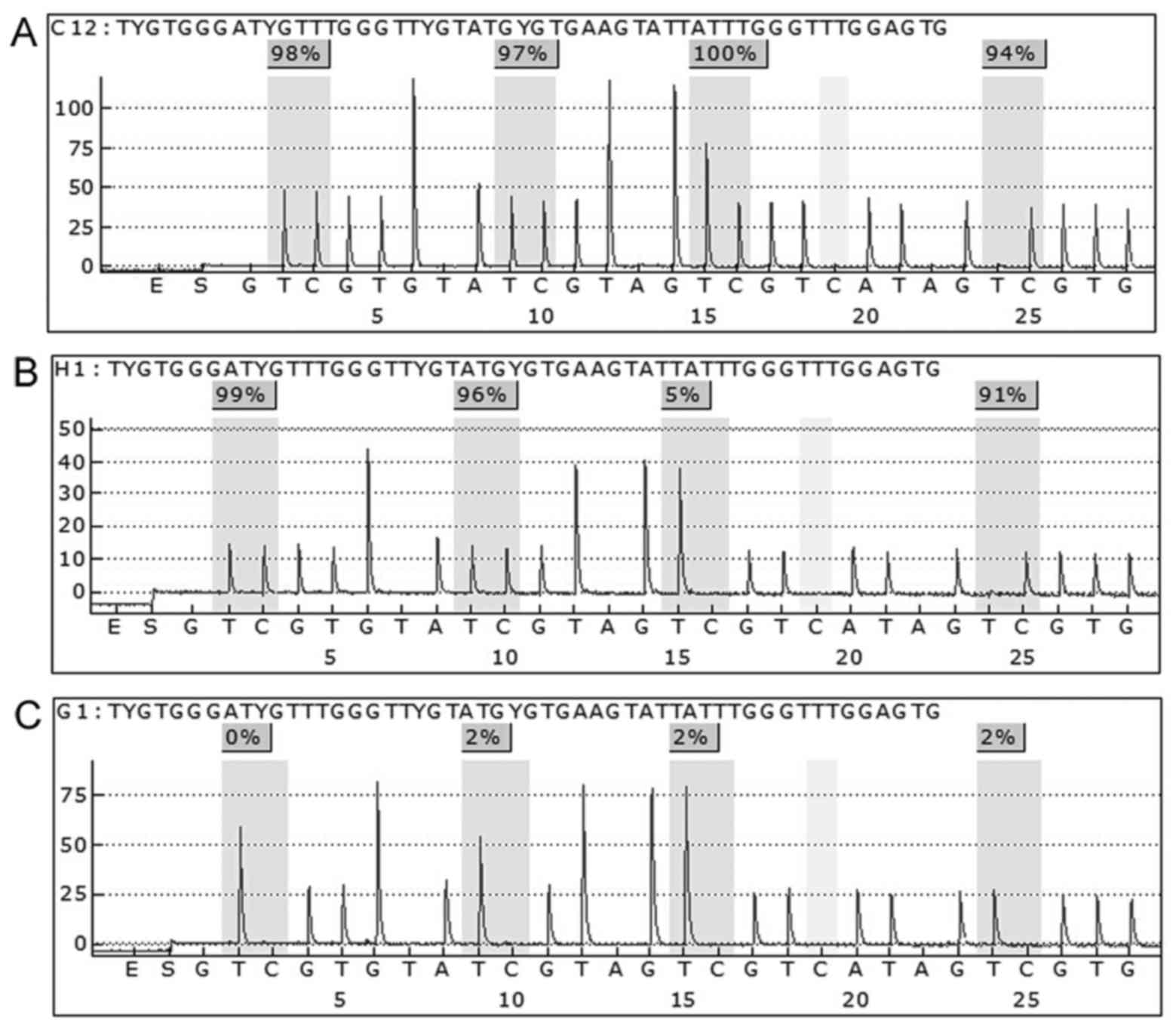
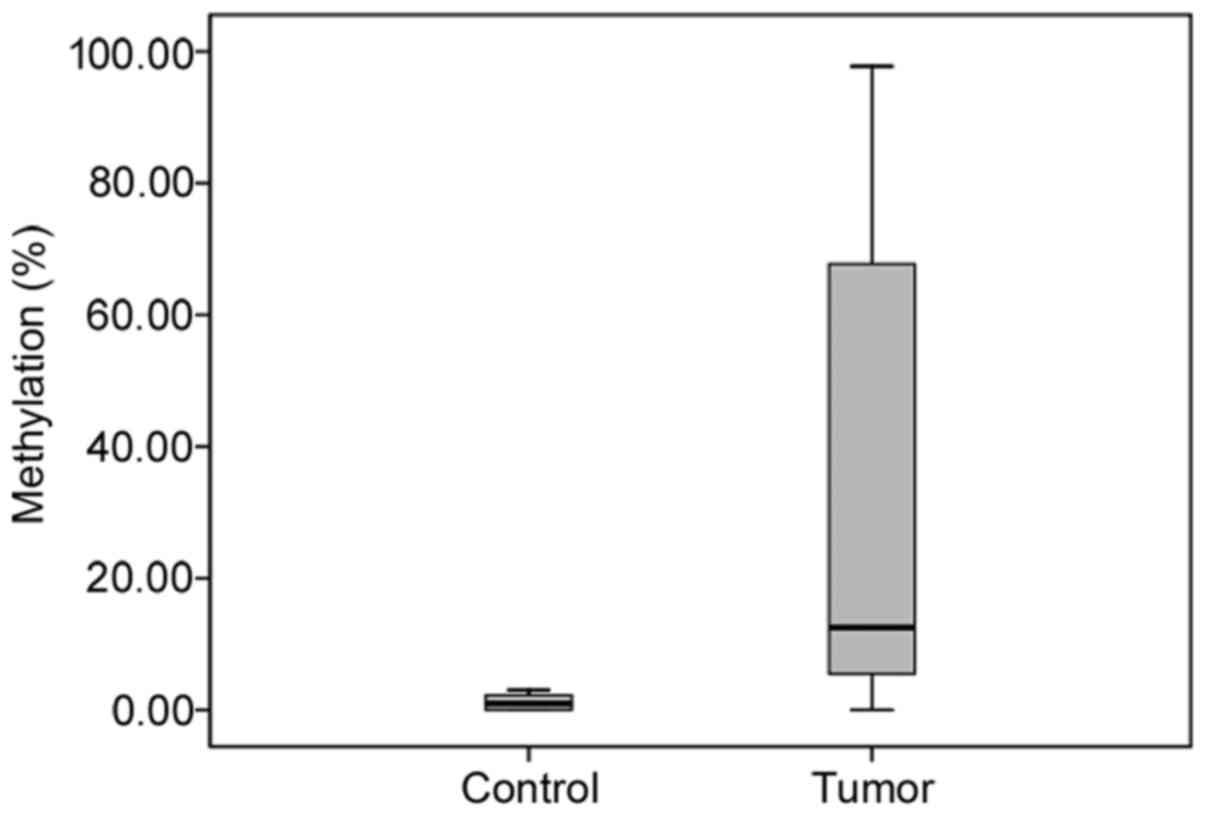
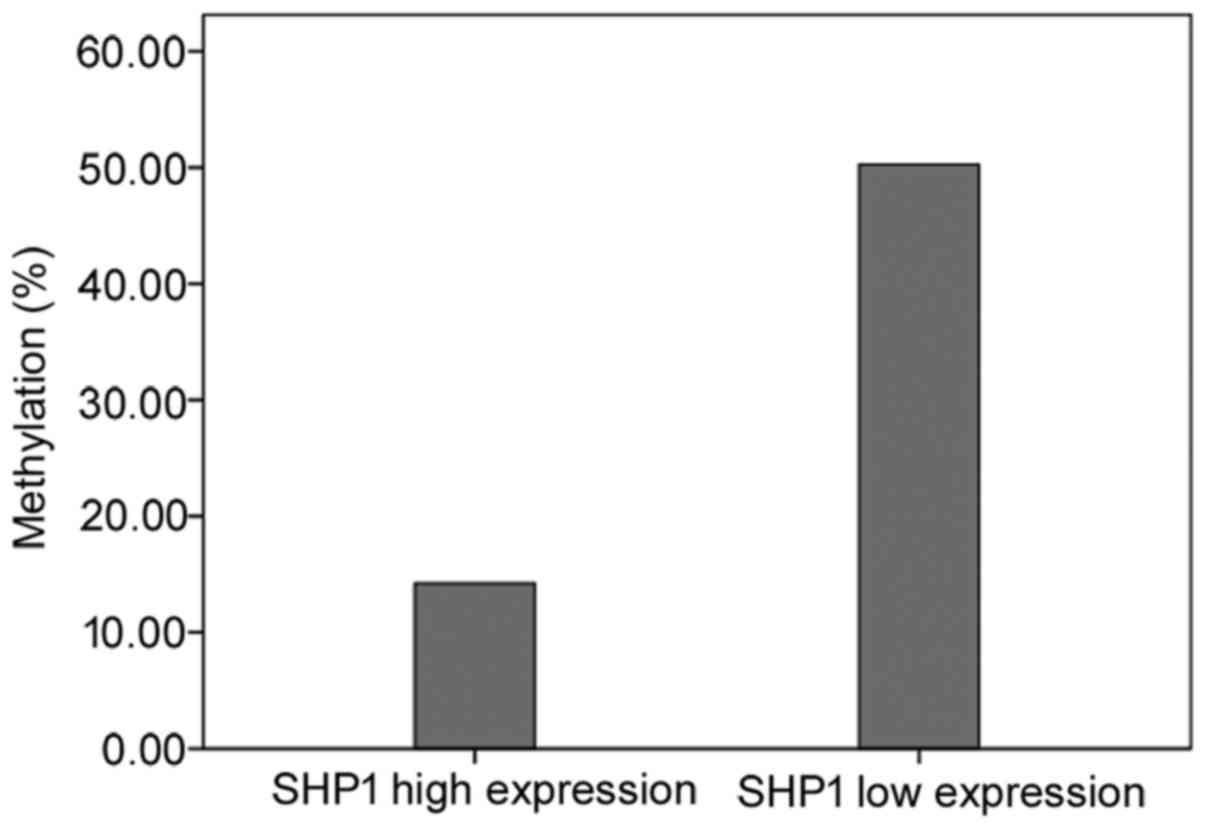
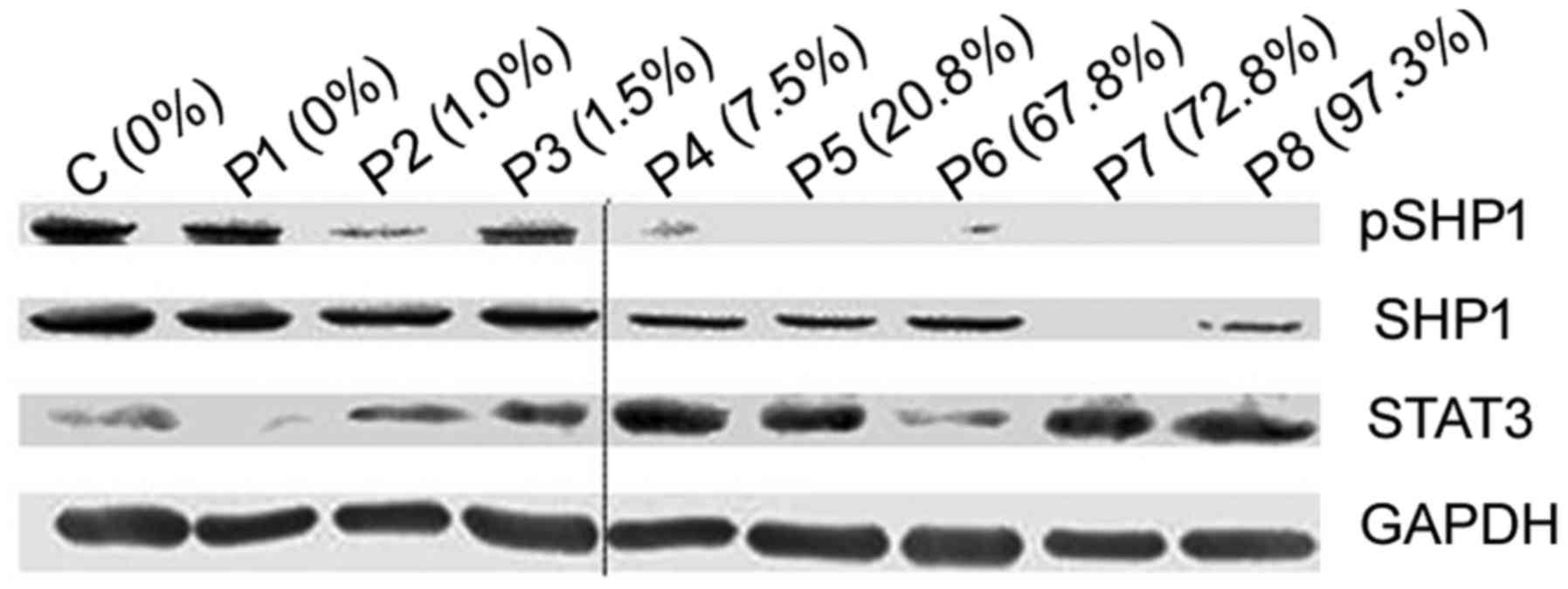
|
1
|
Batchelor T and Loeffler JS: Primary CNS
lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 24:1281–1288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang CC, Carnevale J and Rubenstein JL:
Progress in central nervous system lymphomas. Br J Haematol.
166:311–325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S,
Stein H and Jaffe ES: The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid
neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications.
Blood. 117:5019–5032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rubenstein JL, Fridlyand J, Shen A, Aldape
K, Ginzinger D, Batchelor T, Treseler P, Berger M, McDermott M,
Prados M, et al: Gene expression and angiotropism in primary CNS
lymphoma. Blood. 107:3716–3723. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ponzoni M, Issa S, Batchelor TT and
Rubenstein JL: Beyond high-dose methotrexate and brain
radiotherapy: Novel targets and agents for primary CNS lymphoma.
Ann Oncol. 25:316–322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jordanova ES, Riemersma SA, Philippo K,
Giphart-Gassler M, Schuuring E and Kluin PM: Hemizygous deletions
in the HLA region account for loss of heterozygosity in the
majority of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the testis and the
central nervous system. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 35:38–48. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tun HW, Personett D, Baskerville KA, Menke
DM, Jaeckle KA, Kreinest P, Edenfield B, Zubair AC, O'Neill BP, Lai
WR, et al: Pathway analysis of primary central nervous system
lymphoma. Blood. 111:3200–3210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Booman M, Szuhai K, Rosenwald A, Hartmann
E, Kluin-Nelemans H, de Jong D, Schuuring E and Kluin P: Genomic
alterations and gene expression in primary diffuse large B-cell
lymphomas of immune-privileged sites: The importance of apoptosis
and immunomodulatory pathways. J Pathol. 216:209–217. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sung CO, Kim SC, Karnan S, Karube K, Shin
HJ, Nam DH, Suh YL, Kim SH, Kim JY, Kim SJ, et al: Genomic
profiling combined with gene expression profiling in primary
central nervous system lymphoma. Blood. 117:1291–1300. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deckert M, Montesinos-Rongen M, Brunn A
and Siebert R: Systems biology of primary CNS lymphoma: From
genetic aberrations to modeling in mice. Acta Neuropathol.
127:175–188. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Komohara Y, Horlad H, Ohnishi K, Ohta K,
Makino K, Hondo H, Yamanaka R, Kajiwara K, Saito T, Kuratsu J, et
al: M2 macrophage/microglial cells induce activation of Stat3 in
primary central nervous system lymphoma. J Clin Exp Hematop.
51:93–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang SH, Lee KS, Kim IS, Hong JT, Sung JH,
Son BC, Lee SW and Hong YK: Long-term survival in primary CNS
lymphoma treated by high-dose methotrexate monochemotherapy: Role
of STAT6 activation as prognostic determinant. J Neurooncol.
92:65–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rubenstein JL, Wong VS, Kadoch C, Gao HX,
Barajas R, Chen L, Josephson SA, Scott B, Douglas V, Maiti M, et
al: CXCL13 plus interleukin 10 is highly specific for the diagnosis
of CNS lymphoma. Blood. 121:4740–4748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu BM, Ishida Y, Robinson GW,
Pacher-Zavisin M, Yoshimura A, Murphy PM and Hennighausen L: SOCS3
negatively regulates the gp130-STAT3 pathway in mouse skin wound
healing. J Invest Dermatol. 128:1821–1829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakata K, Suzuki Y, Inoue T, Ra C, Yakura
H and Mizuno K: Deficiency of SHP1 leads to sustained and increased
ERK activation in mast cells, thereby inhibiting IL-3-dependent
proliferation and cell death. Mol Immunol. 48:472–480. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yi TL, Cleveland JL and Ihle JN: Protein
tyrosine phosphatase containing SH2 domains: Characterization,
preferential expression in hematopoietic cells, and localization to
human chromosome 12p12-p13. Mol Cell Biol. 12:836–846. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dixon JE: Protein tyrosine phosphatases:
their roles in signal transduction. Recent Prog Horm Res.
51:405–415. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Healy JI and Goodnow CC: Positive versus
negative signaling by lymphocyte antigen receptors. Annu Rev
Immunol. 16:645–670. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu C, Sun M, Liu L and Zhou GW: The
function of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 in cancer. Gene.
306:1–12. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chim CS, Wong AS and Kwong YL: Epigenetic
dysregulation of the Jak/STAT pathway by frequent aberrant
methylation of SHP1 but not SOCS1 in acute leukaemias. Ann Hematol.
83:527–532. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen HE, Chang S, Trub T and Neel BG:
Regulation of colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor signaling by the
SH2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase SHPTP1. Mol Cell Biol.
16:3685–3697. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Law CL, Sidorenko SP, Chandran KA, Zhao Z,
Shen SH, Fischer EH and Clark EA: CD22 associates with protein
tyrosine phosphatase 1C, Syk, and phospholipase C-gamma(1) upon B
cell activation. J Exp Med. 183:547–560. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yi T, Zhang J, Miura O and Ihle JN:
Hematopoietic cell phosphatase associates with erythropoietin (Epo)
receptor after Epo-induced receptor tyrosine phosphorylation:
Identification of potential binding sites. Blood. 85:87–95.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sugita Y, Tokunaga O, Nakashima A and
Shigemori M: SHP-1 expression in primary central nervous system
B-cell lymphomas in immunocompetent patients reflects maturation
stage of normal B cell counterparts. Pathol Int. 54:659–666. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oka T, Ouchida M, Koyama M, Ogama Y,
Takada S, Nakatani Y, Tanaka T, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Ohara N, et
al: Gene silencing of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 gene by
aberrant methylation in leukemias/lymphomas. Cancer Res.
62:6390–6394. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, Banks PM,
Chan JK, Cleary ML, Delsol G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Falini B, Gatter
KC, et al: A revised European-American classification of lymphoid
neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group.
Blood. 84:1361–1392. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patel B, Chacko G, Nair S, Anandan J,
Chacko AG, Rajshekhar V and Turel M: Clinicopathological correlates
of primary central nervous system lymphoma: Experience from a
tertiary care center in South India. Neurol India. 63:77–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mounier N, Briere J, Gisselbrecht C, Emile
JF, Lederlin P, Sebban C, Berger F, Bosly A, Morel P, Tilly H, et
al: Rituximab plus CHOP (R-CHOP) overcomes bcl-2--associated
resistance to chemotherapy in elderly patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood. 101:4279–4284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Feng W, Shen L, Wen S, Rosen DG, Jelinek
J, Hu X, Huan S, Huang M, Liu J, Sahin AA, et al: Correlation
between CpG methylation profiles and hormone receptor status in
breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 9:R572007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hans CP, Weisenburger DD, Greiner TC,
Gascoyne RD, Delabie J, Ott G, Müller-Hermelink HK, Campo E,
Braziel RM, Jaffe ES, et al: Confirmation of the molecular
classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by
immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood. 103:275–282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kossev PM, Raghunath PN, Bagg A, Schuster
S, Tomaszewski JE and Wasik MA: SHP-1 expression by malignant small
B-cell lymphomas reflects the maturation stage of their normal
B-cell counterparts. Am J Surg Pathol. 25:949–955. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koyama M, Oka T, Ouchida M, Nakatani Y,
Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Akagi T and Seino Y: Activated
proliferation of B-cell lymphomas/leukemias with the SHP1 gene
silencing by aberrant CpG methylation. Lab Invest. 83:1849–1858.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han Y, Amin HM, Frantz C, Franko B, Lee J,
Lin Q and Lai R: Restoration of shp1 expression by
5-AZA-2′-deoxycytidine is associated with downregulation of
JAK3/STAT3 signaling in ALK-positive anaplastic large cell
lymphoma. Leukemia. 20:1602–1609. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bittorf T, Seiler J, Zhang Z, Jaster R and
Brock J: SHP1 protein tyrosine phosphatase negatively modulates
erythroid differentiation and suppression of apoptosis in J2E
erythroleukemic cells. Biol Chem. 380:1201–1209. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiao H, Berrada K, Yang W, Tabrizi M,
Platanias LC and Yi T: Direct association with and
dephosphorylation of Jak2 kinase by the SH2-domain-containing
protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Mol Cell Biol. 16:6985–6992.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kozlowski M, Mlinaric-Rascan I, Feng GS,
Shen R, Pawson T and Siminovitch KA: Expression and catalytic
activity of the tyrosine phosphatase PTP1C is severely impaired in
motheaten and viable motheaten mice. J Exp Med. 178:2157–2163.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma XZ, Jin T, Sakac D, Fahim S, Zhang X,
Katsman Y, Bali M and Branch DR: Abnormal splicing of SHP-1 protein
tyrosine phosphatase in human T cells. Implications for
lymphomagenesis. Exp Hematol. 31:131–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brell M, Tortosa A, Verger E, Gil JM,
Viñolas N, Villá S, Acebes JJ, Caral L, Pujol T, Ferrer I, et al:
Prognostic significance of O6-methylguanine-DNA
methyltransferase determined by promoter hypermethylation and
immunohistochemical expression in anaplastic gliomas. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:5167–5174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baeza N, Weller M, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P
and Ohgaki H: PTEN methylation and expression in glioblastomas.
Acta Neuropathol. 106:479–485. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cameron EE, Baylin SB and Herman JG:
p15(INK4B) CpG island methylation in primary acute leukemia is
heterogeneous and suggests density as a critical factor for
transcriptional silencing. Blood. 94:2445–2451. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lenz G, Hutter G, Hiddemann W and Dreyling
M: Promoter methylation and expression of DNA repair genes hMLH1
and MGMT in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann Hematol. 83:628–633. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Amara K, Trimeche M, Ziadi S, Laatiri A,
Hachana M and Korbi S: Prognostic significance of aberrant promoter
hypermethylation of CpG islands in patients with diffuse large
B-cell lymphomas. Ann Oncol. 19:1774–1786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Khoury JD, Rassidakis GZ, Medeiros LJ,
Amin HM and Lai R: Methylation of SHP1 gene and loss of SHP1
protein expression are frequent in systemic anaplastic large cell
lymphoma. Blood. 104:1580–1581. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu J, Sun XF, Qian J, Bai XY, Zhu H, Cui
QU, Li XY, Chen YD, Wang YM and Liu YB: Immunochemotherapy for
primary central nervous system lymphoma with rituximab,
methotrexate, cytarabine and dexamethasone: Retrospective analysis
of 18 cases. Mol Clin Oncol. 3:949–953. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tassidis H, Brokken LJ, Jirström K,
Ehrnström R, Pontén F, Ulmert D, Bjartell A, Härkönen P and Wingren
AG: Immuno-histochemical detection of tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1
predicts outcome after radical prostatectomy for localized prostate
cancer. Int J Cancer. 126:2296–2307. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang L, Wang M, Wang W and Mo J:
Incidence and prognostic value of multiple gene promoter
methylations in gliomas. J Neurooncol. 116:349–356. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|