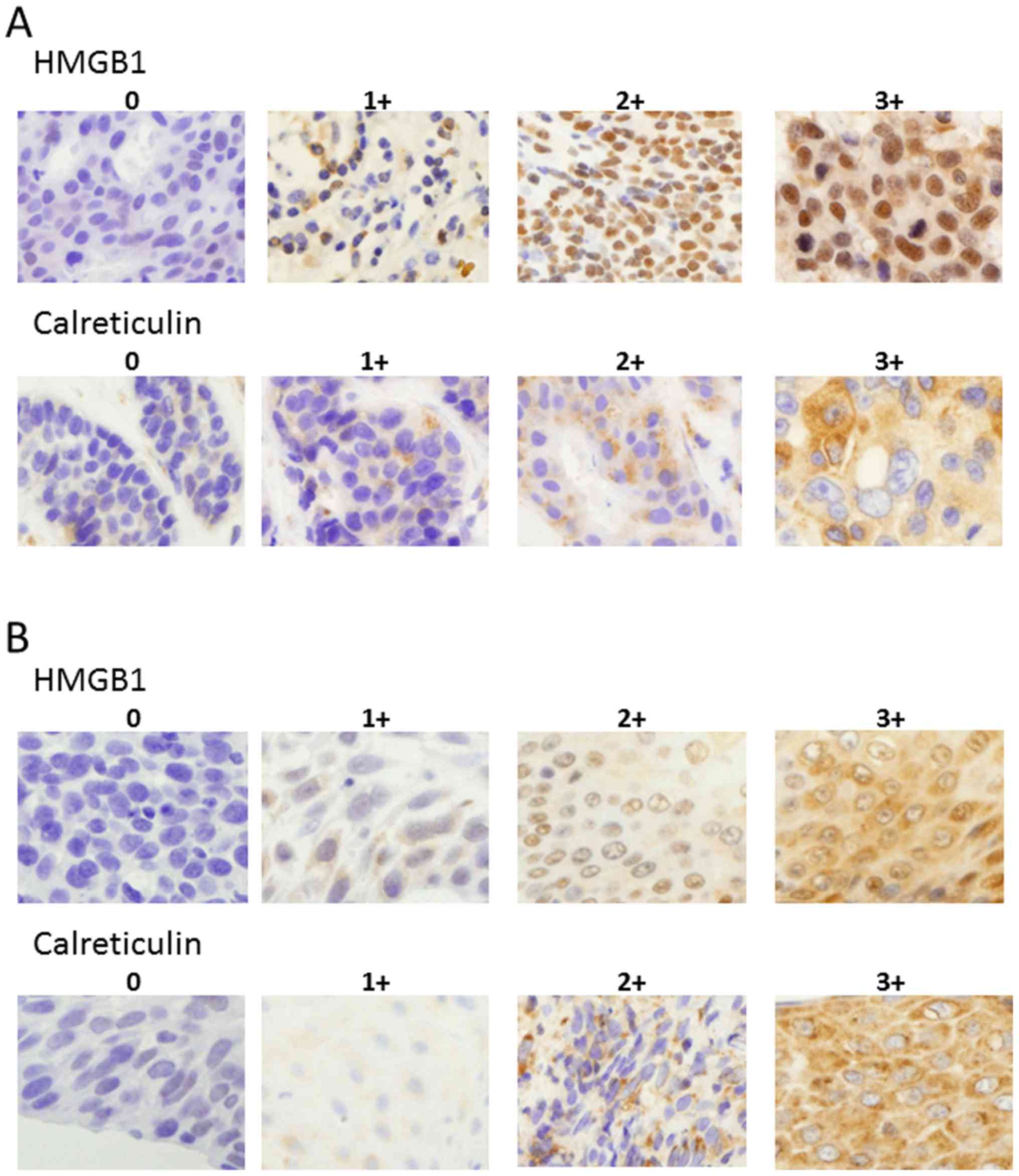
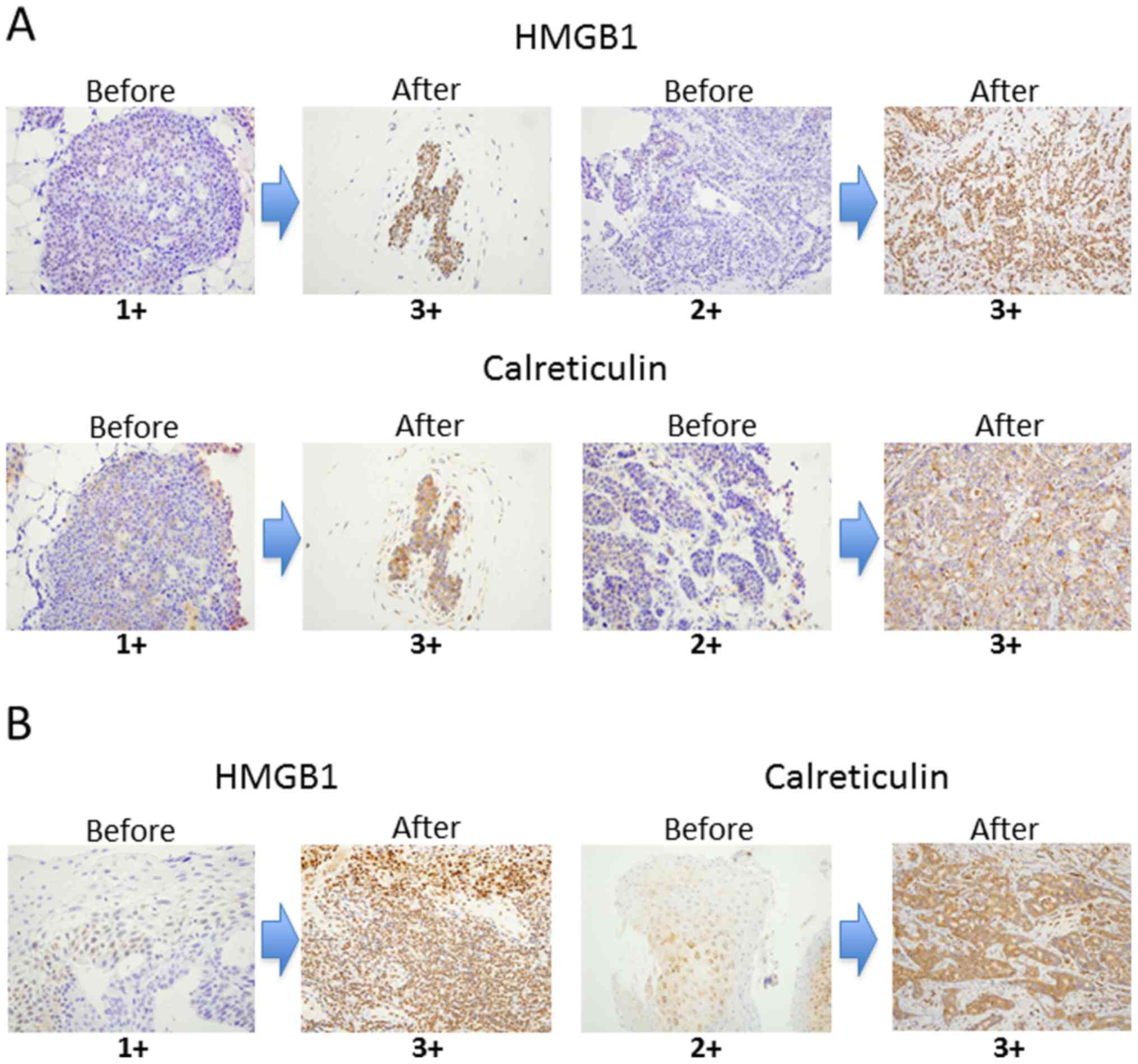
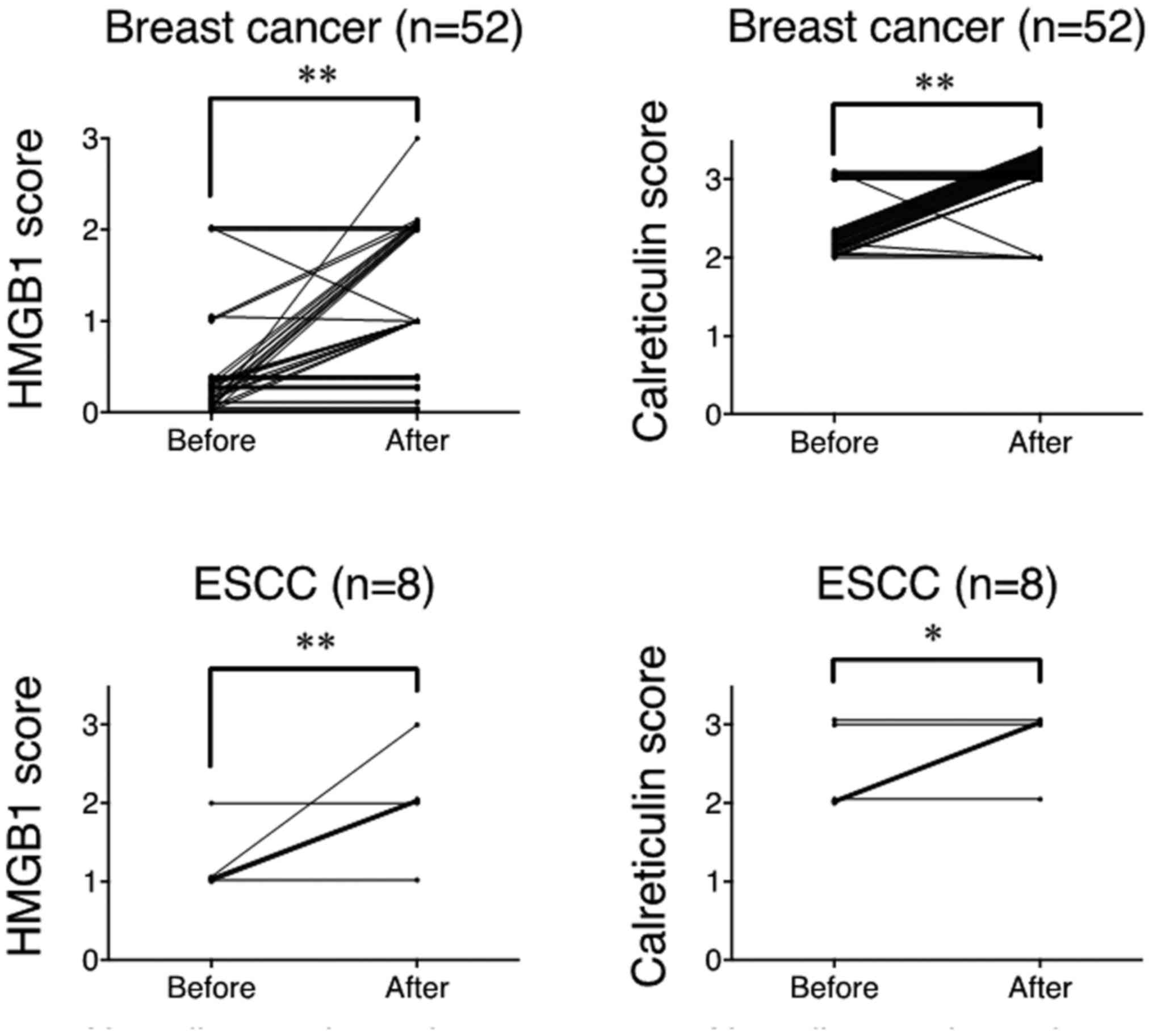
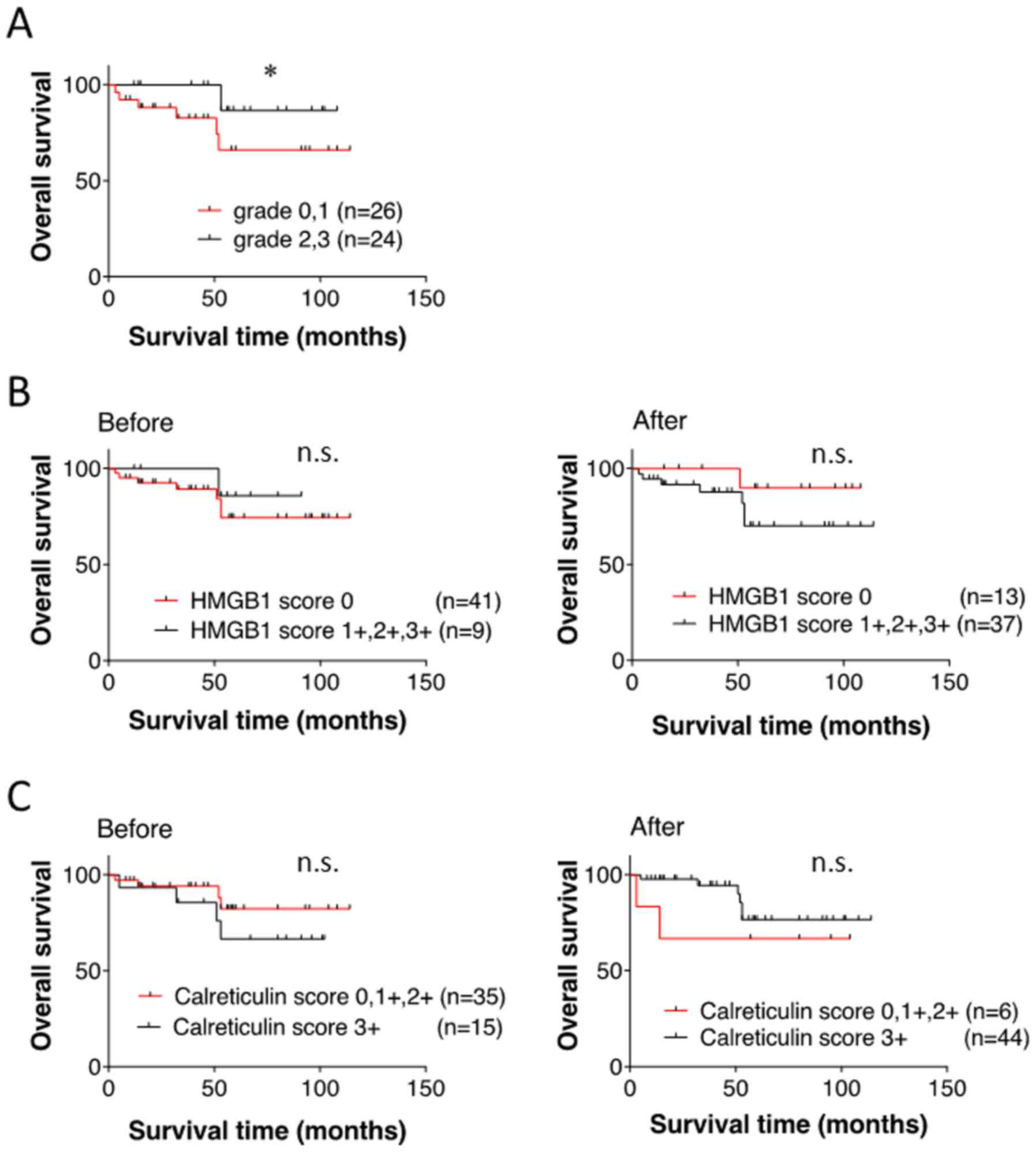
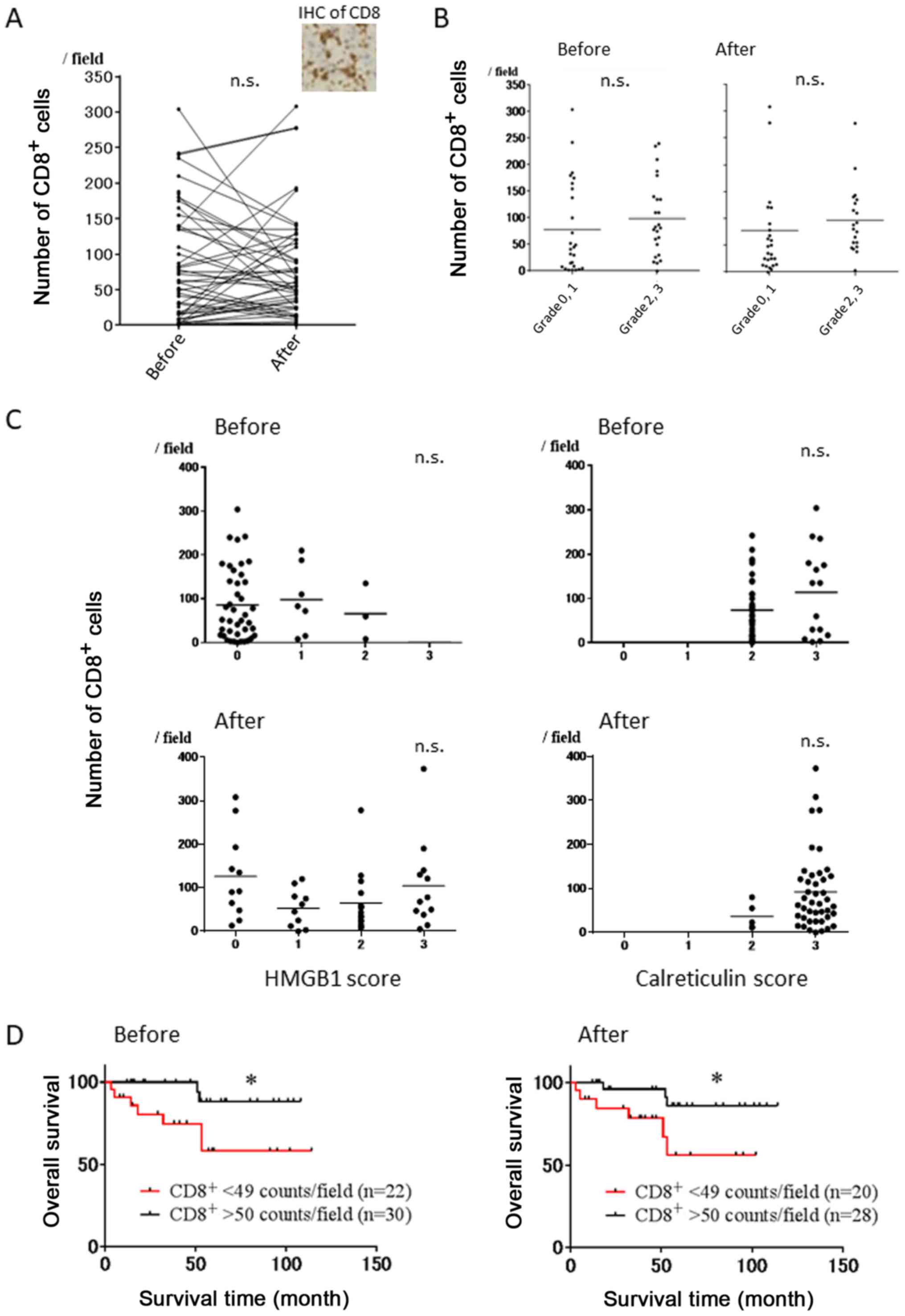
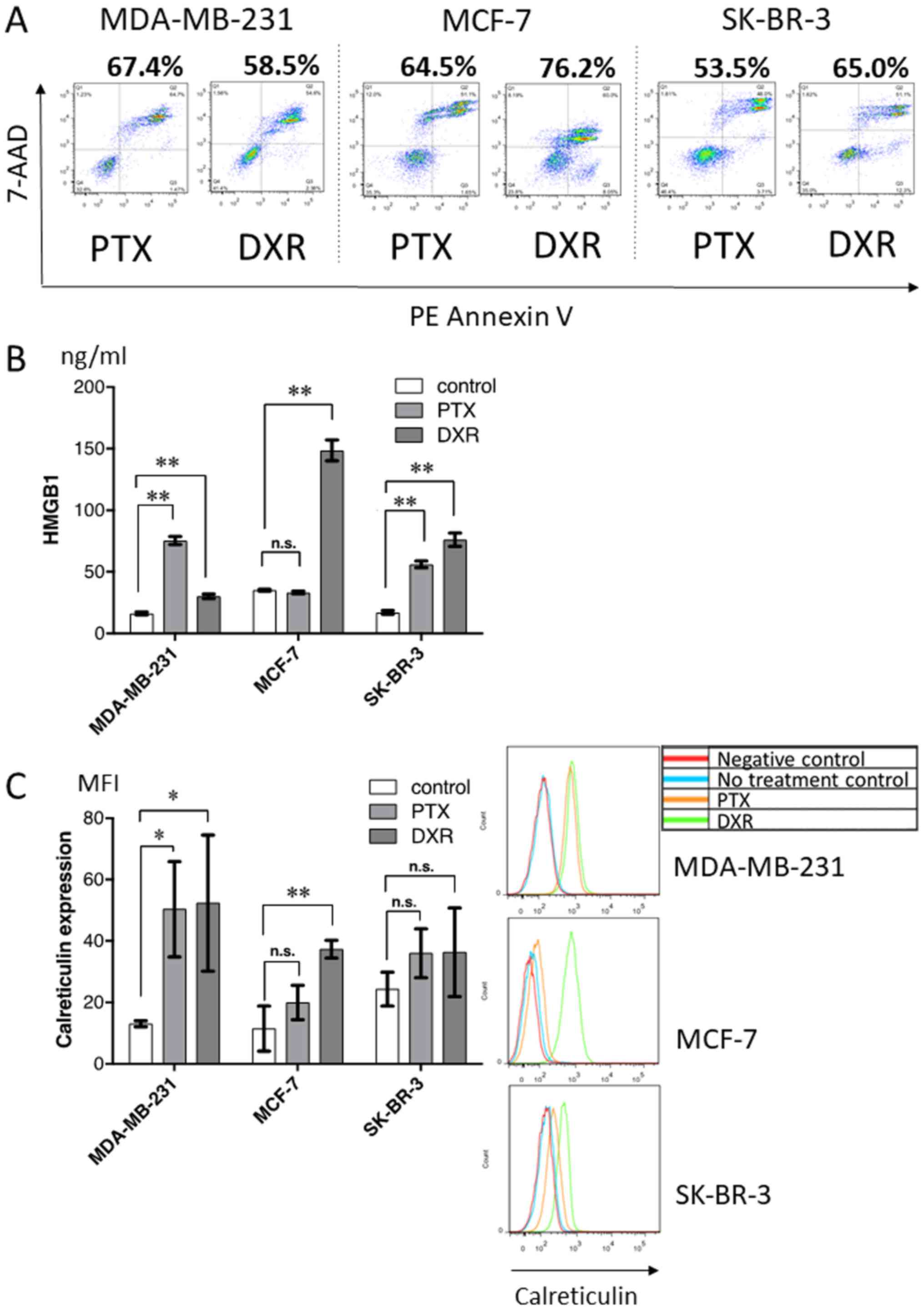
|
1
|
Ishikura S, Nihei K, Ohtsu A, Boku N,
Hironaka S, Mera K, Muto M, Ogino T and Yoshida S: Long-term
toxicity after definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell
carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Clin Oncol. 21:2697–2702.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Manzoni G, Pedrazzani C, Laterza E,
Pasini F, Grandinetti A, Bernini M, Ruzzenente A, Zerman G,
Tomezzoli A and Cordiano C: Induction chemoradiotherapy for
squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: Impact of
increased dosage on long-term results. Ann Thorac Surg.
80:1176–1183. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), . Effects of chemotherapy and
hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year
survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet.
365:1687–1717. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolmark N, Wang J, Mamounas E, Bryant J
and Fisher B: Preoperative chemotherapy in patients with operable
breast cancer: Nine-year results from National Surgical Adjuvant
Breast and Bowel Project B-18. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr.
30:96–102. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, Smith R,
Mamounas EP, Fisher B, Margolese R, Theoret H, Soran A, Wickerham
DL, et al National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project
Protocol B-27, : The effect on tumor response of adding sequential
preoperative docetaxel to preoperative doxorubicin and
cyclophosphamide: Preliminary results from National Surgical
Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol.
21:4165–4174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rastogi P, Anderson SJ, Bear HD, Geyer CE,
Kahlenberg MS, Robidoux A, Margolese RG, Hoehn JL, Vogel VG, Dakhil
SR, et al: Preoperative chemotherapy: Updates of National Surgical
Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Protocols B-18 and B-27. J Clin
Oncol. 26:778–785. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kono K and Mimura K: Immunogenic tumor
cell death induced by chemoradiotherapy in a clinical setting.
OncoImmunology. 2:e221972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kono K, Mimura K and Kiessling R:
Immunogenic tumor cell death induced by chemoradiotherapy:
Molecular mechanisms and a clinical translation. Cell Death Dis.
4:e6882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O and Zitvogel
L: Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol.
31:51–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O,
Agostinis P and Vandenabeele P: Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:860–875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krysko O, Løve Aaes T, Bachert C,
Vandenabeele P and Krysko DV: Many faces of DAMPs in cancer
therapy. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ladoire S, Enot D, Andre F, Zitvogel L and
Kroemer G: Immunogenic cell death-related biomarkers: Impact on the
survival of breast cancer patients after adjuvant chemotherapy.
OncoImmunology. 5:e10827062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stoll G, Enot D, Mlecnik B, Galon J,
Zitvogel L and Kroemer G: Immune-related gene signatures predict
the outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. OncoImmunology.
3:e278842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gebremeskel S and Johnston B: Concepts and
mechanisms underlying chemotherapy induced immunogenic cell death:
Impact on clinical studies and considerations for combined
therapies. Oncotarget. 6:41600–41619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Casares N, Pequignot MO, Tesniere A,
Ghiringhelli F, Roux S, Chaput N, Schmitt E, Hamai A, Hervas-Stubbs
S, Obeid M, et al: Caspase-dependent immunogenicity of
doxorubicin-induced tumor cell death. J Exp Med. 202:1691–1701.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wong DY, Ong WW and Ang WH: Induction of
immunogenic cell death by chemotherapeutic platinum complexes.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 54:6483–6487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Galluzzi L, Buqué A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L
and Kroemer G: Immunological Effects of conventional chemotherapy
and targeted anticancer agents. Cancer Cell. 28:690–714. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hodge JW, Garnett CT, Farsaci B, Palena C,
Tsang KY, Ferrone S and Gameiro SR: Chemotherapy-induced
immunogenic modulation of tumor cells enhances killing by cytotoxic
T lymphocytes and is distinct from immunogenic cell death. Int J
Cancer. 133:624–636. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kepp O, Senovilla L, Vitale I, Vacchelli
E, Adjemian S, Agostinis P, Apetoh L, Aranda F, Barnaba V, Bloy N,
et al: Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell
death. OncoImmunology. 3:e9556912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Okano M, Kumamoto K, Saito M, Onozawa H,
Saito K, Abe N, Ohtake T and Takenoshita S: Upregulated Annexin A1
promotes cellular invasion in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol
Rep. 33:1064–1070. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masafumi K, Sadako A, Futoshi A, Y K, H M
and S N: Histological criteria for assessment of therapeutic
response in breast cancer (2007 version). Breast Cancer. 15:5–7.
2007.
|
|
22
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Criollo A, Ortiz C, Lidereau R, Mariette C, Chaput N, Mira JP,
Delaloge S, et al: The interaction between HMGB1 and TLR4 dictates
the outcome of anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Immunol
Rev. 220:47–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A,
Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E,
Saulnier P, et al: Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of
the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat
Med. 13:1050–1059. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miyamoto S, Inoue H, Nakamura T, Yamada M,
Sakamoto C, Urata Y, Okazaki T, Marumoto T, Takahashi A, Takayama
K, et al: Coxsackievirus B3 is an oncolytic virus with
immunostimulatory properties that is active against lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 72:2609–2621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Diaconu I, Cerullo V, Hirvinen ML,
Escutenaire S, Ugolini M, Pesonen SK, Bramante S, Parviainen S,
Kanerva A, Loskog AS, et al: Immune response is an important aspect
of the antitumor effect produced by a CD40L-encoding oncolytic
adenovirus. Cancer Res. 72:2327–2338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takasu A, Masui A, Hamada M, Imai T, Iwai
S and Yura Y: Immunogenic cell death by oncolytic herpes simplex
virus type 1 in squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther.
23:107–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Garg AD, Krysko DV, Verfaillie T,
Kaczmarek A, Ferreira GB, Marysael T, Rubio N, Firczuk M, Mathieu
C, Roebroek AJ, et al: A novel pathway combining calreticulin
exposure and ATP secretion in immunogenic cancer cell death. EMBO
J. 31:1062–1079. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tanaka M, Kataoka H, Yano S, Sawada T,
Akashi H, Inoue M, Suzuki S, Inagaki Y, Hayashi N, Nishie H, et al:
Immunogenic cell death due to a new photodynamic therapy (PDT) with
glycoconjugated chlorin (G-chlorin). Oncotarget. 7:47242–47251.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Michaud M, Martins I, Sukkurwala AQ,
Adjemian S, Ma Y, Pellegatti P, Shen S, Kepp O, Scoazec M, Mignot
G, et al: Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced
by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Science. 334:1573–1577. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zappasodi R, Pupa SM, Ghedini GC,
Bongarzone I, Magni M, Cabras AD, Colombo MP, Carlo-Stella C,
Gianni AM and Di Nicola M: Improved clinical outcome in indolent
B-cell lymphoma patients vaccinated with autologous tumor cells
experiencing immunogenic death. Cancer Res. 70:9062–9072. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fucikova J, Kralikova P, Fialova A,
Brtnicky T, Rob L, Bartunkova J and Spísek R: Human tumor cells
killed by anthracyclines induce a tumor-specific immune response.
Cancer Res. 71:4821–4833. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O,
Martins I, Ghiringhelli F, Aymeric L, Michaud M, Apetoh L, Barault
L, et al: Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with
oxaliplatin. Oncogene. 29:482–491. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Senovilla L, Menger L,
Chaput N and Kroemer G: Immunogenic tumor cell death for optimal
anticancer therapy: The calreticulin exposure pathway. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:3100–3104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia
GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL, Castedo M, Mignot G, Panaretakis T,
Casares N, et al: Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity
of cancer cell death. Nat Med. 13:54–61. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bruchard M, Mignot G, Derangère V, Chalmin
F, Chevriaux A, Végran F, Boireau W, Simon B, Ryffel B, Connat JL,
et al: Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in
myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome
and promotes tumor growth. Nat Med. 19:57–64. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Suzuki Y, Mimura K, Yoshimoto Y, Watanabe
M, Ohkubo Y, Izawa S, Murata K, Fujii H, Nakano T and Kono K:
Immunogenic tumor cell death induced by chemoradiotherapy in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res.
72:3967–3976. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku
IP, Taylor EJ, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu
V, et al: PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive
immune resistance. Nature. 515:568–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A,
Rengan R, Pauken KE, Stelekati E, Benci JL, Xu B, Dada H, Odorizzi
PM, et al: Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate
non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature. 520:373–377.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|