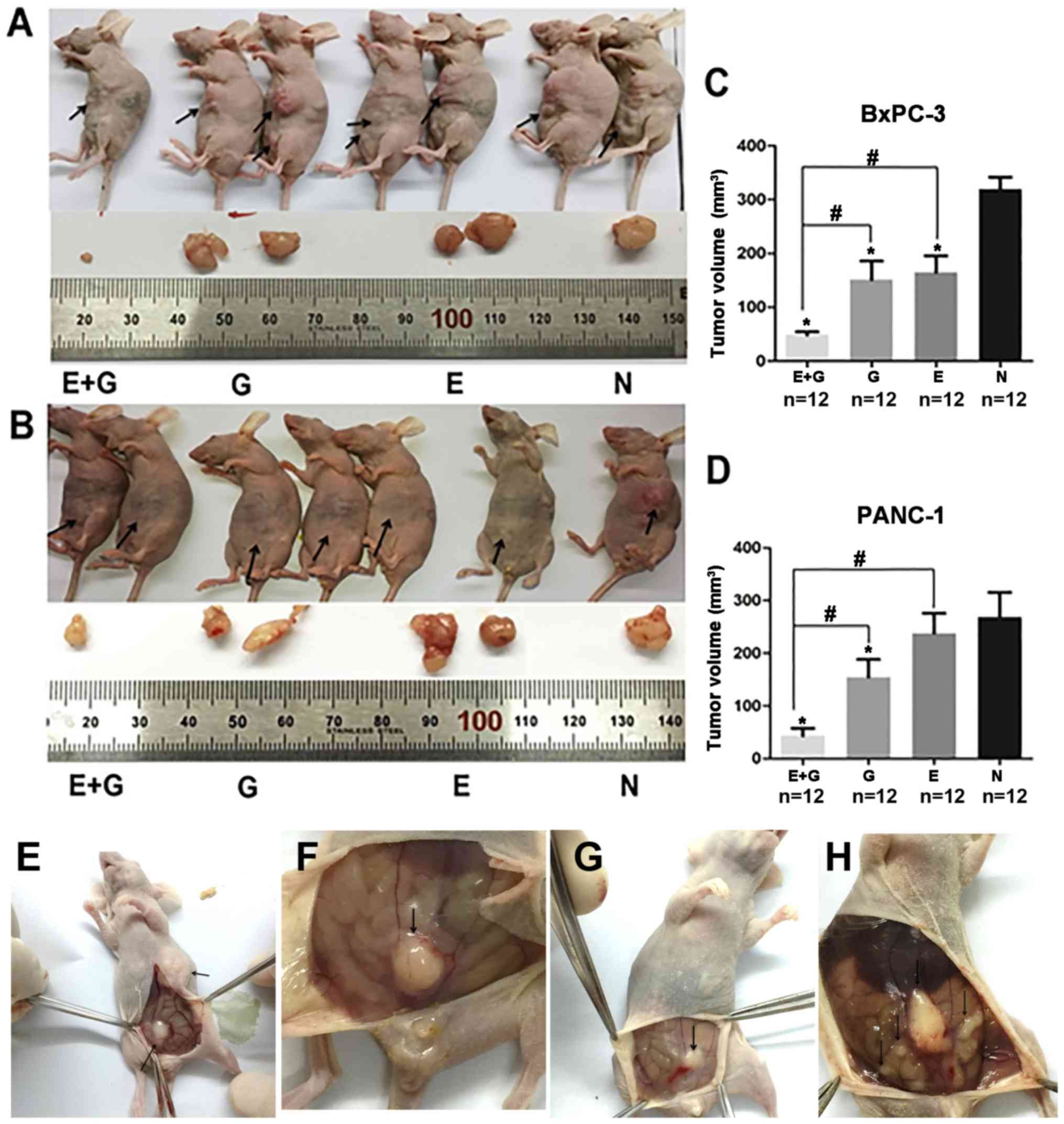
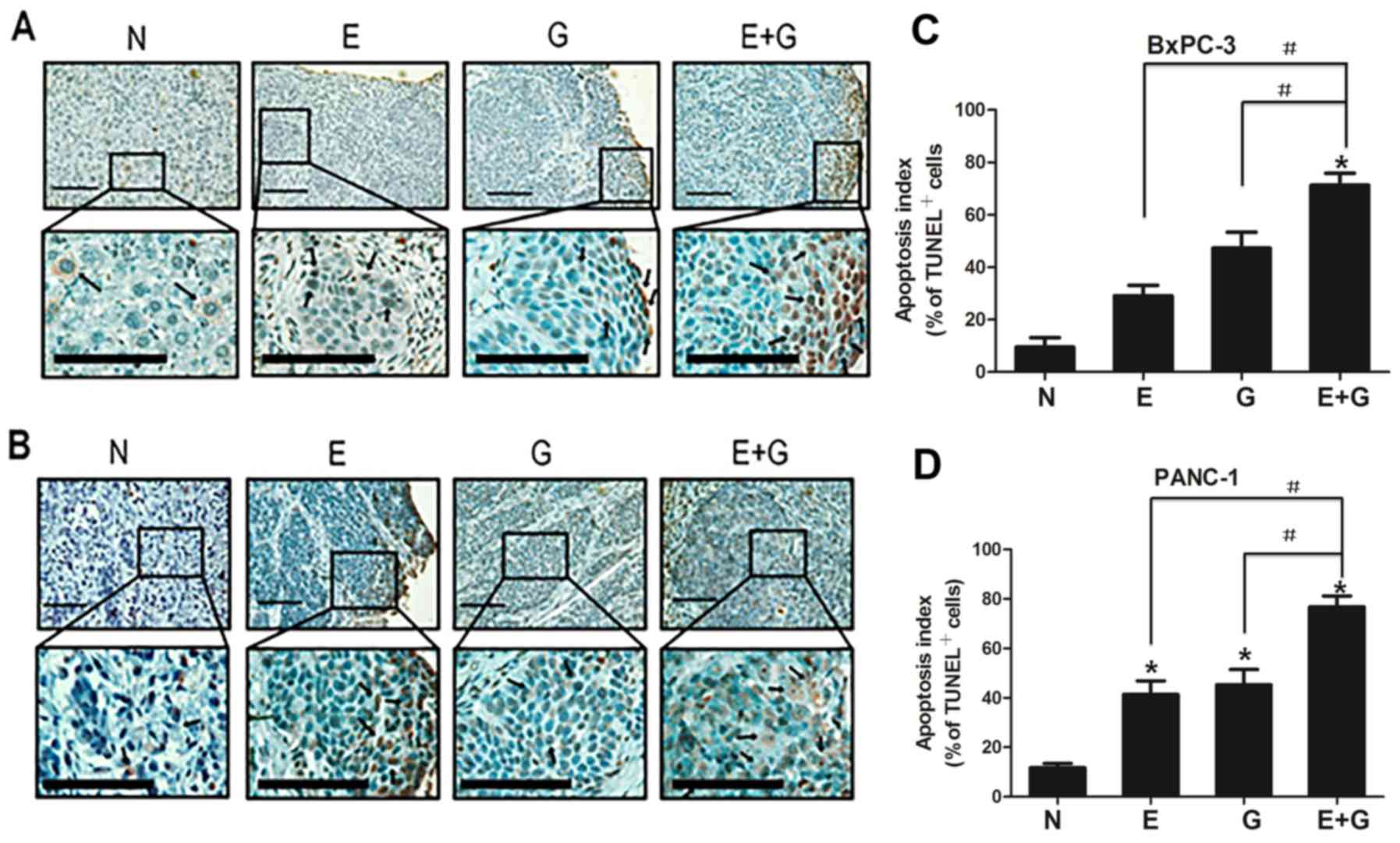
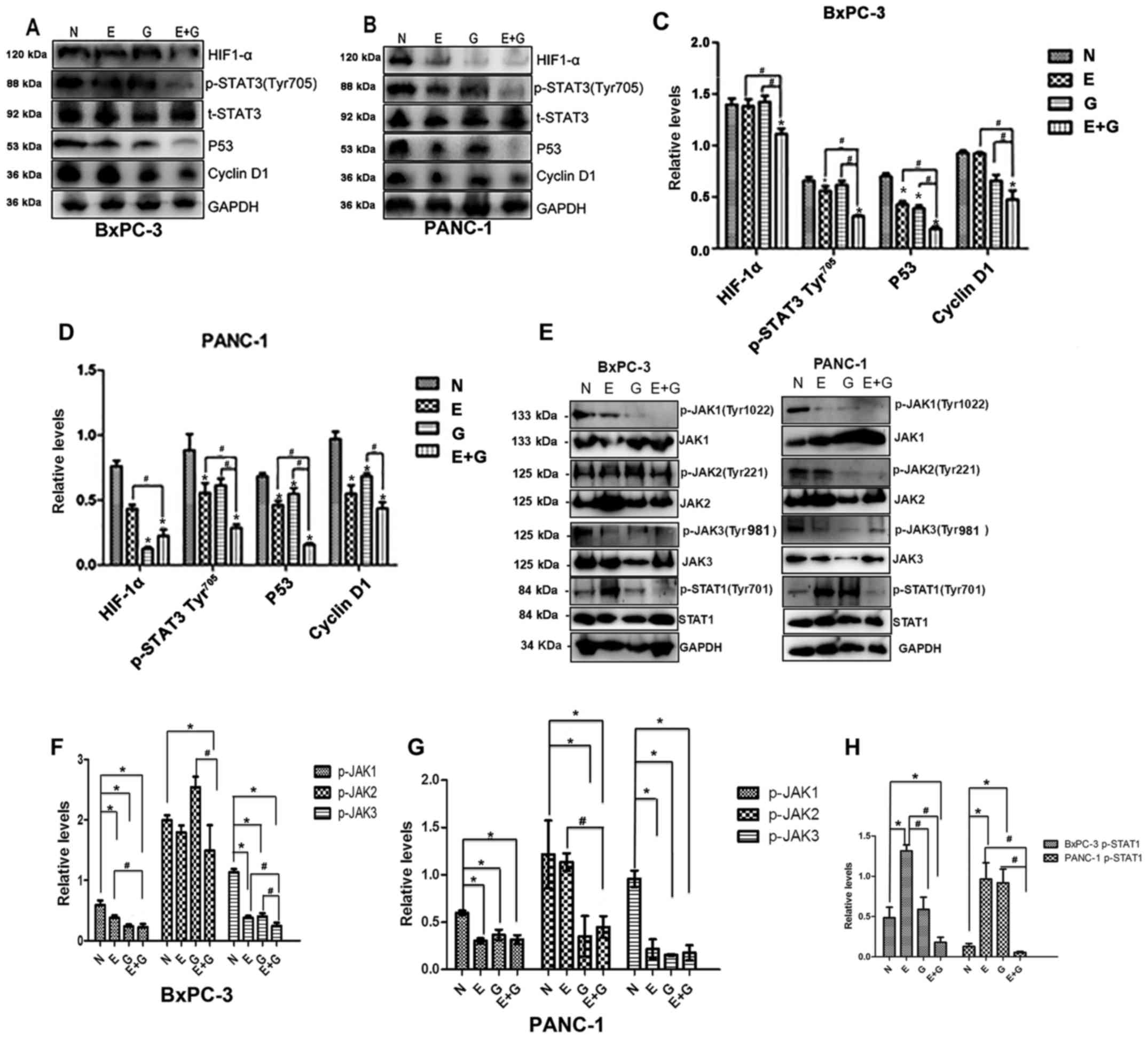
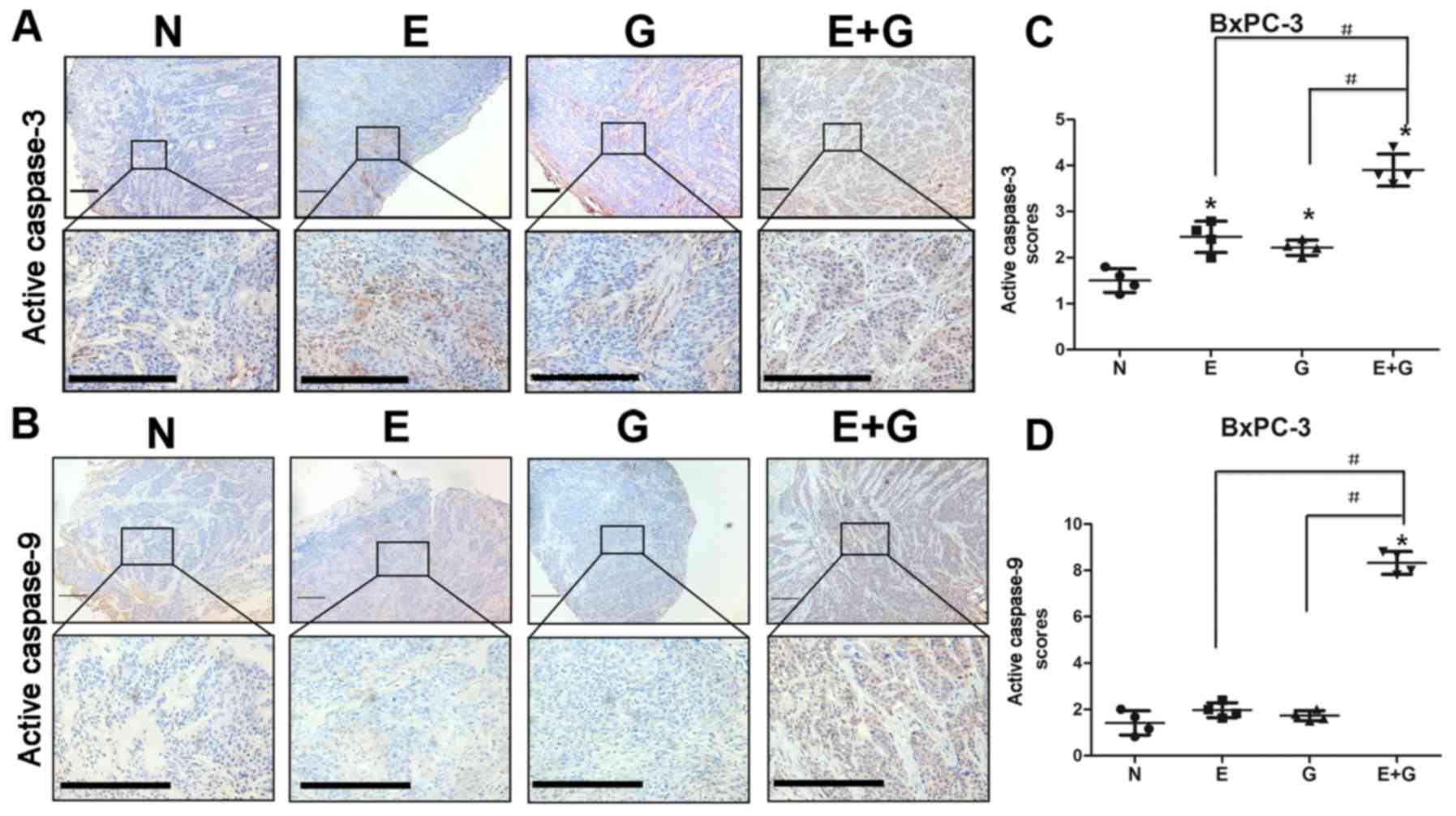
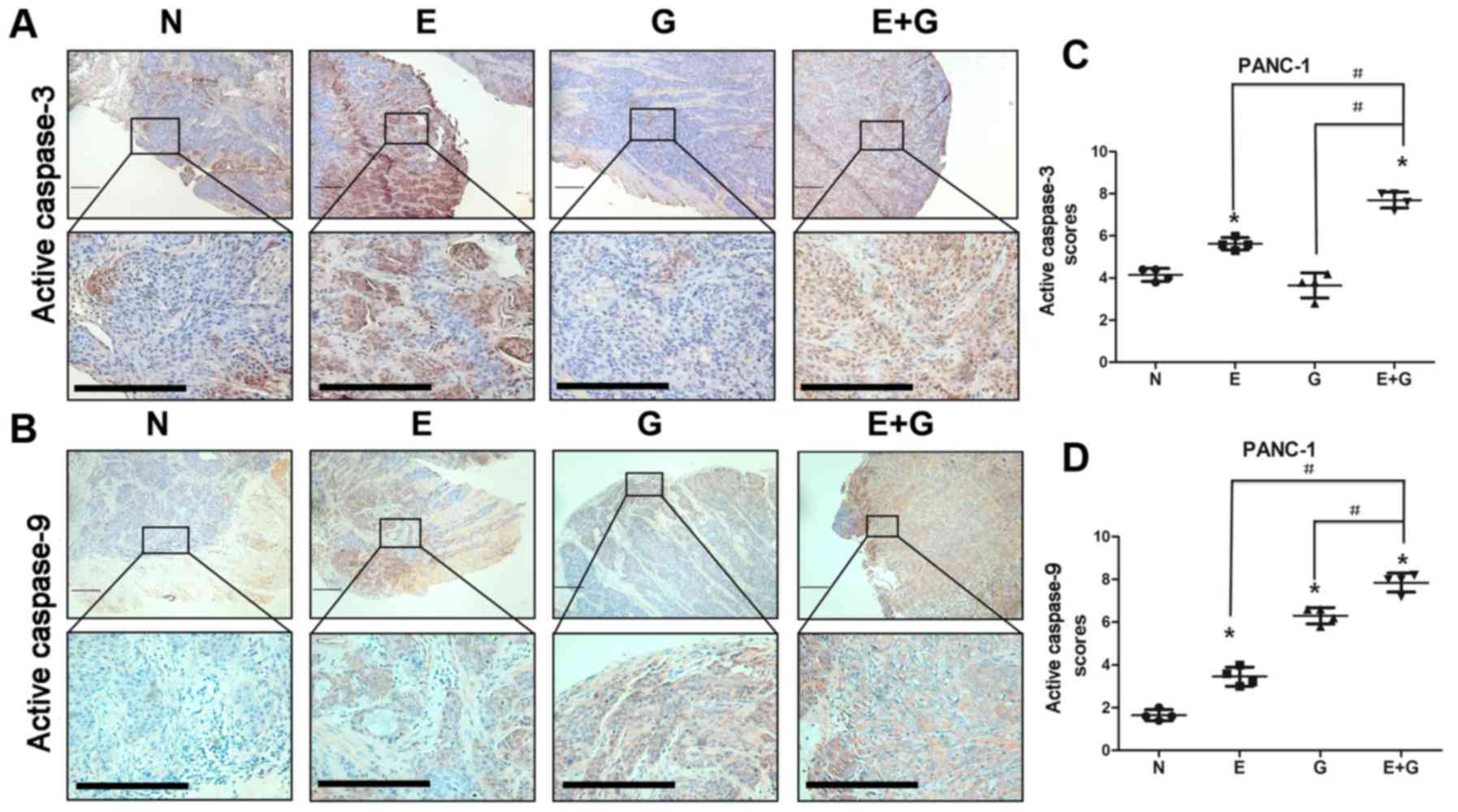
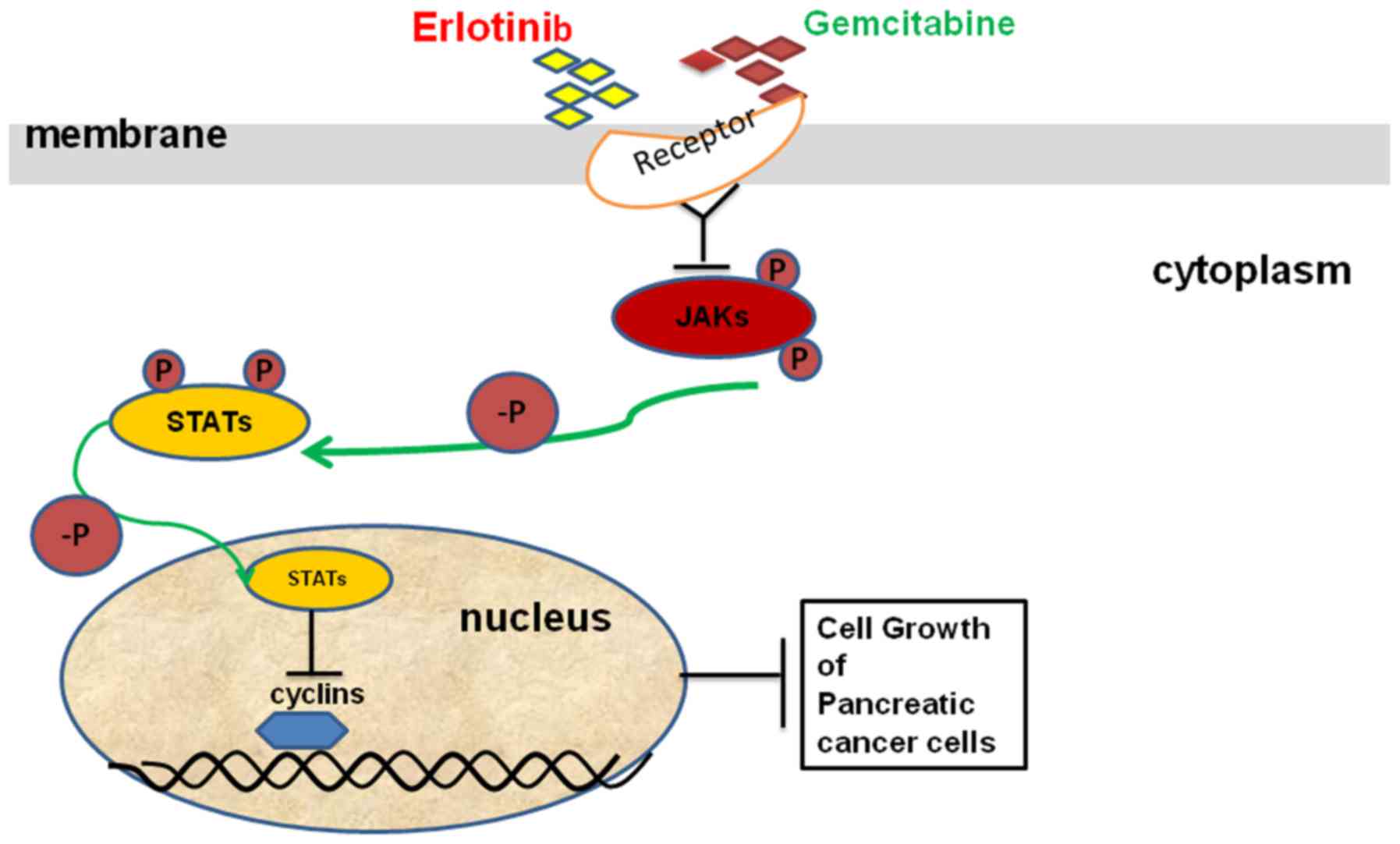
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartwig W, Werner J, Jäger D, Debus J and
Büchler MW: Improvement of surgical results for pancreatic cancer.
Lancet Oncol. 14:e476–e485. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Q, Zeng L, Chen Y, Lian G, Qian C,
Chen S, Li J and Huang K: Pancreatic cancer epidemiology,
detection, and management. Gastroenterol Res Pract.
2016:89623212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Hu GF, Zhang QQ, Tang N, Guo J,
Liu LY, Han X, Wang X and Wang ZH: Efficacy and safety of
gemcitabine plus erlotinib for locally advanced or metastatic
pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 10:1961–1972. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ducreux M, Cuhna AS, Caramella C,
Hollebecque A, Burtin P, Goéré D, Seufferlein T, Haustermans K, Van
Laethem JL, Conroy T, et al ESMO Guidelines Committee, : Cancer of
the pancreas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 26 Suppl 5:v56–v68. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burris HA III, Moore MJ, Andersen J, Green
MR, Rothenberg ML, Modiano MR, Cripps MC, Portenoy RK, Storniolo
AM, Tarassoff P, et al: Improvements in survival and clinical
benefit with gemcitabine as first-line therapy for patients with
advanced pancreas cancer: A randomized trial. J Clin Oncol.
15:2403–2413. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Binenbaum Y, Na'ara S and Gil Z:
Gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Drug
Resist Updat. 23:55–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bareschino MA, Schettino C, Troiani T,
Martinelli E, Morgillo F and Ciardiello F: Erlotinib in cancer
treatment. Ann Oncol. 18 Suppl 6:vi35–vi41. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Czarnecka AM, Korzeń P, Nowak-Dement A,
Kukwa W, Korniluk J and Szczylik C: Prolonged complete response
following gemcitabine-erlotinib combined therapy in advanced
pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett. 11:1101–1104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rawlings JS, Rosler KM and Harrison DA:
The JAK/STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Sci. 117:1281–1283. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mace TA, Shakya R, Elnaggar O, Wilson K,
Komar HM, Yang J, Pitarresi JR, Young GS, Ostrowski MC, Ludwig T,
et al: Single agent BMS-911543 Jak2 inhibitor has distinct
inhibitory effects on STAT5 signaling in genetically engineered
mice with pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 6:44509–44522. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Egberts JH, Cloosters V, Noack A,
Schniewind B, Thon L, Klose S, Kettler B, von Forstner C, Kneitz C,
Tepel J, et al: Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy inhibits
pancreatic tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:1443–1450.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Naito S, von Eschenbach AC, Giavazzi R and
Fidler IJ: Growth and metastasis of tumor cells isolated from a
human renal cell carcinoma implanted into different organs of nude
mice. Cancer Res. 46:4109–4115. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang G, Yan H, Ye S, Tong C and Ying QL:
STAT3 phosphorylation at tyrosine 705 and serine 727 differentially
regulates mouse ESC fates. Stem Cells. 32:1149–1160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Agarwal C, Tyagi A, Kaur M and Agarwal R:
Silibinin inhibits constitutive activation of Stat3, and causes
caspase activation and apoptotic death of human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells. Carcinogenesis. 28:1463–1470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Torres C, Linares A, Alejandre MJ,
Palomino-Morales RJ, Delgado JR and Perales S: Interplay between
gemcitabine and erlotinib over pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.
Pancreas. 45:269–280. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Yang S, Sun N and Chen J:
Differential expression of STAT1 and p21 proteins predicts
pancreatic cancer progression and prognosis. Pancreas. 43:619–623.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Rachagani
S, Lakshmanan I, Haridas D, Yan Y, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting
EGF-receptor(s) - STAT1 axis attenuates tumor growth and metastasis
through downregulation of MUC4 mucin in human pancreatic cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:5164–5181. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye C, Zhao W, Li M, Zhuang J, Yan X, Lu Q,
Chang C, Huang X, Zhou J, Xie B, et al: δ-tocotrienol induces human
bladder cancer cell growth arrest, apoptosis and chemosensitization
through inhibition of STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01227122015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nagaraj NS, Washington MK and Merchant NB:
Combined blockade of Src kinase and epidermal growth factor
receptor with gemcitabine overcomes STAT3-mediated resistance of
inhibition of pancreatic tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res. 17:483–493.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ouédraogo ZG, Biau J, Kemeny JL, Morel L,
Verrelle P and Chautard E: Role of STAT3 in genesis and progression
of human malignant gliomas. Mol Neurobiol. 54:5780–5797. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuen A and Díaz B: The impact of hypoxia
in pancreatic cancer invasion and metastasis. Hypoxia (Auckl).
2:91–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kizaka-Kondoh S, Itasaka S, Zeng L, Tanaka
S, Zhao T, Takahashi Y, Shibuya K, Hirota K, Semenza GL and Hiraoka
M: Selective killing of hypoxia-inducible factor-1-active cells
improves survival in a mouse model of invasive and metastatic
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:3433–3441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun C, Zhang M, Shan X, Zhou X, Yang J,
Wang Y, Li-Ling J and Deng Y: Inhibitory effect of cucurbitacin E
on pancreatic cancer cells growth via STAT3 signaling. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 136:603–610. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stojanovic N, Hassan Z, Wirth M, Wenzel P,
Beyer M, Schäfer C, Brand P, Kroemer A, Stauber RH, Schmid RM, et
al: HDAC1 and HDAC2 integrate the expression of p53 mutants in
pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 36:1804–1815. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rosenfeldt MT, O'Prey J, Morton JP, Nixon
C, MacKay G, Mrowinska A, Au A, Rai TS, Zheng L, Ridgway R, et al:
p53 status determines the role of autophagy in pancreatic tumour
development. Nature. 504:296–300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Izetti P, Hautefeuille A, Abujamra AL, de
Farias CB, Giacomazzi J, Alemar B, Lenz G, Roesler R, Schwartsmann
G, Osvaldt AB, et al: PRIMA-1, a mutant p53 reactivator, induces
apoptosis and enhances chemotherapeutic cytotoxicity in pancreatic
cancer cell lines. Invest New Drugs. 32:783–794. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Ma Y, Wright GM, Huang
M, Irby R, Briggs J, Karras J, Cress WD, Pardoll D, et al: Role of
Stat3 in regulating p53 expression and function. Mol Cell Biol.
25:7432–7440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qie S and Diehl JA: Cyclin D1, cancer
progression, and opportunities in cancer treatment. J Mol Med
(Berl). 94:1313–1326. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun
J, Yang S and Hao J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating
transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res.
74:2455–2464. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Berry W, Algar E, Kumar B, Desmond C, Swan
M, Jenkins BJ and Croagh D: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided
fine-needle aspirate-derived preclinical pancreatic cancer models
reveal panitumumab sensitivity in KRAS wild-type tumors. Int J
Cancer. 140:2331–2343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zehir A, Benayed R, Shah RH, Syed A,
Middha S, Kim HR, Srinivasan P, Gao J, Chakravarty D, Devlin SM, et
al: Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from
prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat Med.
23:703–713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|