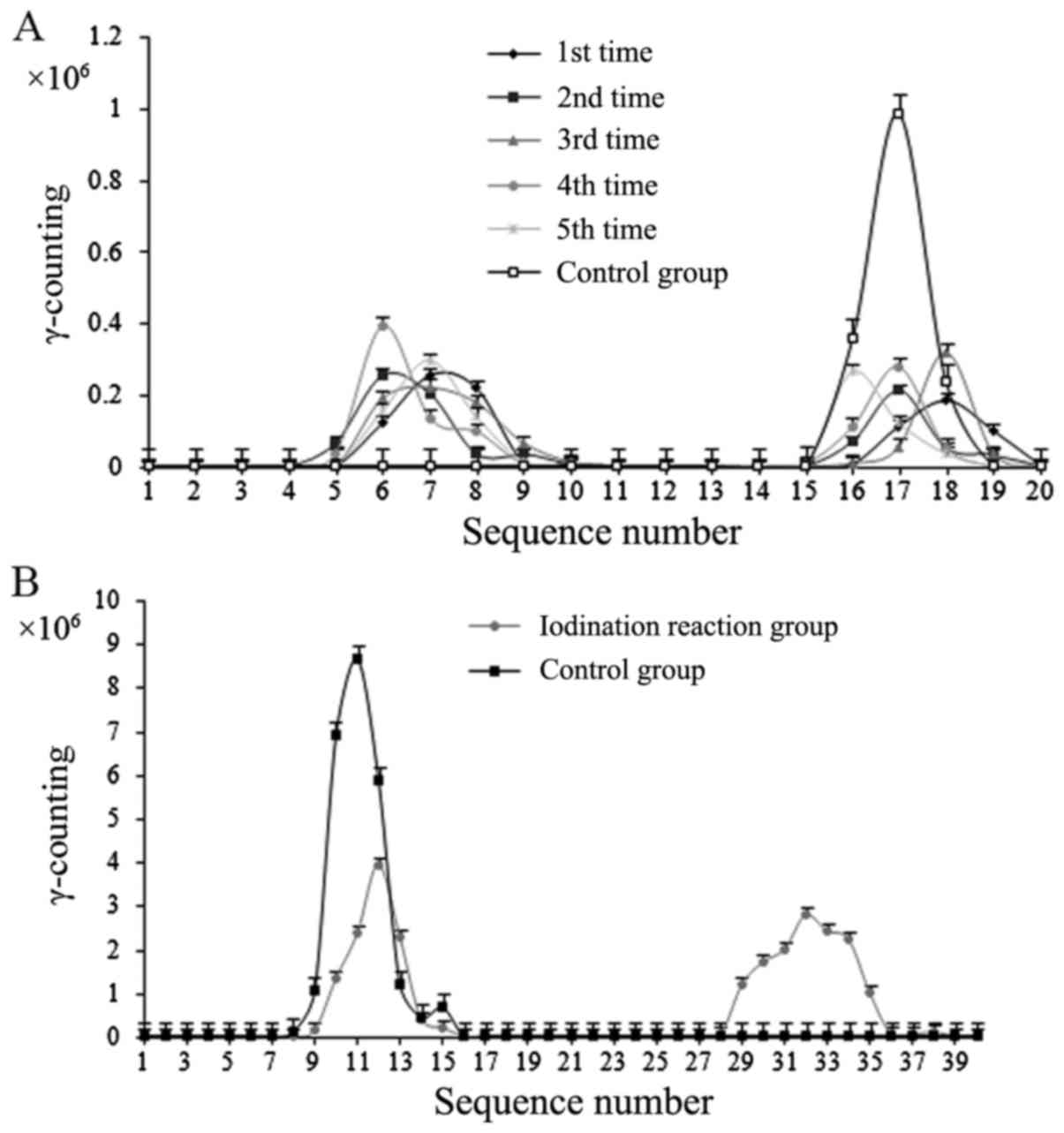
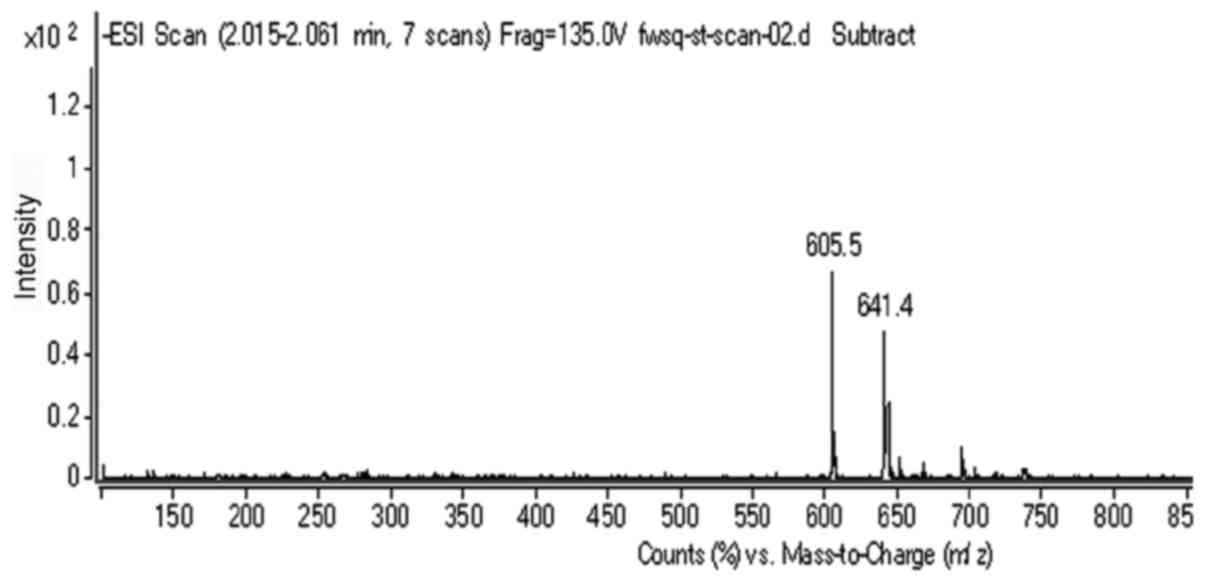
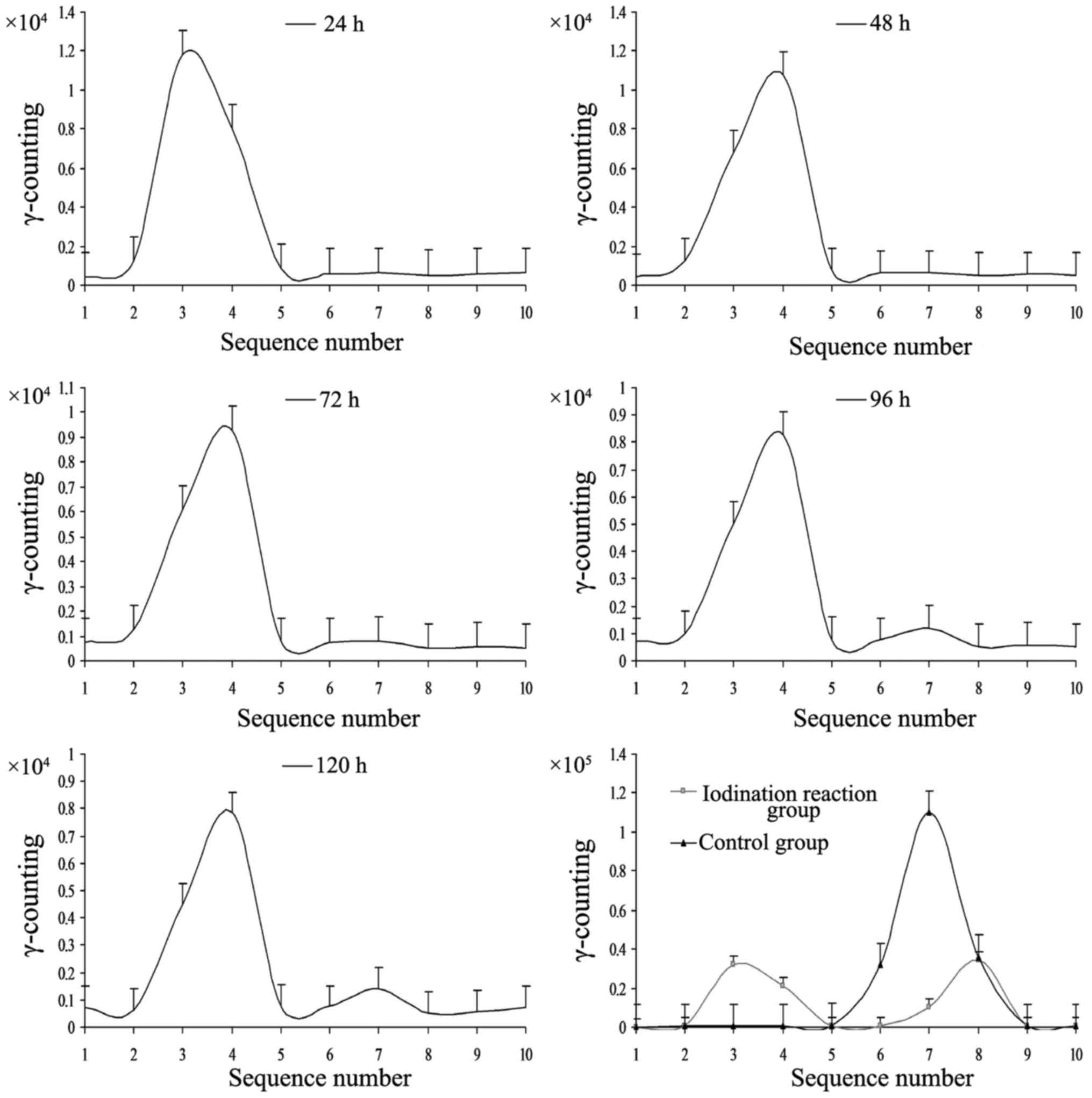
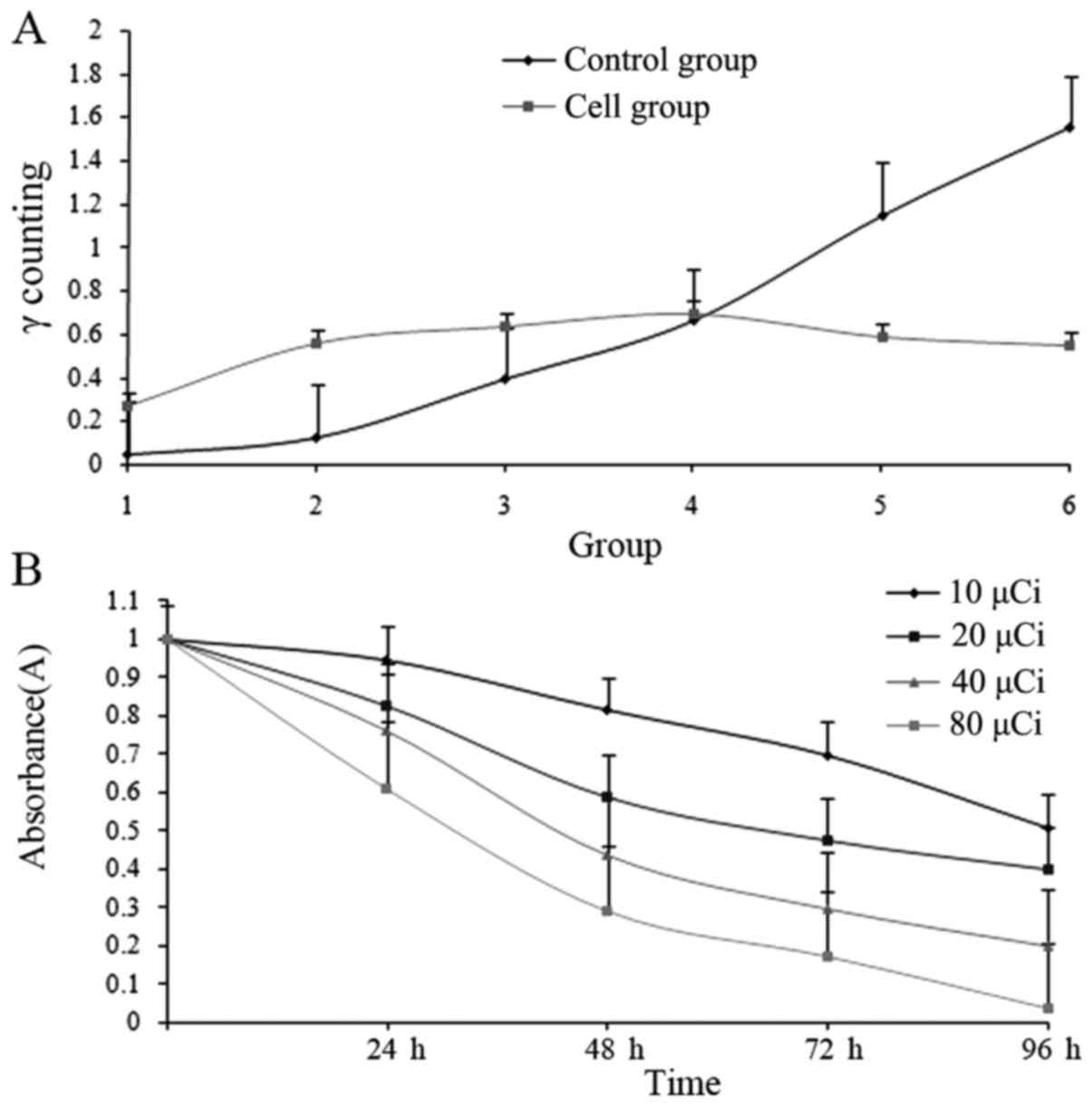
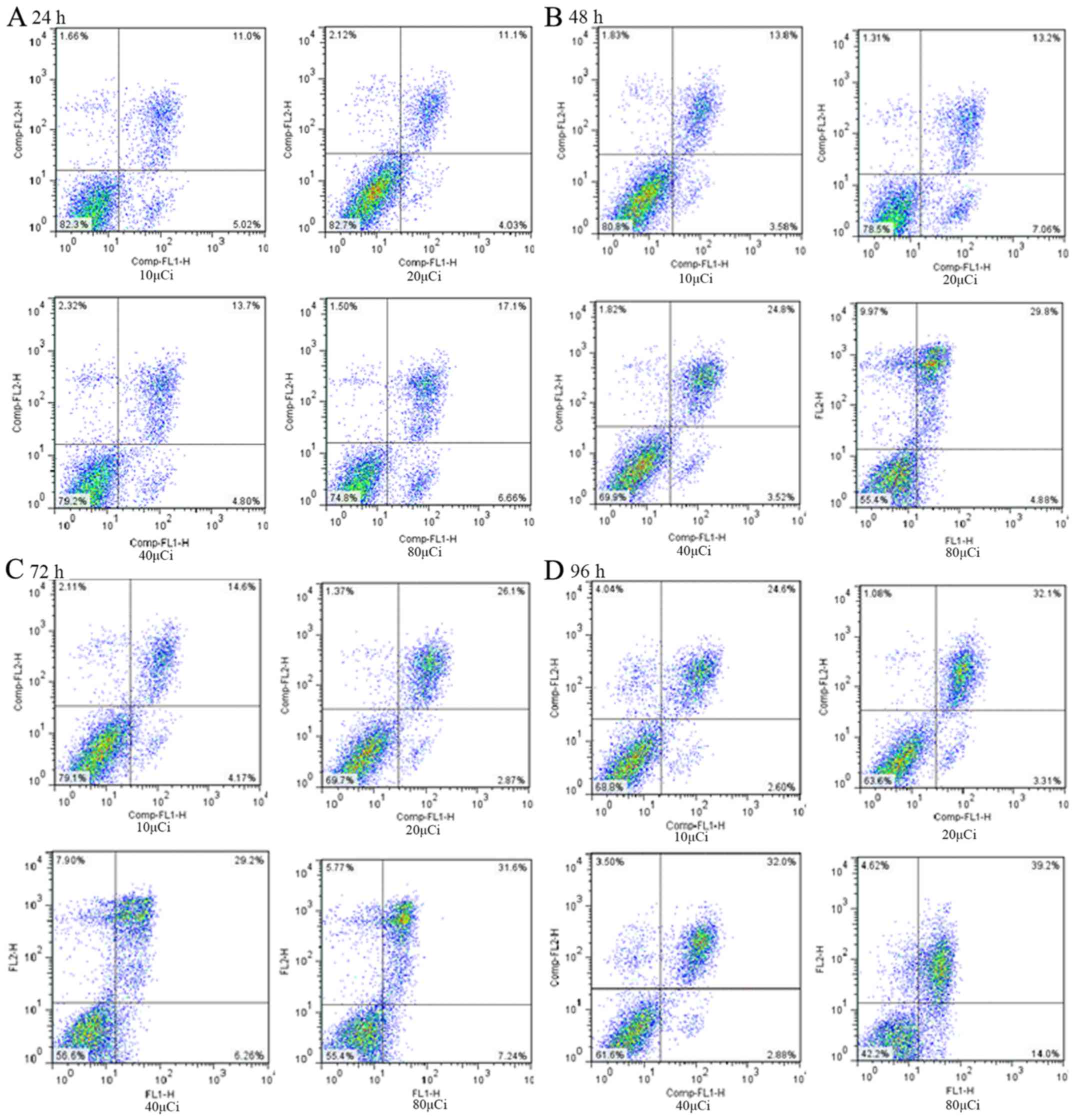
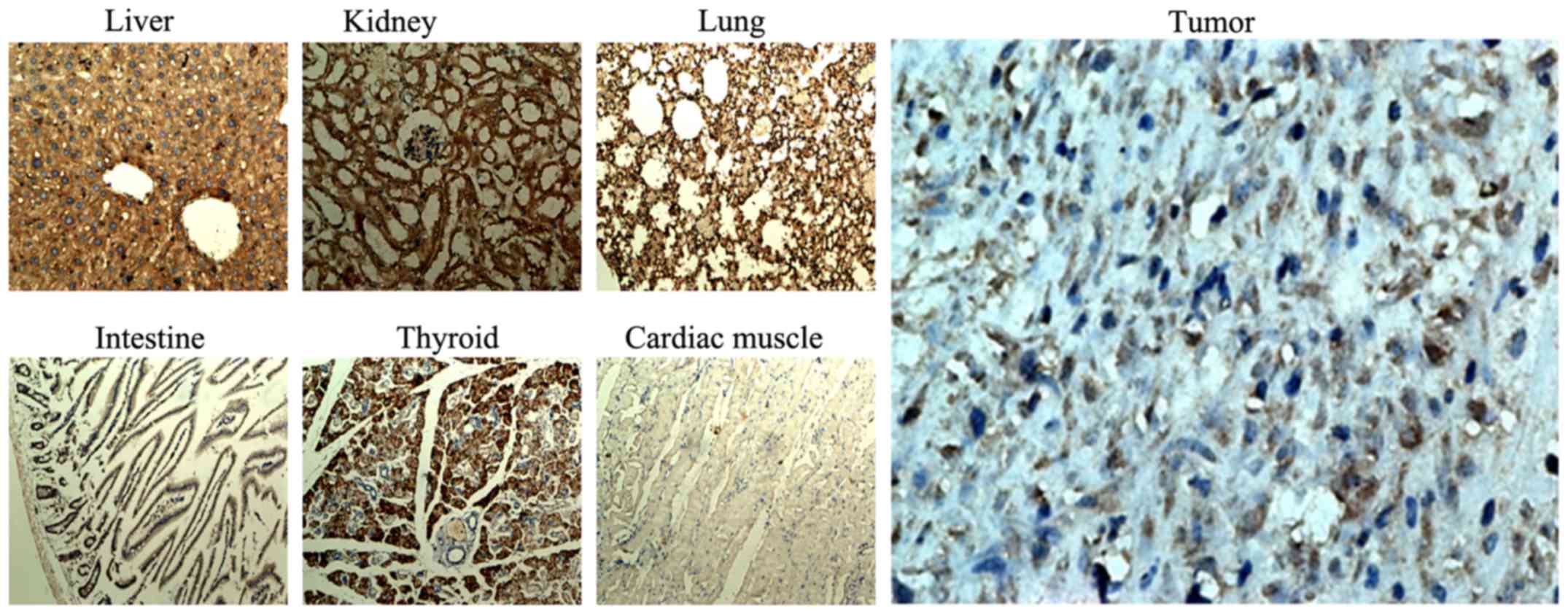
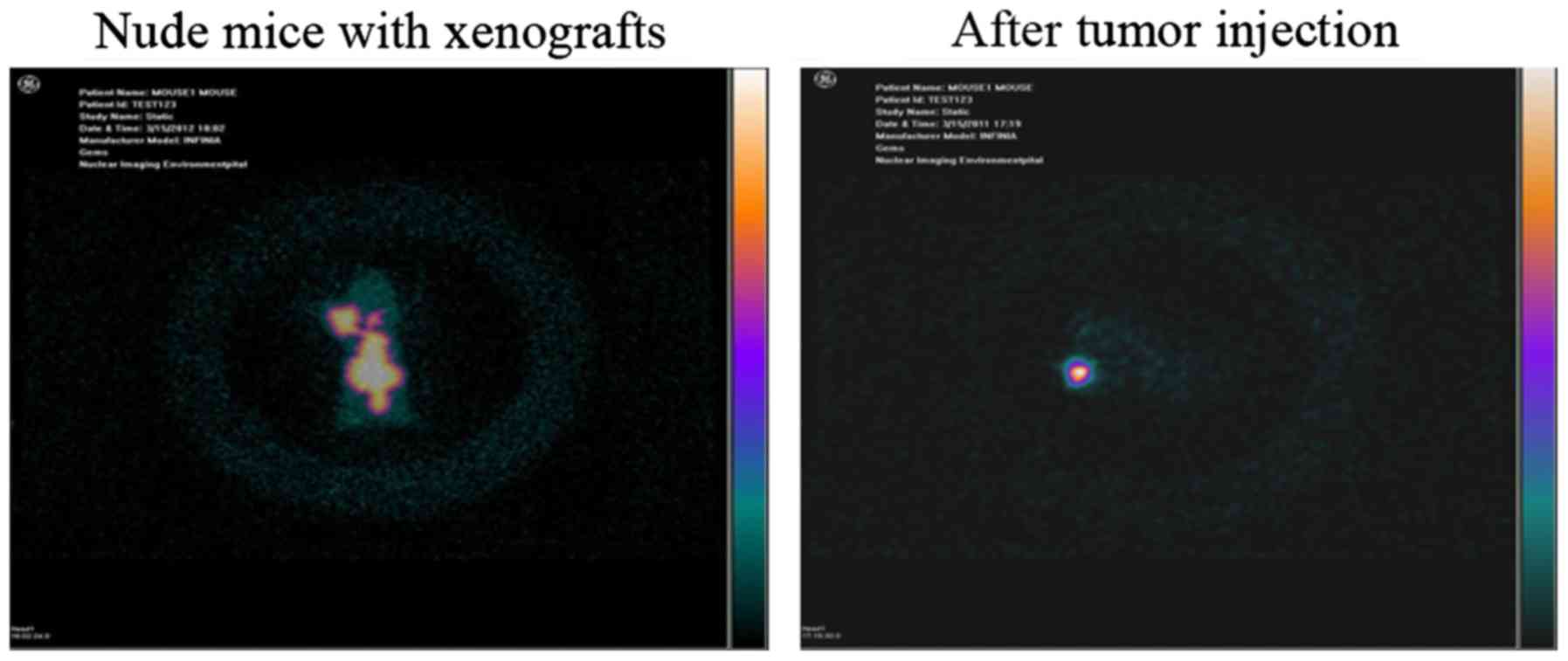
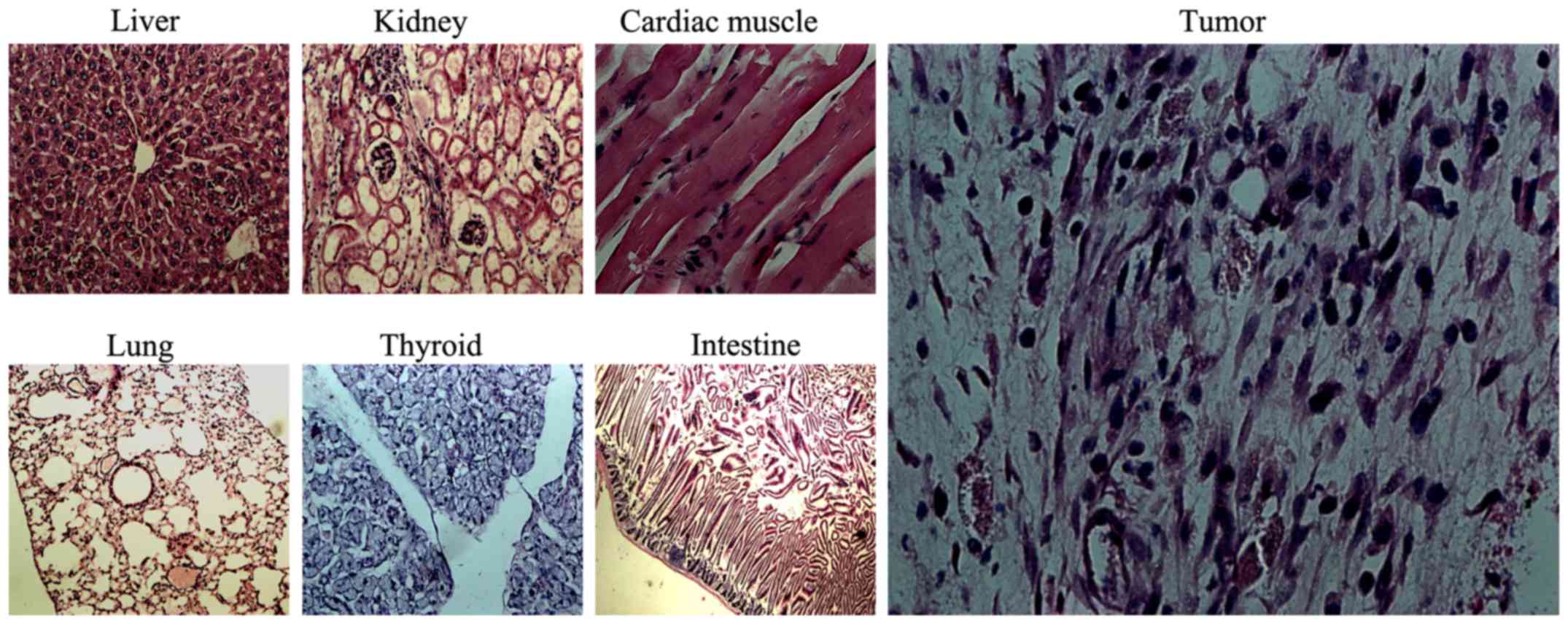
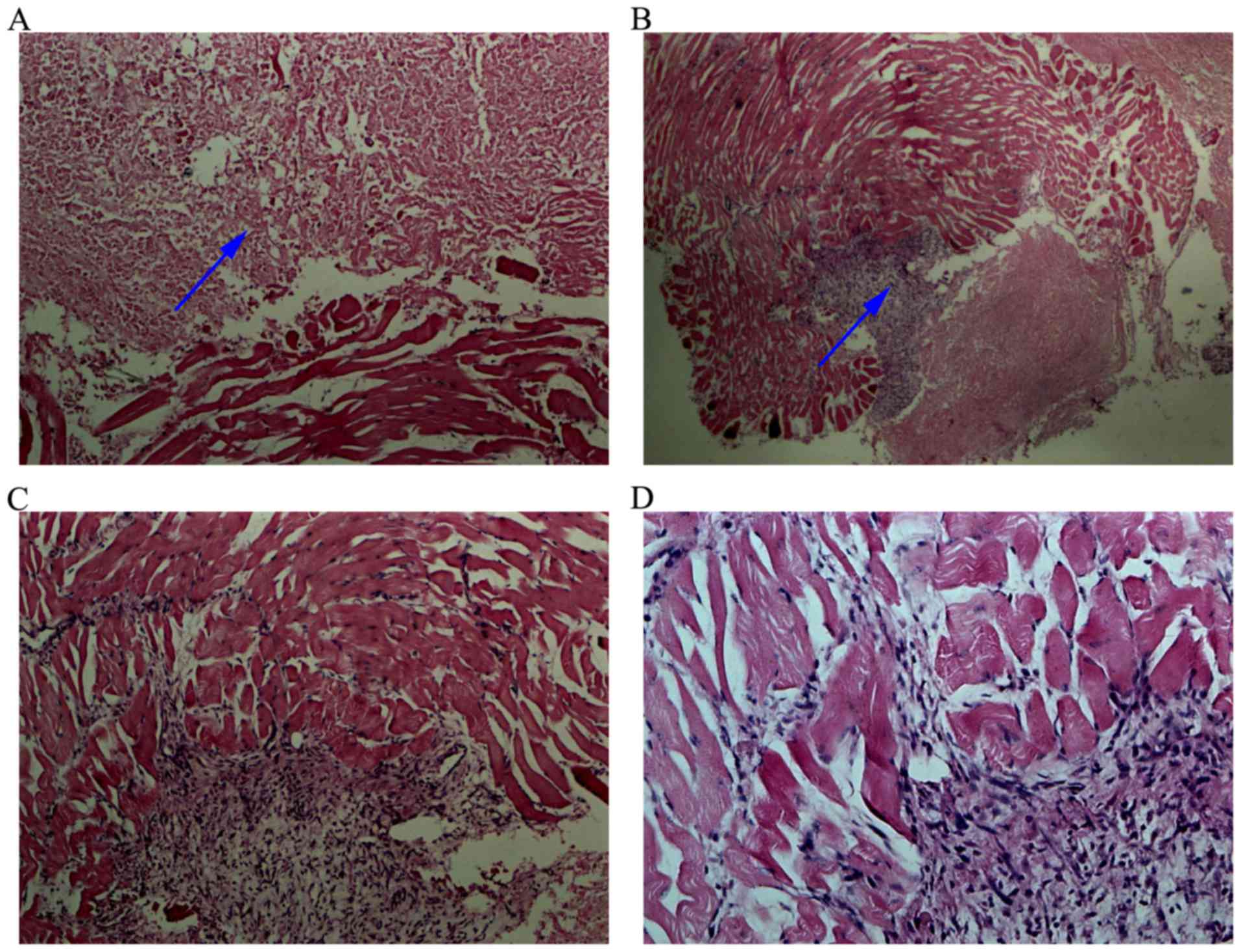
|
1
|
Pitoia F and Miyauchi A: 2015 American
thyroid association guidelines for thyroid nodules and
differentiated thyroid cancer and their implementation in various
care settings. Thyroid. 26:319–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Higashi T, Kudo T and Kinuya S:
Radioactive iodine (131I) therapy for differentiated
thyroid cancer in Japan: Current issues with historical review and
future perspective. Ann Nucl Med. 26:99–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sawka AM, Straus S, Gafni A, Meiyappan S,
David D, Rodin G, Brierley JD, Tsang RW, Thabane L, Rotstein L, et
al: Thyroid cancer patients' involvement in adjuvant radioactive
iodine treatment decision-making and decision regret: An
exploratory study. Support Care Cancer. 20:641–645. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haymart MR, Banerjee M, Stewart AK, Koenig
RJ, Birkmeyer JD and Griggs JJ: Use of radioactive iodine for
thyroid cancer. JAMA. 306:721–728. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tuttle RM, Rondeau G and Lee NY: A
risk-adapted approach to the use of radioactive iodine and external
beam radiation in the treatment of well-differentiated thyroid
cancer. Cancer Contr. 18:89–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sacks W, Fung CH, Chang JT, Waxman A and
Braunstein GD: The effectiveness of radioactive iodine for
treatment of low-risk thyroid cancer: A systematic analysis of the
peer-reviewed literature from 1966 to April 2008. Thyroid.
20:1235–1245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hosseinzadeh M, Eivazi Ziaei J, Mahdavi N,
Aghajari P, Vahidi M, Fateh A and Asghari E: Risk factors for
breast cancer in Iranian women: A hospital-based case-control study
in tabriz, iran. J Breast Cancer. 17:236–243. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Howard-Anderson J, Ganz PA, Bower JE and
Stanton AL: Quality of life, fertility concerns, and behavioral
health outcomes in younger breast cancer survivors: A systematic
review. J Natl Cancer Inst. 104:386–405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gradilone A, Raimondi C, Naso G, Silvestri
I, Repetto L, Palazzo A, Gianni W, Frati L, Cortesi E and Gazzaniga
P: How circulating tumor cells escape from multidrug resistance:
Translating molecular mechanisms in metastatic breast cancer
treatment. Am J Clin Oncol. 34:625–627. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen WJ, Wang H, Tang Y, Liu CL, Li HL and
Li WT: Multidrug resistance in breast cancer cells during
epithelial-mesenchymal transition is modulated by breast cancer
resistant protein. Chin J Cancer. 29:151–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dall G, Vieusseux J, Unsworth A, Anderson
R and Britt K: Low dose, low cost estradiol pellets can support
MCF-7 tumour growth in nude mice without bladder symptoms. J
Cancer. 6:1331–1336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang ZY, Wang MW, Zhang YP, Xu JY, Yuan HY
and Zhang YJ: The biodistribution and imaging of 16α-(18F)
fluroroestradiol (18F-FES) in rats and breast tumor-bearing nude
mice. Shanghai Medical Imaging. 20:234–238. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Turner NC, Neven P, Loibl S and Andre F:
Advances in the treatment of advanced oestrogen-receptor-positive
breast cancer. Lancet. 389:2403–2414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dalmau E, Armengol-Alonso A, Muñoz M and
Seguí-Palmer MÁ: Current status of hormone therapy in patients with
hormone receptor positive (HR+) advanced breast cancer.
Breast. 23:710–720. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
James R, Thriveni K, Krishnamoorthy L,
Deshmane V, Bapsy PP and Ramaswamy G: Clinical outcome of adjuvant
endocrine treatment according to Her-2/neu status in breast cancer.
Indian J Med Res. 133:70–75. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Al-Mubarak M, Sacher AG, Ocana A,
Vera-Badillo F, Seruga B and Amir E: Fulvestrant for advanced
breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:753–758. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wardell SE, Nelson ER, Chao CA and
McDonnell DP: Bazedoxifene exhibits antiestrogenic activity in
animal models of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer: Implications
for treatment of advanced disease. Clin Cancer Res. 19:2420–2431.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mishra AK, Abrahamsson A and Dabrosin C:
Fulvestrant inhibits growth of triple negative breast cancer and
synergizes with tamoxifen in ERα positive breast cancer by
up-regulation of ERβ. Oncotarget. 7:56876–56888. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He S, Wang M, Yang Z, Zhang J and Zhang Y,
Luo J and Zhang Y: Comparison of 18F-FES, 18F-FDG, and 18F-FMISO
PET imaging probes for early prediction and monitoring of response
to endocrine therapy in a mouse xenograft model of ER-positive
breast cancer. PLoS One. 11:e01599162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fernandes SA, Gomes GR, Siu ER,
Damas-Souza DM, Bruni-Cardoso A, Augusto TM, Lazari MF, Carvalho HF
and Porto CS: The anti-oestrogen fulvestrant (ICI 182,780) reduces
the androgen receptor expression, ERK1/2 phosphorylation and cell
proliferation in the rat ventral prostate. Int J Androl.
34:486–500. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang MH, Xu YJ, Wang ZZ, Liu M, Li Z, Weng
W and Fan W: Radiolabeling of paclitaxel with 125I. J
Isotopes. 21:82–87. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Mi C and Wang W: Establishment of
lymph node metastasis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer model in nude
mice. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 95:1862–1865. 2015.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nofiele JT and Cheng HL: Establishment of
a lung metastatic breast tumor xenograft model in nude rats. PLoS
One. 9:e97950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishihara E, Nagayama Y, Inoue S, Hiroi H,
Muramatsu M, Yamashita S and Koji T: Ontogenetic changes in the
expression of estrogen receptor α and β in rat pituitary gland
detected by immunohistochemistry. Endocrinology. 141:615–620. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Giacinti L, Giacinti C, Gabellini C,
Rizzuto E, Lopez M and Giordano A: Scriptaid effects on breast
cancer cell lines. J Cell Physiol. 227:3426–3433. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu L, Ma H, Tang Y, Chen W, Lu Y, Guo J
and Duan JA: Discovery of estrogen receptor α modulators from
natural compounds in Si-Wu-Tang series decoctions using
estrogen-responsive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem
Lett. 22:154–163. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ko YM, Wu TY, Wu YC, Chang FR, Guh JY and
Chuang LY: Annonacin induces cell cycle-dependent growth arrest and
apoptosis in estrogen receptor-α-related pathways in MCF-7 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:1283–1290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mendoza RA, Enriquez MI, Mejia SM, Moody
EE and Thordarson G: Interactions between IGF-I, estrogen
receptor-α (ERα), and ERβ in regulating growth/apoptosis of MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. J Endocrinol. 208:1–9. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hong W, Chen L, Li J and Yao Z: Inhibition
of MAP kinase promotes the recruitment of corepressor SMRT by
tamoxifen-bound estrogen receptor alpha and potentiates tamoxifen
action in MCF-7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 396:299–303.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kelkar MG, Senthilkumar K, Jadhav S, Gupta
S, Ahn BC and De A: Enhancement of human sodium iodide symporter
gene therapy for breast cancer by HDAC inhibitor mediated
transcriptional modulation. Sci Rep. 6:193412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Renier C, Do J, Reyna-Neyra A, Foster D,
De A, Vogel H, Jeffrey SS, Tse V, Carrasco N and Wapnir I:
Regression of experimental NIS-expressing breast cancer brain
metastases in response to radioiodide/gemcitabine dual therapy.
Oncotarget. 7:54811–54824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chatterjee S, Thaker N and De A: Combined
2-deoxy glucose and metformin improves therapeutic efficacy of
sodium-iodide symporter-mediated targeted radioiodine therapy in
breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 7:251–265.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Poole VL and McCabe CJ: Iodide transport
and breast cancer. J Endocrinol. 227:R1–R12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jan KC, Ku KL, Chu YH, Hwang LS and Ho CT:
Tissue distribution and elimination of estrogenic and
anti-inflammatory catechol metabolites from sesaminol triglucoside
in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 58:7693–7700. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Younes M and Honma N: Estrogen receptor β.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 135:63–66. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ur Rahman MS and Cao J: Estrogen receptors
in gastric cancer: Advances and perspectives. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:2475–2482. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|