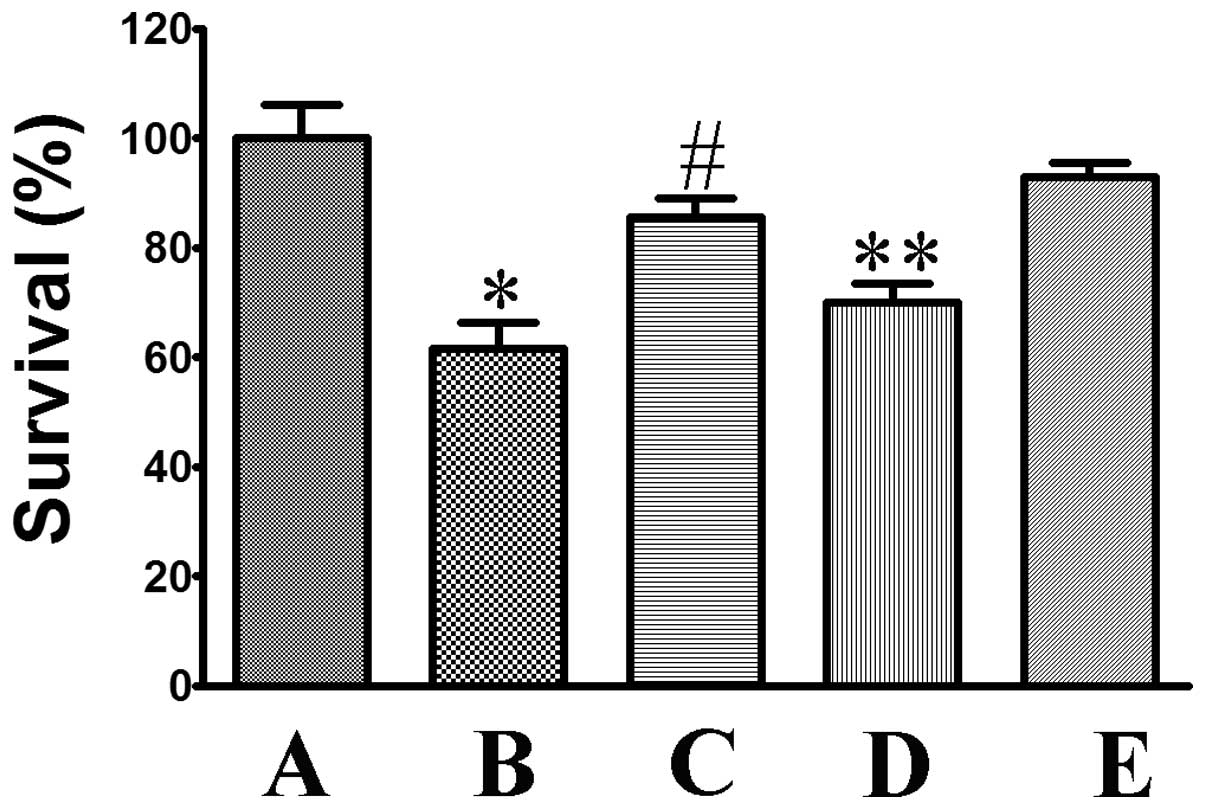
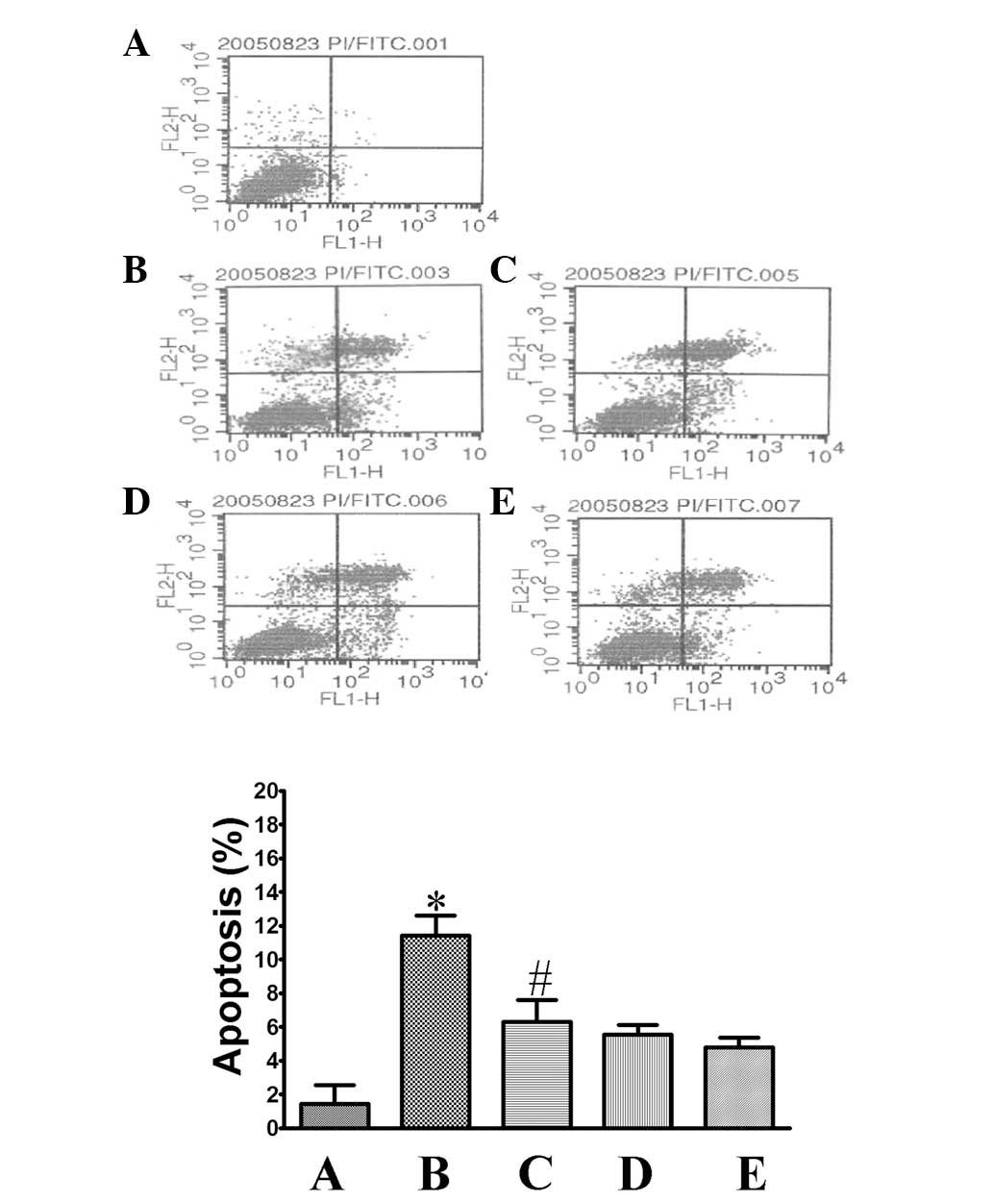
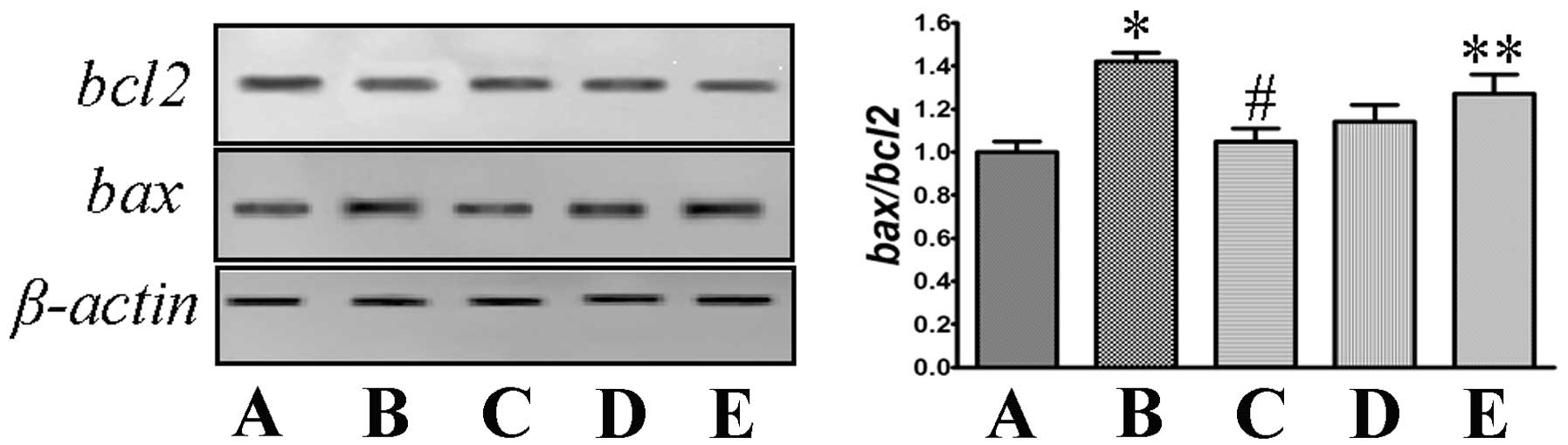
|
1
|
Read SJ, Hirano T, Davis SM and Donnan GA:
Limiting neurological damage after stroke: a review of
pharmacological treatment options. Drugs Aging. 14:11–39. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baron JC: Perfusion thresholds in human
cerebral ischemia: historical perspective and therapeutic
implications. Cerebrovasc Dis. 11(Suppl 1): 2–8. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Okouchi M, Ekshyyan O, Maracine M and Aw
TY: Neuronal apoptosis in neurodegeneration. Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:1059–1096. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–e339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, Chen H, et al:
Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in
cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1802:92–99. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shamas-Din A, Kale J, Leber B and Andrews
DW: Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0087142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ayaloglu-Butun F, Terzioglu-Kara E,
Tokcaer-Keskin Z and Akcali KC: The effect of estrogen on bone
marrow-derived rat mesenchymal stem cell maintenance: inhibiting
apoptosis through the expression of Bcl-xL and Bcl-2. Stem Cell
Rev. 8:393–401. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Warren JS, Zhao Y, Yung R and Desai A:
Recombinant human erythropoietin suppresses endothelial cell
apoptosis and reduces the ratio of Bax to Bcl-2 proteins in the
aortas of apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
57:424–433. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ramin M, Azizi P, Motamedi F, Haghparast A
and Khodagholi F: Inhibition of JNK phosphorylation reverses memory
deficit induced by β-amyloid (1–42) associated with decrease of
apoptotic factors. Behav Brain Res. 217:424–431. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wysocki J, Ye M, Rodriguez E, et al:
Targeting the degradation of angiotensin II with recombinant
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: prevention of angiotensin
II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension. 55:90–98. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reis WL, Saad WA, Camargo LA, Elias LL and
Antunes-Rodrigues J: Central nitrergic system regulation of
neuroendocrine secretion, fluid intake and blood pressure induced
by angiotensin-II. Behav Brain Funct. 6:642010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grobe JL, Grobe CL, Beltz TG, et al: The
brain renin-angiotensin system controls divergent efferent
mechanisms to regulate fluid and energy balance. Cell Metab.
12:431–442. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao X, Peterson JR, Wang G, et al:
Angiotensin II-dependent hypertension requires cyclooxygenase
1-derived prostaglandin E2 and EP1 receptor signaling in the
subfornical organ of the brain. Hypertension. 59:869–876. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCarthy CA, Vinh A, Broughton BR, Sobey
CG, Callaway JK and Widdop RE: Angiotensin II type 2 receptor
stimulation initiated after stroke causes neuroprotection in
conscious rats. Hypertension. 60:1531–1537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pont-Lezica L, Colasse S and Bessis A:
Depletion of microglia from primary cellular cultures. Methods Mol
Biol. 1041:55–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang H, Yu P, Gou H, et al:
Cardioprotective effects of 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 against
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2012:5062142012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Yu P, Bai J, et al: Ocotillol
enhanced the antitumor activity of doxorubicin via p53-dependent
apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:4685372013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xilouri M and Stefanis L: Autophagy in the
central nervous system: implications for neurodegenerative
disorders. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 9:701–719. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou T, Jiang J, Zhang M, Fu Y, Yang Z and
Jiang L: Protective effect of mild hypothermia on oxygen-glucose
deprivation injury in rat hippocampal neurons after hypoxia. Mol
Med Rep. 7:1859–1864. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dominguez C, Delgado P, Vilches A, et al:
Oxidative stress after thrombolysis-induced reperfusion in human
stroke. Stroke. 41:653–660. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang X, Chen Y, Jenkins LW, Kochanek PM
and Clark RS: Bench-to-bedside review: Apoptosis/programmed cell
death triggered by traumatic brain injury. Crit Care. 9:66–75.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krysko DV, Vanden Berghe T, D’Herde K and
Vandenabeele P: Apoptosis and necrosis: detection, discrimination
and phagocytosis. Methods. 44:205–221. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaschina E and Unger T: Angiotensin
AT1/AT2 receptors: regulation, signalling and function. Blood
Press. 12:70–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goldenberg I, Grossman E, Jacobson KA,
Shneyvays V and Shainberg A: Angiotensin II-induced apoptosis in
rat cardiomyocyte culture: a possible role of AT1 and AT2
receptors. J Hypertens. 19:1681–1689. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fortuno MA, Ravassa S, Etayo JC and Diez
J: Overexpression of Bax protein and enhanced apoptosis in the left
ventricle of spontaneously hypertensive rats: effects of AT1
blockade with losartan. Hypertension. 32:280–286. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|