|
1
|
Nokoff NJ, Rewers M and Cree Green M: The
interplay of autoimmunity and insulin resistance in type 1
diabetes. Discov Med. 13:115–122. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tooley JE, Waldron-Lynch F and Herold KC:
New and future immunomodulatory therapy in type 1 diabetes. Trends
Mol Med. 18:173–181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Daneman D: Type 1 diabetes. Lancet.
367:847–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Redondo MJ and Eisenbarth GS: Genetic
control of autoimmunity in Type I diabetes and associated
disorders. Diabetologia. 45:605–622. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gan MJ, Albanese-O’Neill A and Haller MJ:
Type 1 diabetes: current concepts in epidemiology, pathophysiology,
clinical care, and research. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health
Care. 42:269–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Knip M: Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes:
implications for incidence trends. Horm Res Paediatr. 76:57–64.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Risch N: Assessing the role of HLA-linked
and unlinked determinants of disease. Am J Hum Genet. 40:1–14.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rabinovitch A: An update on cytokines in
the pathogenesis of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes
Metab Rev. 14:129–151. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nicoletti F, Conget I, Di Marco R, et al:
Serum levels of the interferon-gamma-inducing cytokine
interleukin-18 are increased in individuals at high risk of
developing type I diabetes. Diabetologia. 44:309–311. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rothe H, Ito Y and Kolb H: Disease
resistant, NOD-related strains reveal checkpoints of
immunoregulation in the pancreas. J Mol Med (Berl). 79:190–197.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rothe H, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG and Kolb
H: Active stage of autoimmune diabetes is associated with the
expression of a novel cytokine, IGIF, which is located near Idd2. J
Clin Invest. 99:469–474. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zaccone P, Phillips J, Conget I, Cooke A
and Nicoletti F: IL-18 binding protein fusion construct delays the
development of diabetes in adoptive transfer and
cyclophosphamide-induced diabetes in NOD mouse. Clin Immunol.
115:74–79. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kruse S, Kuehr J, Moseler M, et al:
Polymorphisms in the IL 18 gene are associated with specific
sensitization to common allergens and allergic rhinitis. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 111:117–122. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cochran WG: The combination of estimates
from different experiments. Biometrics. 10:101–129. 1954.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M and Minder
C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ.
315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
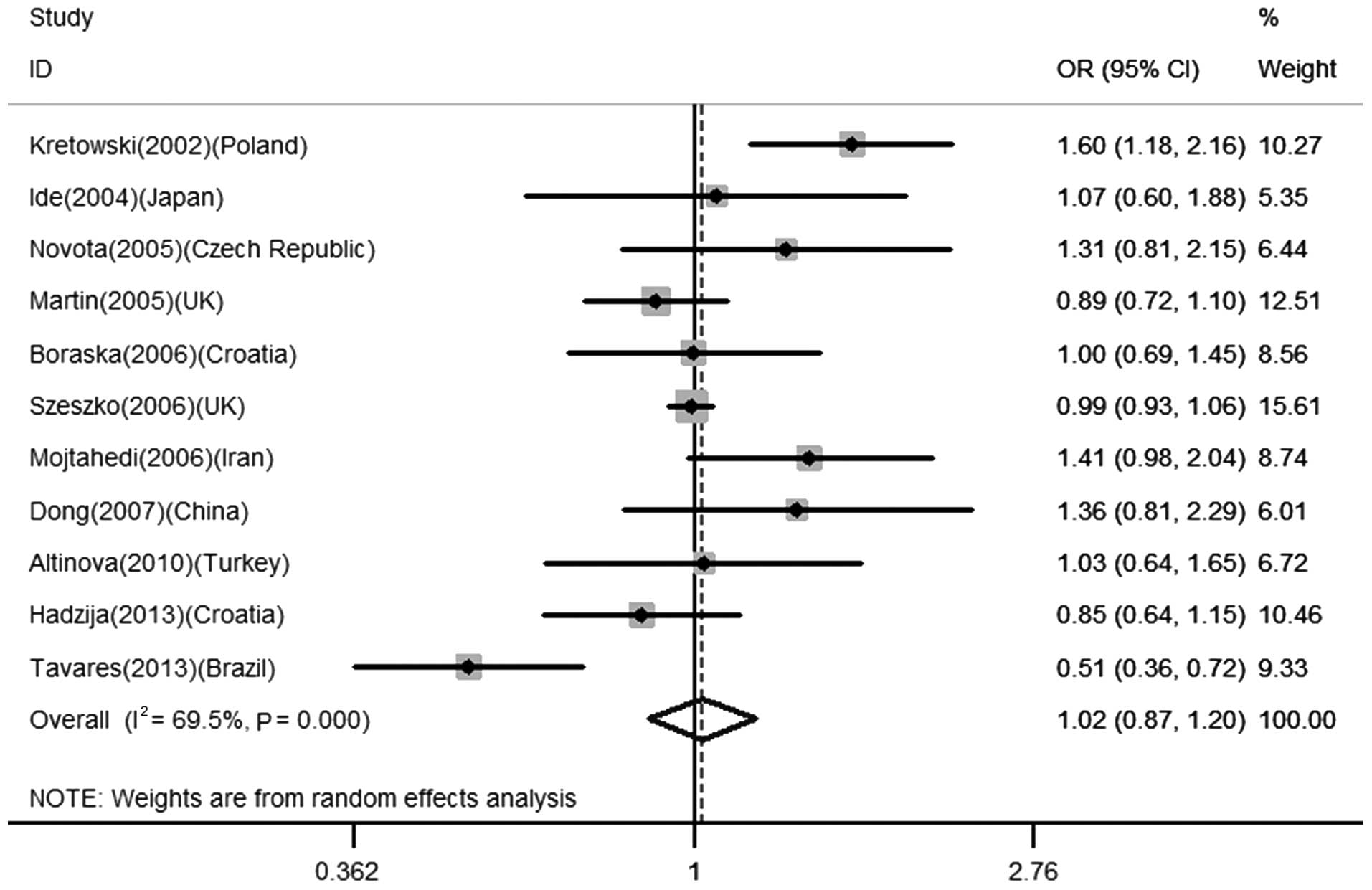
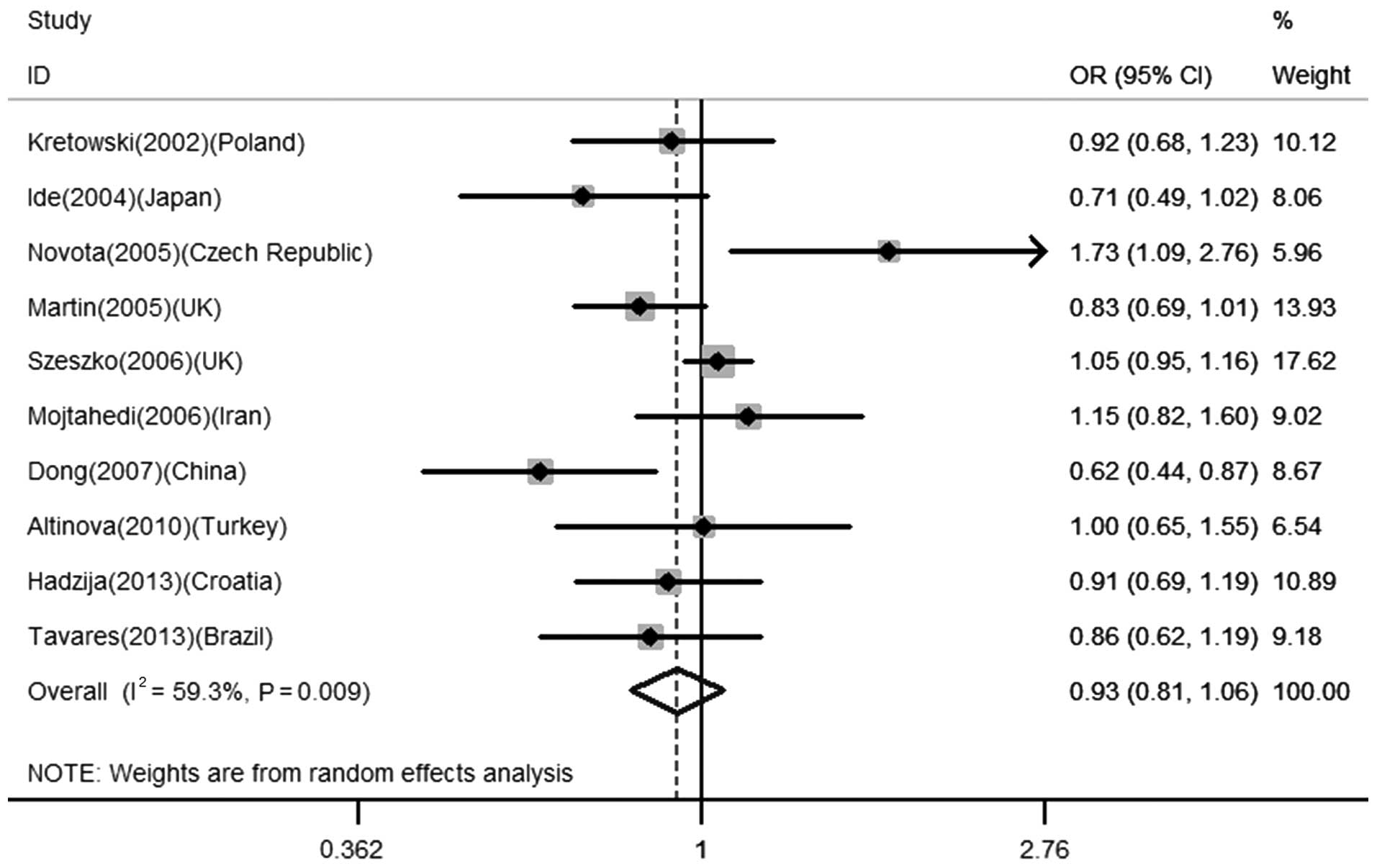
Tavares NA, Santos MM, Moura R, Araújo J,
Guimarães R, Crovella S and Brandão L: Interleukin 18 (IL18) gene
promoter polymorphisms are associated with type 1 diabetes mellitus
in Brazilian patients. Cytokine. 62:286–289. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hadžija MP, Korolija M, Jemin N, et al:
Polymorphisms in the IL-18 and IL-12B genes and their association
with the clinical outcome in Croatian patients with Type 1
diabetes. Gene. 512:477–481. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Altinova AE, Engin D, Akbay E, et al:
Association of polymorphisms in the IL-18 and IL-12 genes with
susceptibility to Type 1 diabetes in Turkish patients. J Endocrinol
Invest. 33:451–454. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boraska V, Terzić J, Skrabić V, et al:
NeuroD1 gene and interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms in type 1
diabetes in Dalmatian population of Southern Croatia. Croat Med J.
47:571–578. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong GP, Yu ZS, Liang L, Zou CC, Fu JF and
Wang CL: IL-18 gene promoter −137C/G and −607C/A polymorphisms in
Chinese Han children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Int J
Immunogenet. 34:75–79. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Ide A, Kawasaki E, Abiru N, et al:
Association between IL-18 gene promoter polymorphisms and CTLA-4
gene 49A/G polymorphism in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes.
J Autoimmun. 22:73–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kretowski A, Mironczuk K, Karpinska A, et
al: Interleukin-18 promoter polymorphisms in type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes. 51:3347–3349. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martin RJ, Savage DA, Carson DJ, Maxwell
AP and Patterson CC: Interleukin 18 promoter polymorphisms are not
strongly associated with type I diabetes in a UK population. Genes
Immun. 6:171–174. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mojtahedi Z, Naeimi S, Farjadian S, Omrani
GR and Ghaderi A: Association of IL-18 promoter polymorphisms with
predisposition to Type 1 diabetes. Diabet Med. 23:235–239. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Novota P, Kolostova K, Pinterova D, et al:
Interleukin IL-18 gene promoter polymorphisms in adult patients
with type 1 diabetes mellitus and latent autoimmune diabetes in
adults. Immunol Lett. 96:247–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Szeszko JS, Howson JM, Cooper JD, et al:
Analysis of polymorphisms of the interleukin-18 gene in type 1
diabetes and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium testing. Diabetes.
55:559–562. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Noble JA and Erlich HA: Genetics of type 1
diabetes. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0077322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bradfield JP, Qu HQ, Wang K, et al: A
genome-wide meta-analysis of six type 1 diabetes cohorts identifies
multiple associated loci. PloS Genet. 7:e10022932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Frigerio S, Hollander GA and Zumsteg U:
Functional IL-18 is produced by primary pancreatic mouse islets and
NIT-1 beta cells and participates in the progression towards
destructive insulitis. Horm Res. 57:94–104. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lukic ML, Mensah-Brown E, Wei X, Shahin A
and Liew FY: Lack of the mediators of innate immunity attenuate the
development of autoimmune diabetes in mice. J Autoimmun.
21:239–246. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Giedraitis V, He B, Huang WX and Hillert
J: Cloning and mutation analysis of the human IL-18 promoter: a
possible role of polymorphisms in expression regulation. J
Neuroimmunol. 112:146–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yoon JW and Jun HS: Role of viruses in the
pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Mellitus.
LeRoith D, Taylor SI and Olefsky JM: 2nd edition. Lippincott
Williams and Wilkins; New York: pp. 575–589. 2004
|
|
34
|
McKinney PA, Okasha M, Parslow RC, et al:
Early social mixing and childhood Type 1 diabetes mellitus: a
case-control study in Yorkshire, UK. Diabet Med. 17:236–242. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thompson SR and Humphries SE:
Interleukin-18 genetics and inflammatory disease susceptibility.
Genes Immun. 8:91–99. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|