|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gunderson K, Wang CY and Wang R: Global
prostate cancer incidence and the migration, settlement, and
admixture history of the Northern Europeans. Cancer Epidemiol.
35:320–327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Wang S, Lin YW, et al:
Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and
the risk of prostate cancer in the Han population of China. Med
Oncol. 29:1964–1971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Giovannucci E, Stampfer MJ, Krithivas K,
et al: The CAG repeat within the androgen receptor gene and its
relationship to prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
94:3320–3323. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Merrill RM and Lyon JL: Explaining the
difference in prostate cancer mortality rates between white and
black men in the United States. Urology. 55:730–735. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Souiden Y, Mahdouani M, Chaieb K, Elkamel
R and Mahdouani K: Polymorphisms of glutathione-S-transferase M1
and T1 and prostate cancer risk in a Tunisian population. Cancer
Epidemiol. 34:598–603. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
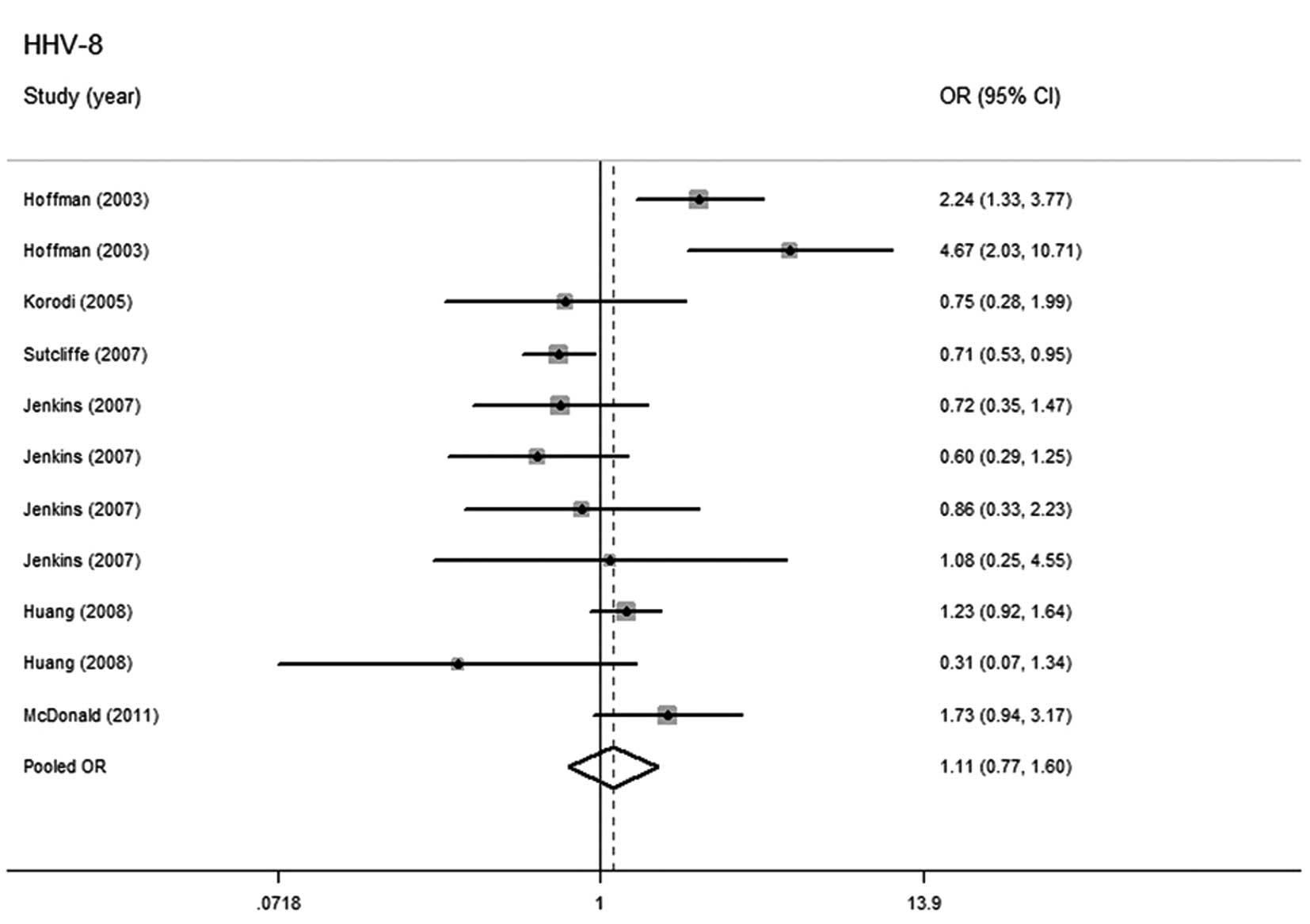
McDonald AC, Jenkins FJ, Bunker CH, Wilson
JW, Patrick AL and Weissfeld JL: A case-cohort study of human
herpesvirus 8 seropositivity and incident prostate cancer in
Tobago. Infect Agent Cancer. 6:252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hoffman LJ, Bunker CH, Pellett PE, et al:
Elevated seroprevalence of human herpesvirus 8 among men with
prostate cancer. J Infect Dis. 189:15–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
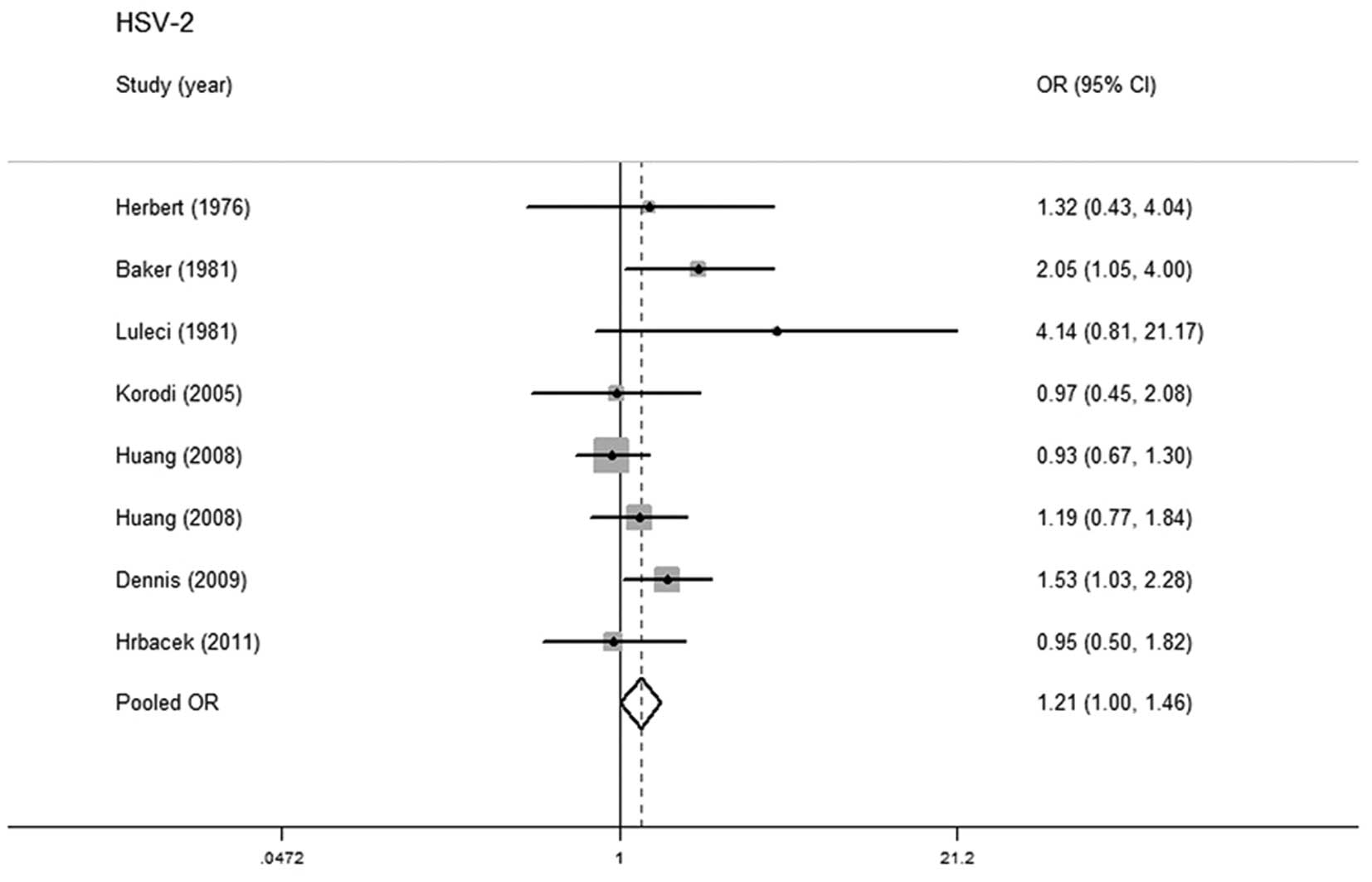
Hrbacek J, Urban M, Hamsikova E, et al:
Serum antibodies against genitourinary infectious agents in
prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia patients: a
case-control study. BMC Cancer. 11:532011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang WY, Hayes R, Pfeiffer R, et al:
Sexually transmissible infections and prostate cancer risk. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:2374–2381. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ewald PW: An evolutionary perspective on
parasitism as a cause of cancer. Adv Parasitol. 68:21–43. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haid M and Sharon N: Immunofluorescent
evidence of prior herpes simplex virus type-2 infection in prostate
carcinoma. Urology. 24:623–625. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dennis LK, Coughlin JA, McKinnon BC, et
al: Sexually transmitted infections and prostate cancer among men
in the U.S. military. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:2665–2671. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Korodi Z, Wang X, Tedeschi R, Knekt P and
Dillner J: No serological evidence of association between prostate
cancer and infection with herpes simplex virus type 2 or human
herpesvirus type 8: a nested case-control study. J Infect Dis.
191:2008–2011. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jenkins FJ, Hayes RB, Jackson A, et al:
Human herpesvirus 8 seroprevalence among prostate cancer case
patients and control subjects. J Infect Dis. 196:208–211. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sutcliffe S, Giovannucci E, Gaydos CA, et
al: Plasma antibodies against Chlamydia trachomatis, human
papillomavirus, and human herpesvirus type 8 in relation to
prostate cancer: a prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 16:1573–1580. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mantel N and Haenszel W: Statistical
aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of
disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 22:719–748. 1959.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fleiss JL: The statistical basis of
meta-analysis. Stat Methods Med Res. 2:121–145. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
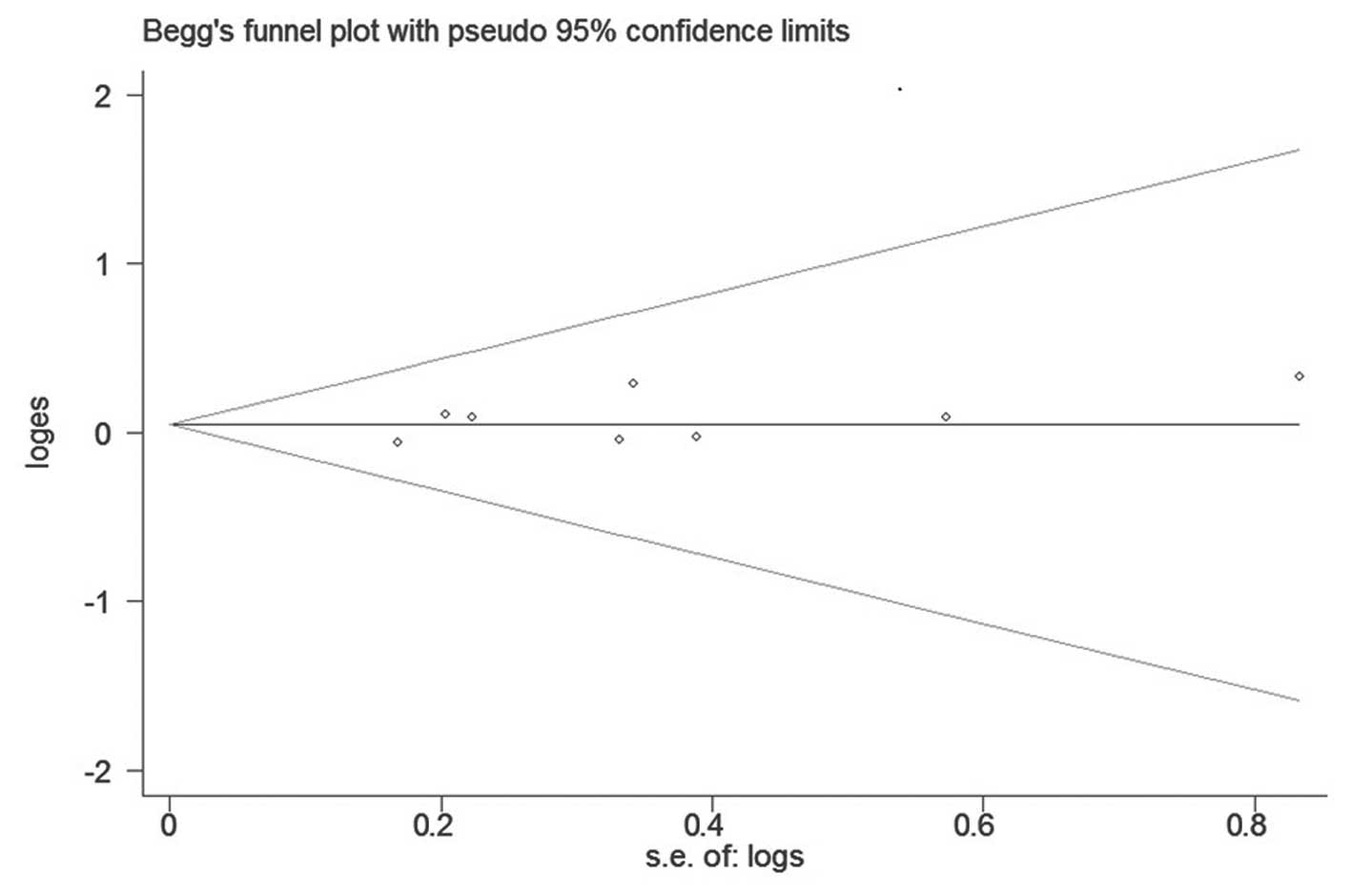
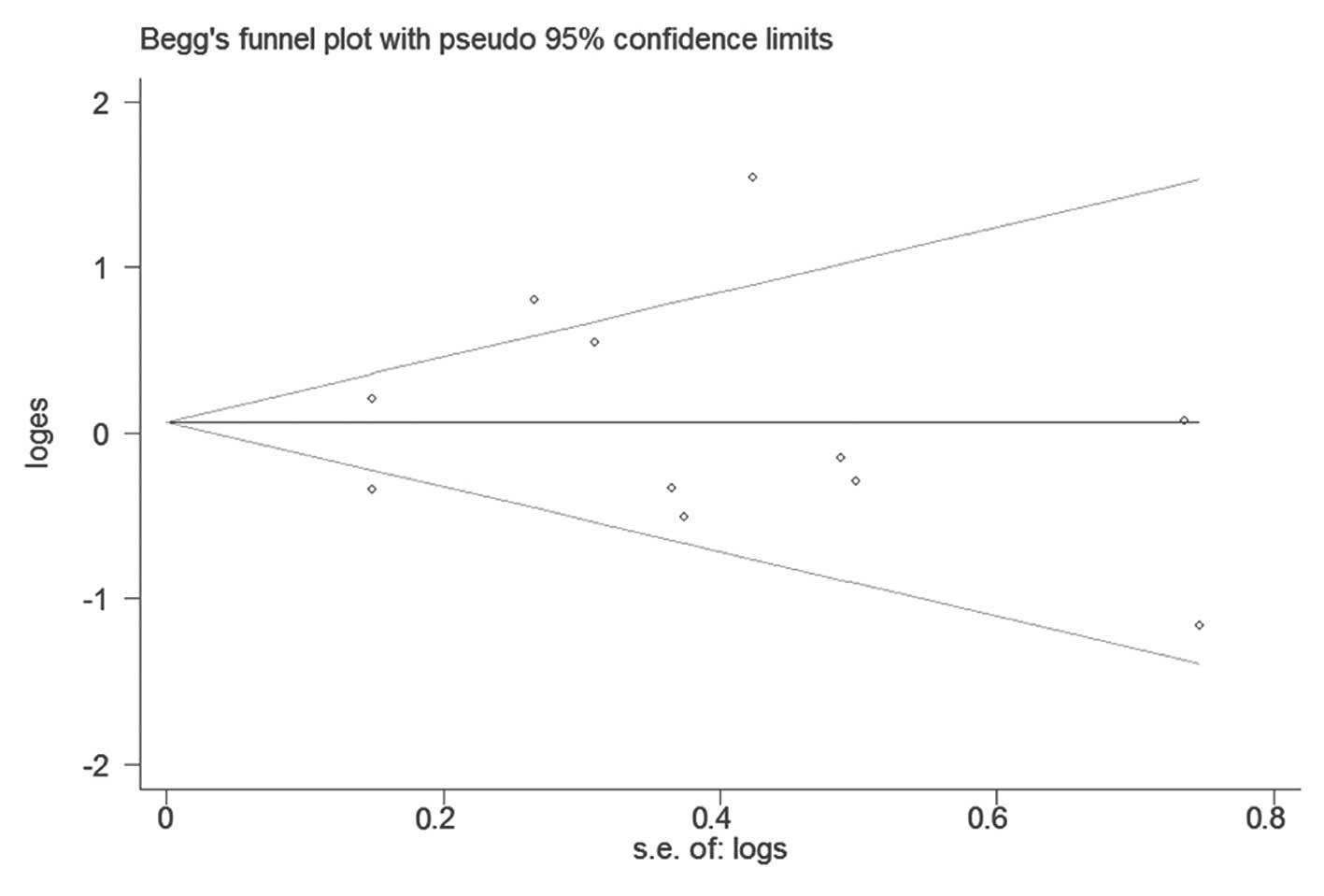
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Begg CB and Mazumdar M: Operating
characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias.
Biometrics. 50:1088–1101. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Herbert JT, Birkhoff JD, Feorino PM and
Caldwell GG: Herpes simplex virus type 2 and cancer of the
prostate. J Urol. 116:611–612. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baker LH, Mebust WK, Chin TD, Chapman AL,
Hinthorn D and Towle D: The relationship of herpesvirus to
carcinoma of the prostate. J Urol. 125:370–374. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luleci G, Sakizli M, Gunalp A, Erkan I and
Remzi D: Herpes simplex type 2 neutralization antibodies in
patients with cancers of urinary bladder, prostate, and cervix. J
Surg Oncol. 16:327–331. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Siracusano F, Tarro G and Biviano D:
TAF-test: a tumor diagnosis device in oncologic urology. Cancer.
50:2215–2217. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Csata S, Dan P, Kulcsar G, Horvath J, Nasz
I and Verebelyi A: Viral examinations in malignant tumours of the
urogenital system. Acta Chir Hung. 25:201–205. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mandel JS and Schuman LM: Sexual factors
and prostatic cancer: results from a case-control study. J
Gerontol. 42:259–264. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sabin AB and Tarro G: Herpes simplex and
herpes genitalis viruses in etiology of some human cancers. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 70:3225–3229. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Marzo AM, Platz EA, Sutcliffe S, et al:
Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:256–269.
2007.
|
|
34
|
Palapattu GS, Sutcliffe S, Bastian PJ, et
al: Prostate carcinogenesis and inflammation: emerging insights.
Carcinogenesis. 26:1170–1181. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Platz EA and De Marzo AM: Epidemiology of
inflammation and prostate cancer. J Urol. 171:S36–S40. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kundu SD, Lee C, Billips BK, et al: The
toll-like receptor pathway: a novel mechanism of infection-induced
carcinogenesis of prostate epithelial cells. Prostate. 68:223–229.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Smith JS and Robinson NJ: Age-specific
prevalence of infection with herpes simplex virus types 2 and 1: a
global review. J Infect Dis. 186(Suppl 1): S3–S28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
National Cancer Institute; Howlader N,
Noone AM, Krapcho M, et al: SEER Cancer Statistics Review,
1975–2009 (Vintage 2009 Populations). http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2009_pops09/uri.
Accessed July 22, 2012.
|
|
39
|
Diamond C, Brodie SJ, Krieger JN, et al:
Human herpesvirus 8 in the prostate glands of men with Kaposi’s
sarcoma. J Virol. 72:6223–6227. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Staskus KA, Zhong W, Gebhard K, et al:
Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus gene expression in
endothelial (spindle) tumor cells. J Virol. 71:715–719. 1997.
|
|
41
|
Monini P, de Lellis L, Fabris M, Rigolin F
and Cassai E: Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus DNA sequences
in prostate tissue and human semen. N Engl J Med. 334:1168–1172.
1996.
|
|
42
|
Rubin MA, Parry JP and Singh B: Kaposi’s
sarcoma associated herpesvirus deoxyribonucleic acid sequences:
lack of detection in prostatic tissue of human immunodeficiency
virus-negative immunocompetent adults. J Urol. 159:146–148.
1998.
|
|
43
|
Diamond C, Huang ML, Kedes DH, et al:
Absence of detectable human herpesvirus 8 in the semen of human
immunodeficiency virus-infected men without Kaposi’s sarcoma. J
Infect Dis. 176:775–777. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Corbellino M, Bestetti G, Galli M and
Parravicini C: Absence of HHV-8 in prostate and semen. N Engl J
Med. 335:1237author reply 1238–1239. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tasaka T, Said JW, Morosetti R, et al: Is
Kaposi’s sarcoma - associated herpesvirus ubiquitous in urogenital
and prostate tissues? Blood. 89:1686–1689. 1997.
|
|
46
|
Moore PS and Chang Y: Kaposi’s
sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Fields’ Virology. 2nd edition.
Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B and
Straus SE: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: pp.
2803–2833. 2001
|
|
47
|
Boldogh I, Baskar JF, Mar EC and Huang ES:
Human cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex type 2 virus in normal and
adenocarcinomatous prostate glands. J Natl Cancer Inst. 70:819–826.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|