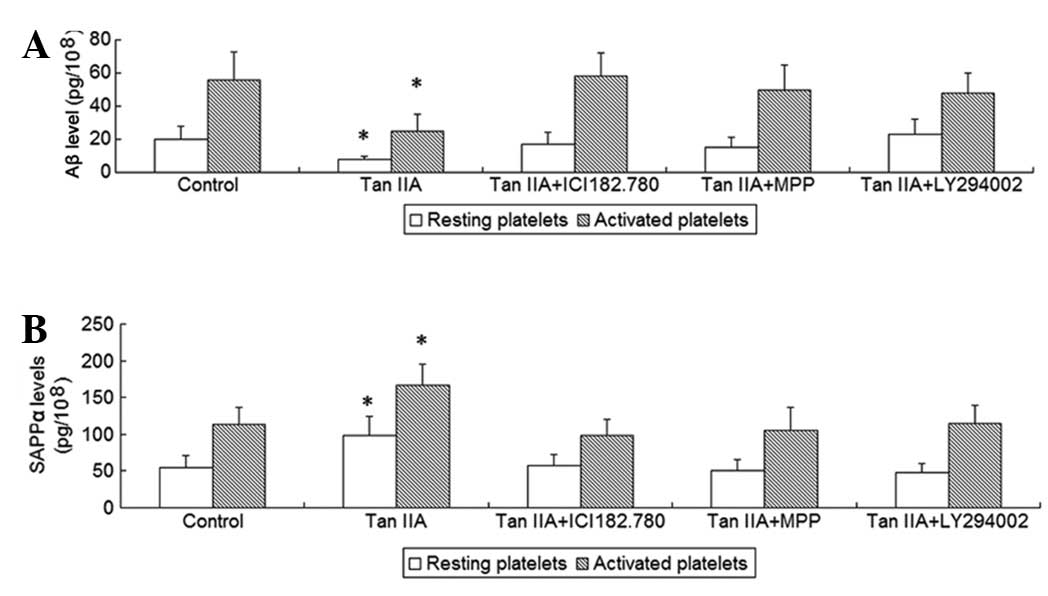
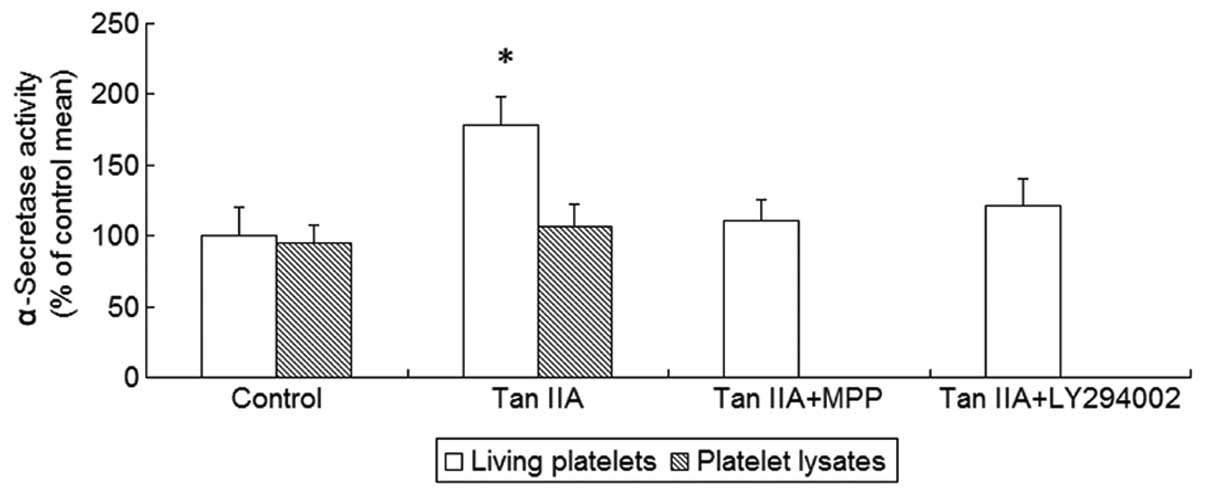
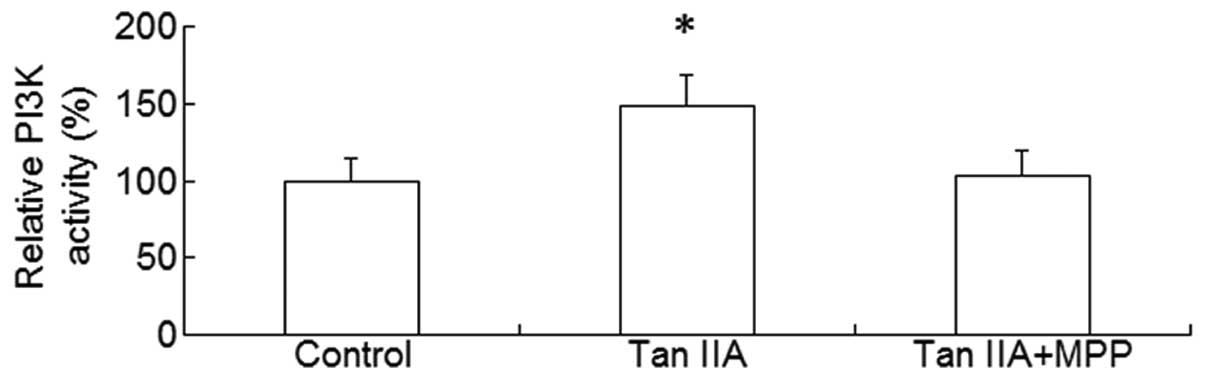
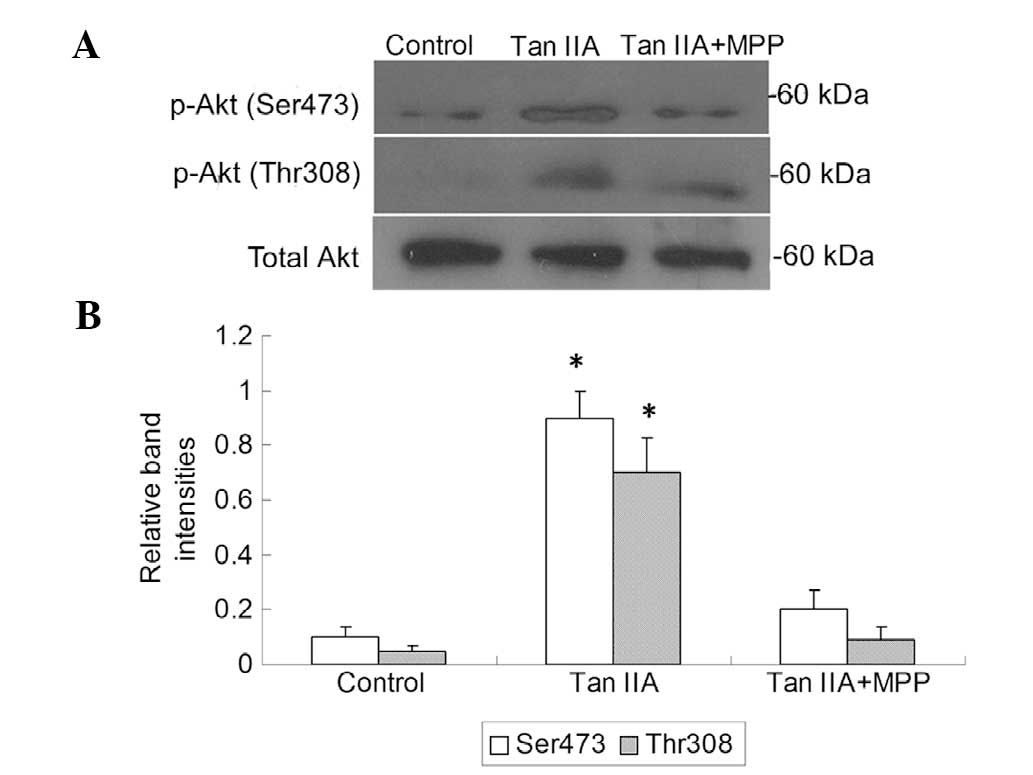
|
1
|
Shi C, Na N, Zhu X and Xu J: Estrogenic
effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on APP processing in post-menopausal
platelets. Platelets. 24:51–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gandy S and DeKosky ST: Toward the
treatment and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease: rational
strategies and recent progress. Annu Rev Med. 64:367–383. 2013.
|
|
3
|
Mandel S, Amit T, Reznichenko L, Weinreb O
and Youdim MB: Green tea catechins as brain-permeable, natural iron
chelators-antioxidants for the treatment of neurodegenerative
disorders. Mol Nutr Food Res. 50:229–234. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li QX, Fuller SJ, Beyreuther K and Masters
CL: The amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease in human
brain and blood. J Leukoc Biol. 66:567–574. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kokjohn TA, Van Vickle GD, Maarouf CL, et
al: Chemical characterization of pro-inflammatory amyloid-beta
peptides in human atherosclerotic lesions and platelets. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1812.1508–1514. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Howlett GJ and Moore KJ: Untangling the
role of amyloid in atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 17:541–547.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan GW, Gao XM, Wang H, et al: The
anti-inflammatory activities of tanshinone IIA, an active component
of TCM, are mediated by estrogen receptor activation and inhibition
of iNOS. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 113:275–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu S, Little PJ, Lan T, et al: Tanshinone
II-A attenuates and stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in
apolipoprotein-E knockout mice fed a high cholesterol diet. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 515:72–79. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao S, Liu Z, Li H, Little PJ, Liu P and
Xu S: Cardiovascular actions and therapeutic potential of
tanshinone IIA. Atherosclerosis. 220:3–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fan G, Zhu Y, Guo H, Wang X, Wang H and
Gao X: Direct vasorelaxation by a novel phytoestrogen tanshinone
IIA is mediated by nongenomic action of estrogen receptor through
endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and calcium
mobilization. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 57:340–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shi C, Zheng DD, Fang L, Wu F, Kwong WH
and Xu J: Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes nonamyloidgenic cleavage of APP
via estrogen receptor signaling to MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1820.453–460. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shi C, Wu F, Xu J and Zou J: Bilobalide
regulates soluble amyloid precursor protein release via
phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase-dependent pathway. Neurochem Int.
59:59–64. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi C, Zheng DD, Wu FM, Liu J and Xu J:
The phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase-glycogen synthase kinase 3β
pathway mediates bilobalide-induced reduction in amyloid β-peptide.
Neurochem Res. 37:298–306. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grove-Strawser D, Boulware MI and
Mermelstein PG: Membrane estrogen receptors activate the
metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR5 and mGluR3 to
bidirectionally regulate CREB phosphorylation in female rat
striatal neurons. Neurosci. 170:1045–1055. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gilad LA and Schwartz B: Association of
estrogen receptor beta with plasma-membrane caveola components:
implication in control of vitamin D receptor. J Mol Endocrinol.
38:603–618. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chambliss KL, Yuhanna IS, Mineo C, et al:
Estrogen receptor alpha and endothelial nitric oxide synthase are
organized into a functional signaling module in caveolae. Circ Res.
87:E44–E52. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Losel RM, Falkenstein E, Feuring M,
Schultz A, Tillmann HC, Rossol-Haseroth K and Wehling M: Nongenomic
steroid action: controversies, questions, and answers. Physiol Rev.
83:965–1016. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Simoncini T, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Brazil DP,
Ley K, Chin WW and Liao JK: Interaction of oestrogen receptor with
the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature.
407:538–541. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|