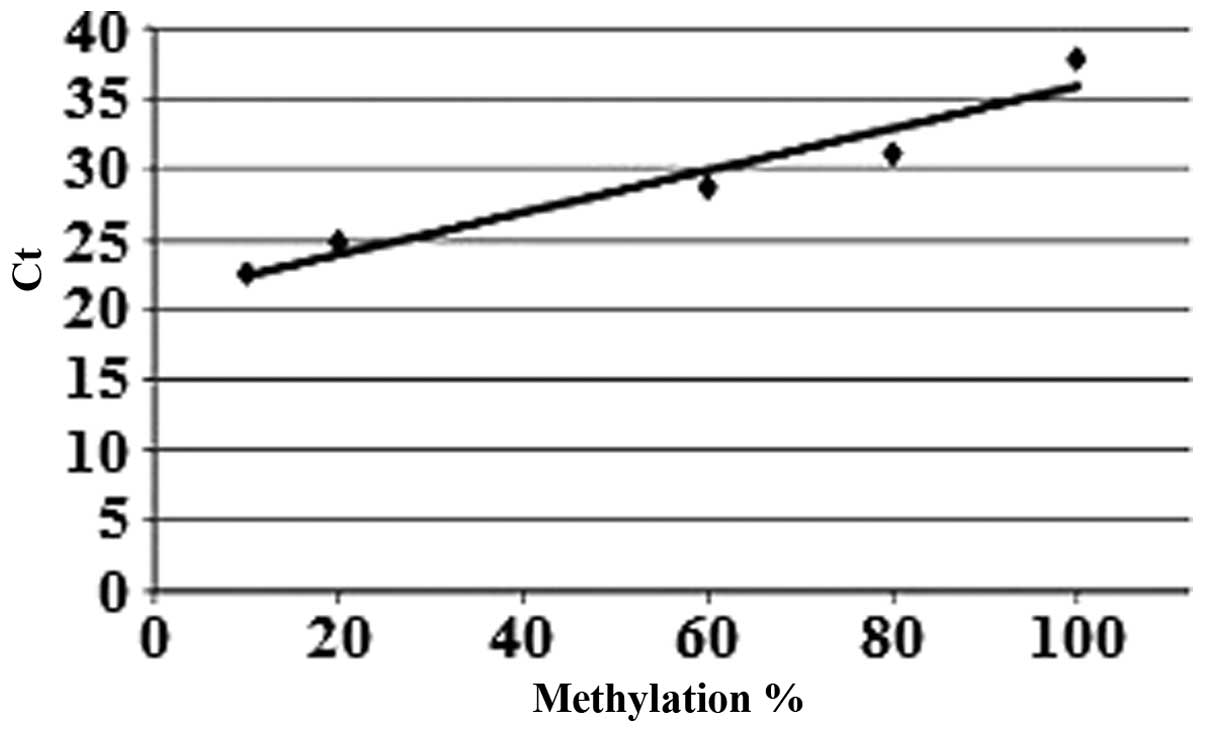
|
1
|
Kawahara TL, Michishita E, Adler AS, et
al: SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to
NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell.
136:62–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McCord RA, Michishita E, Hong T, et al:
SIRT6 stabilizes DNA-dependent protein kinase at chromatin for DNA
double-strand break repair. Aging (Albany NY). 1:109–121.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Michishita E, McCord RA, Berber E, et al:
SIRT6 is a histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylase that modulates telomeric
chromatin. Nature. 452:492–496. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sebastian C, Zwaans BM, Silberman DM, et
al: The histone deacetylase SIRT6 is a tumor suppressor that
controls cancer metabolism. Cell. 151:1185–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mahlknecht U, Ho AD and Voelter-Mahlknecht
S: Chromosomal organization and fluorescence in situ
hybridization of the human sirtuin 6 gene. Int J Oncol. 28:447–456.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tennen RI, Berber E and Chua KF:
Functional dissection of SIRT6: identification of domains that
regulate histone deacetylase activity and chromatin localization.
Mech Ageing Dev. 131:185–192. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mao Z, Hine C, Tian X, et al: SIRT6
promotes DNA repair under stress by activating PARP1. Science.
332:1443–1446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cardus A, Uryga AK, Walters G and
Erusalimsky JD: SIRT6 protects human endothelial cells from DNA
damage, telomere dysfunction, and senescence. Cardiovasc Res.
97:571–579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaidi A, Weinert BT, Choudhary C and
Jackson SP: Human SIRT6 promotes DNA end resection through CtIP
deacetylation. Science. 329:1348–1353. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mostoslavsky R, Chua KF, Lombard DB, et
al: Genomic instability and aging-like phenotype in the absence of
mammalian SIRT6. Cell. 124:315–329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burnett C, Valentini S, Cabreiro F, et al:
Absence of effects of Sir2 overexpression on lifespan in C.
elegans and Drosophila. Nature. 477:482–485. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kanfi Y, Naiman S, Amir G, et al: The
sirtuin SIRT6 regulates lifespan in male mice. Nature. 483:218–221.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Moschen AR, Wieser V, Gerner RR, et al:
Adipose tissue and liver expression of SIRT1, 3, and 6 increase
after extensive weight loss in morbid obesity. J Hepatol.
59:1315–1322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee OH, Kim J, Kim JM, et al: Decreased
expression of sirtuin 6 is associated with release of high mobility
group box-1 after cerebral ischemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:388–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kundu TK and Rao MR: CpG islands in
chromatin organization and gene expression. J Biochem. 125:217–222.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Michishita E, Park JY, Burneskis JM,
Barrett JC and Horikawa I: Evolutionarily conserved and
nonconserved cellular localizations and functions of human SIRT
proteins. Mol Biol Cell. 16:4623–4635. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren Y, Shan TZ, Zhu LN, Wu T, Guo J and
Wang YZ: Effect of breed on the expression of sirtuins (Sirt1–7 and
antioxidant capacity in porcine brain. Animal. 7:1994–1998.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Ghiraldini FG, Crispim AC and Mello ML:
Effects of hyperglycemia and aging on nuclear sirtuins and DNA
damage of mouse hepatocytes. Mol Biol Cell. 24:2467–2476. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koltai E, Szabo Z, Atalay M, et al:
Exercise alters SIRT1, SIRT6, NAD and NAMPT levels in skeletal
muscle of aged rats. Mech Ageing Dev. 131:21–28. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakahata Y, Sahar S, Astarita G, Kaluzova
M and Sassone-Corsi P: Circadian control of the
NAD+salvage pathway by CLOCK-SIRT1. Science.
324:654–657. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bellet MM and Sassone-Corsi P: Mammalian
circadian clock and metabolism - the epigenetic link. J Cell Sci.
123:3837–3848. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HS, Xiao C, Wang RH, et al:
Hepatic-specific disruption of SIRT6 in mice results in fatty liver
formation due to enhanced glycolysis and triglyceride synthesis.
Cell Metab. 12:224–236. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marquardt JU, Fischer K, Baus K, et al:
Sirtuin-6-dependent genetic and epigenetic alterations are
associated with poor clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Hepatology. 58:1054–1064. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ban N, Ozawa Y, Inaba T, Miyake S,
Watanabe M, Shinmura K and Tsubota K: Light-dark condition
regulates sirtuin mRNA levels in the retina. Exp Gerontol.
48:1212–1217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kanfi Y, Shalman R, Peshti V, et al:
Regulation of SIRT6 protein levels by nutrient availability. FEBS
Lett. 582:543–548. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|