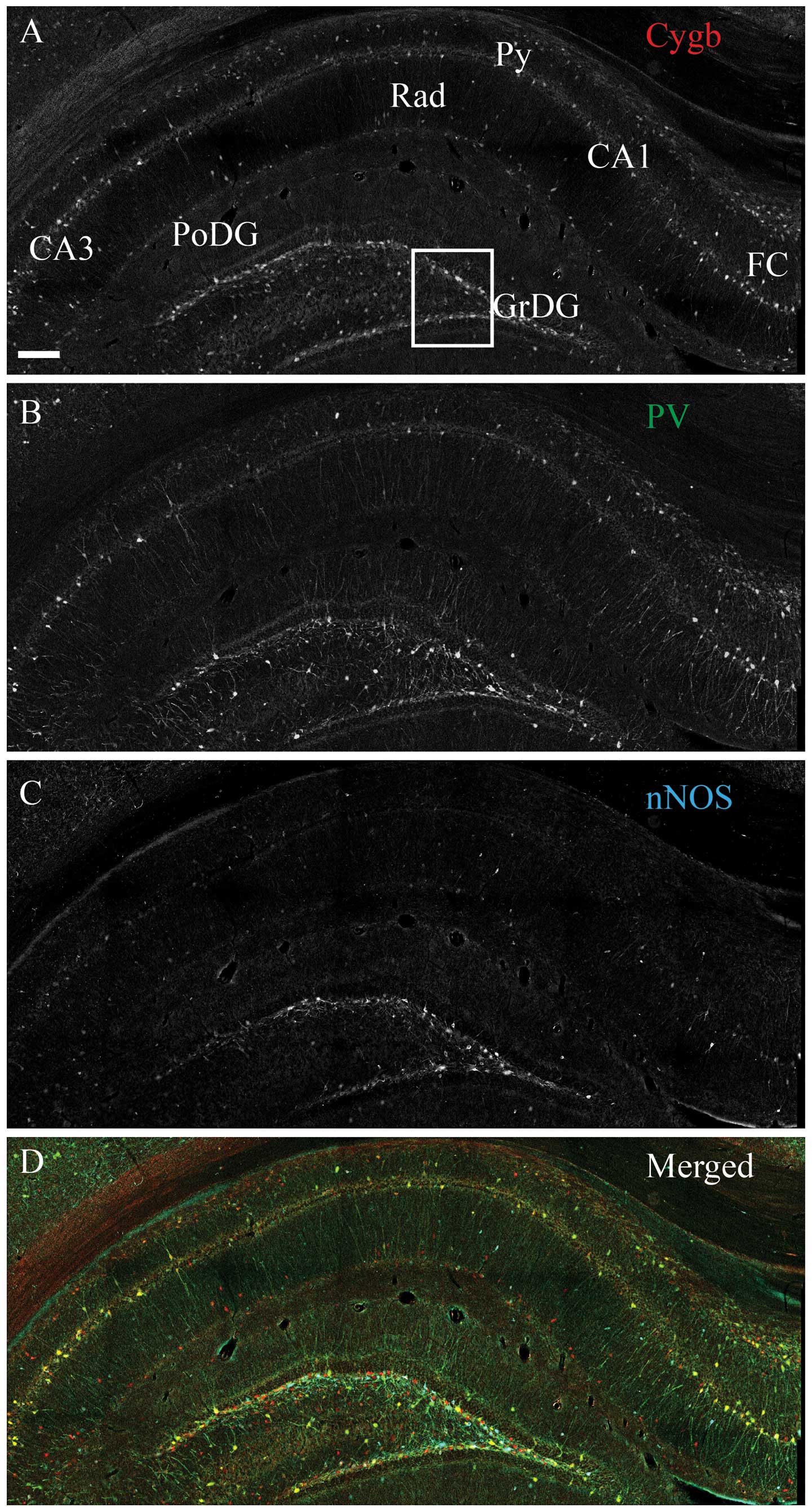
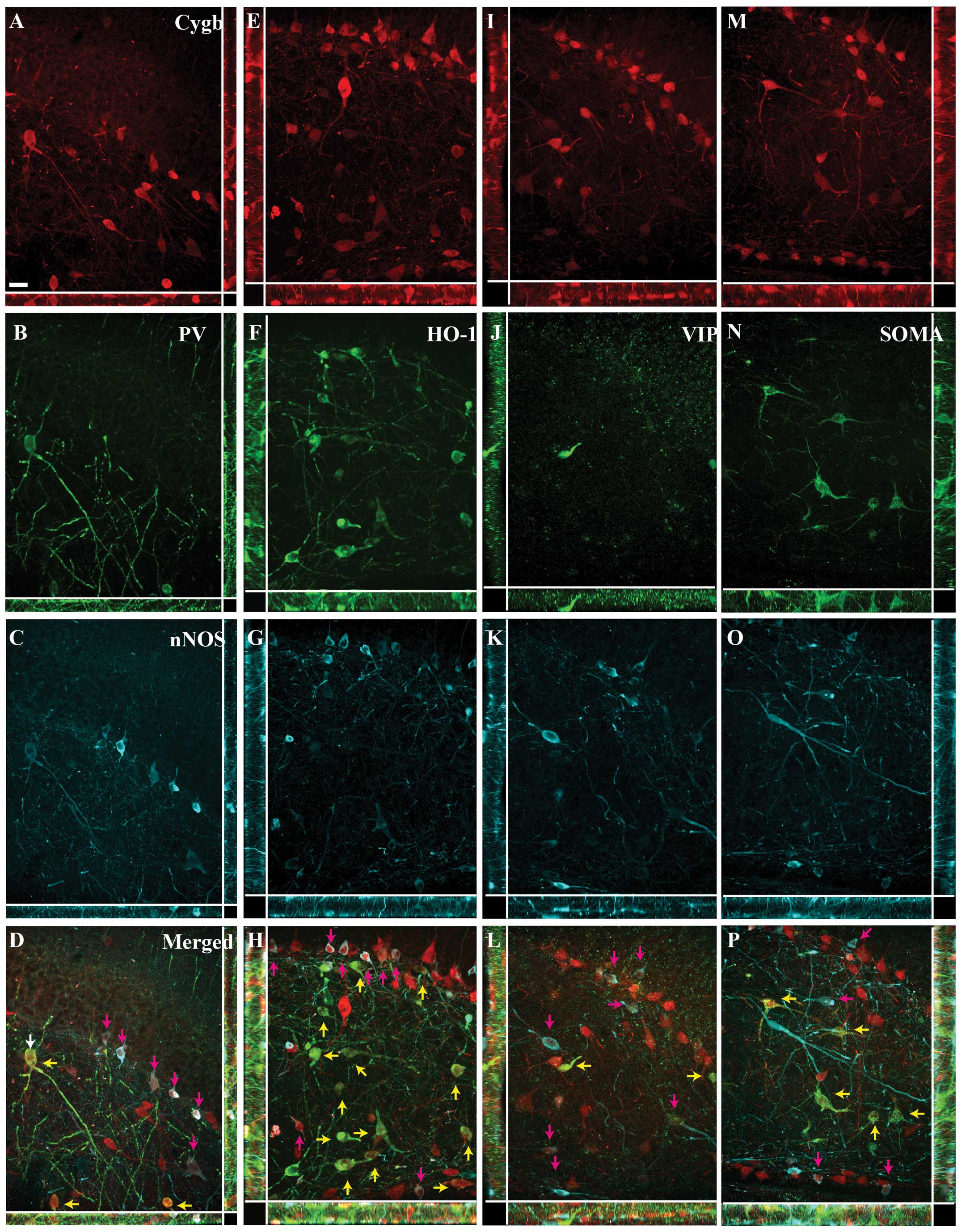
|
1
|
McEwen BS: Physiology and neurobiology of
stress and adaptation: central role of the brain. Physiol Rev.
87:873–904. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hampel H, Bürger K, Teipel SJ, Bokde AL,
Zetterberg H and Blennow K: Core candidate neurochemical and
imaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement.
4:38–48. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Harrison PJ: The hippocampus in
schizophrenia: a review of the neuropathological evidence and its
pathophysiological implications. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
174:151–162. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Michaelis EK: The Clinical Neurobiology Of
The Hippocampus: An Integrative View. Bartsch T: Oxford University
Press; Oxford; pp. 59–70. 2012
|
|
5
|
Burmester T, Ebner B, Weich B and Hankeln
T: Cytoglobin: a novel globin type ubiquitously expressed in
vertebrate tissues. Mol Biol Evol. 19:416–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trent JT III and Hargrove MS: A
ubiquitously expressed human hexacoordinate hemoglobin. J Biol
Chem. 277:19538–19545. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fago A, Hundahl C, Malte H and Weber RE:
Functional properties of neuroglobin and cytoglobin. Insights into
the ancestral physiological roles of globins. IUBMB Life.
56:689–696. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmidt M, Gerlach F, Avivi A, et al:
Cytoglobin is a respiratory protein in connective tissue and
neurons, which is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem.
279:8063–8069. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hundahl CA, Allen GC, Hannibal J, et al:
Anatomical characterization of cytoglobin and neuroglobin mRNA and
protein expression in the mouse brain. Brain Res. 1331:58–73. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hundahl CA, Hannibal J, Fahrenkrug J,
Dewilde S and Hay-Schmidt A: Neuroglobin expression in the rat
suprachiasmatic nucleus: colocalization, innervation, and response
to light. J Comp Neurol. 518:1556–1569. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mammen PP, Shelton JM, Ye Q, et al:
Cytoglobin is a stress-responsive hemoprotein expressed in the
developing and adult brain. J Histochem Cytochem. 54:1349–1361.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hundahl CA, Kelsen J and Hay-Schmidt A:
Neuroglobin and cytoglobin expression in the human brain. Brain
Struct Funct. 218:603–609. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hundahl CA, Elfving B, Müller HK,
Hay-Schmidt A and Wegener G: A gene-environment study of cytoglobin
in the human and rat hippocampus. PLoS One. 8:e632882013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fordel E, Thijs L, Martinet W, Schrijvers
D, Moens L and Dewilde S: Anoxia or oxygen and glucose deprivation
in SH-SY5Y cells: a step closer to the unraveling of neuroglobin
and cytoglobin functions. Gene. 398:114–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fordel E, Thijs L, Moens L and Dewilde S:
Neuroglobin and cytoglobin expression in mice. Evidence for a
correlation with reactive oxygen species scavenging. FEBS J.
274:1312–1317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li D, Chen XQ, Li WJ, Yang YH, Wang JZ and
Yu AC: Cytoglobin up-regulated by hydrogen peroxide plays a
protective role in oxidative stress. Neurochem Res. 32:1375–1380.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hodges NJ, Innocent N, Dhanda S and Graham
M: Cellular protection from oxidative DNA damage by over-expression
of the novel globin cytoglobin in vitro. Mutagenesis. 23:293–298.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gardner AM, Cook MR and Gardner PR:
Nitric-oxide dioxygenase function of human cytoglobin with cellular
reductants and in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 285:23850–23857.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Halligan KE, Jourd’heuil FL and
Jourd’heuil D: Cytoglobin is expressed in the vasculature and
regulates cell respiration and proliferation via nitric oxide
dioxygenation. J Biol Chem. 284:8539–8547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singh S, Canseco DC, Manda SM, et al:
Cytoglobin modulates myogenic progenitor cell viability and muscle
regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:E129–E138. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tian SF, Yang HH, Xiao DP, et al:
Mechanisms of neuroprotection from hypoxia-ischemia (HI) brain
injury by up-regulation of cytoglobin (CYGB) in a neonatal rat
model. J Biol Chem. 288:15988–16003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Raida Z, Reimets R, Hay-Schmidt A and
Hundahl CA: Effect of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion on
Cytoglobin expression in the mouse brain. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 424:274–278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hundahl CA, Fahrenkrug J, Hay-Schmidt A,
Georg B, Faltoft B and Hannibal J: Circadian behaviour in
neuroglobin deficient mice. PLoS One. 7:e344622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hao MM, Bornstein JC and Young HM:
Development of myenteric cholinergic neurons in ChAT-Cre;R26R-YFP
mice. J Comp Neurol. 521:3358–3370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan H and Keast JR: Neurturin regulates
postnatal differentiation of parasympathetic pelvic ganglion
neurons, initial axonal projections, and maintenance of terminal
fields in male urogenital organs. J Comp Neurol. 507:1169–1183.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cox DJ and Racca C: Differential dendritic
targeting of AMPA receptor subunit mRNAs in adult rat hippocampal
principal neurons and interneurons. J Comp Neurol. 521:1954–2007.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spiegel AM, Koh MT, Vogt NM, Rapp PR and
Gallagher M: Hilar interneuron vulnerability distinguishes aged
rats with memory impairment. J Comp Neurol. 521:3508–3523. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fahrenkrug J, Buhl T and Hannibal J:
PreproPACAP-derived peptides occur in VIP-producing tumours and
co-exist with VIP. Regul Pept. 58:89–98. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schwaller B, Dick J, Dhoot G, et al:
Prolonged contraction-relaxation cycle of fast-twitch muscles in
parvalbumin knockout mice. Am J Physiol. 276:C395–C403.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stephenson-Jones M, Ericsson J, Robertson
B and Grillner S: Evolution of the basal ganglia: dual-output
pathways conserved throughout vertebrate phylogeny. J Comp Neurol.
520:2957–2973. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hundahl CA, Kelsen J, Dewilde S and
Hay-Schmidt A: Neuroglobin in the rat brain (II): co-localisation
with neurotransmitters. Neuroendocrinology. 88:183–198. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Burmester T and Hankeln T: Function and
evolution of vertebrate globins. Acta Physiol (Oxf). May
8–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
33
|
Hundahl CA, Luuk H, Ilmjärv S, et al:
Neuroglobin-deficiency exacerbates Hif1A and c-FOS response, but
does not affect neuronal survival during severe hypoxia in vivo.
PLoS One. 6:e281602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schipper HM: Heme oxygenase-1: transducer
of pathological brain iron sequestration under oxidative stress.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1012:84–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Verret L, Mann EO, Hang GB, et al:
Inhibitory interneuron deficit links altered network activity and
cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer model. Cell. 149:708–721. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takahashi H, Brasnjevic I, Rutten BP, et
al: Hippocampal interneuron loss in an APP/PS1 double mutant mouse
and in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Struct Funct. 214:145–160.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Brady DR and Mufson EJ:
Parvalbumin-immunoreactive neurons in the hippocampal formation of
Alzheimer’s diseased brain. Neuroscience. 80:1113–1125.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Popović M, Caballero-Bleda M, Kadish I and
Van Groen T: Subfield and layer-specific depletion in
calbindin-D28K, calretinin and parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the
dentate gyrus of amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 transgenic
mice. Neuroscience. 155:182–191. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schipper HM, Cissé S and Stopa EG:
Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in the senescent and
Alzheimer-diseased brain. Ann Neurol. 37:758–768. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schipper HM: Heme oxygenase-1: role in
brain aging and neurodegeneration. Exp Gerontol. 35:821–830. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schipper HM: Glial HO-1 expression, iron
deposition and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases.
Neurotox Res. 1:57–70. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Beal MF: Metabolic disorders and
neurotoxicology. Curr Opin Neurol. 8:467–468. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dournaud P, Cervera-Pierot P, Hirsch E, et
al: Somatostatin messenger RNA-containing neurons in Alzheimer’s
disease: an in situ hybridization study in hippocampus,
parahippocampal cortex and frontal cortex. Neuroscience.
61:755–764. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rossor MN, Emson PC, Mountjoy CQ, Roth M
and Iversen LL: Reduced amounts of immunoreactive somatostatin in
the temporal cortex in senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neurosci
Lett. 20:373–377. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Delgado M, Varela N and Gonzalez-Rey E:
Vasoactive intestinal peptide protects against beta-amyloid-induced
neurodegeneration by inhibiting microglia activation at multiple
levels. Glia. 56:1091–1103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Delgado M and Ganea D: Neuroprotective
effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in a mouse model of
Parkinson’s disease by blocking microglial activation. FASEB J.
17:944–946. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Offen D, Sherki Y, Melamed E, Fridkin M,
Brenneman DE and Gozes I: Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)
prevents neurotoxicity in neuronal cultures: relevance to
neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 854:257–262.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Thuy le TT, Morita T, Yoshida K, et al:
Promotion of liver and lung tumorigenesis in DEN-treated
cytoglobin-deficient mice. Am J Pathol. 179:1050–1060.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|