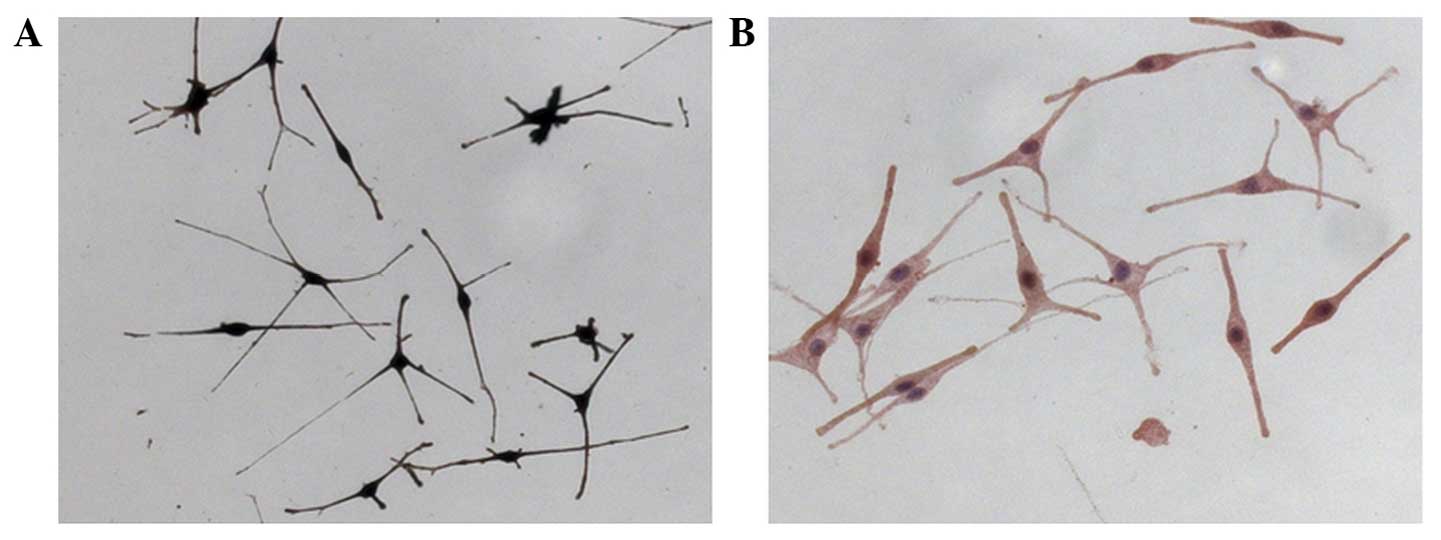
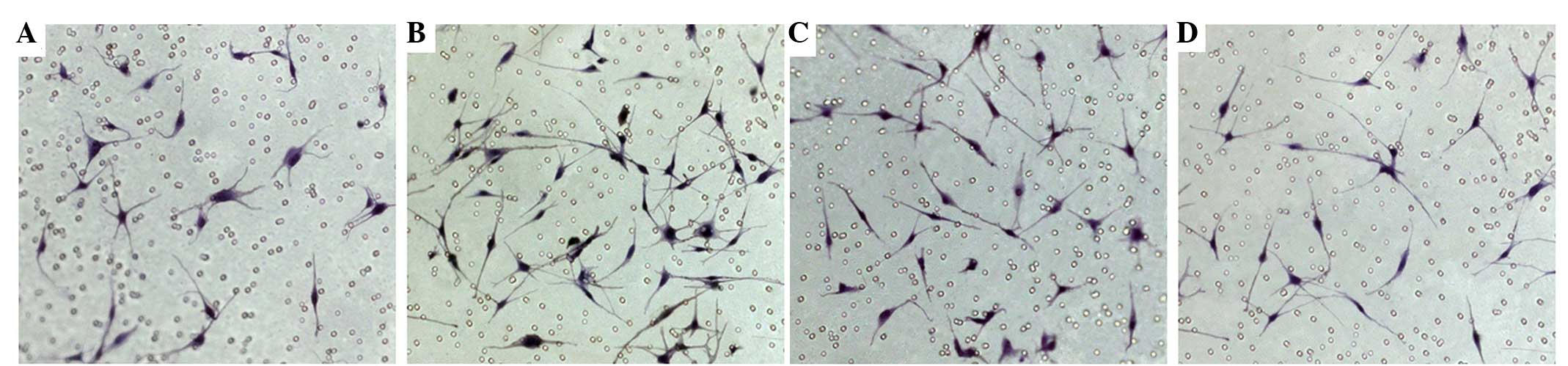
|
1
|
Moretti S, Spallanzani A, Amato L,
Hautmann G, Gallerani I, Fabiani M and Fabbri P: New insights into
the pathogenesis of vitiligo: Imbalance of epidermal cytokines at
sites of lesions. Pigment Cell Res. 15:87–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yoshida H, Kunisada T, Grimm T, Nishimura
EK, Nishioka E and Nishikawa SI: Review: Melanocyte migration and
survival controlled by SCF/c-kit expression. J Investig Dermatol
Symp Proc. 6:1–5. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vickaryous MK and Hall BK: Human cell type
diversity, evolution, development, and classification with special
reference to cells derived from the neural crest. Biol Rev Camb
Philos Soc. 81:425–455. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng M and Hu ZH: The Ligustrum
biological and chemical composition of progress. Chin Tradit Herbal
Drugs. 41:1219–1221. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Tian LT, Ma L and Du NS: Survey of
pharmacology of oleanolic acid. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
27:884–886, 901. 2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chouaïb K, Hichri F, Nguir A, Daami-Remadi
M, Elie N, Touboul D, Ben Jannet H and Hamza MA: Semi-synthesis of
new antimicrobial esters from the natural oleanolic and maslinic
acids. Food Chem. 183:8–17. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hoek-van den Hil EF, van Schothorst EM,
van der Stelt I, Hollman PC, Keijer J and Rietjens IM: Quercetin
tests negative for genotoxicity in transcriptome analyses of liver
and small intestine of mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 81:34–39. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wiczkowski W, Szawara-Nowak D, Topolska J,
et al: Metabolites of dietary quercetin: Profile, isolation,
identification, and antioxidant capacity. J Funct Foods.
11:121–129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cai LV and Zhang J: Pharmacological
effects of the quercetin. World Phytomedicines. 20:108–112.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Liu ZL, Tu CX, Ren F and Lin XR: Research
the role of the 56 herbs alcohol extract to tyrosinase activity and
animals pigments. Chin J Dermatol. 34:284–285. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Chang SB, Xu AE, Li YW, Zhang DM and Wei
XD: Effects of extracts from seven kinds of traditional Chinese
medicine on the proliferation and melanogenesis of a melanocyte
cell line B10BR by interaction with HaCaT cells. Chin J Dermatol.
40:409–411. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Zhang DM, Li YW, Wei XD and Xu AE: Effects
of Fructus Ligustri Lucidi on the tyrosinase activity and
melanogenesis of cultured human melanocytes. Chin J Dermatol.
39:197–199. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Takeyama R, Takekoshi S, Nagata H, Osamura
RY and Kawana S: Quercetin-induced melanogenesis in a reconstituted
three-dimensional human epidermal model. J Mol Histol. 35:157–165.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagata H, Takekoshi S, Takeyama R, Homma T
and Yoshiyuki Osamura R: Quercetin enhances melanogenesis by
increasing the activity and synthesis of tyrosinase in human
melanoma cells and in normal human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res.
17:66–73. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nylander K, Bourdon JC, Bray SE, Gibbs NK,
Kay R, Hart I and Hall PA: Transcriptional activation of tyrosinase
and TRP-1 by p53 links UV irradiation to the protective tanning
response. J Pathol. 190:39–46. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Plaumann B, Fritsche M, Rimpler H,
Brandner G and Hess RD: Flavonoids activate wild-type p53.
Oncogene. 13:1605–1614. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ma HJ, Yue XZ, Wang DG, Li CR and Zhu WY:
A modified method for purifying amelanotic melanocytes from human
hair follicles. J Dermatol. 33:239–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cui J, Shen LY and Wang GC: Role of hair
follicles in the repigmentation of vitiligo. J Invest Dermatol.
97:410–416. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miao L: Review: Cell movement, cell
migration, and cytoskeletal research progress. Acta Biophys Sin.
23:281–288. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Chen HQ, Tian W, Chen YS, Li L, Raum J and
Sung KL: Effect of steady and oscillatory shear stress on F-actin
content and distribution in neutrophils. Biorheology. 41:655–664.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wehrle-Haller B: The role of Kit-ligand in
melanocyte development and epidermal homeostasis. Pigment Cell Res.
16:287–296. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|