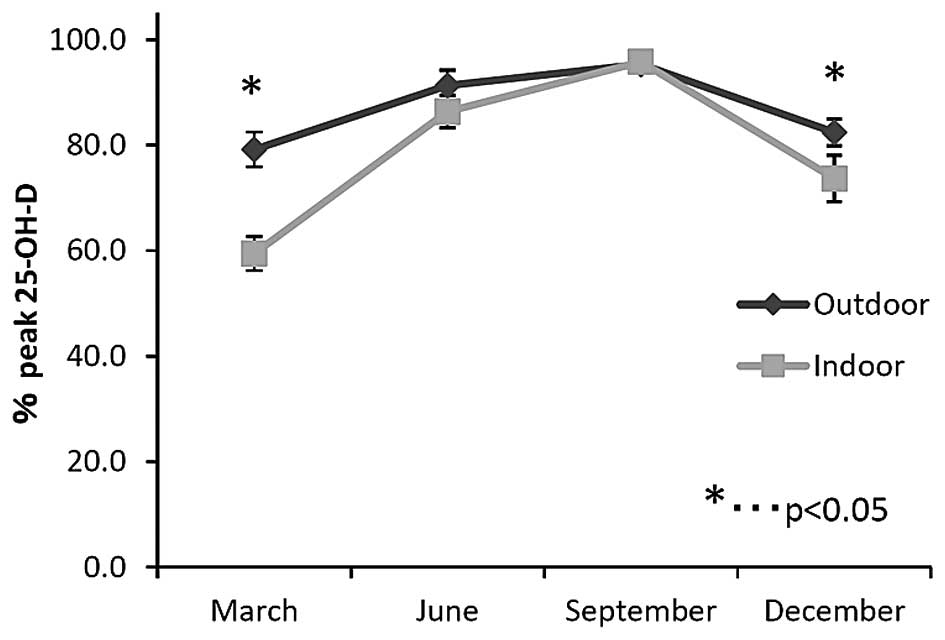
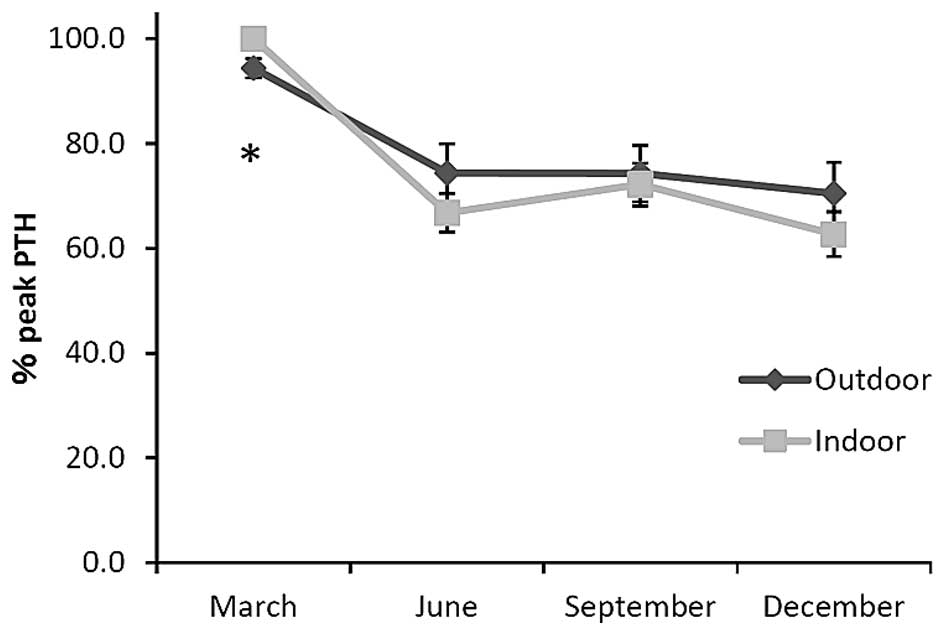
|
1
|
Orito S, Kuroda T, Onoe Y, Sato Y and Ohta
H: Age-related distribution of bone and skeletal parameters in
1,322 Japanese young women. J Bone Miner Metab. 27:698–704. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mithal A, Wahl DA, Bonjour JP, Burckhardt
P, Dawson-Hughes B, Eisman JA, El-Hajj Fuleihan G, Josse RG, Lips P
and Morales-Torres J: IOF Committee of Scientific Advisors (CSA)
Nutrition Working Group: Global vitamin D status and determinants
of hypovitaminosis D. Osteoporos Int. 20:1807–1820. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakamura K, Nashimoto M, Tsuchiya Y, Obata
A, Miyanishi K and Yamamoto M: Vitamin D insufficiency in Japanese
female college students: A preliminary report. Int J Vitam Nutr
Res. 71:302–305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakamura K, Nashimoto M, Matsuyama S and
Yamamoto M: Low serum concentrations of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in
young adult Japanese women: A cross sectional study. Nutrition.
17:921–925. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Foo LH, Zhang Q, Zhu K, Ma G, Trube A,
Greenfield H and Fraser DR: Relationship between vitamin D status,
body composition and physical exercise of adolescent girls in
Beijing. Osteoporos Int. 20:417–425. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Courteix D, Lespessailles E, Peres SL,
Obert P, Germain P and Benhamou CL: Effect of physical training on
bone mineral density in prepubertal girls: A comparative study
between impact-loading and non-impact-loading sports. Osteoporos
Int. 8:152–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Creighton DL, Morgan AL, Boardley D and
Brolinson PG: Weight-bearing exercise and markers of bone turnover
in female athletes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 90:565–570.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohta H, Kuroda T, Onoe Y, Orito S, Ohara
M, Kume M, Harada A, Tsugawa N, Okano T and Sasaki S: The impact of
lifestyle factors on serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels: A
cross-sectional study in Japanese women aged 19–25 years. J Bone
Miner Metab. 27:682–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lovell G: Vitamin D status of females in
an elite gymnastics program. Clin J Sport Med. 18:159–161. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Constantini NW, Arieli R, Chodick G and
Dubnov-Raz G: High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in
athletes and dancers. Clin J Sport Med. 20:368–371. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ono Y, Suzuki A, Kotake M, Zhang X,
Nishiwaki-Yasuda K, Ishiwata Y, Imamura S, Nagata M, Takamoto S and
Itoh M: Seasonal changes of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and intact
parathyroid hormone levels in a normal Japanese population. J Bone
Miner Metab. 23:147–151. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Halliday TM, Peterson NJ, Thomas JJ,
Kleppinger K, Hollis BW and Larson-Meyer DE: Vitamin D status
relative to diet, lifestyle, injury, and illness in college
athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 43:335–343. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sasaki M, Harata S, Kumazawa Y, Mita R,
Kida K and Tsuge M: Bone mineral density and osteo sono assessment
index in adolescents. J Orthop Sci. 5:185–191. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong Y, Pollock N, Stallmann-Jorgensen IS,
Gutin B, Lan L, Chen TC, Keeton D, Petty K, Holick MF and Zhu H:
Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in adolescents: Race, season,
adiposity, physical activity, and fitness. Pediatrics.
125:1104–1111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hamilton B, Grantham J, Racinais S and
Chalabi H: Vitamin D deficiency is endemic in Middle Eastern
sportsmen. Public Health Nutr. 13:1528–1534. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bolland MJ, Grey AB, Ames RW, Mason BH,
Horne AM, Gamble GD and Reid IR: The effects of seasonal variation
of 25-hydroxyvitamin D and fat mass on a diagnosis of vitamin D
sufficiency. Am J Clin Nutr. 86:959–964. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patterson KY, Phillips KM, Horst RL,
Byrdwell WC, Exler J, Lemar LE and Holden JM: Vitamin D content and
variability in fluid milks from a US Department of Agriculture
nationwide sampling to update values in the National Nutrient
Database for Standard Reference. J Dairy Sci. 93:5082–5090. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and
Fisheries: Fisheries of Japan-FY2011 (2011/2012) Fisheries Policy
Outline for FY2012 (White Paper on Fisheries: Summary). http://www.jfa.maff.go.jp/j/kikaku/wpaper/pdf/2011_jfa_wp.pdf
|
|
19
|
Ministry of Health: Labour and Welfare:
The National Health and Nutrition Survey in Japan. 2012 (In
Japanese). http://www.mhlw.go.jp/bunya/kenkou/eiyou/dl/h24-houkoku.pdf2014.
|
|
20
|
Peeling P, Fulton SK, Binnie M and Goodman
C: Training environment and Vitamin D status in athletes. Int J
Sports Med. 34:248–252. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Miyauchi M, Hirai C and Nakajima H: The
solar exposure time required for vitamin D3 synthesis in the human
body estimated by numerical simulation and observation in Japan. J
Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 59:257–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gannagé-Yared MH, Chemali R, Yaacoub N and
Halaby G: Hypovitaminosis D in a sunny country: Relation to
lifestyle and bone markers. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1856–1862. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takada H, Washino K, Hanai T and Iwata H:
Response of parathyroid hormone to exercise and bone mineral
density in adolescent female athletes. Environ Health Prev Med.
2:161–166. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pasco JA, Henry MJ, Kotowicz MA, Sanders
KM, Seeman E, Pasco JR, Schneider HG and Nicholson GC: Seasonal
periodicity of serum vitamin D and parathyroid hormone, bone
resorption, and fractures: The Geelong Osteoporosis Study. J Bone
Miner Res. 19:752–758. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|