|
1
|
Elferink RO and Groen AK: Genetic defects
in hepatobiliary transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1586:129–145.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
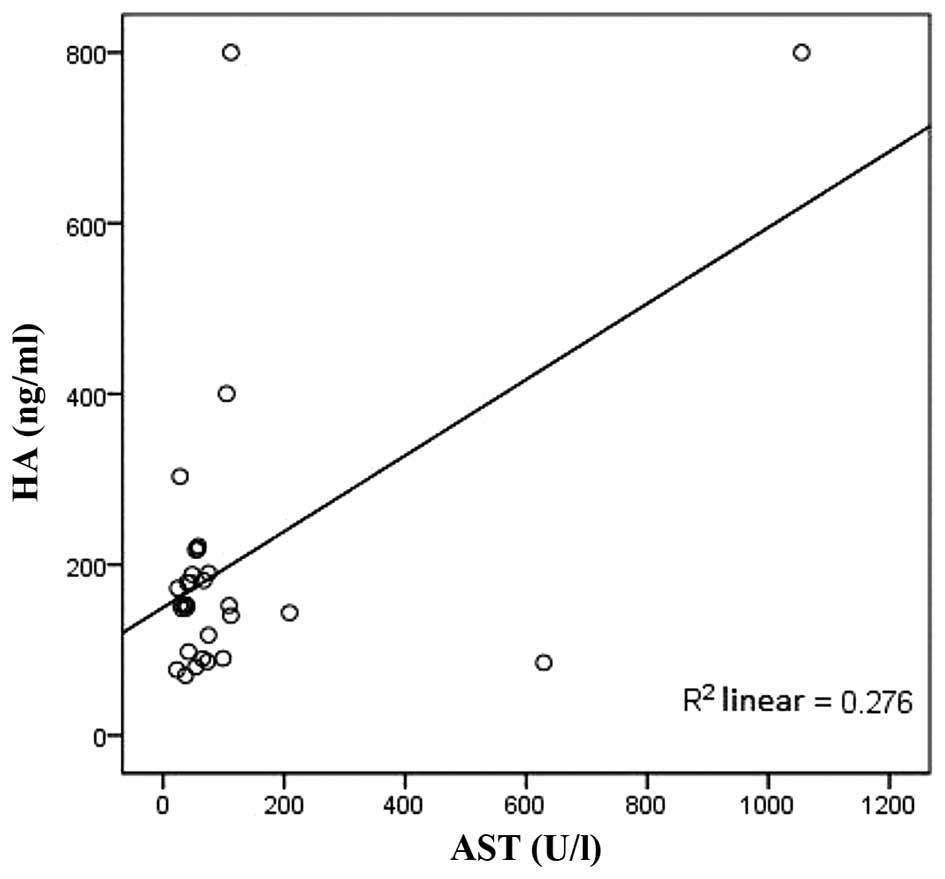
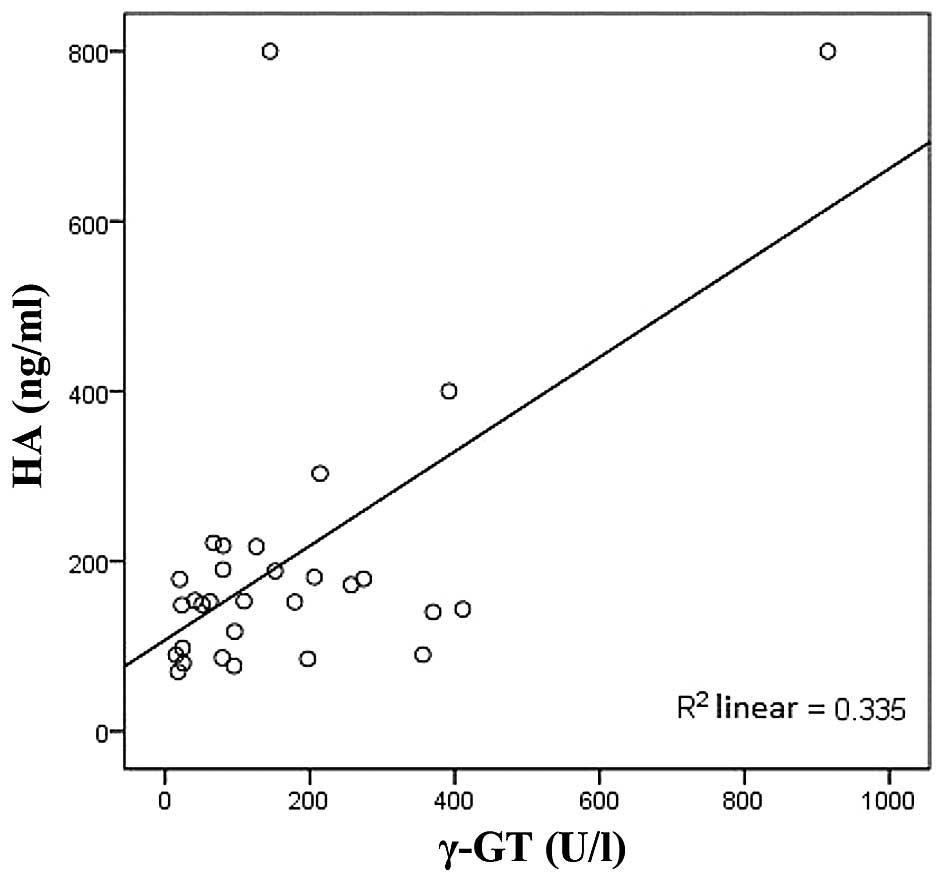
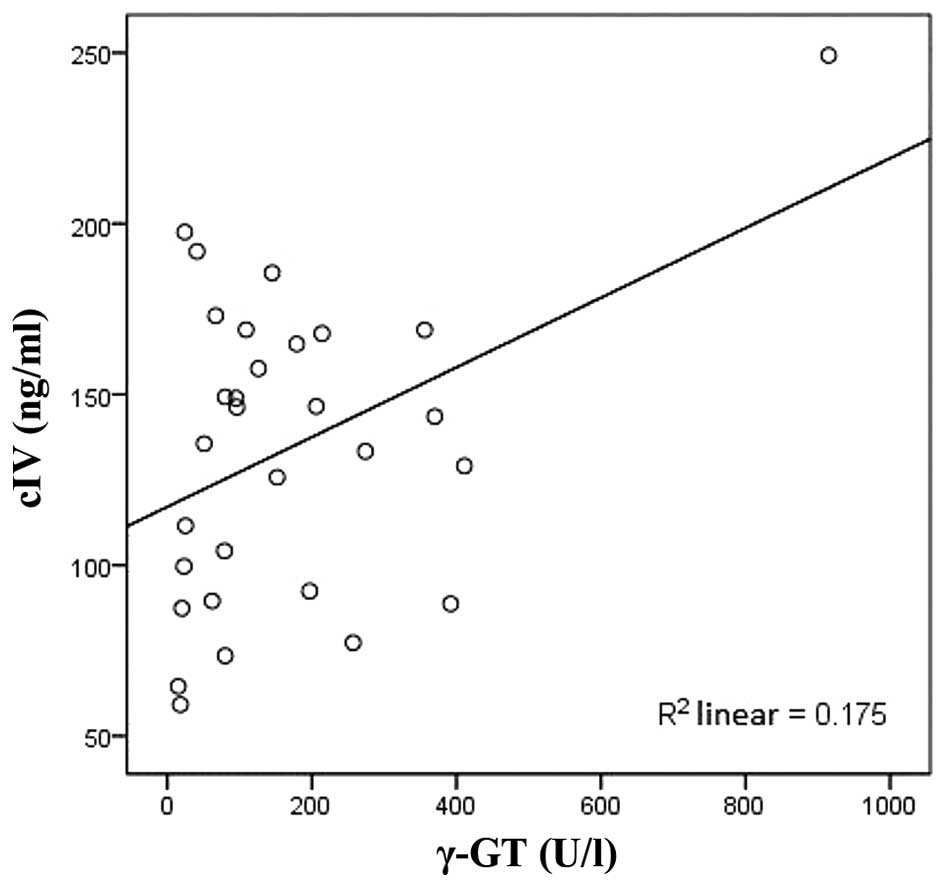
|
2
|
Benchimol EI, Walsh CM and Ling SC: Early
diagnosis of neonatal cholestatic jaundice: Test at 2 weeks. Can
Fam Physician. 55:1184–1192. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong C and Huang ZH: Diagnosis and
treatment of cholestatic liver disease in infants. Zhonghua
Linchuang Yishi Zazhi. 40:16–18. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Morgan NV, Hartley JL, Setchell KD,
Simpson MA, Brown R, Tee L, Kirkham S, Pasha S, Trembath RC, Maher
ER, et al: A combination of mutations in AKR1D1 and SKIV2L in a
family with severe infantile liver disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis.
8:742013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moyer V, Freese DK, Whitington PF, Olson
AD, Brewer F, Colletti RB and Heyman MB: North American Society for
Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition: Guideline for
the evaluation of cholestatic jaundice in infants: Recommendations
of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology,
Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 39:115–128.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee HH, Seo YS, Um SH, Won NH, Yoo H, Jung
ES, Kwon YD, Park S, Keum B, Kim YS, et al: Usefulness of
non-invasive markers for predicting significant fibrosis in
patients with chronic liver disease. J Korean Med Sci. 25:67–74.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
El-Shabrawi MH, El Zein Abedin MY, Omar N,
Kamal NM, Elmakarem SA, Khattab S, El-Sayed HM, El-Hennawy A and
Ali AS: Predictive accuracy of serum hyaluronic acid as a
non-invasive marker of fibrosis in a cohort of multi-transfused
Egyptian children with β-thalassaemia major. Arab J Gastroenterol.
13:45–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nath NC, Rahman MA, Khan MR, Hasan MS,
Bhuiyan TM, Hoque MN, Kabir MM, Raha AK and Jahan B: Serum
hyaluronic acid as a predictor of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B
and C virus infection. Mymensingh Med J. 20:614–619.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nobili V, Alisi A, Torre G, De Vito R,
Pietrobattista A, Morino G, De Ville De Goyet J, Bedogni G and
Pinzani M: Hyaluronic acid predicts hepatic fibrosis in children
with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Transl Res. 156:229–234.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Timpl R, Rohde H, Robey PG, Rennard SI,
Foidart JM and Martin GR: Laminin - a glycoprotein from basement
membranes. J Biol Chem. 254:9933–9937. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Green RM and Flamm S: AGA technical review
on the evaluation of liver chemistry tests. Gastroenterology.
123:1367–1384. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu D and Huang ZH: Differential
diagnostic value of 5′-NT and γ-GT in infantile hepatitis syndrome
(HIS) and biliary astresia. J Clin Exp Med. 8:16–17. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Tarantino G, Finelli C, Colao A, Capone D,
Tarantino M, Grimaldi E, Chianese D, Gioia S, Pasanisi F, Contaldo
F, et al: Are hepatic steatosis and carotid intima media thickness
associated in obese patients with normal or slightly elevated
gamma-glutamyl-transferase? J Transl Med. 10:502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tavian D, Degiorgio D, Roncaglia N,
Vergani P, Cameroni I, Colombo R and Coviello DA: A new splicing
site mutation of the ABCB4 gene in intrahepatic cholestasis of
pregnancy with raised serum gamma-GT. Dig Liver Dis. 41:671–675.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang HL: Diagnostic value of serum ChE and
TGF-β combined detection in liver fibrosis. Pract Prev Med.
16:l237–l1238. 2009.
|
|
16
|
Matsui S, Yamane T, Takita T, Oishi Y and
Kobayashi-Hattori K: The hypocholesterolemic activity of Momordica
charantia fruit is mediated by the altered cholesterol- and bile
acid-regulating gene expression in rat liver. Nutr Res. 33:580–585.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|