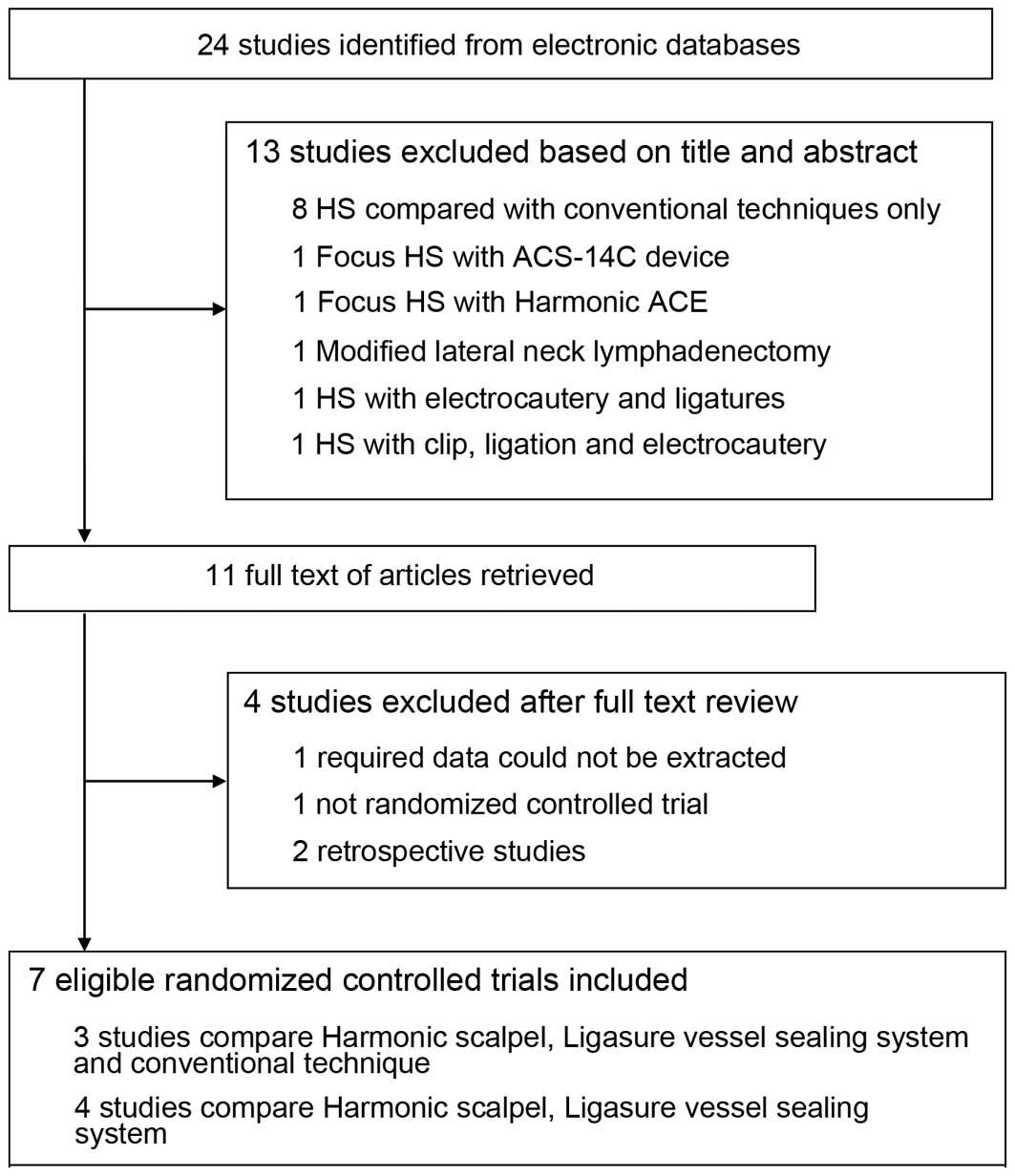
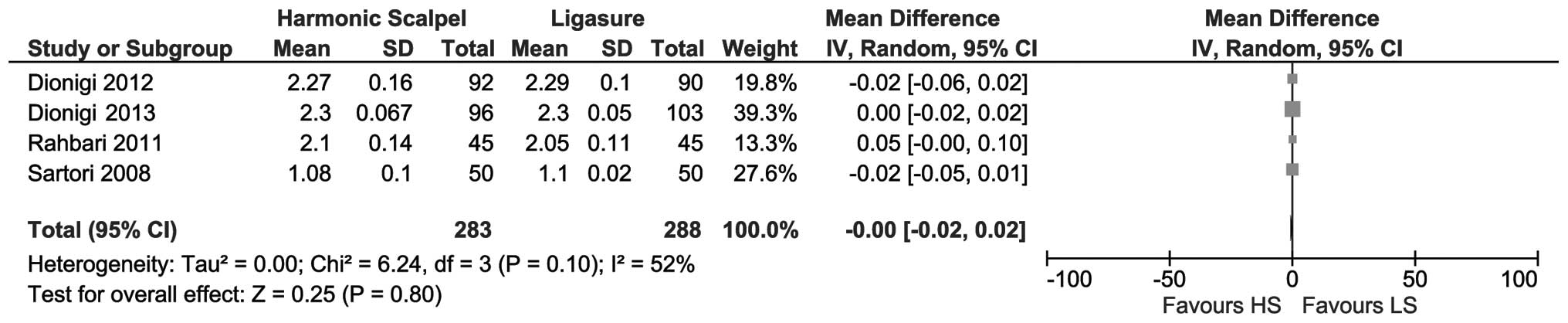
|
1
|
Bhattacharyya N and Fried MP: Assessment
of the morbidity and complications of total thyroidectomy. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 128:389–392. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiang FY, Lee KW, Huang YF, Wang LF and
Kuo WR: Risk of vocal palsy after thyroidecitomy with
identification of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Kaohsiung J Med
Sci. 20:431–436. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lo CY, Kwok KF and Yuen PW: A prospective
evaluation of recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis during
thyroidectomy. Arch Surg. 135:204–207. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dedivitis RA, Pfuetzenreiter EG Jr, Castro
MA and Denardin OV: Analysis of safety of short-stay thyroid
surgery. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 29:326–330. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shindo M and Stern A: Total thyroidectomy
with and without selective central compartment dissection: A
comparison of complication rates. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
136:584–587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slakey DP: Laparoscopic liver resection
using a bipolar vessel-sealing device: LigaSure. HPB Oxf.
10:253–255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Meurisse M, Defechereux T, Maweja S,
Degauque C, Vandelaer M and Hamoir E: Evaluation of the Ultracision
ultrasonic dissector in thyroid surgery. Prospective randomized
study. Ann Chir. 125:468–472. 2000.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Macario A, Dexter F, Sypal J, Cosgriff N
and Heniford BT: Operative time and other outcomes of the
electrothermal bipolar vessel sealing system (LigaSure) versus
other methods for surgical hemostasis: A meta-analysis. Surg Innov.
15:284–291. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao HS, Wang Q, Wang WJ and Ruan CP:
Prospective clinical trials of thyroidectomy with LigaSure vs
conventional vessel ligation: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Arch Surg. 144:1167–1174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cirocchi R, D'Ajello F, Trastulli S,
Santoro A, Di Rocco G, Vendettuoli D, Rondelli F, Giannotti D,
Sanguinetti A, Minelli L, et al: Meta-analysis of thyroidectomy
with ultrasonic dissector versus conventional clamp and tie. World
J Surg Oncol. 8:1122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ecker T, Carvalho AL, Choe JH, Walosek G
and Preuss KJ: Hemostasis in thyroid surgery: Harmonic scalpel
versus other techniques - a meta-analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 143:17–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Melck AL and Wiseman SM: Harmonic scalpel
compared to conventional hemostasis in thyroid surgery: A
meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Int J Surg Oncol.
2010:3960792010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang ZJ, Zhang P, Tian JH, Li J, Li L,
Tian J and Yang KH: Ultrasonic coagulator for thyroidectomy: A
systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Surg Innov.
17:41–47. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garas G, Okabayashi K, Ashrafian H, Shetty
K, Palazzo F, Tolley N, Darzi A, Athanasiou T and Zacharakis E:
Which hemostatic device in thyroid surgery? A network meta-analysis
of surgical technologies. Thyroid. 23:1138–1150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D,
Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P and Stewart LA: PRISMA-P Group:
Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis
protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev. 4:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG: PRISMA Group: Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 8:336–341.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L and Sterne JA:
Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group:
The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343:d59282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hopp L: Risk of bias reporting in Cochrane
systematic reviews. Int J Nurs Pract. 21:683–686. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B and Hozo I:
Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the
size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methodol. 5:132005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sartori PV, De Fina S, Colombo G, Pugliese
F, Romano F, Cesana G and Uggeri F: Ligasure versus Ultracision in
thyroid surgery: A prospective randomized study. Langenbecks Arch
Surg. 393:655–658. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rahbari R, Mathur A, Kitano M, Guerrero M,
Shen WT, Duh QY, Clark OH and Kebebew E: Prospective randomized
trial of ligasure versus harmonic hemostasis technique in
thyroidectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1023–1027. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pons Y, Gauthier J, Ukkola-Pons E, Clément
P, Roguet E, Poncet JL and Conessa C: Comparison of LigaSure vessel
sealing system, harmonic scalpel, and conventional hemostasis in
total thyroidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 141:496–501. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kwak HY, Chae BJ, Park YG, Kim SH, Chang
EY, Kim EJ, Song BJ, Jung SS and Bae JS: Comparison of surgical
outcomes between papillary thyroid cancer patients treated with the
Harmonic ACE scalpel and LigaSure Precise instrument during
conventional thyroidectomy: A single-blind prospective randomized
controlled trial. J Surg Res. 187:484–489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dionigi G, Van Slycke S, Rausei S, Boni L
and Dionigi R: Parathyroid function after open thyroidectomy: A
prospective randomized study for ligasure precise versus harmonic
FOCUS. Head Neck. 35:562–567. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dionigi G, Boni L, Rausei S, Frattini F,
Ferrari CC, Mangano A, Leotta A and Franchin M: The safety of
energy-based devices in open thyroidectomy: A prospective,
randomised study comparing the LigaSure™ (LF1212) and the
Harmonic® FOCUS. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 397:817–823.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bove A, Bongarzoni G, Palone G, Di Renzo
R, Di Nicola M, Corradetti L and Corbellini L: Comparative study of
an electrothermal bipolar vessel sealing system
(LigaSure®), a harmonic curved shears (Harmonic Focus™),
and traditional technique in total thyroidectomy. Am Surg.
76:E94–E96. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McNally MM, Agle SC, Williams RF and
Pofahl WE: A comparison of two methods of hemostasis in
thyroidectomy. Am Surg. 75:1073–1076. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Manouras A, Lagoudianakis EE, Antonakis
PT, Filippakis GM, Markogiannakis H and Kekis PB: Electrothermal
bipolar vessel sealing system is a safe and time-saving alternative
to classic suture ligation in total thyroidectomy. Head Neck.
27:959–962. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kiriakopoulos A, Dimitrios T and Dimitrios
L: Use of a diathermy system in thyroid surgery. Arch Surg.
139:997–1000. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miccoli P: Minimally invasive surgery for
thyroid and parathyroid diseases. Surg Endosc. 16:3–6. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miccoli P, Materazzi G, Fregoli L,
Panicucci E, Kunz-Martinez W and Berti P: Modified lateral neck
lymphadenectomy: Prospective randomized study comparing harmonic
scalpel with clamp-and-tie technique. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
140:61–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Siperstein AE, Berber E and Morkoyun E:
The use of the harmonic scalpel vs conventional knot tying for
vessel ligation in thyroid surgery. Arch Surg. 137:137–142. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Voutilainen PE and Haglund CH:
Ultrasonically activated shears in thyroidectomies: A randomized
trial. Ann Surg. 231:322–328. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dralle H, Sekulla C, Haerting J,
Timmermann W, Neumann HJ, Kruse E, Grond S, Mühlig HP, Richter C,
Voss J, et al: Risk factors of paralysis and functional outcome
after recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery.
Surgery. 136:1310–1322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boddy SA, Ramsay JW, Carter SS, Webster
PJ, Levison DA and Whitfield HN: Tissue effects of an ultrasonic
scalpel for clinical surgical use. Urol Res. 15:49–52. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gossot D: Ultrasonic dissectors in
endoscopic surgery. Ann Chir. 52:635–642. 1998.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Youssef T, Mahdy T, Farid M and Latif AA:
Thyroid surgery: Use of the LigaSure Vessel Sealing System versus
conventional knot tying. Int J Surg. 6:323–327. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lachanas VA, Prokopakis EP, Mpenakis AA,
Karatzanis AD and Velegrakis GA: The use of Ligasure Vessel Sealing
System in thyroid surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 132:487–489.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Contin P, Gooßen K, Grummich K, Jensen K,
Schmitz-Winnenthal H, Büchler MW and Diener MK: ENERgized vessel
sealing systems versus CONventional hemostasis techniques in
thyroid surgery - the ENERCON systematic review and network
meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 398:1039–1056. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|