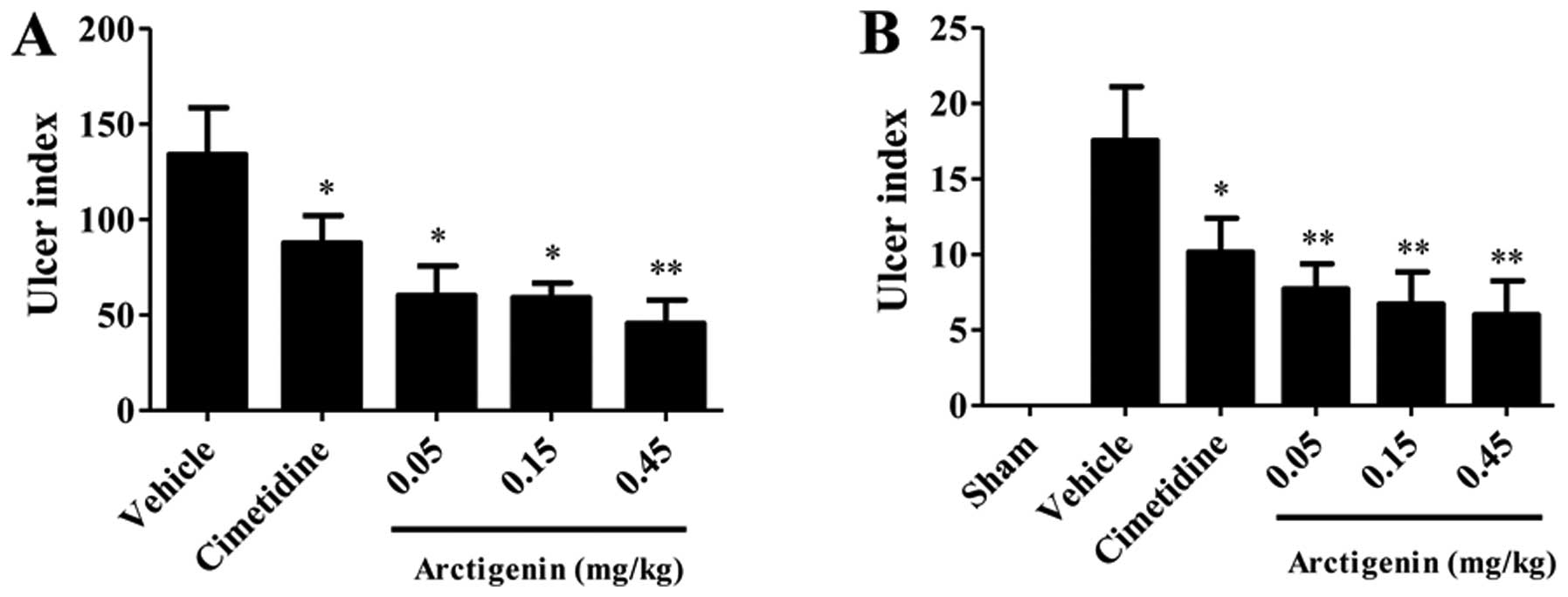
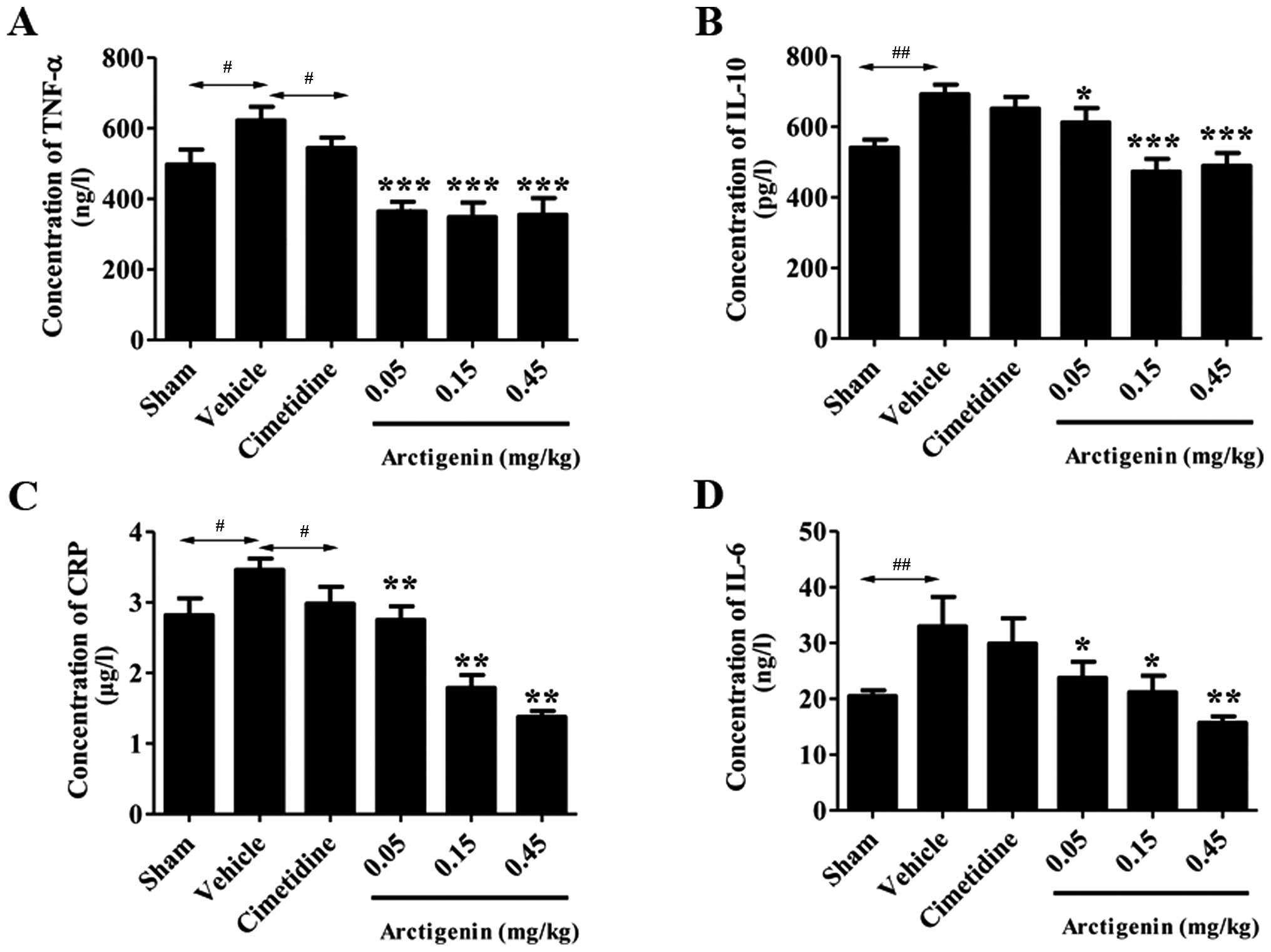
|
1
|
de Souza Almeida ES, Filho VC, Niero R,
Clasen BK, Balogun SO and de Oliveira Martins DT: Pharmacological
mechanisms underlying the anti-ulcer activity of methanol extract
and canthin-6-one of Simaba ferruginea A. St-Hil. in animal models.
J Ethnopharmacol. 134:630–636. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Groenen MJ, Kuipers EJ, Hansen BE and
Ouwendijk RJ: Incidence of duodenal ulcers and gastric ulcers in a
Western population: Back to where it started. Can J Gastroenterol.
23:604–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong WG, Cheng CS, Liu SP and Yu JP:
Epidemiology of peptic ulcer disease in Wuhan area of China from
1997 to 2002. World J Gastroenterol. 10:3377–3379. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Zou D, Ma X, Chen J, Shi X, Gong Y,
Man X, Gao L, Zhao Y, Wang R, et al: Epidemiology of peptic ulcer
disease: Endoscopic results of the systematic investigation of
gastrointestinal disease in China. Am J Gastroenterol.
105:2570–2577. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maity P, Biswas K, Roy S, Banerjee RK and
Bandyopadhyay U: Smoking and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal
ulcer - recent mechanistic update. Mol Cell Biochem. 253:329–338.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
García Rodríguez LA and Hernández-Díaz S:
Risk of uncomplicated peptic ulcer among users of aspirin and
nonaspirin nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. Am J Epidemiol.
159:23–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ko JK and Cho CH: Alcohol drinking and
cigarette smoking: A ‘partner’ for gastric ulceration. Zhonghua Yi
Xue Za Zhi (Taipei). 63:845–854. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wysocki A, Budzyński P, Kulawik J and
Drożdż W: Changes in the localization of perforated peptic ulcer
and its relation to gender and age of the patients throughout the
last 45 years. World J Surg. 35:811–816. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bhattacharya S, Banerjee D, Bauri AK,
Chattopadhyay S and Bandyopadhyay SK: Healing property of the Piper
betel phenol, allylpyrocatechol against indomethacin-induced
stomach ulceration and mechanism of action. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3705–3713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pakrashi A, Pandit S, Bandyopadhyay SK and
Pakrashi SC: Antioxidant effect of Phyllanthus emblica fruits on
healing of indomethacin induced gastric ulcer in rats. Indian J
Clin Biochem. 18:15–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng XG, Zhang JJ and Huang YC: Study on
the effect of weitongning on epidermal growth factor and nitric
oxide contents in tissue of stomach of rats with gastric ulcer.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 24:549–551. 2004.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin PC, Chang CH, Hsu PI, Tseng PL and
Huang YB: The efficacy and safety of proton pump inhibitors vs
histamine-2 receptor antagonists for stress ulcer bleeding
prophylaxis among critical care patients: A meta-analysis. Crit
Care Med. 38:1197–1205. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vasconcelos PC, Andreo MA, Vilegas W,
Hiruma-Lima CA and Pellizzon CH: Effect of Mouriri pusa tannins and
flavonoids on prevention and treatment against experimental gastric
ulcer. J Ethnopharmacol. 131:146–153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karakoyun B, Yüksel M, Ercan F, Erzik C
and Yeğen BC: Alpha-lipoic acid improves acetic acid-induced
gastric ulcer healing in rats. Inflammation. 32:37–46. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park SY, Hong SS, Han XH, Hwang JS, Lee D,
Ro JS and Hwang BY: Lignans from Arctium lappa and their inhibition
of LPS-induced nitric oxide production. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
55:150–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kamkaen N, Matsuki Y, Ichino C, Kiyohara H
and Yamada H: The isolation of the anti-helicobacter pylori
compoundsin seeds of Arctium lappa Linn. Thai Pharm Health Sci J.
1:12–18. 2006.
|
|
17
|
Kang HS, Lee JY and Kim CJ:
Anti-inflammatory activity of arctigenin from Forsythiae Fructus. J
Ethnopharmacol. 116:305–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kou X, Qi S, Dai W, Luo L and Yin Z:
Arctigenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS expression in
RAW264.7 cells through suppressing JAK-STAT signal pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:1095–1102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao F, Wang L and Liu K: In vitro
anti-inflammatory effects of arctigenin, a lignan from Arctium
lappa L., through inhibition on iNOS pathway. J Ethnopharmacol.
122:457–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsai WJ, Chang CT, Wang GJ, Lee TH, Chang
SF, Lu SC and Kuo YC: Arctigenin from Arctium lappa inhibits
interleukin-2 and interferon gene expression in primary human T
lymphocytes. Chin Med. 6:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Awale S, Lu J, Kalauni SK, Kurashima Y,
Tezuka Y, Kadota S and Esumi H: Identification of arctigenin as an
antitumor agent having the ability to eliminate the tolerance of
cancer cells to nutrient starvation. Cancer Res. 66:1751–1757.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morimoto Y, Shimohara K, Oshima S and
Sukamoto T: Effects of the new anti-ulcer agent KB-5492 on
experimental gastric mucosal lesions and gastric mucosal defensive
factors, as compared to those of teprenone and cimetidine. Jpn J
Pharmacol. 57:495–505. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guth PH, Aures D and Paulsen G: Topical
asprin plus HCl gastric lesions in the rats. Cytoprotective effect
of prostaglandin, cimetidine, and probanthine. Gastroenterology.
76:88–93. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okabe S and Amagase K: An overview of
acetic acid ulcer models - the history and state of the art of
peptic ulcer research. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:1321–1341. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mutoh H, Hiraishi H, Ota S, Ivey KJ,
Terano A and Sugimoto T: Role of oxygen radicals in ethanol-induced
damage to cultured gastric mucosal cells. Am J Physiol.
258:G603–G609. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jung J, Bae KH and Jeong CS:
Anti-Helicobacter pylori and antiulcerogenic activities of the root
cortex of Paeonia suffruticosa. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1535–1539.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang FY, Yang FJ, Yang JL, Wang L and
Zhang Y: Renin inhibition improves ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis
of lumbar vertebra in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:1994–1997. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jainu M and Devi CS: Antiulcerogenic and
ulcer healing effects of Solanum nigrum (L.) on experimental ulcer
models: Possible mechanism for the inhibition of acid formation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 104:156–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kwiecień S, Brzozowski T and Konturek SJ:
Effects of reactive oxygen species action on gastric mucosa in
various models of mucosal injury. J Physiol Pharmacol. 53:39–50.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bradding P, Feather IH, Wilson S, Bardin
PG, Heusser CH, Holgate ST and Howarth PH: Immunolocalization of
cytokines in the nasal mucosa of normal and perennial rhinitic
subjects. The mast cell as a source of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-6 in
human allergic mucosal inflammation. J Immunol. 151:3853–3865.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Su SC, Hua KF, Lee H, Chao LK, Tan SK, Lee
H, Yang SF and Hsu HY: LTA and LPS mediated activation of protein
kinases in the regulation of inflammatory cytokines expression in
macrophages. Clin Chim Acta. 374:106–115. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang HD, Lu DX and Qi RB: Therapeutic
strategies targeting the LPS signaling and cytokines.
Pathophysiology. 16:291–296. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Beserra AM, Calegari PI, Souza MC, Dos
Santos RA, Lima JC, Silva RM, Balogun SO and Martins DT:
Gastroprotective and ulcer-healing mechanisms of ellagic acid in
experimental rats. J Agric Food Chem. 59:6957–6965. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martin GR and Wallace JL: Gastrointestinal
inflammation: A central component of mucosal defense and repair.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 231:130–137. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Appleyard CB, McCafferty DM, Tigley AW,
Swain MG and Wallace JL: Tumor necrosis factor mediation of
NSAID-induced gastric damage: Role of leukocyte adherence. Am J
Physiol. 270:G42–G48. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li TT and Liu XH: Clinical value of
determination of changes of serum Gas, IL-2, IL-10 and IL-18 levels
after transfusion of Red blood cells in patients with peptic ulcer.
Journal of Radioimmunology. 24:515–517. 2011.
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y: Impact of esomeprazole on
gastrointestinal hormones and inflammatory state of patients with
gastric ulcer. Journal of Clinical Medicine in Practice. 17:68–70.
2013.
|
|
38
|
Boehme MW, Autschbach F, Ell C and Raeth
U: Prevalence of silent gastric ulcer, erosions or severe acute
gastritis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus - a
cross-sectional study. Hepatogastroenterology. 54:643–648.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hyam SR, Lee IA, Gu W, Kim KA, Jeong JJ,
Jang SE, Han MJ and Kim DH: Arctigenin ameliorates inflammation in
vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway and polarizing
M1 macrophages to M2-like macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 708:21–29.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|