|
1
|
Wang K, Zhang X, Jin Z, Ma H, Teng Z and
Wang L: Modeling and analysis of the transmission of Echinococcosis
with application to Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China. J
Theor Biol. 333:78–90. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torgerson PR: The emergence of
echinococcosis in central Asia. Parasitology. 140:1667–1673. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moldovan R, Neghina AM, Calma CL, Marincu
I and Neghina R: Human cystic echinococcosis in two south-western
and central-western Romanian counties: A 7-year epidemiological and
clinical overview. Acta Trop. 121:26–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siracusano A, Delunardo F, Teggi A and
Ortona E: Host-parasite relationship in cystic echinococcosis: An
evolving story. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012:6393622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu CY, Ma XM, Ding JB and Shen HM:
Different host status of echinococcus infection in China. Chin J
Zoonoses. 25:586–588. 2009.
|
|
6
|
Nasrieh MA, Abdel-Hafez SK, Kamhawi SA,
Craig PS and Schantz PM: Cystic echinococcosis in Jordan:
Socioeconomic evaluation and risk factors. Parasitol Res.
90:456–466. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gonlugur U, Ozcelik S, Gonlugur TE and
Celiksoz A: The role of Casoni's skin test and indirect
haemagglutination test in the diagnosis of hydatid disease.
Parasitol Res. 97:395–398. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalantari E, Bandehpour M, Pazoki R,
Taghipoor-Lailabadi N, Khazan H, Mosaffa N, Nazaripouya MR and
Kazemi B: Application of recombinant Echinococcus granulosus
antigen B to ELISA kits for diagnosing hydatidosis. Parasitol Res.
106:847–851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tawfeek GM, Elwakil HS, El-Hoseiny L,
Thabet HS, Sarhan RM, Awad NS and Anwar WA: Comparative analysis of
the diagnostic performance of crude sheep hydatid cyst fluid,
purified antigen B and its subunit (12 Kda), assessed by ELISA, in
the diagnosis of human cystic echinococcosis. Parasitol Res.
108:371–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wen H, Aji T and Shao YM: Diagnosis and
management against the complications of human cystic
echinococcosis. Front Med China. 4:394–398. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lightowlers MW, Lawrence SB, Gauci CG,
Young J, Ralston MJ, Maas D and Heath DD: Vaccination against
hydatidosis using a defined recombinant antigen. Parasite Immunol.
18:457–462. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Strohmaier K, Franze R and Adam KH:
Location and characterization of the antigenic portion of the FMDV
immunizing protein. J Gen Virol. 59:295–306. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Katoh Y, Oku Y,
Suzuki T and Yagi K: The vaccination potential of EMY162 antigen
against Echinococcus multilocularis infection. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 363:915–920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Yamano K, Katoh
Y, Oku Y, Suzuki T and Yagi K: Echinococcus multilocularis:
Purification and characterization of glycoprotein antigens with
serodiagnostic potential for canine infection. Exp Parasitol.
128:50–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katoh Y, Kouguchi H, Matsumoto J, Goto A,
Suzuki T, Oku Y and Yagi K: Characterization of emY162 encoding an
immunogenic protein cloned from an adult worm-specific cDNA library
of Echinococcus multilocularis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1780:1–6.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lorenzo C, Salinas G, Brugnini A,
Wernstedt C, Hellman U and González-Sapienza G: Echinococcus
granulosus antigen 5 is closely related to proteases of the trypsin
family. Biochem J. 369:191–198. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lightowlers MW, Liu DY, Haralambous A and
Rickard MD: Subunit composition and specificity of the major cyst
fluid antigens of Echinococcus granulosus. Mol Biochem Parasitol.
37:171–182. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Xu H, Chen J, Gan W, Wu W, Wu W and
Hu X: Gene cloning, expression, and localization of antigen 5 in
the life cycle of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitol Res.
110:2315–2323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Paul M and Stefaniak J: Detection of
specific Echinococcus granulosus antigen 5 in liver cyst bioptate
from human patients. Acta Trop. 64:65–77. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yarzabal LA, Bout DT, Naquira FR and
Capron AR: Further observations on the specificity of antigen 5 of
Echinococcus granulosus. J Parasitol. 63:495–499. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geourjon C and Deléage G: SOPMA:
Significant improvements in protein secondary structure prediction
by consensus prediction from multiple alignments. Comput Appl
Biosci. 11:681–684. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
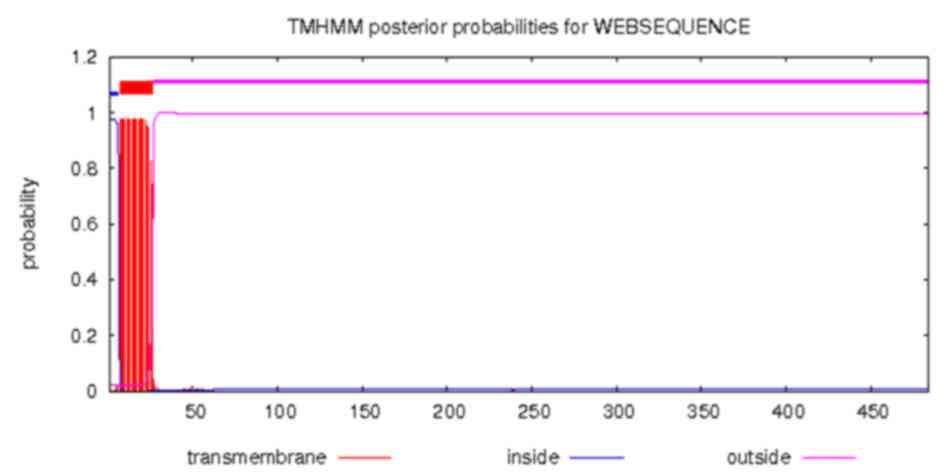
Melén K, Krogh A and von Heijne G:
Reliability measures for membrane protein topology prediction
algorithms. J Mol Biol. 327:735–744. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
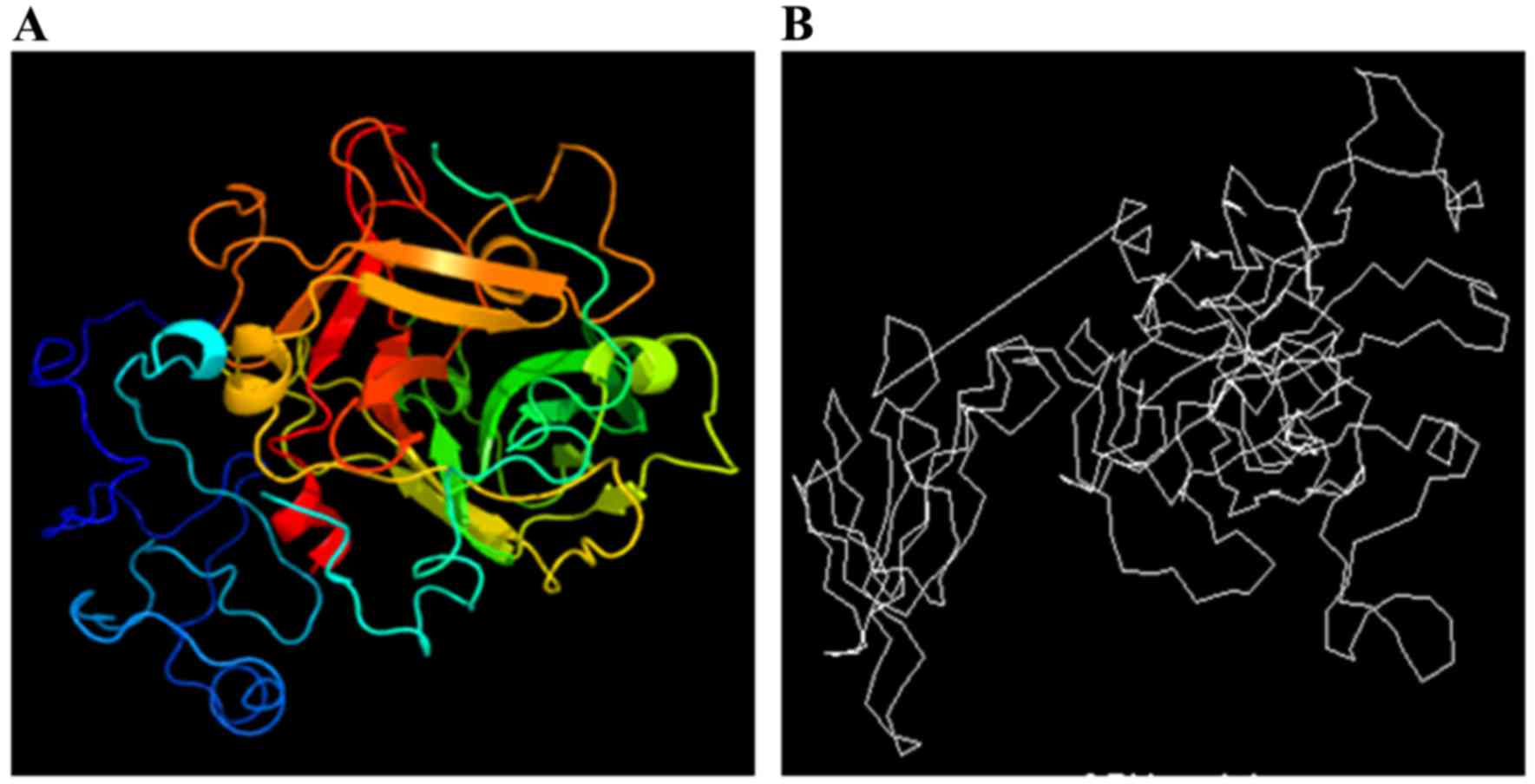
Wass MN, Kelley LA and Sternberg MJ:
3DLigandSite: Predicting ligand-binding sites using similar
structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:W469–W473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nielsen M, Lundegaard C, Lund O and
Petersen TN: CPHmodels-3.0-remote homology modeling using
structure-guided sequence profiles. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:W576–W581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vita R, Zarebski L, Greenbaum JA, Emami H,
Hoof I, Salimi N, Damle R, Sette A and Peters B: The immune epitope
database 2.0. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:(Database). D854–D862. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parker KC, Bednarek MA and Coligan JE:
Scheme for ranking potential HLA-A2 binding peptides based on
independent binding of individual peptide side-chains. J Immunol.
152:163–175. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rammensee H, Bachmann J, Emmerich NP,
Bachor OA and Stevanović S: SYFPEITHI: Database for MHC ligands and
peptide motifs. Immunogenetics. 50:213–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C,
Ivanyi I, Appel RD and Bairoch A: ExPASy: The proteomics server for
in-depth protein knowledge and analysisNucleic. Acids Res.
31:3784–3788. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li YJ, Wang J, Zhao H, Jia HY, Li B, Ma
XM, Wen H and Ding JB: Bioinformatics prediction on Eg95 antigen
epitopes of Echinococcus granulosus. Chin J Zoonoses. 27:892–895.
2011.
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Zhang M, Hu H, Liu S and Lu Z: On
predicting the T cell and B cell epitopes of platelet membrane
glycoprotein II b/III a antibody from human and mice]. Sheng Wu Yi
Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 27:1146–1151. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shen ZG, Yan P, He W, Chen Z, He H, Zhang
J, Yang X, Wu Y, Liang Z and Li J: Prediction of the secondary
structure and the B cell epitope of the extracellular domin of
FSHR. J Chongqing Med Univ. 35:1317–1320. 2010.
|
|
32
|
Yan C, Wang R, Li J, Deng Y, Wu D, Zhang
H, Zhang H, Wang L, Zhang C, Sun H, et al: HLA-A gene polymorphism
defined by high-resolution sequence-based typing in 161 Northern
Chinese Han people. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 1:304–309.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|