|
1
|
Petersson F: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A
review. Semin Diagn Pathol. 32:54–73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
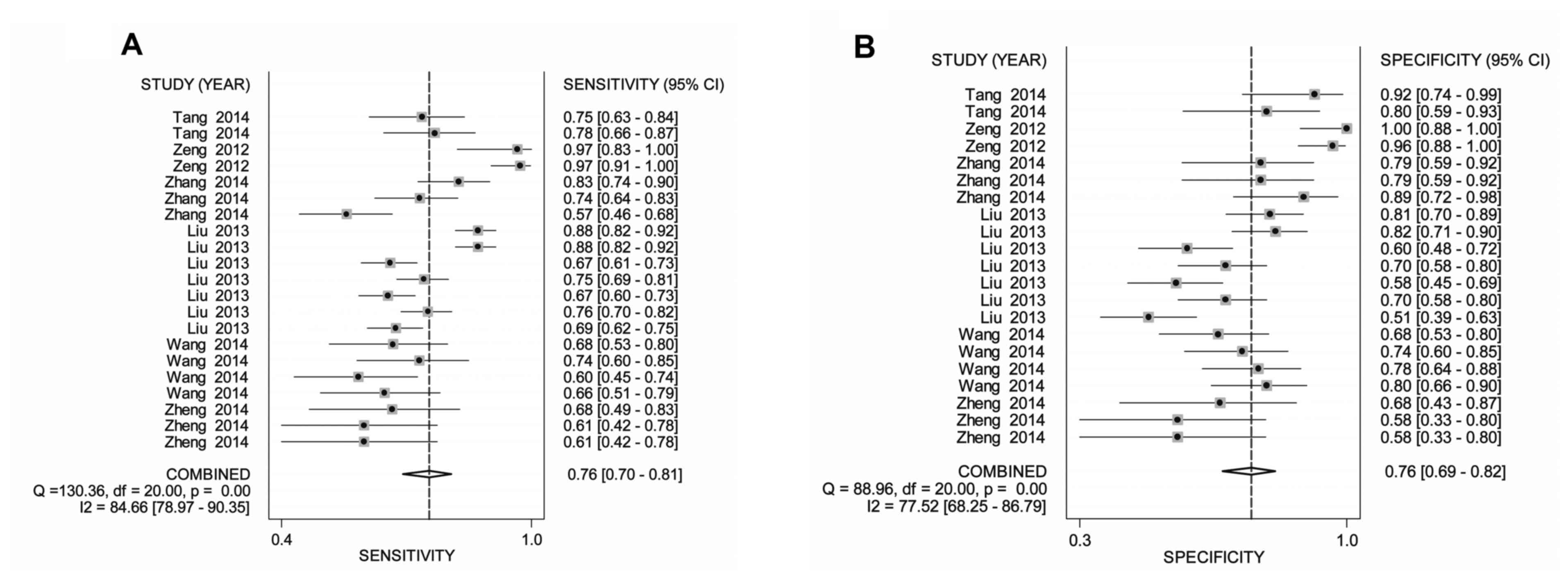
Wei KR, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Liang ZH, Ou
ZX and Chen WQ: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in
China in 2010. Chin J Cancer. 33:381–387. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cao SM, Simons MJ and Qian CN: The
prevalence and prevention of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in China.
Chin J Cancer. 30:114–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pritchard CC, Cheng HH and Tewari M:
MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat Rev Genet.
13:358–369. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pileczki V, Cojocneanu-Petric R, Maralani
M, Neagoe IB and Sandulescu R: MicroRNAs as regulators of apoptosis
mechanisms in cancer. Clujul medical 1957. 89:50–55.
2016.https://doi.org/10.15386/cjmed-512 View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frixa T, Donzelli S and Blandino G:
Oncogenic MicroRNAs: Key Players in Malignant Transformation.
Cancers (Basel). 7:2466–2485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tuna M, Machado AS and Calin GA: Genetic
and epigenetic alterations of microRNAs and implications for human
cancers and other diseases. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 55:193–214.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee KT, Tan JK, Lam AK and Gan SY:
MicroRNAs serving as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A critical review. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 103:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Luo HN, Tian WD, Lu J, Li G, Wang
L, Zhang B, Liang BJ, Peng XH, Lin SX, et al: Diagnostic and
prognostic value of plasma microRNA deregulation in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 14:1133–1142. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang JF, Yu ZH, Liu T, Lin ZY, Wang YH,
Yang LW, He HJ, Cao J, Huang HL and Liu G: Five miRNAs as novel
diagnostic biomarker candidates for primary nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7575–7581. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang HY, Yan LX, Shao Q, Fu S, Zhang ZC,
Ye W, Zeng YX and Shao JY: Profiling plasma microRNA in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma with deep sequencing. Clin Chem.
60:773–782. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng X, Xiang J, Wu M, Xiong W, Tang H,
Deng M, Li X, Liao Q, Su B, Luo Z, et al: Circulating miR-17,
miR-20a, miR-29c, and miR-223 combined as non-invasive biomarkers
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e463672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang G, Zong J, Lin S, Verhoeven RJ, Tong
S, Chen Y, Ji M, Cheng W, Tsao SW, Lung M, et al: Circulating
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs miR-BART7 and miR-BART13 as biomarkers
for nasopharyngeal carcinoma diagnosis and treatment. Int J Cancer.
136:E301–E312. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zheng XH, Cui C, Ruan HL, Xue WQ, Zhang
SD, Hu YZ, Zhou XX and Jia WH: Plasma microRNA profiling in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients reveals miR-548q and miR-483-5p
as potential biomarkers. Chin J Cancer. 33:330–338. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J Clin Epidemiol.
62:1006–1012. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
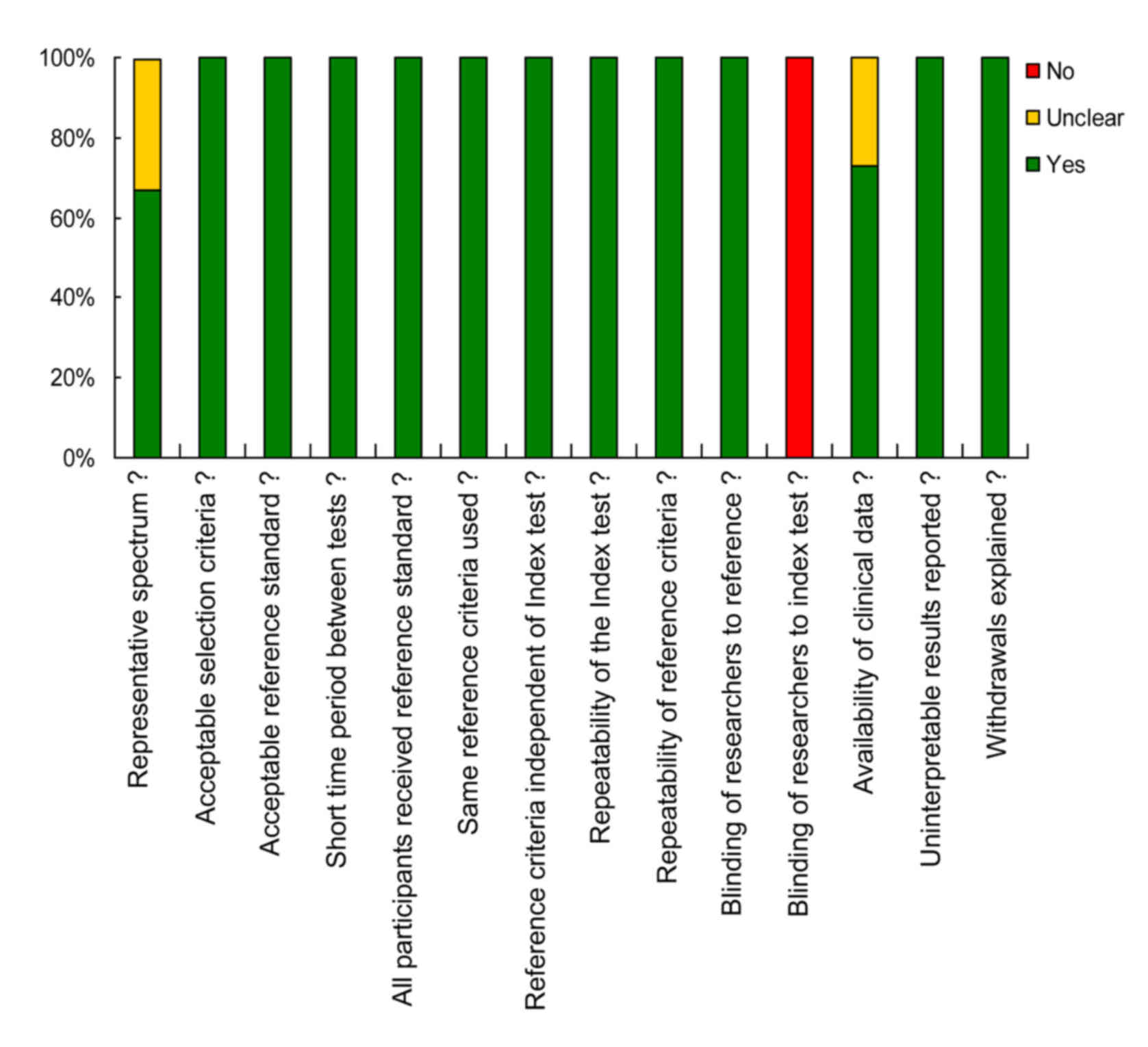
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt
PM and Kleijnen J: The development of QUADAS: A tool for the
quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in
systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 3:252003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
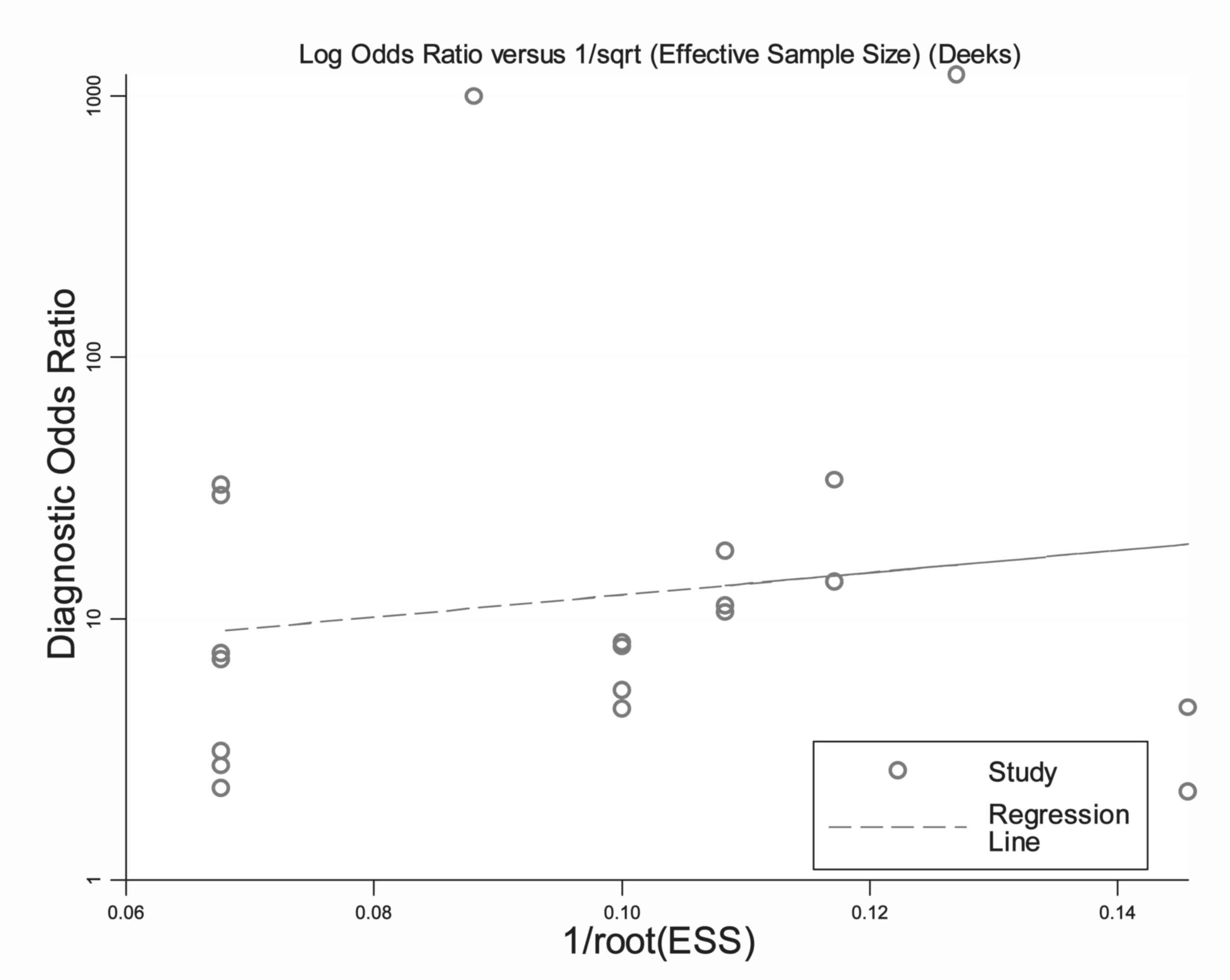
Cui ZL, Zheng DZ, Liu YH, Chen LY, Lin DH
and Feng-Hua Lan: Diagnostic Accuracies of the TUNEL SCD, and Comet
Based Sperm DNA Fragmentation Assays for Male Infertility: A
Meta-analysis Study. Clin Lab. 61:525–535. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Cui Z, Xiao Z, Hu M, Jiang C, Lin
Y and Chen Y: PAX1 and SOX1 methylation as an initial screening
method for cervical cancer: A meta-analysis of individual studies
in Asians. Ann Transl Med. 4:3652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui Z, Chen Y, Xiao Z, Hu M, Lin Y, Chen Y
and Zheng Y: Long noncoding RNAs as auxiliary biomarkers for
gastric cancer screening: A pooled analysis of individual studies.
Oncotarget. 7:25791–25800. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang K, Yuan Y, Cho JH, McClarty S, Baxter
D and Galas DJ: Comparing the MicroRNA spectrum between serum and
plasma. PLoS One. 7:e415612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|