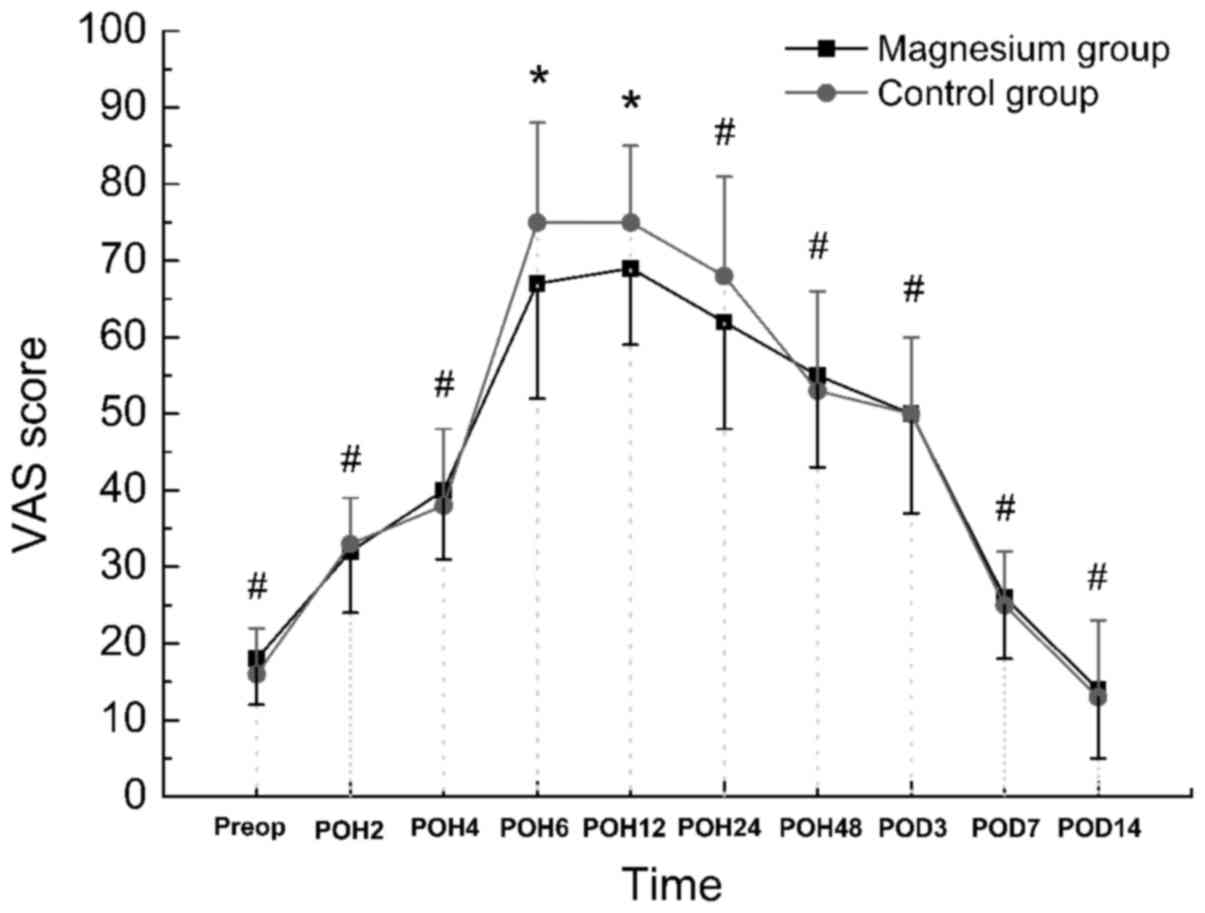
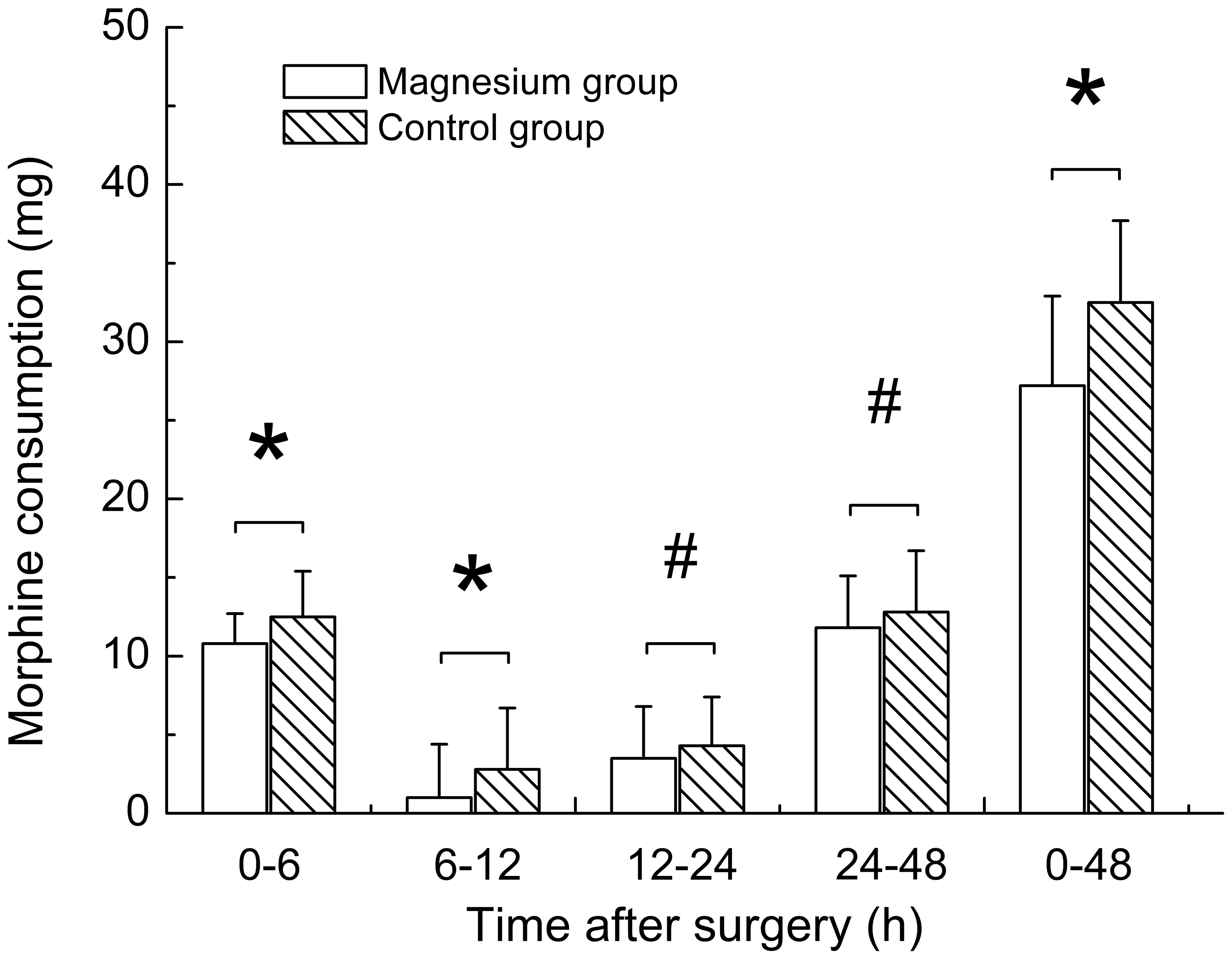
|
1
|
McKenzie JC, Goyal N and Hozack WJ:
Multimodal pain management for total hip arthroplasty. Seminars in
Arthroplasty. 24:87–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Young AC and Buvanendran A: Pain
management for total hip arthroplasty. J Surg Orthop Adv. 23:13–21.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Badica CIG, Badica L, Grecu I, Bradis AA
and Grintescu IM: Opioids or NSAID in postoperative analgesia after
total hip arthroplasty? Comparison of adverse events: 14AP4-4. Eur
J Anaesthesiol. 24:177–178. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fransen M and Neal B: Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs for preventing heterotopic bone formation
after hip arthroplasty. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2004:CD0011602004.
|
|
5
|
Kuchálik J, Granath B, Ljunggren A,
Magnuson A, Lundin A and Gupta A: Postoperative pain relief after
total hip arthroplasty: A randomized, double-blind comparison
between intrathecal morphine and local infiltration analgesia. Br J
Anaesth. 111:793–799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soave PM, Conti G, Costa R and Arcangeli
A: Magnesium and anaesthesia. Curr Drug Targets. 10:734–743. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abdulatif M, Amin SMM, Aboul-Ela A, Samuel
EWM and Abdel-Hakim SMA: Intra-articular versus intravenous
magnesium-sulfate as adjuvant to femoral nerve block in
arthroscopic knee surgery under general anesthesia: Randomized
controlled trial. Egypt J Anaesth. 31:239–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Saritas TB, Borazan H, Okesli S, Yel M and
Otelcioglu Ş: Is intra-articular magnesium effective for
postoperative analgesia in arthroscopic shoulder surgery? Pain Res
Manag. 20:35–38. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ekmekci P, Bengisun ZK, Akan B, Kazbek BK,
Ozkan KS and Suer AH: The effect of magnesium added to
levobupivacaine for femoral nerve block on postoperative analgesia
in patients undergoing ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports
Traumatol Arthrosc. 21:1119–1124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Farouk S and Aly A: A comparison of
intra-articular magnesium and/or morphine with bupivacaine for
postoperative analgesia after arthroscopic knee surgery. J Anesth.
23:508–512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee AR, Yi HW, Chung IS, Ko JS, Ahn HJ,
Gwak MS, Choi DH and Choi SJ: Magnesium added to bupivacaine
prolongs the duration of analgesia after interscalene nerve block.
Can J Anaesth. 59:21–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bondok RS and Abd El-Hady AM:
Intra-articular magnesium is effective for postoperative analgesia
in arthroscopic knee surgery. Br J Anaesth. 97:389–392. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Elsharnouby NM, Eid HE, Abou Elezz NF and
Moharram AN: Intraarticular injection of magnesium sulphate and/or
bupivacaine for postoperative analgesia after arthroscopic knee
surgery. Anesth Analg. 106:1548–1552. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rozner MA: The American Society of
Anesthesiologists physical status score and risk of perioperative
infection. JAMA. 275:1544. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mahomed NN, Arndt DC, McGrory BJ and
Harris WH: The Harris hip score: Comparison of patient self-report
with surgeon assessment. J Arthroplasty. 16:575–580. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim SJ, Huh J, Odrobina R and Kim JH:
Systemic review of published literature on Candida infection
following total hip arthroplasty. Mycopathologia. 179:173–185.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsertsvadze A, Grove A, Freeman K, Court
R, Johnson S, Connock M, Clarke A and Sutcliffe P: Total hip
replacement for the treatment of end stage arthritis of the hip: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e998042014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ascher P and Nowak L: Electrophysiological
studies of NMDA receptors. Trends Neurosci. 10:284–288. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Coderre TJ, Katz J, Vaccarino AL and
Melzack R: Contribution of central neuroplasticity to pathological
pain: Review of clinical and experimental evidence. Pain.
52:259–285. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fisher K, Coderre TJ and Hagen NA:
Targeting the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor for chronic pain
management. Preclinical animal studies, recent clinical experience
and future research directions. J Pain Symptom Manage. 20:358–373.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hewitt DJ: The use of NMDA-receptor
antagonists in the treatment of chronic pain. Clin J Pain.
16:(Suppl 2). S73–S79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Memiş D, Turan A, Karamanlioğlu B, Süt N
and Pamukçu Z: The use of magnesium sulfate to prevent pain on
injection of propofol. Anesth Analg. 95:606–608. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Silverman R, Bendick PJ and Wasvary HJ: A
randomized, prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of
the effect of a calcium channel blocker ointment on pain after
hemorrhoidectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 48:1913–1916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arcioni R, Palmisani S, Tigano S,
Santorsola C, Sauli V, Romanò S, Mercieri M, Masciangelo R, De
Blasi RA and Pinto G: Combined intrathecal and epidural magnesium
sulfate supplementation of spinal anesthesia to reduce
post-operative analgesic requirements: A prospective, randomized,
double-blind, controlled trial in patients undergoing major
orthopedic surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 51:482–489. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lawand NB, Willis WD and Westlund KN:
Excitatory amino acid receptor involvement in peripheral
nociceptive transmission in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 324:169–177.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mercieri M, De Blasi RA, Palmisani S,
Forte S, Cardelli P, Romano R, Pinto G and Arcioni R: Changes in
cerebrospinal fluid magnesium levels in patients undergoing spinal
anaesthesia for hip arthroplasty: Does intravenous infusion of
magnesium sulphate make any difference? A prospective, randomized,
controlled study. Br J Anaesth. 109:208–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Samir EM, Badawy SS and Hassan AR:
Intrathecal vs intravenous magnesium as an adjuvant to bupivacaine
spinal anesthesia for total hip arthroplasty. Egypt J Anaesth.
29:395–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lin CY, Tsai PS, Hung YC and Huang CJ:
L-type calcium channels are involved in mediating the
anti-inflammatory effects of magnesium sulphate. Br J Anaesth.
104:44–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koltka K, Koknel-Talu G, Asik M and
Ozyalcin S: Comparison of efficacy of intraarticular application of
magnesium, levobupivacaine and lornoxicam with placebo in
arthroscopic surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.
19:1884–1889. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|