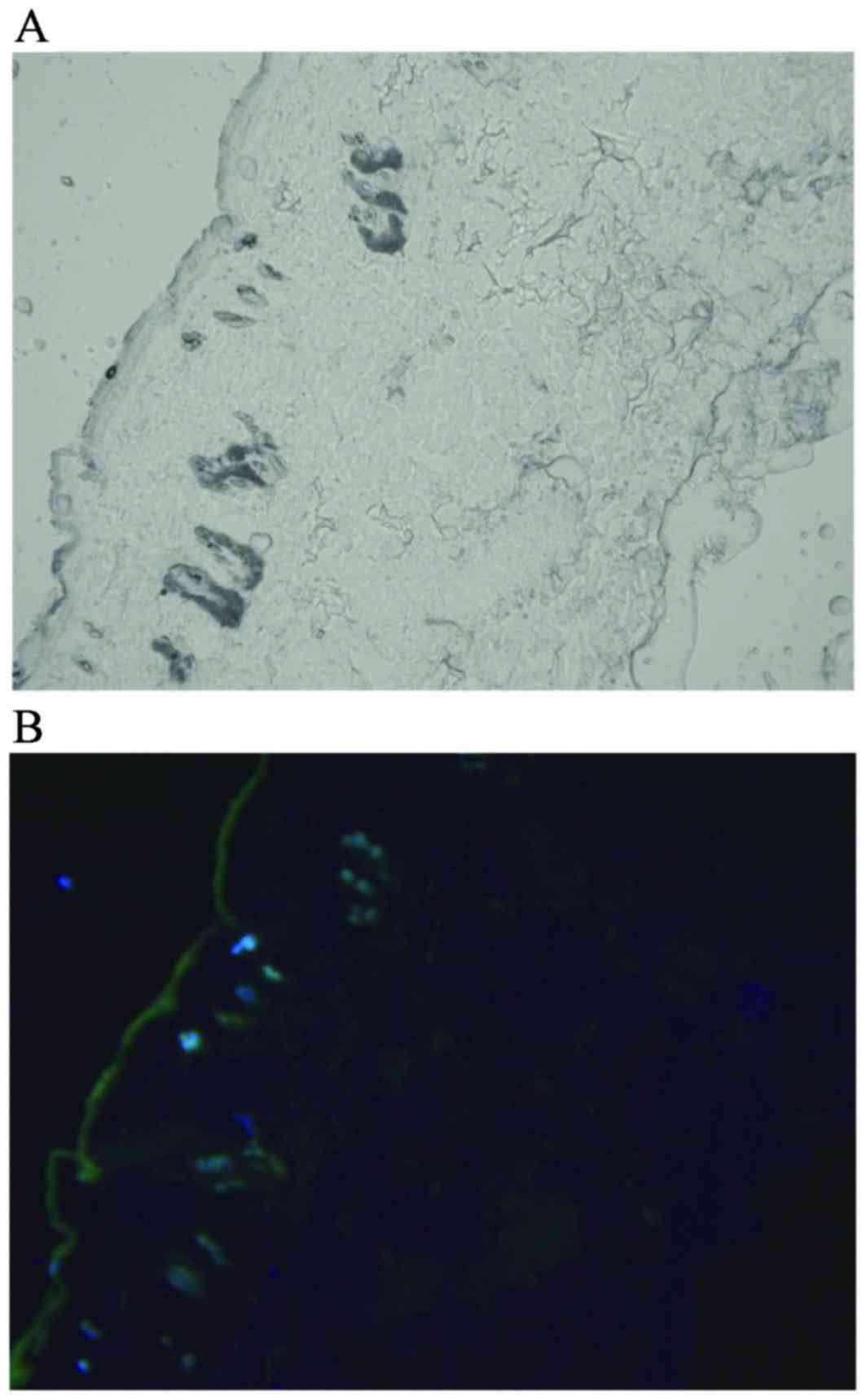
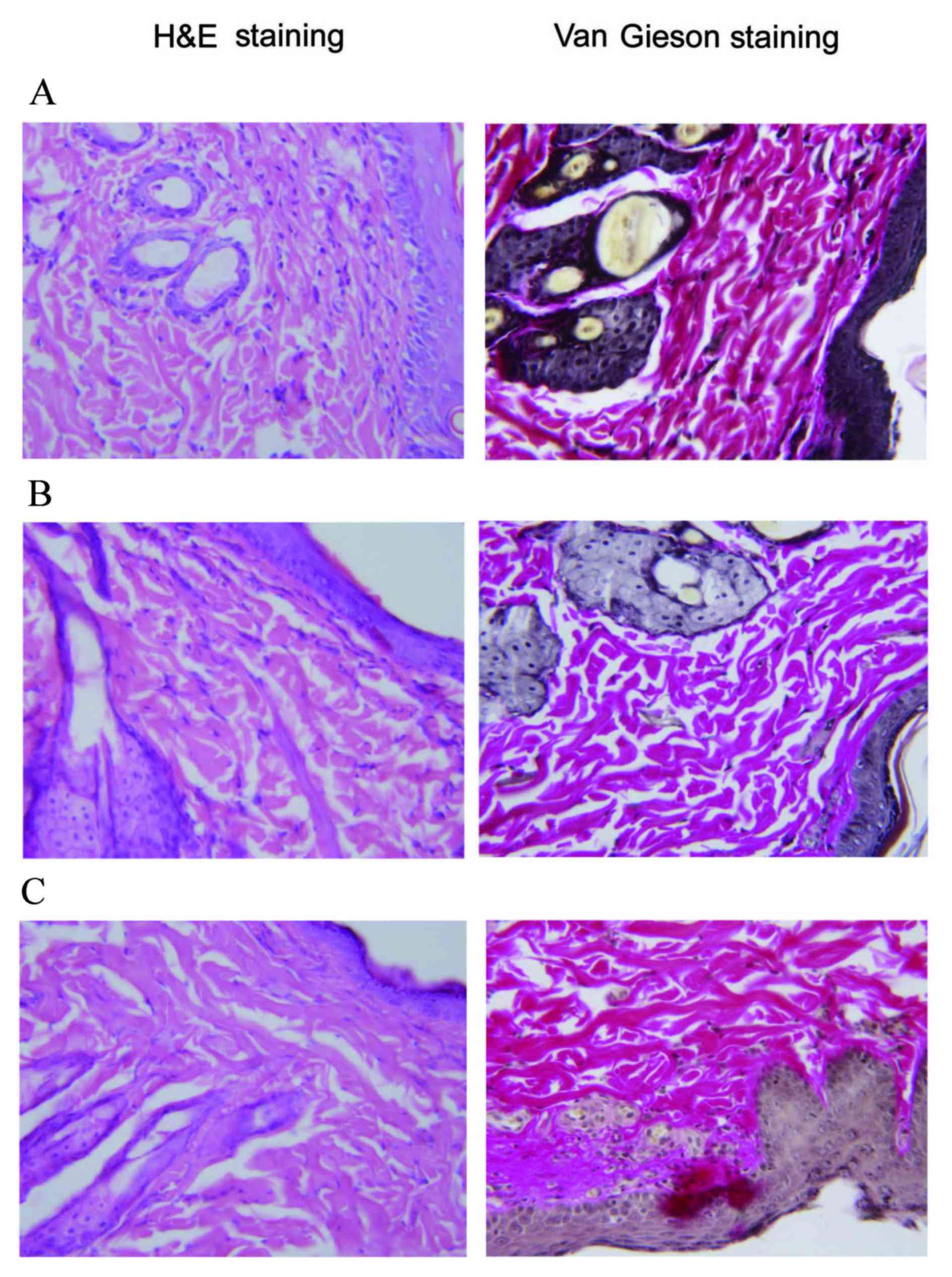
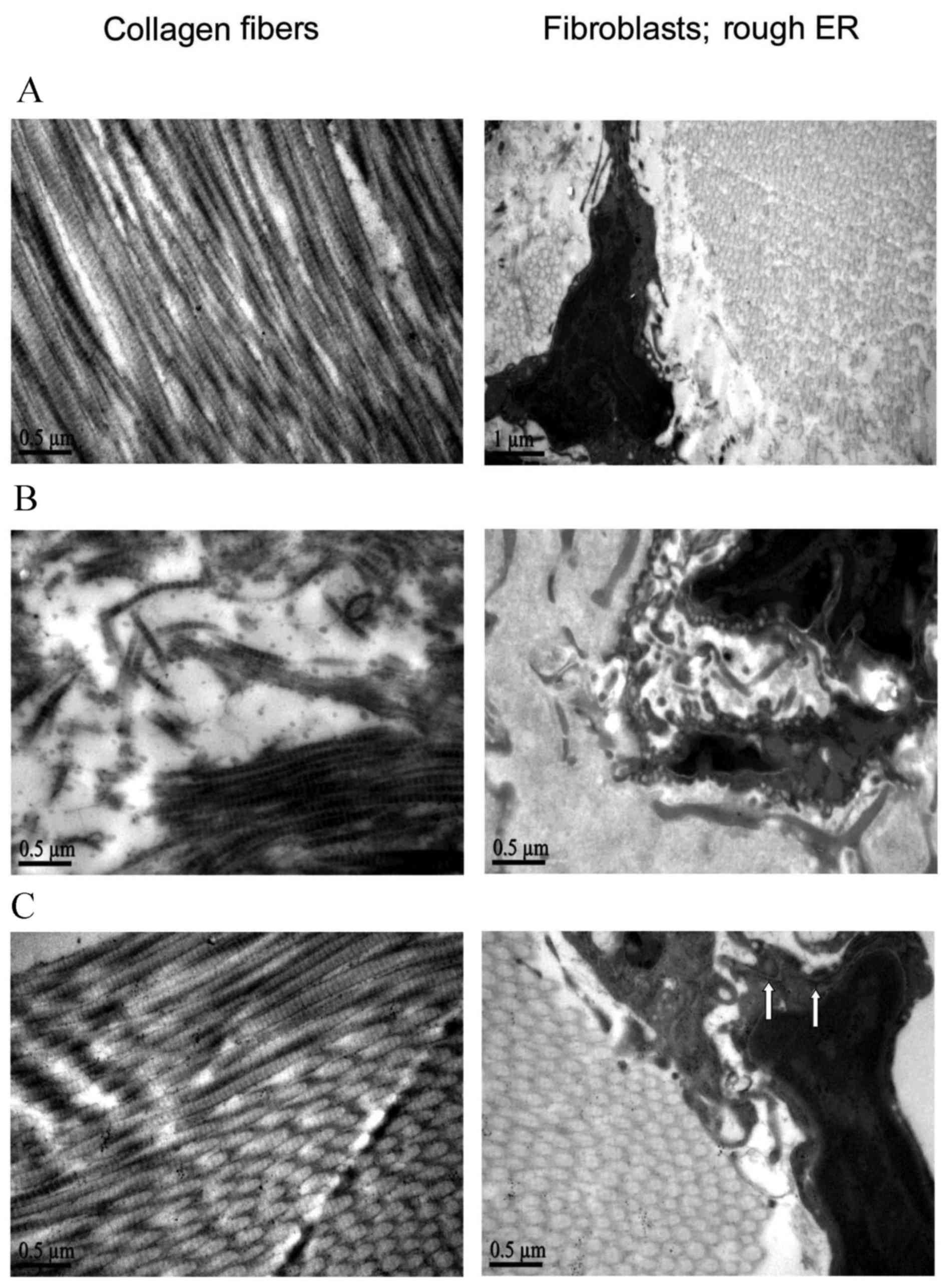
|
1
|
Quan T and Fisher GJ: Role of
age-associated alterations of the dermal extracellular matrix
microenvironment in human skin aging: A mini-review. Gerontology.
61:427–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gunin AG, Kornilova NK, Vasilieva OV and
Petrov VV: Age-related changes in proliferation, the numbers of
mast cells, eosinophils, and cd45-positive cells in human dermis. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 66:385–392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McCullough JL and Kelly KM: Prevention and
treatment of skin aging. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1067:323–331. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hwang KA, Yi BR and Choi KC: Molecular
mechanisms and in vivo mouse models of skin aging associated with
dermal matrix alterations. Lab Anim Res. 27:1–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Varani J, Dame MK, Rittie L, Fligiel SE,
Kang S, Fisher GJ and Voorhees JJ: Decreased collagen production in
chronologically aged skin: Roles of age-dependent alteration in
fibroblast function and defective mechanical stimulation. Am J
Pathol. 168:1861–1868. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cui H, Kong Y and Zhang H: Oxidative
stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and aging. J Signal Transduct.
2012:6463542012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Panich U, Sittithumcharee G, Rathviboon N
and Jirawatnotai S: Ultraviolet radiation-induced skin aging: The
role of DNA damage and oxidative stress in epidermal stem cell
damage mediated skin aging. Stem Cells Int. 2016:73706422016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhatia-Dey N, Kanherkar RR, Stair SE,
Makarev EO and Csoka AB: Cellular senescence as the causal nexus of
aging. Front Genet. 7:132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lv FJ, Tuan RS, Cheung KM and Leung VY:
Concise review: The surface markers and identity of human
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 32:1408–1419. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chamberlain G, Fox J, Ashton B and
Middleton J: Concise review: Mesenchymal stem cells: Their
phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and
potential for homing. Stem Cells. 25:2739–2749. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Liao L and Tan J:
Mesenchymal-stem-cell-based experimental and clinical trials:
Current status and open questions. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
11:893–909. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Isakson M, de Blacam C, Whelan D, McArdle
A and Clover AJ: Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cutaneous Wound
Healing: Current Evidence and Future Potential. Stem Cells Int.
2015:8310952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hocking AM and Gibran NS: Mesenchymal stem
cells: Paracrine signaling and differentiation during cutaneous
wound repair. Exp Cell Res. 316:2213–2219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen JS, Wong VW and Gurtner GC:
Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
for cutaneous wound healing. Front Immunol. 3:1922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu H, McTaggart SJ, Johnson DW and Gobe
GC: Original article anti-oxidant pathways are stimulated by
mesenchymal stromal cells in renal repair after ischemic injury.
Cytotherapy. 14:162–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu Q, Luo Z, He S, Peng X, Xiong S, Wang
Y, Zhong X, Zhou X, Eisenberg CA and Gao BZ: Conditioned serum-free
medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells has
anti-photoaging properties. Biotechnol Lett. 35:1707–1714. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim WS, Park BS, Park SH, Kim HK and Sung
JH: Antiwrinkle effect of adipose-derived stem cell: Activation of
dermal fibroblast by secretory factors. J Dermatol Sci. 53:96–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim WS, Park BS and Sung JH: Protective
role of adipose-derived stem cells and their soluble factors in
photoaging. Arch Dermatol Res. 301:329–336. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhen YZ, Lin YJ, Li KJ, Zhang GL, Zhao YF,
Wang MM, Wei JB, Wei J and Hu G: Effects of rhein lysinate on
D-galactose-induced aging mice. Exp Ther Med. 11:303–308.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Dong Z, Peng Z and Lu F:
Anti-aging effect of adipose-derived stem cells in a mouse model of
skin aging induced by D-galactose. PLoS One. 9:e975732014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei H, Li L, Song Q, Ai H, Chu J and Li W:
Behavioural study of the D-galactose induced aging model in
C57BL/6J mice. Behav Brain Res. 157:245–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Y, Zhao RC and Tredget EE: Concise
review: Bone marrow-derived stem/progenitor cells in cutaneous
repair and regeneration. Stem Cells. 28:905–915. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aoki S, Toda S, Ando T and Sugihara H:
Bone marrow stromal cells, preadipocytes, and dermal fibroblasts
promote epidermal regeneration in their distinctive fashions. Mol
Biol Cell. 15:4647–4657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SH, Jin SY, Song JS, Seo KK and Cho
KH: Paracrine effects of adipose-derived stem cells on
keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts. Ann Dermatol. 24:136–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cassino TR, Drowley L, Okada M, Beckman
SA, Keller B, Tobita K, Leduc PR and Huard J: Mechanical loading of
stem cells for improvement of transplantation outcome in a model of
acute myocardial infarction: The role of loading history. Tissue
Eng Part A. 18:1101–1108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Treiber N, Maity P, Singh K, Ferchiu F,
Wlaschek M and Scharffetter-Kochanek K: The role of manganese
superoxide dismutase in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol. 4:232–235.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen H, Long Y and Guo L: Antiaging Effect
of Inula britannica on Aging Mouse Model Induced by D-Galactose.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:60490832016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sandhu SK and Kaur G: Alterations in
oxidative stress scavenger system in aging rat brain and
lymphocytes. Biogerontology. 3:161–173. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim WS, Park BS and Sung JH: The
wound-healing and antioxidant effects of adipose-derived stem
cells. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:879–887. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim Y, Jo SH, Kim WH and Kweon OK:
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of intravenously injected
adipose derived mesenchymal stem cells in dogs with acute spinal
cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 6:2292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ayatollahi M, Hesami Z, Jamshidzadeh A and
Gramizadeh B: Antioxidant Effects of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem
Cell against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Oxidative Damage in Rat
Livers. Int J Organ Transplant Med. 5:166–173. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhuo W, Liao L, Xu T, Wu W, Yang S and Tan
J: Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced
renal dysfunction by improving the antioxidant/oxidant balance in
the ischemic kidney. Urol Int. 86:191–196. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|