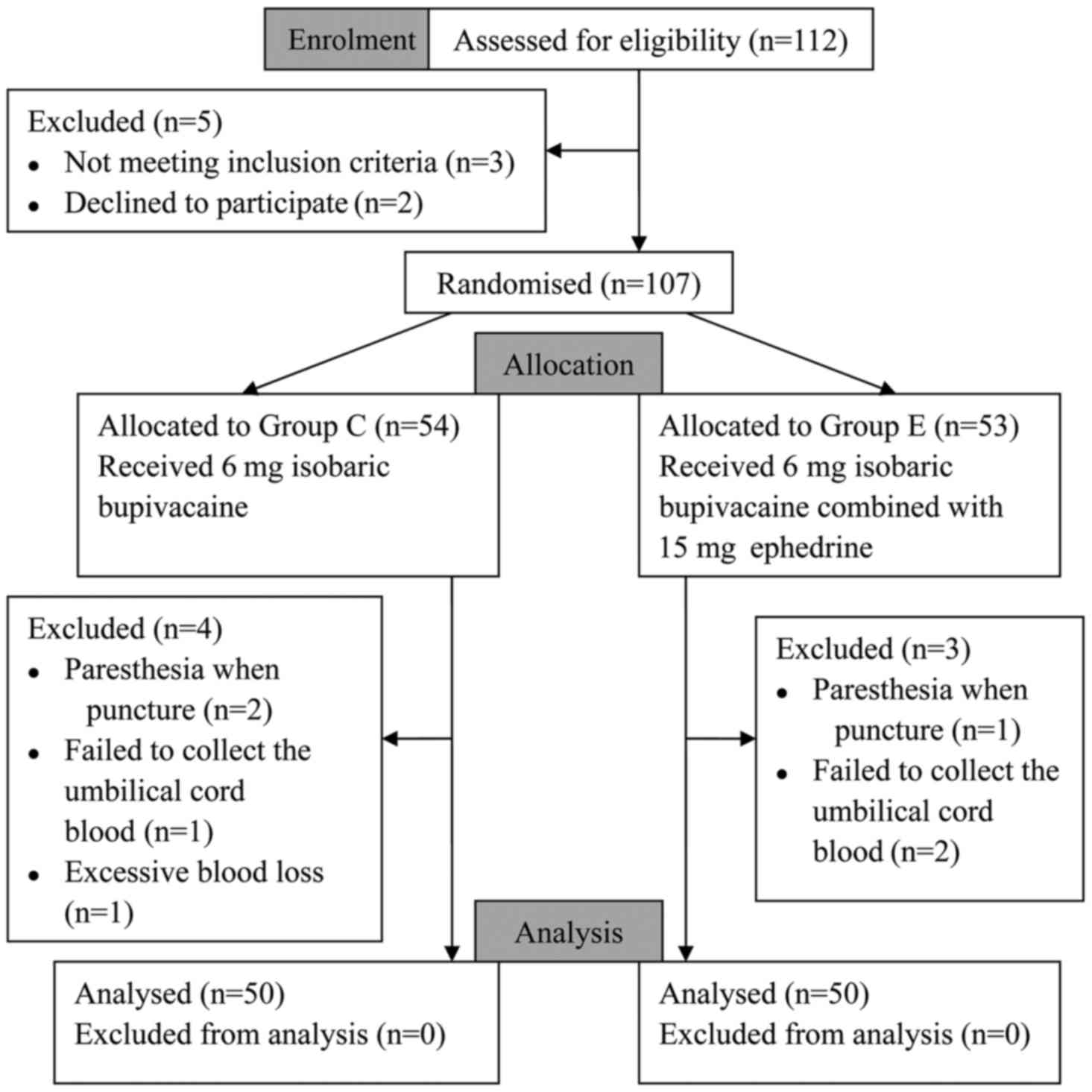
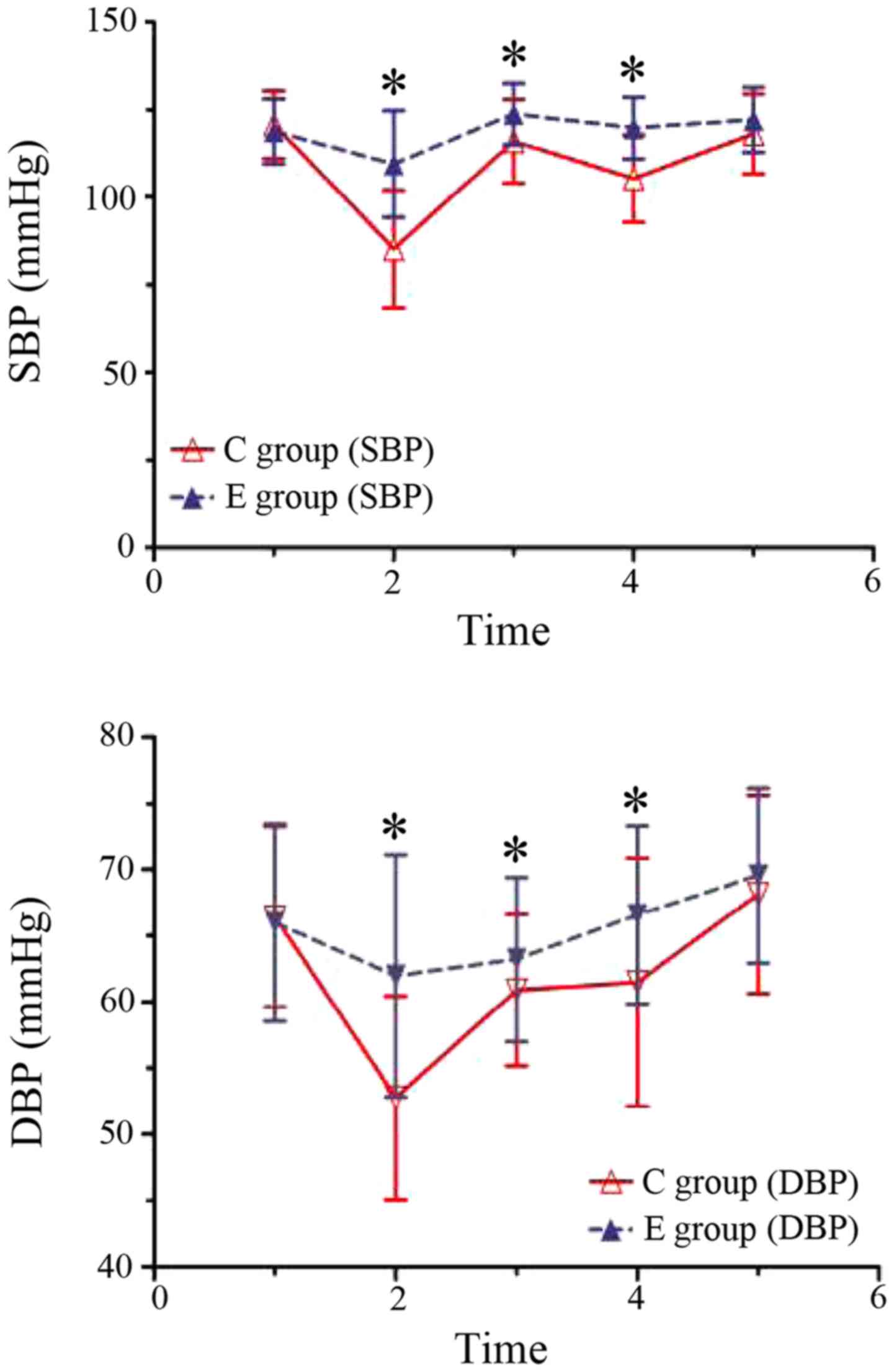
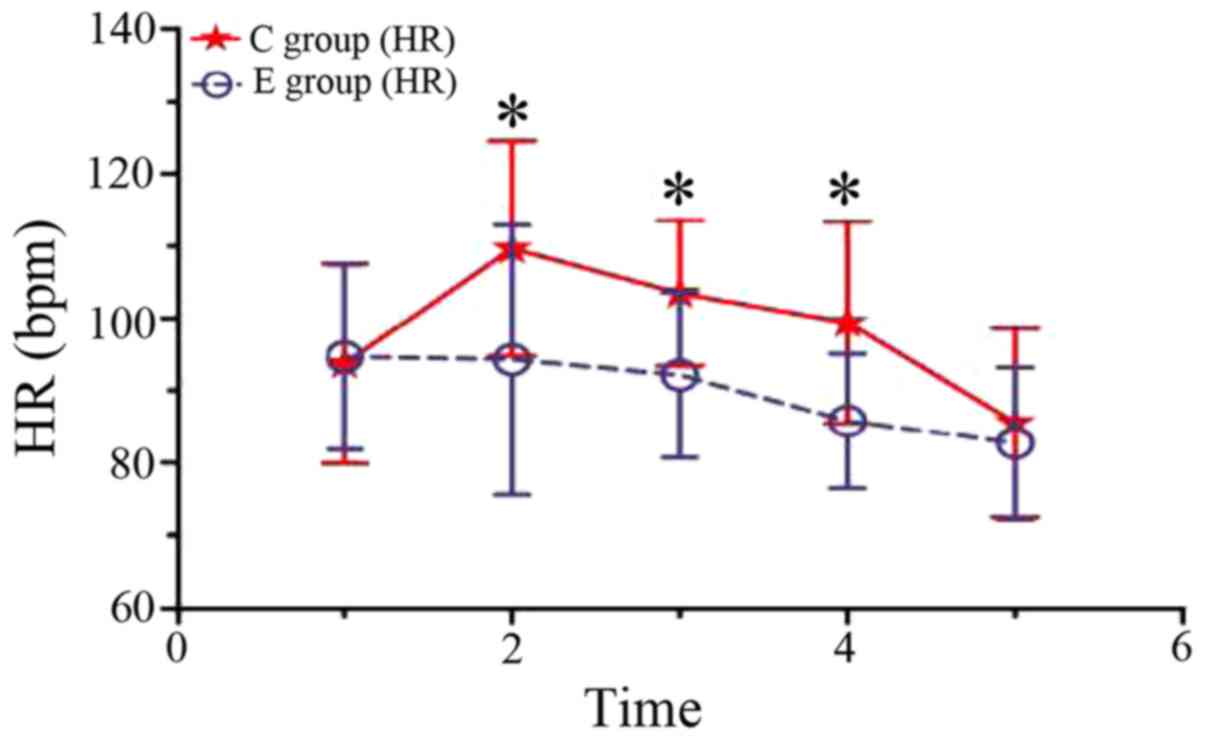
|
1
|
Kol IO, Kaygusuz K, Gursoy S, Cetin A,
Kahramanoglu Z, Ozkan F and Mimaroglu C: The effects of intravenous
ephedrine during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: A
randomized controlled trial. J Korean Med Sci. 24:883–888. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Moslemi F and Rasooli S: Comparison of
prophylactic infusion of phenylephrine with ephedrine for
prevention of hypotension in elective cesarean section under spinal
anesthesia: A randomized clinical trial. Iran J Med Sci. 40:19–26.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tamilselvan P, Fernando R, Bray J, Sodhi M
and Columb M: The effects of crystalloid and colloid preload on
cardiac output in the parturient undergoing planned cesarean
delivery under spinal anesthesia: A randomized trial. Anesth Analg.
109:1916–1921. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
De-Giorgio F, Grassi VM, Vetrugno G,
d'Aloja E, Pascali VL and Arena V: Supine hypotensive syndrome as
the probable cause of both maternal and fetal death. J Forensic
Sci. 57:1646–1649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller R, Eriksson L, Fleisher L,
Wiener-Kronish J and Young W: Anaesthesia for Orthopaedic
SurgeryMiller's Anesthesia. 2. 7th. Churchill Livingstone
Publishers; Philadelphia (PA): pp. 22522010
|
|
6
|
Simin A, Zahra F, Pouya HM and Reza T:
Comparison of the effect of ephedrine and phenylephrine in
treatment of hypotension after spinal anesthesia during cesarean
section. Open J Obstet Gynecol. 2:192–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Loubert C: Fluid and vasopressor
management for Cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia:
continuing professional development. Can J Anaesth. 59:604–619.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Turhanoglu S, Kaya S and Erdogan H: Is
there an advantage in using low-dose intrathecal bupivacaine for
cesarean section? J Anesth. 23:353–357. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gunda CP, Malinowski J, Tegginmath A,
Suryanarayana VG and Chandra SB: Vasopressor choice for hypotension
in elective Cesarean section: Ephedrine or phenylephrine? Arch Med
Sci. 6:257–263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhar D, Bharati S, Halder PS, Mondal S,
Sarkar M and Jana S: Efficacy of prophylactic intramuscular
ephedrine in prevention of hypotension during caesarean section
under spinal anaesthesia: A comparative study. J Indian Med Assoc.
109:300–303, 307. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Egger C, McCrackin M-A, Hofmeister E,
Touzot-Jourde G and Rohrbach B: Efficacy of preanesthetic
intramuscular administration of ephedrine for prevention of
anesthesia-induced hypotension in cats and dogs. Can Vet J.
50:179–184. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Veeser M, Hofmann T, Roth R, Klöhr S,
Rossaint R and Heesen M: Vasopressors for the management of
hypotension after spinal anesthesia for elective caesarean section.
Systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. Acta Anaesthesiol
Scand. 56:810–816. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin FQ, Qiu MT, Ding XX, Fu SK and Li Q:
Ephedrine versus phenylephrine for the management of hypotension
during spinal anesthesia for cesarean section: An updated
meta-analysis. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:591–597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo Q, Yao S, Wang G, et al: Clinical
anesthesiology. 4. 3rd. People's Medical Publishing Press; Beijing:
pp. 127–128. 2011
|
|
15
|
Rout CC and Rocke DA: Prevention of
hypotension following spinal anesthesia for cesarean section. Int
Anesthesiol Clin. 32:117–135. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Critchley LA, Stuart JC, Conway F and
Short TG: Hypotension during subarachnoid anaesthesia: Haemodynamic
effects of ephedrine. Br J Anaesth. 74:373–378. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee A, Kee WD Ngan and Gin T: A
dose-response meta-analysis of prophylactic intravenous ephedrine
for the prevention of hypotension during spinal anesthesia for
elective cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 98:483–490. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aragão FF, Aragão PW, Martins CA, Filho N
Salgado and Ede S Barroqueiro: Comparison of metaraminol,
phenylephrine and ephedrine in prophylaxis and treatment of
hypotension in cesarean section under spinal anesthesia. Rev Bras
Anestesiol. 64:299–306. 2014.(In Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cooper DW, Carpenter M, Mowbray P, Desira
WR, Ryall DM and Kokri MS: Fetal and maternal effects of
phenylephrine and ephedrine during spinal anesthesia for cesarean
delivery. Anesthesiology. 97:1582–1590. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Al-Mustafa MM, Abu-Halaweh SA, Aloweidi
AS, Murshidi MM, Ammari BA, Awwad ZM, Al-Edwan GM and Ramsay MA:
Effect of dexmedetomidine added to spinal bupivacaine for
urological procedures. Saudi Med J. 30:365–370. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kawasaki Y, Kumamoto E, Furue H and
Yoshimura M: Alpha 2 adrenoceptor mediated presynaptic inhibition
of primary afferent glutamatergic transmission in rat substantia
gelatinosa neurons. Anesthesiology. 98:682–689. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Djalali AG, Wang JC-F, Perez-Valdivieso
JR, Danninger T, Fritsch G, Zurakowski D and Gerner P: Ephedrine
shows synergistic motor blockade when combined with bupivacaine or
lidocaine for spinal anesthesia in a rat model. Anesth Analg.
116:944–948. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kroin JS, Buvanendran A, Beck DR, Topic
JE, Watts DE and Tuman KJ: Clonidine prolongation of lidocaine
analgesia after sciatic nerve block in rats Is mediated via the
hyperpolarization-activated cation current, not by
alpha-adrenoreceptors. Anesthesiology. 101:488–494. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|