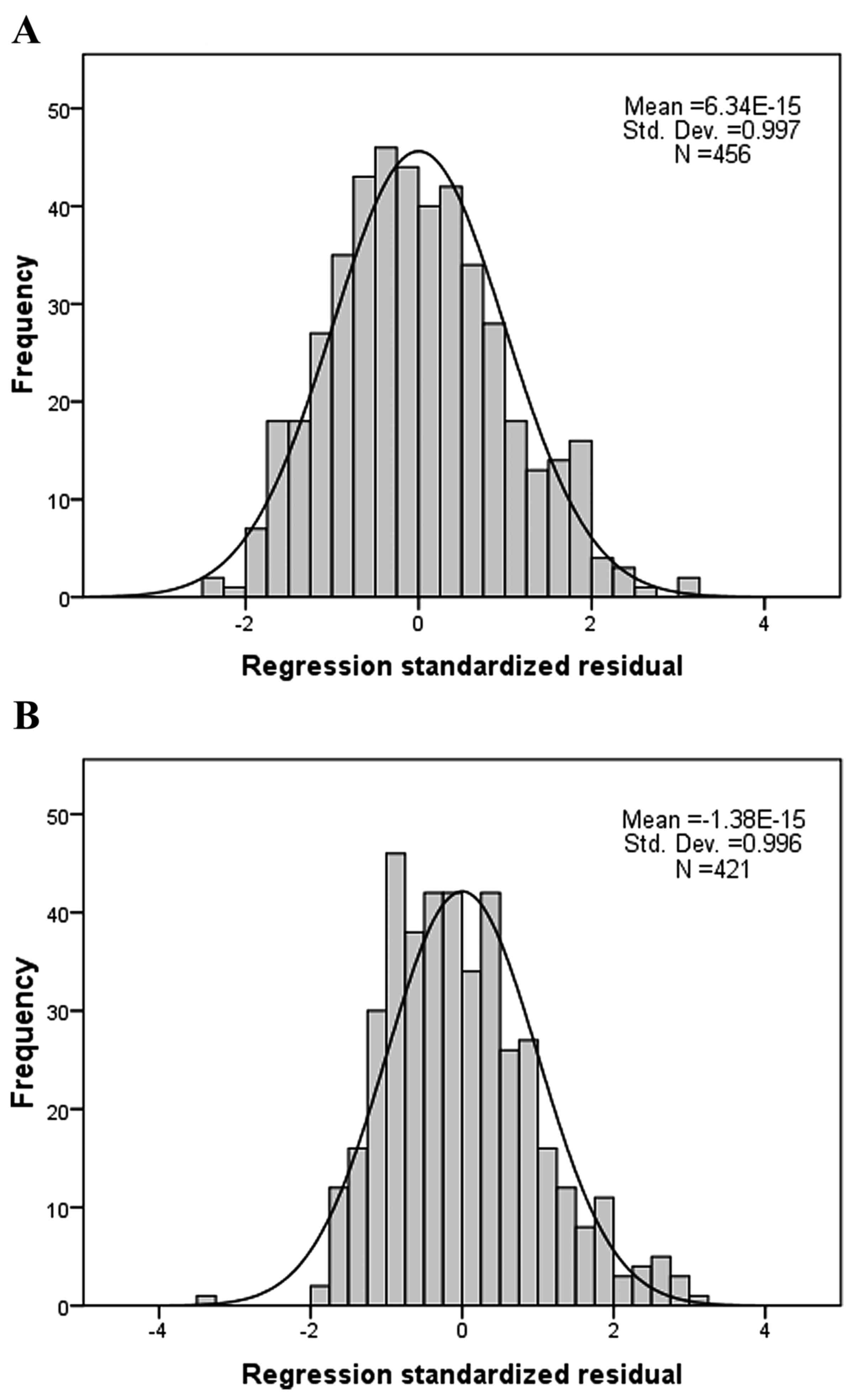
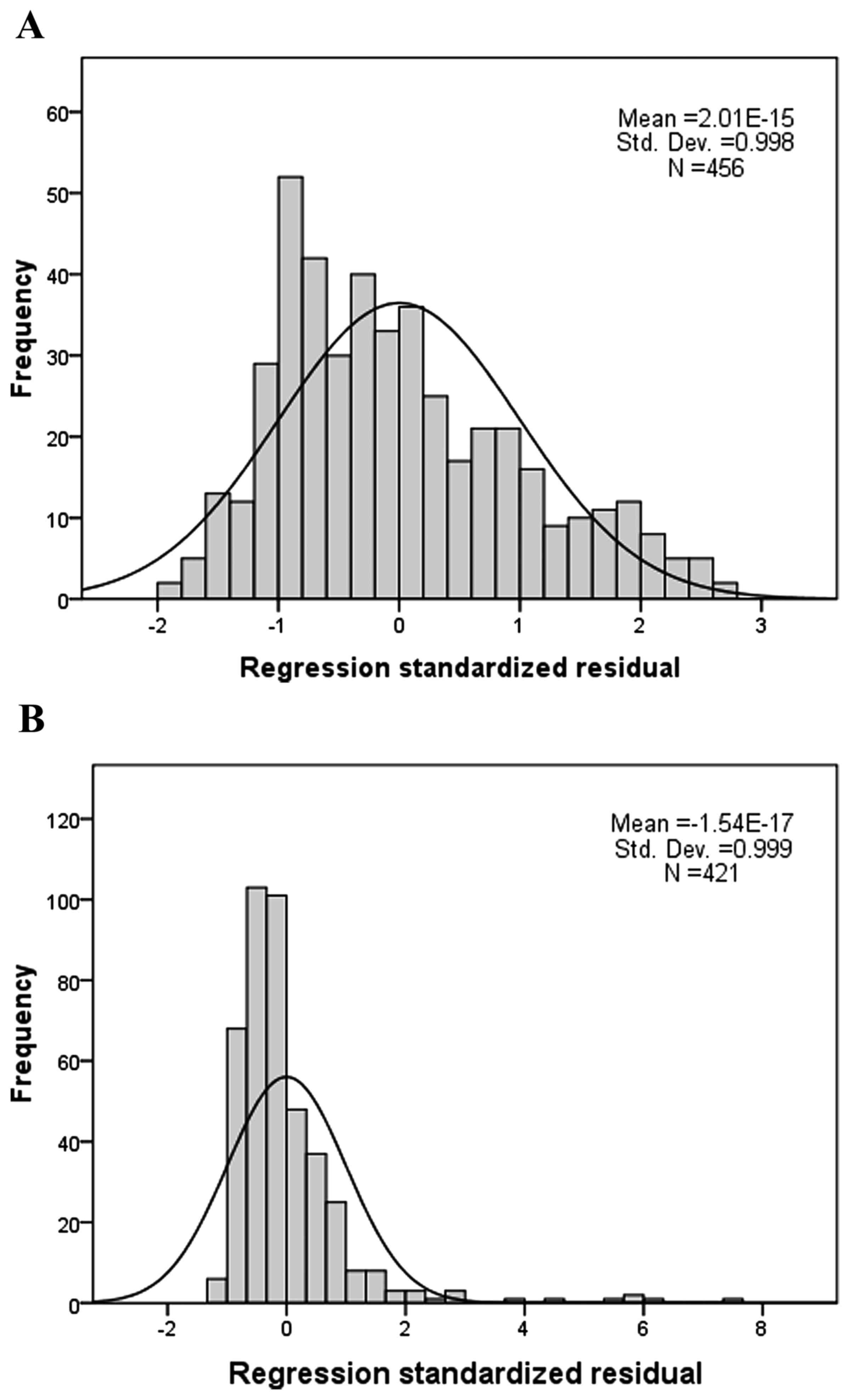
|
1
|
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I,
Beagley J, Linnenkamp U and Shaw JE: Global estimates of diabetes
prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin
Pract. 103:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khine AA and Marais DA: High prevalence of
primary dyslipidaemia in black South African patients at a tertiary
hospital in northern Gauteng, South Africa. S Afr Med J.
106:724–729. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jameson K, Amber V, D'Oca K, Mills D,
Giles A and Ambegaonkar B: Impact of lipid-lowering therapy on the
prevalence of dyslipidaemia in patients at high-risk of
cardiovascular events in UK primary care - a retrospective database
study. Int J Clin Pract. 67:1228–1237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tran HA, Chua Y and Petrovsky N: Test and
teach. Number Fifty-three. Diagnosis: Diabetes-related
dyslipidaemia. Pathology. 36:576–579. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agoşton-Coldea L, Zdrenghea D, Pop D,
Crăciun A, Rusu ML and Mocan T: Prevalence and particularities of
dyslipidaemia in subjects with coronary heart disease. Rom J Intern
Med. 45:341–347. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Qiao Q, Laatikainen T, Söderberg
S, Jousilahti P, Onat A, Nilsson P and Tuomilehto J: DECODE Study
Group: The impact of dyslipidaemia on incidence of coronary heart
disease in Finns and Swedes with different categories of glucose
tolerance. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 91:406–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fiorentino TV, Prioletta A, Zuo P and
Folli F: Hyperglycemia-induced oxidative stress and its role in
diabetes mellitus related cardiovascular diseases. Curr Pharm Des.
19:5695–5703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Teramoto T, Sasaki J, Ishibashi S, Birou
S, Daida H, Dohi S, Egusa G, Hiro T, Hirobe K, Iida M, et al: Other
types of primary hyperlipoproteinemia(hyperlipidemia). Executive
summary of the Japan Atherosclerosis Society (JAS) guidelines for
the diagnosis and prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
diseases in Japan - 2012 version. J Atheroscler Thromb. 21:82–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Myers L and Mendis S: Cardiovascular
disease research output in WHO priority areas between 2002 and
2011. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 4:23–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen H, Yang B, Liu D, Liu W, Liu Y, Zhang
X and Hu L: Using blood indexes to predict overweight statuses: An
extreme learning machine-based approach. PLoS One. 10:e01430032015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hartman ML, Goodson JM, Barake R, Alsmadi
O, Al-Mutawa S, Ariga J, Soparkar P, Behbehani J, Behbehani K and
Welty F: Salivary glucose concentration exhibits threshold kinetics
in normal-weight, overweight, and obese children. Diabetes Metab
Syndr Obes. 8:9–15. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mateo-Gallego R, Perez-Calahorra S, Cofán
M, Baila-Rueda L, Cenarro A, Ros E, Puzo J and Civeira F: Serum
lipid responses to weight loss differ between overweight adults
with familial hypercholesterolemia and those with familial combined
hyperlipidemia. J Nutr. 144:1219–1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Di Bonito P, Pacifico L, Chiesa C, Invitti
C, Del Giudice E Miraglia, Baroni MG, Moio N, Pellegrin MC, Tomat
M, Licenziati MR, et al: ‘CARdiometabolic risk factors in
overweight and obese children in ITALY’ (CARITALY) Study Group:
White blood cell count may identify abnormal cardiometabolic
phenotype and preclinical organ damage in overweight/obese
children. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 26:502–509. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
No authors listed: Guidelines (2013) for
managing overweight and obesity in adults. Preface to the Expert
Panel Report (comprehensive version which includes systematic
evidence review, evidence statements, and recommendations). Obesity
(Silver Spring). 22:(Suppl 2). S402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li PF, Chen JS, Chang JB, Chang HW, Wu CZ,
Chuang TJ, Huang CL, Pei D, Hsieh CH and Chen YL: Association of
complete blood cell counts with metabolic syndrome in an elderly
population. BMC Geriatr. 16:102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hassan U, Reddy B Jr, Damhorst G, Sonoiki
O, Ghonge T, Yang C and Bashir R: A microfluidic biochip for
complete blood cell counts at the point-of-care. Technology (Singap
World Sci). 3:201–213. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Wang F, Liu Y, Xu J, Lin H, Jia B,
Zuo W, Jiang Y, Hu L and Lin F: Multiple Linear Regression and
Artificial Neural Network to Predict Blood Glucose in Overweight
Patients: Multiple Linear Regression and Artificial Neural Network
to Predict Blood Glucose in Overweight Patients. Exp Clin
Endocrinol Diabetes. 124:34–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu L, Hong G, Ma J, Wang X, Lin G, Zhang X
and Lu Z: Clearance rate and BP-ANN model in paraquat poisoned
patients treated with hemoperfusion. Biomed Res Int.
2015:2982532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma J, Cai J, Lin G, Chen H, Wang X, Wang X
and Hu L: Development of LC-MS determination method and
back-propagation ANN pharmacokinetic model of corynoxeine in rat. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 959:10–15. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Zhang M, Ma J, Zhang Y, Hong G,
Sun F, Lin G and Hu L: Metabolic changes in paraquat poisoned
patients and support vector machine model of discrimination. Biol
Pharm Bull. 38:470–475. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|