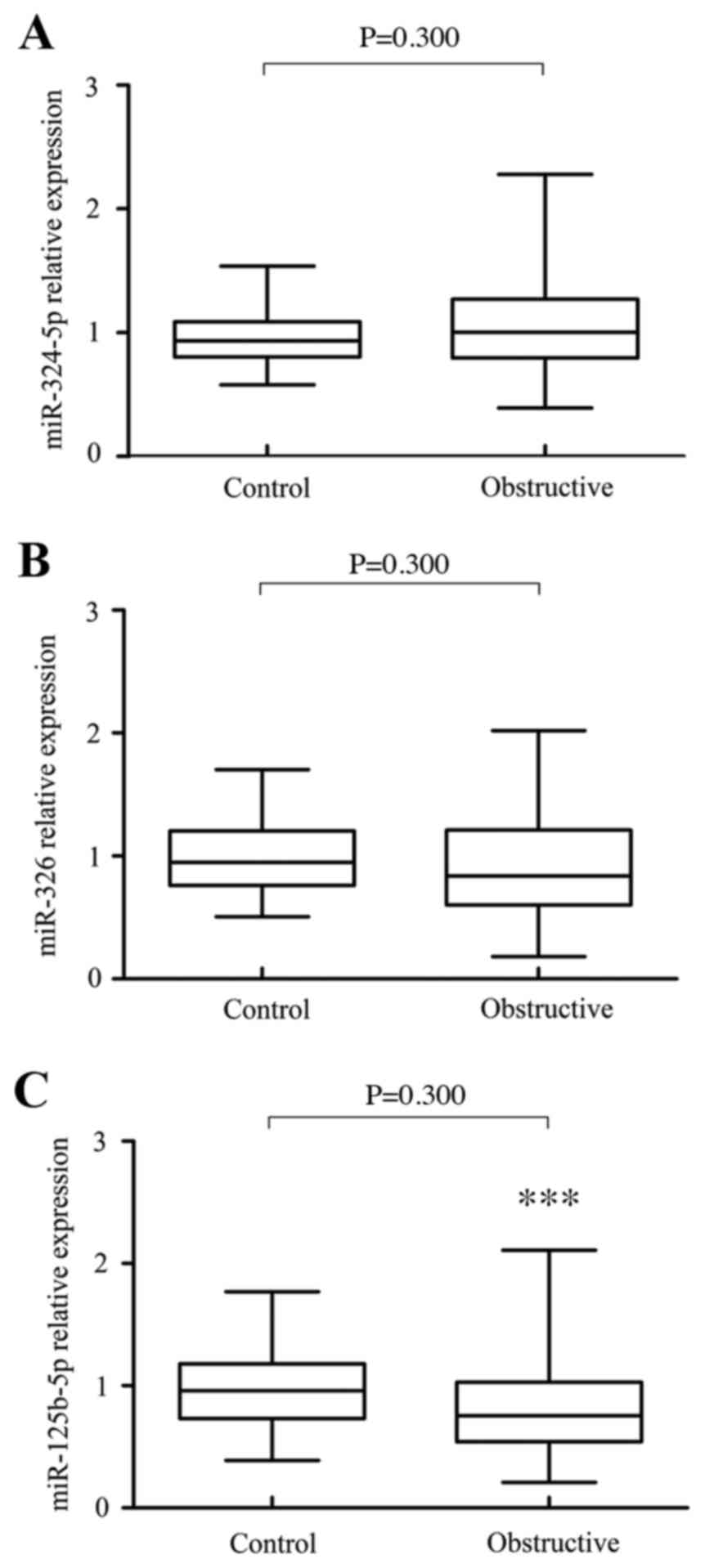
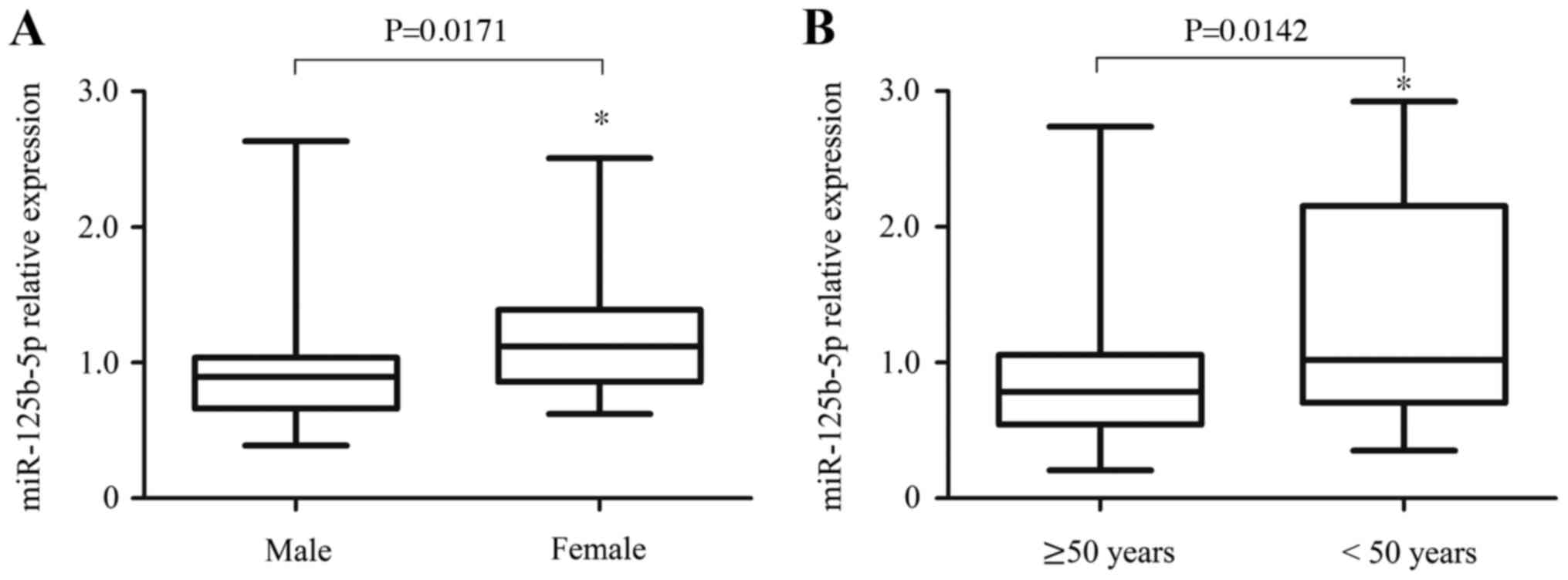
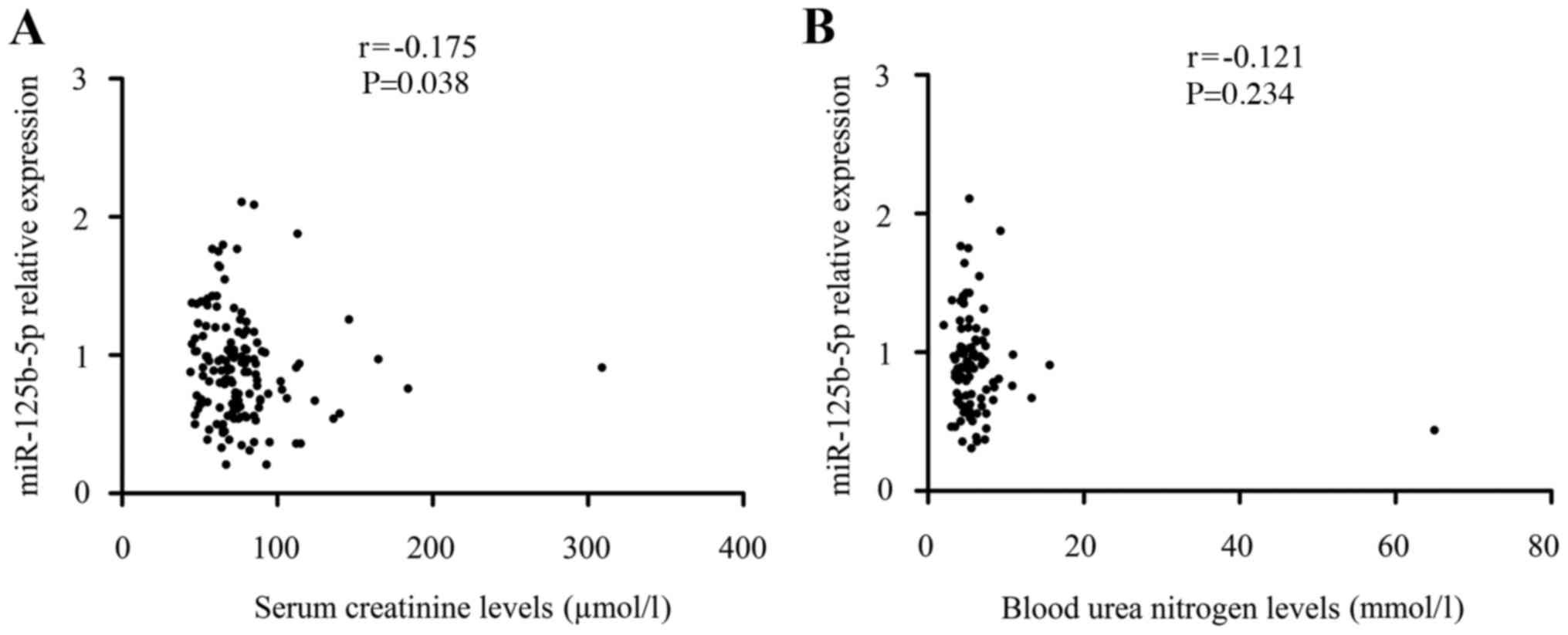
|
1
|
Dikmen B, Yagmurdur H, Akgul T, Astarci M,
Ustun H and Germiyanoglu C: Preventive effects of propofol and
ketamine on renal injury in unilateral ureteral obstruction. J
Anesth. 24:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ucero AC, Benito-Martin A, Izquierdo MC,
Sanchez-Niño MD, Sanz AB, Ramos AM, Berzal S, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido
J and Ortiz A: Unilateral ureteral obstruction: Beyond obstruction.
Int Urol Nephrol. 46:765–776. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kinn AC and Bohman SO: Renal structural
and functional changes after unilateral ureteral obstruction in
rabbits. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 17:223–234. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klahr S: New insights into the
consequences and mechanisms of renal impairment in obstructive
nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 18:689–699. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glowacki F, Savary G, Gnemmi V, Buob D,
van der Hauwaert C, Lo-Guidice JM, Bouyé S, Hazzan M, Pottier N,
Perrais M, et al: Increased circulating miR-21 levels are
associated with kidney fibrosis. PLoS One. 8:e580142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sayed D and Abdellatif M: MicroRNAs in
development and disease. Physiol Rev. 91:827–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Li PK
and Szeto CC: Urinary miR-21, miR-29, and miR-93: Novel biomarkers
of fibrosis. Am J Nephrol. 36:412–418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aguado-Fraile E, Ramos E, Conde E,
Rodríguez M, Martín-Gómez L, Lietor A, Candela Á, Ponte B, Liaño F
and García-Bermejo ML: A Pilot Study Identifying a Set of microRNAs
As Precise Diagnostic Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury. PLoS One.
10:e01271752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang B, Komers R, Carew R, Winbanks CE, Xu
B, Herman-Edelstein M, Koh P, Thomas M, Jandeleit-Dahm K,
Gregorevic P, et al: Suppression of microRNA-29 expression by
TGF-β1 promotes collagen expression and renal fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 23:252–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aguado-Fraile E, Ramos E, Sáenz-Morales D,
Conde E, Blanco-Sánchez I, Stamatakis K, del Peso L, Cuppen E,
Brüne B and Bermejo ML: miR-127 protects proximal tubule cells
against ischemia/reperfusion: Identification of kinesin family
member 3B as miR-127 target. PLoS One. 7:e443052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan PC, Chen CC, Chen YC, Chang YS and Chu
PH: MicroRNAs in acute kidney injury. Hum Genomics. 10:292016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Z, Wang S, Mi QS and Dong Z: MicroRNAs
in Pathogenesis of Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron. 134:149–153. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai Y, Lu H, Lin C, Xu Y, Hu D, Liang Y,
Hong W and Chen B: Sonic hedgehog-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Int J Mol Med.
37:1317–1327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu L, Lin X, Lu H, Chen B and Bai Y: An
overview of hedgehog signaling in fibrosis. Mol Pharmacol.
87:174–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai Y, Lu H, Wu C, Liang Y, Wang S, Lin C,
Chen B and Xia P: Resveratrol inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and renal fibrosis by antagonizing the hedgehog
signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 92:484–493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ferretti E, De Smaele E, Miele E, Laneve
P, Po A, Pelloni M, Paganelli A, Di Marcotullio L, Caffarelli E,
Screpanti I, et al: Concerted microRNA control of Hedgehog
signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO
J. 27:2616–2627. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang J, Na S, Liu C, Pan S, Cai J and Qiu
J: MicroRNA-125b suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cell invasion by targeting ITGA9 in melanoma. Tumour Biol.
37:5941–5949. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou JN, Zeng Q, Wang HY, Zhang B, Li ST,
Nan X, Cao N, Fu CJ, Yan XL, Jia YL, et al: MicroRNA-125b
attenuates epithelial-mesenchymal transitions and targets stem-like
liver cancer cells through small mothers against decapentaplegic 2
and 4. Hepatology. 62:801–815. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Das S, Kumar M, Negi V, Pattnaik B,
Prakash YS, Agrawal A and Ghosh B: MicroRNA-326 regulates
profibrotic functions of transforming growth factor-β in pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:882–892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagpal V, Rai R, Place AT, Murphy SB,
Verma SK, Ghosh AK and Vaughan DE: miR-125b Is Critical for
Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition and Cardiac Fibrosis.
Circulation. 133:291–301. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Song L, Liu D, Zhao Y, He J, Kang H, Dai
Z, Wang X, Zhang S and Zan Y: Sinomenine inhibits breast cancer
cell invasion and migration by suppressing NF-κB activation
mediated by IL-4/miR-324-5p/CUEDC2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 464:705–710. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans
J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL,
et al: The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of
quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Butler J, Chirovsky D, Phatak H, McNeill A
and Cody R: Renal function, health outcomes, and resource
utilization in acute heart failure: A systematic review. Circ Heart
Fail. 3:726–745. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Thiemermann C, Patel NS, Kvale EO,
Cockerill GW, Brown PA, Stewart KN, Cuzzocrea S, Britti D,
Mota-Filipe H and Chatterjee PK: High density lipoprotein (HDL)
reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:1833–1843. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhong X, Chung AC, Chen HY, Meng XM and
Lan HY: Smad3-mediated upregulation of miR-21 promotes renal
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1668–1681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qin W, Chung AC, Huang XR, Meng XM, Hui
DS, Yu CM, Sung JJ and Lan HY: TGF-β/Smad3 signaling promotes renal
fibrosis by inhibiting miR-29. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1462–1474.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chung AC, Huang XR, Meng X and Lan HY:
miR-192 mediates TGF-beta/Smad3-driven renal fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:1317–1325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hyun J, Wang S, Kim J, Kim GJ and Jung Y:
MicroRNA125b-mediated Hedgehog signaling influences liver
regeneration by chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Sci
Rep. 5:141352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|