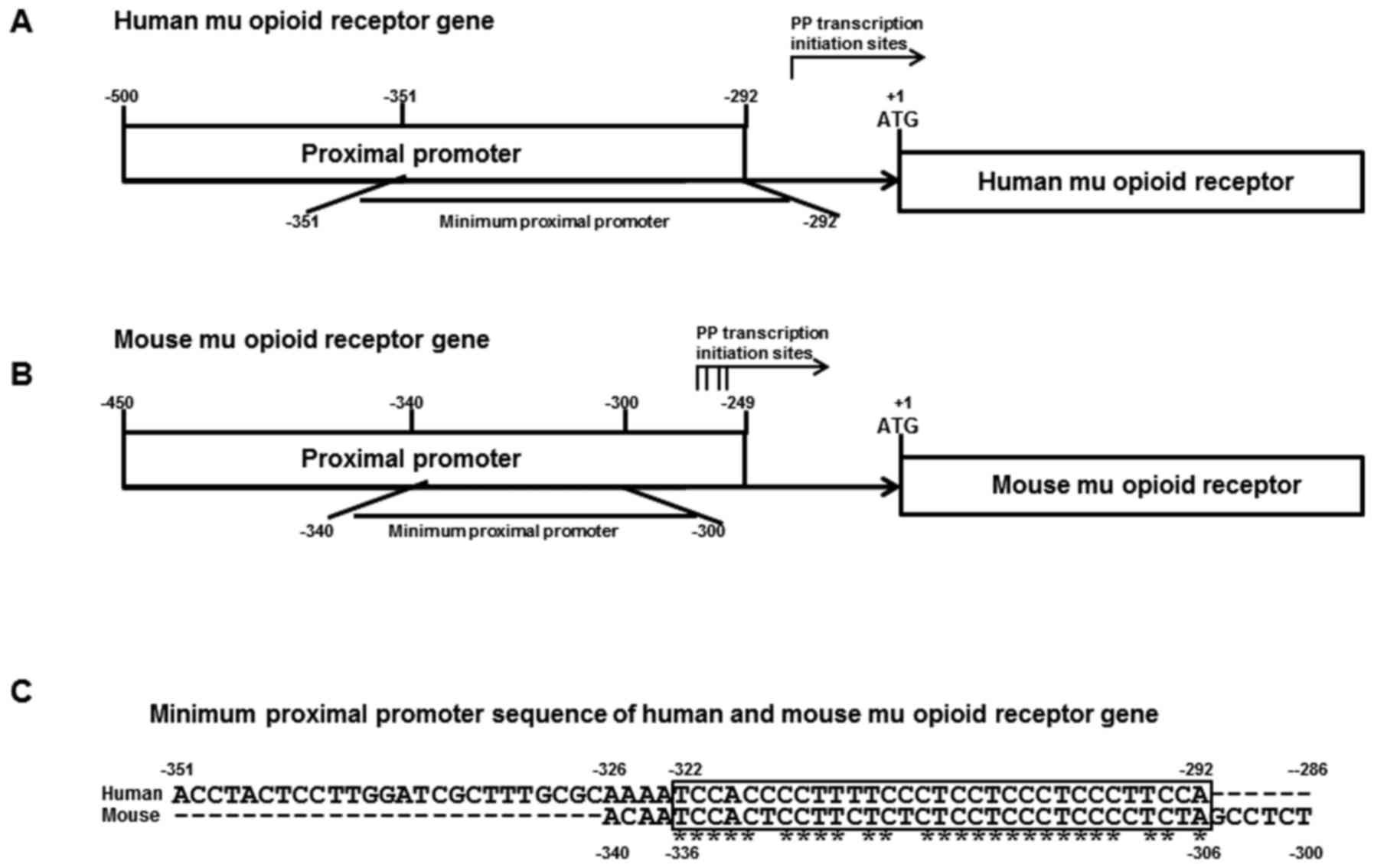
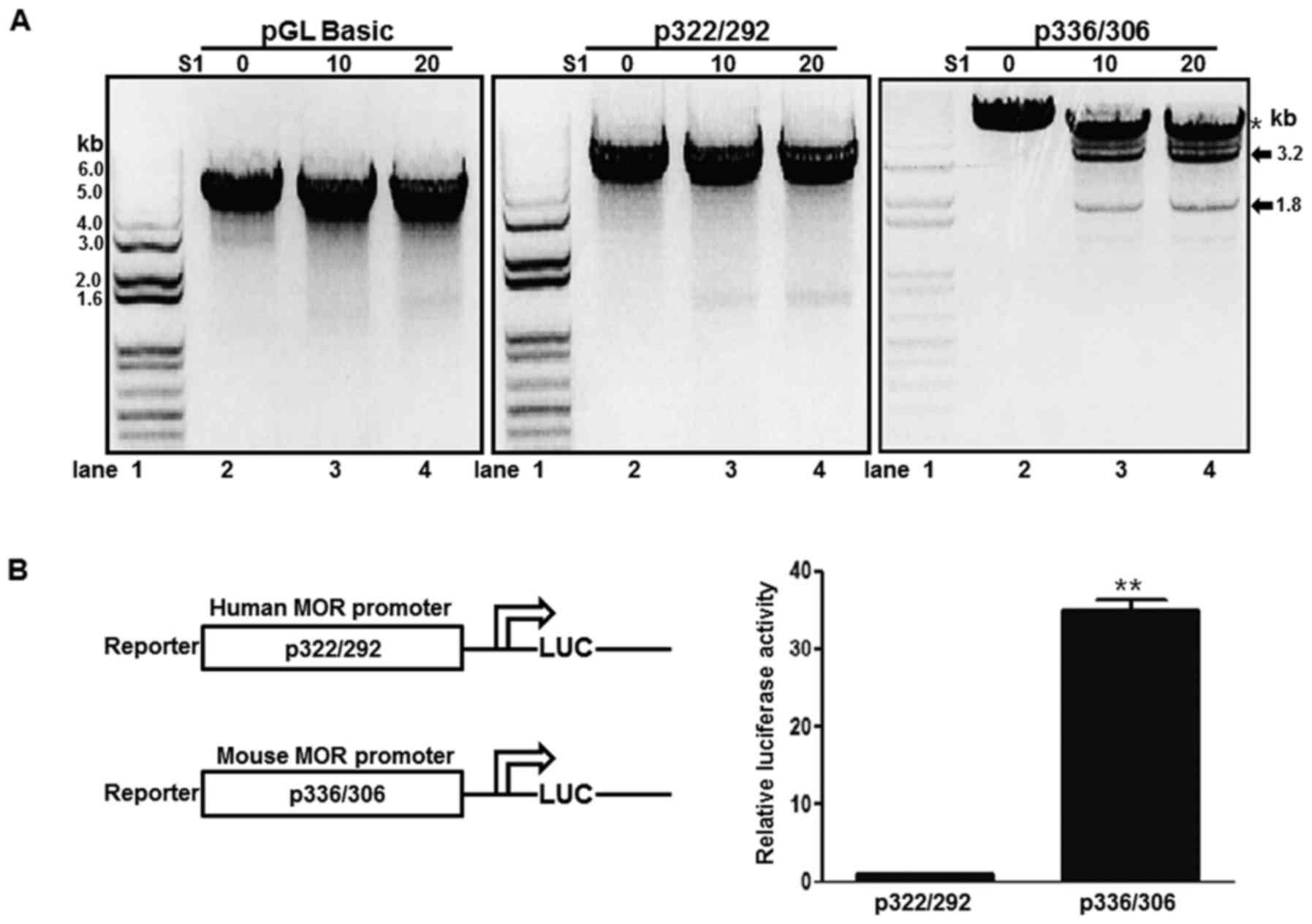
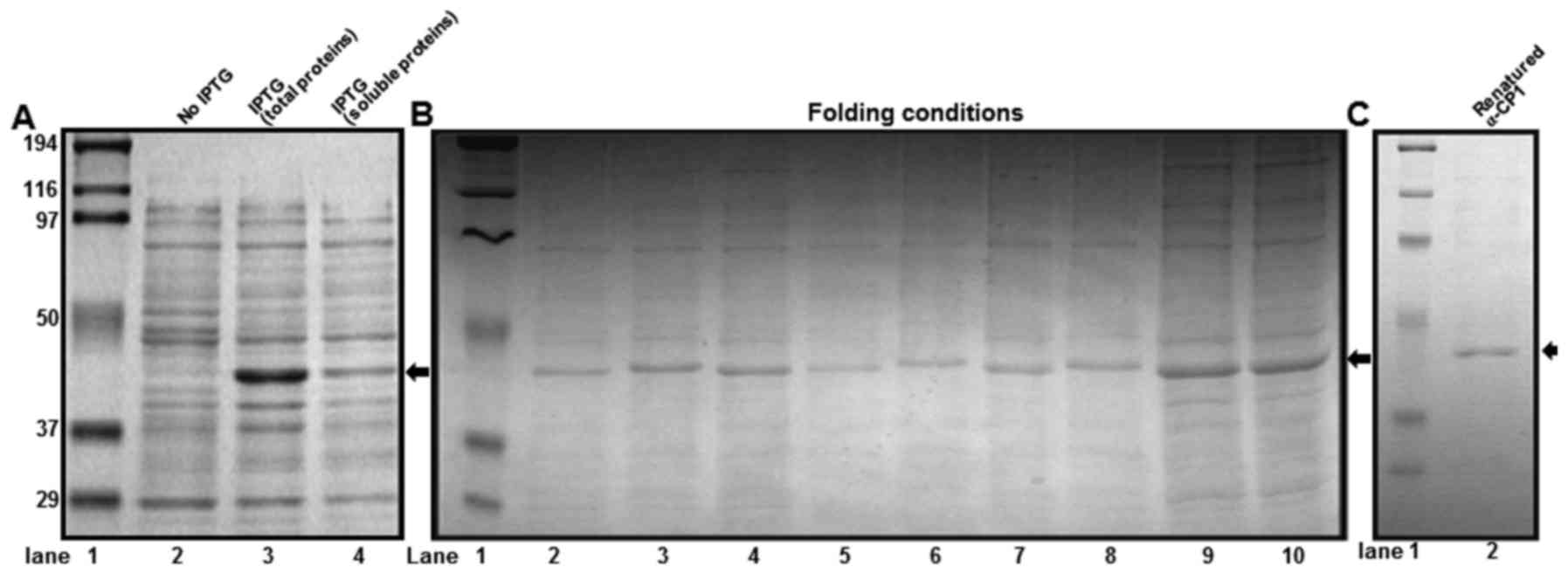
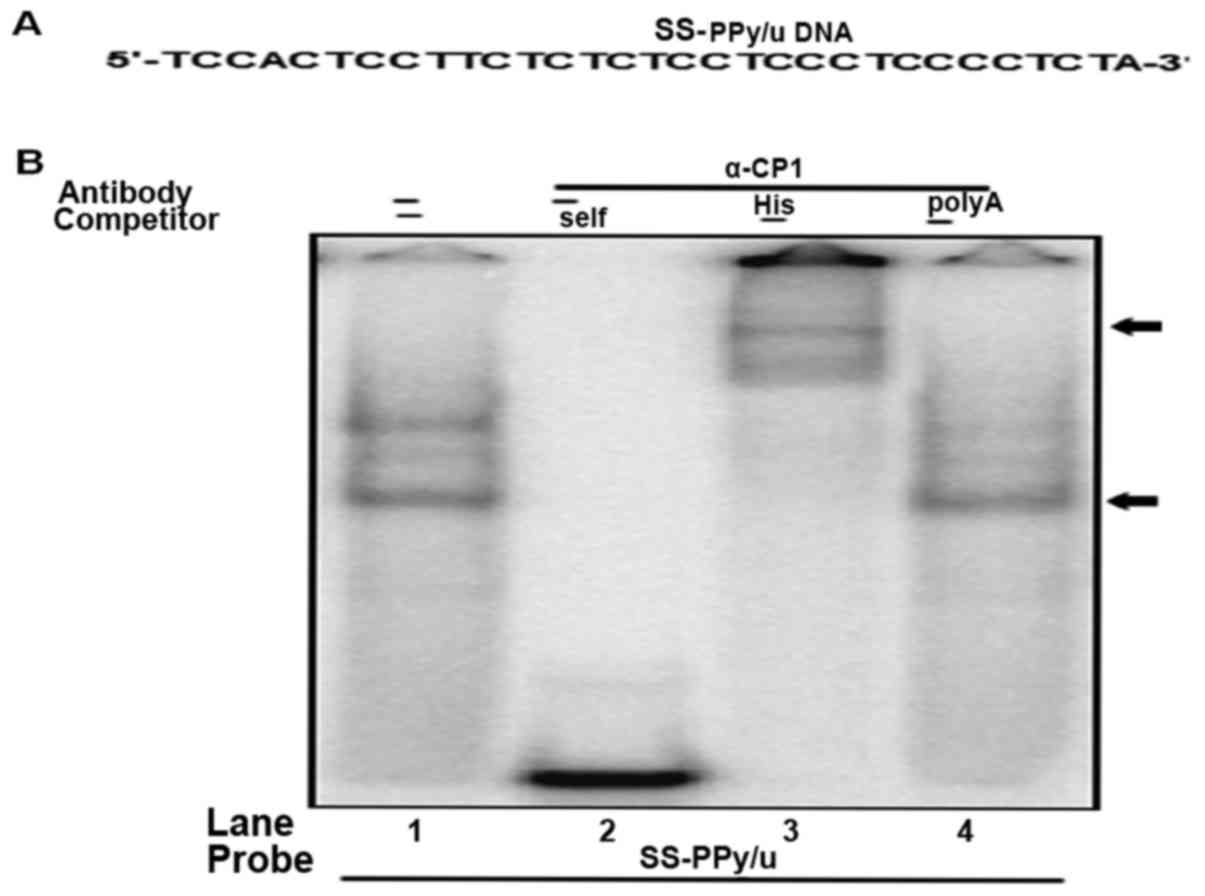
|
1
|
Min BH, Augustin LB, Felsheim RF, Fuchs JA
and Loh HH: Genomic structure analysis of promoter sequence of a
mouse mu opioid receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:9081–9085. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei LN and Loh HH: Regulation of opioid
receptor expression. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2:69–75. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kieffer BL: Recent advances in molecular
recognition and signal transduction of active peptides: Receptors
for opioid peptides. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 15:615–635. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kieffer BL: Opioids: First lessons from
knockout mice. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 20:19–26. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Law PY, Loh HH and Wei LN: Insights into
the receptor transcription and signaling: Implications in opioid
tolerance and dependence. Neuropharmacology. 47:(Suppl 1).
S300–S311. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Law PY, Wong YH and Loh HH: Molecular
mechanisms and regulation of opioid receptor signaling. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 40:389–430. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matthes HW, Maldonado R, Simonin F,
Valverde O, Slowe S, Kitchen I, Befort K, Dierich A, Le Meur M,
Dollé P, et al: Loss of morphine-induced analgesia, reward effect
and withdrawal symptoms in mice lacking the mu-opioid-receptor
gene. Nature. 383:819–823. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mansour A, Fox CA, Akil H and Watson SJ:
Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: Anatomical and
functional implications. Trends Neurosci. 18:22–29. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uhl GR, Sora I and Wang Z: The mu opiate
receptor as a candidate gene for pain: Polymorphisms, variations in
expression, nociception and opiate responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 96:7752–7755. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mogil JS: The genetic mediation of
individual differences in sensitivity to pain and its inhibition.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7744–7751. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Korostynski M, Kaminska-Chowaniec D,
Piechota M and Przewlocki R: Gene expression profiling in the
striatum of inbred mouse strains with distinct opioid-related
phenotypes. BMC Genomics. 7:1462006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doyle GA, Sheng XR, Schwebel CL, Ferraro
TN, Berrettini WH and Buono RJ: Identification and functional
significance of polymorphisms in the mu-opioid receptor gene (Oprm)
promoter of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Neurosci Res. 55:244–254. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ko JL, Chen HC and Loh HH: Differential
promoter usage of mouse mu-opioid receptor gene during development.
Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 104:184–193. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ko JL, Liu HC, Minnerath SR and Loh HH:
Transcriptional regulation of mouse mu-opioid receptor gene. J Biol
Chem. 273:27678–27685. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ko JL and Loh HH: Single-stranded
DNA-binding complex involved in transcriptional regulation of mouse
mu-opioid receptor gene. J Biol Chem. 276:788–795. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choe CY, Dong J, Law PY and Loh HH:
Differential gene expression activity among species-specific
polypyrimidine/polypurine motifs in mu opioid receptor gene
promoters. Gene. 471:27–36. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi HS, Song KY, Hwang CK, Kim CS, Law
PY, Wei LN and Loh HH: A proteomics approach for identification of
single strand DNA-binding proteins involved in transcriptional
regulation of mouse mu opioid receptor gene. Mol Cell Proteomics.
7:1517–1529. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cook RJ, Karch C, Nahar P, Rivera A and Ko
JL: Effects of desferoxamine-induced hypoxia on neuronal human
mu-opioid receptor gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
398:56–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schroth GP and Ho PS: Occurrence of
potential cruciform and H-DNA forming sequences in genomic DNA.
Nucleic Acids Res. 23:1977–1983. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kang DH, Song KY, Wei LN, Law PY, Loh HH
and Choi HS: Novel function of the poly(c)-binding protein α-CP2 as
a transcriptional activator that binds to single-stranded DNA
sequences. Int J Mol Med. 32:1187–1194. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patterson SD and Aebersold R: Mass
spectrometric approaches for the identification of gel-separated
proteins. Electrophoresis. 16:1791–1814. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hwang CK, Wu X, Wang G, Kim CS and Loh HH:
Mouse mu opioid receptor distal promoter transcriptional regulation
by SOX proteins. J Biol Chem. 278:3742–3750. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi HS, Hwang CK, Kim CS, Song KY, Law
PY, Wei LN and Loh HH: Transcriptional regulation of mouse mu
opioid receptor gene: Sp3 isoforms (M1, M2) function as repressors
in neuronal cells to regulate the mu opioid receptor gene. Mol
Pharmacol. 67:1674–1683. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hardison RC: Comparative genomics. PLoS
Biol. 1:E582003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wei LN and Loh HH: Transcriptional and
epigenetic regulation of opioid receptor genes: Present and future.
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 51:75–97. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vuillaumier S, Dixmeras I, Messaï H,
Lapouméroulie C, Lallemand D, Gekas J, Chehab FF, Perret C, Elion J
and Denamur E: Cross-species characterization of the promoter
region of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
gene reveals multiple levels of regulation. Biochem J. 327:651–662.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|