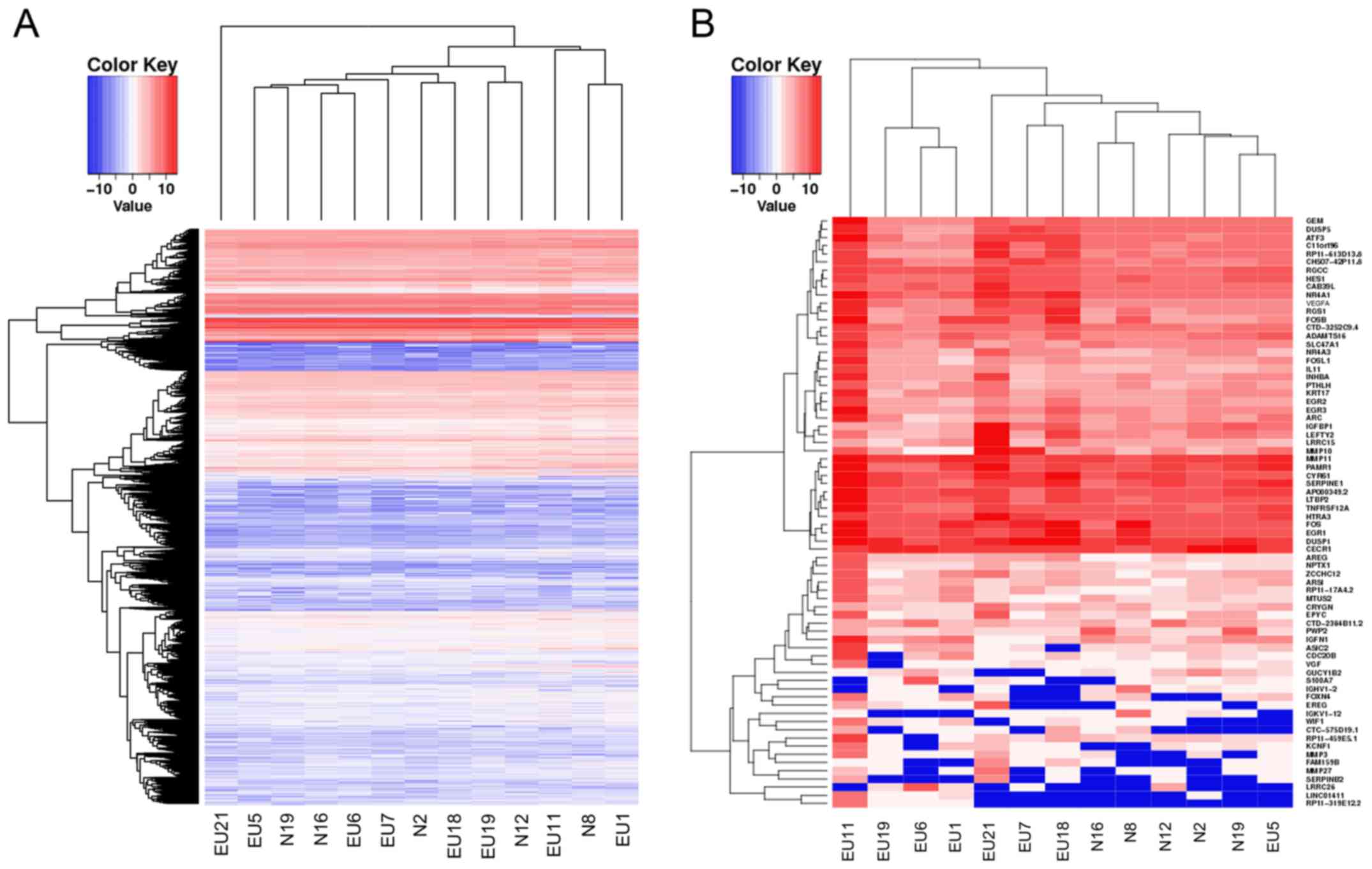
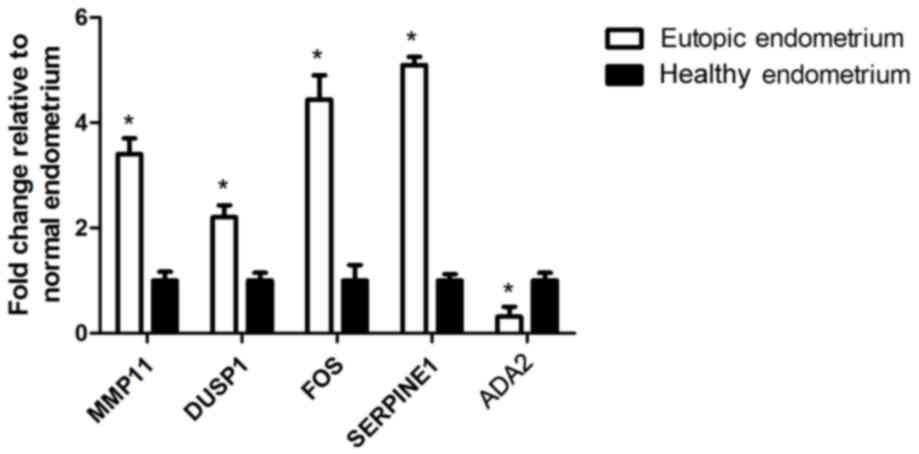
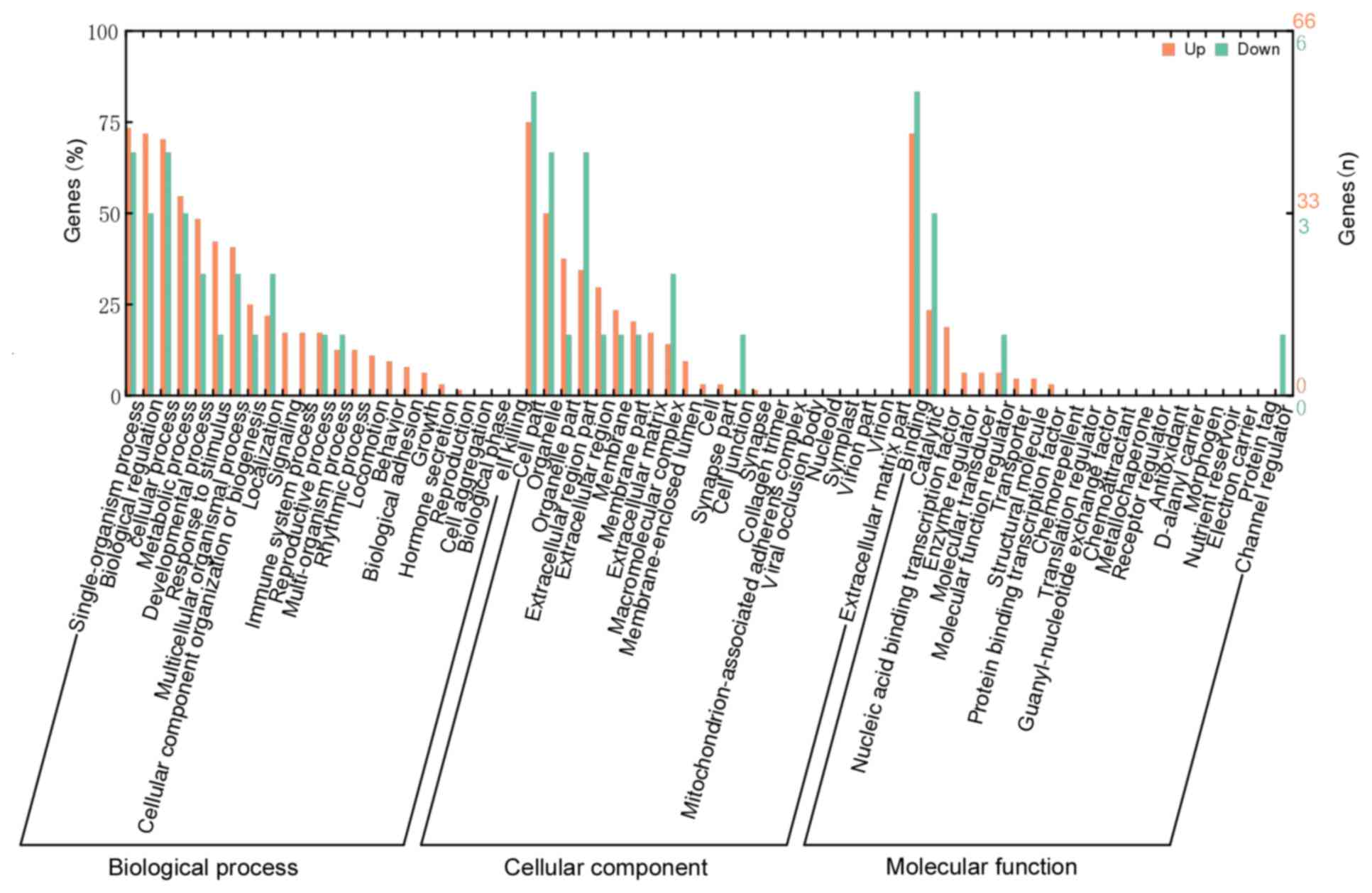
|
1
|
Kennedy S, Bergqvist A, Chapron C,
D'Hooghe T, Dunselman G, Greb R, Hummelshoj L, Prentice A and
Saridogan E: ESHRE Special Interest Group for Endometriosis and
Endometrium Guideline Development Group: ESHRE guideline for the
diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Hum Reprod. 20:2698–2704.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hudelist G, Fritzer N, Thomas A, Niehues
C, Oppelt P, Haas D, Tammaa A and Salzer H: Diagnostic delay for
endometriosis in Austria and Germany: Causes and possible
consequences. Hum Reprod. 27:3412–3416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sourial S, Tempest N and Hapangama DK:
Theories on the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Int J Reprod Med.
2014:1795152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sampson JA: Metastatic or Embolic
Endometriosis, due to the Menstrual Dissemination of Endometrial
Tissue into the Venous Circulation. Am J Pathol. 3:93–110.43.
1927.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu H and Lang JH: Is abnormal eutopic
endometrium the cause of endometriosis? The role of eutopic
endometrium in pathogenesis of endometriosis. Med Sci Monit.
17:RA92–RA99. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lattarulo S, Pezzolla A, Fabiano G and
Palasciano N: Intestinal endometriosis: Role of laparoscopy in
diagnosis and treatment. Int Surg. 94:310–314. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fassbender A, Vodolazkaia A, Saunders P,
Lebovic D, Waelkens E, De Moor B and D'Hooghe T: Biomarkers of
endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 99:1135–1145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
American Society for Reproductive, .
Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification
of endometriosis: 1996. Fertil Steril. 67:817–821. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Noyes RW, Hertig AT and Rock J: Dating the
endometrial biopsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 122:262–263. 1975.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chomczynski P and Sacchi N: The
single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium
thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction: Twenty-something years
on. Nat Protoc. 1:581–585. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
May KE, Villar J, Kirtley S, Kennedy SH
and Becker CM: Endometrial alterations in endometriosis: A
systematic review of putative biomarkers. Hum Reprod Update.
17:637–653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Burney RO, Talbi S, Hamilton AE, Vo KC,
Nyegaard M, Nezhat CR, Lessey BA and Giudice LC: Gene expression
analysis of endometrium reveals progesterone resistance and
candidate susceptibility genes in women with endometriosis.
Endocrinology. 148:3814–3826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sherwin JR, Sharkey AM, Mihalyi A, Simsa
P, Catalano RD and D'Hooghe TM: Global gene analysis of late
secretory phase, eutopic endometrium does not provide the basis for
a minimally invasive test of endometriosis. Hum Reprod.
23:1063–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tamaresis JS, Irwin JC, Goldfien GA,
Rabban JT, Burney RO, Nezhat C, DePaolo LV and Giudice LC:
Molecular classification of endometriosis and disease stage using
high-dimensional genomic data. Endocrinology. 155:4986–4999. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Muramatsu T and Miyauchi T: Basigin
(CD147): A multifunctional transmembrane protein involved in
reproduction, neural function, inflammation and tumor invasion.
Histol Histopathol. 18:981–987. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pitsos M and Kanakas N: The role of matrix
metalloproteinases in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Reprod
Sci. 16:717–726. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gilabert-Estellés J, Ramón LA, España F,
Gilabert J, Vila V, Réganon E, Castelló R, Chirivella M and
Estellés A: Expression of angiogenic factors in endometriosis:
Relationship to fibrinolytic and metalloproteinase systems. Hum
Reprod. 22:2120–2127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramón L, Gilabert-Estellés J, Castelló R,
Gilabert J, España F, Romeu A, Chirivella M, Aznar J and Estellés
A: mRNA analysis of several components of the plasminogen activator
and matrix metalloproteinase systems in endometriosis using a
real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. Hum Reprod. 20:272–278. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uzan C, Cortez A, Dufournet C, Fauvet R,
Siffroi JP and Daraï E: Eutopic endometrium and peritoneal, ovarian
and bowel endometriotic tissues express a different profile of
matrix metalloproteinases-2, −3 and −11, and of tissue inhibitor
metalloproteinases-1 and −2. Virchows Arch. 445:603–609. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cominelli A, Chevronnay HP Gaide, Lemoine
P, Courtoy PJ, Marbaix E and Henriet P: Matrix metalloproteinase-27
is expressed in CD163+/CD206+ M2 macrophages in the cycling human
endometrium and in superficial endometriotic lesions. Mol Hum
Reprod. 20:767–775. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao L, Gu C and Meng Y: Meta-analysis of
the association between endometriosis and polymorphisms in ACE and
PAI-1. Int J Clin Exp Med. 9:10602–10614. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Braza-Boïls A, Marí-Alexandre J, Gilabert
J, Sánchez-Izquierdo D, España F, Estellés A and Gilabert-Estellés
J: MicroRNA expression profile in endometriosis: Its relation to
angiogenesis and fibrinolytic factors. Hum Reprod. 29:978–988.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Milde-Langosch K: The Fos family of
transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis. Eur J
Cancer. 41:2449–2461. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nemos C, Delage-Mourroux R, Jouvenot M and
Adami P: Onset of direct 17-beta estradiol effects on proliferation
and c-fos expression during oncogenesis of endometrial glandular
epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 296:109–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan H, Sheng JZ, Tang L, Zhu R, Zhou TH
and Huang HF: Increased expression of c-fos protein associated with
increased matrix metalloproteinase-9 protein expression in the
endometrium of endometriotic patients. Fertil Steril. 90:1000–1007.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Morsch DM, Carneiro MM, Lecke SB, Araújo
FC, Camargos AF, Reis FM and Spritzer PM: c-fos gene and protein
expression in pelvic endometriosis: A local marker of estrogen
action. J Mol Histol. 40:53–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
O'Donovan KJ, Tourtellotte WG, Millbrandt
J and Baraban JM: The EGR family of transcription-regulatory
factors: Progress at the interface of molecular and systems
neuroscience. Trends Neurosci. 22:167–173. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Birt JA, Nabli H, Stilley JA, Windham EA,
Frazier SR and Sharpe-Timms KL: Elevated peritoneal fluid TNF-α
incites ovarian early growth response factor 1 expression and
downstream protease mediators: A correlation with ovulatory
dysfunction in endometriosis. Reprod Sci. 20:514–523. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Djokovic D and Calhaz-Jorge C:
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in endometriosis. Acta Med
Port. 27:489–497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Groothuis PG, Nap AW, Winterhager E and
Grümmer R: Vascular development in endometriosis. Angiogenesis.
8:147–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Taylor RN, Yu J, Torres PB, Schickedanz
AC, Park JK, Mueller MD and Sidell N: Mechanistic and therapeutic
implications of angiogenesis in endometriosis. Reprod Sci.
16:140–146. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bourlev V, Volkov N, Pavlovitch S, Lets N,
Larsson A and Olovsson M: The relationship between microvessel
density, proliferative activity and expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor-A and its receptors in eutopic
endometrium and endometriotic lesions. Reproduction. 132:501–509.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Iaco P, Marabini A, Stefanetti M, Del
Vecchio C and Bovicelli L: Acceptability and pain of outpatient
hysteroscopy. J Am Assoc Gynecol Laparosc. 7:71–75. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nisolle M, Paindaveine B, Bourdon A,
Berlière M, Casanas-Roux F and Donnez J: Histologic study of
peritoneal endometriosis in infertile women. Fertil Steril.
53:984–988. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|