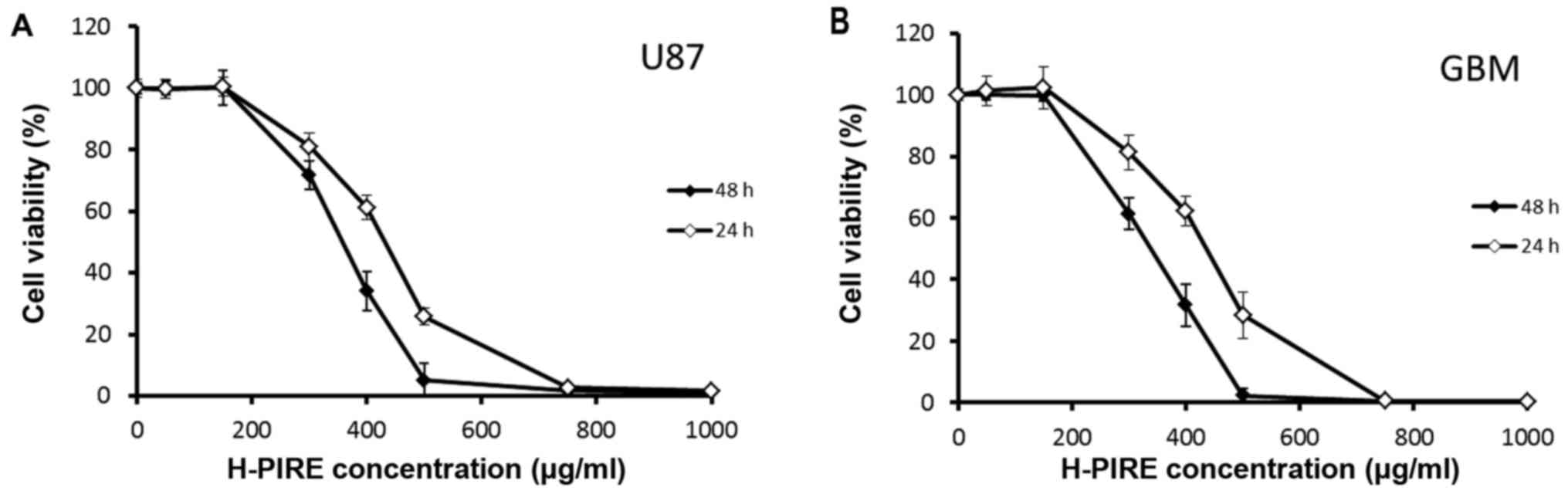
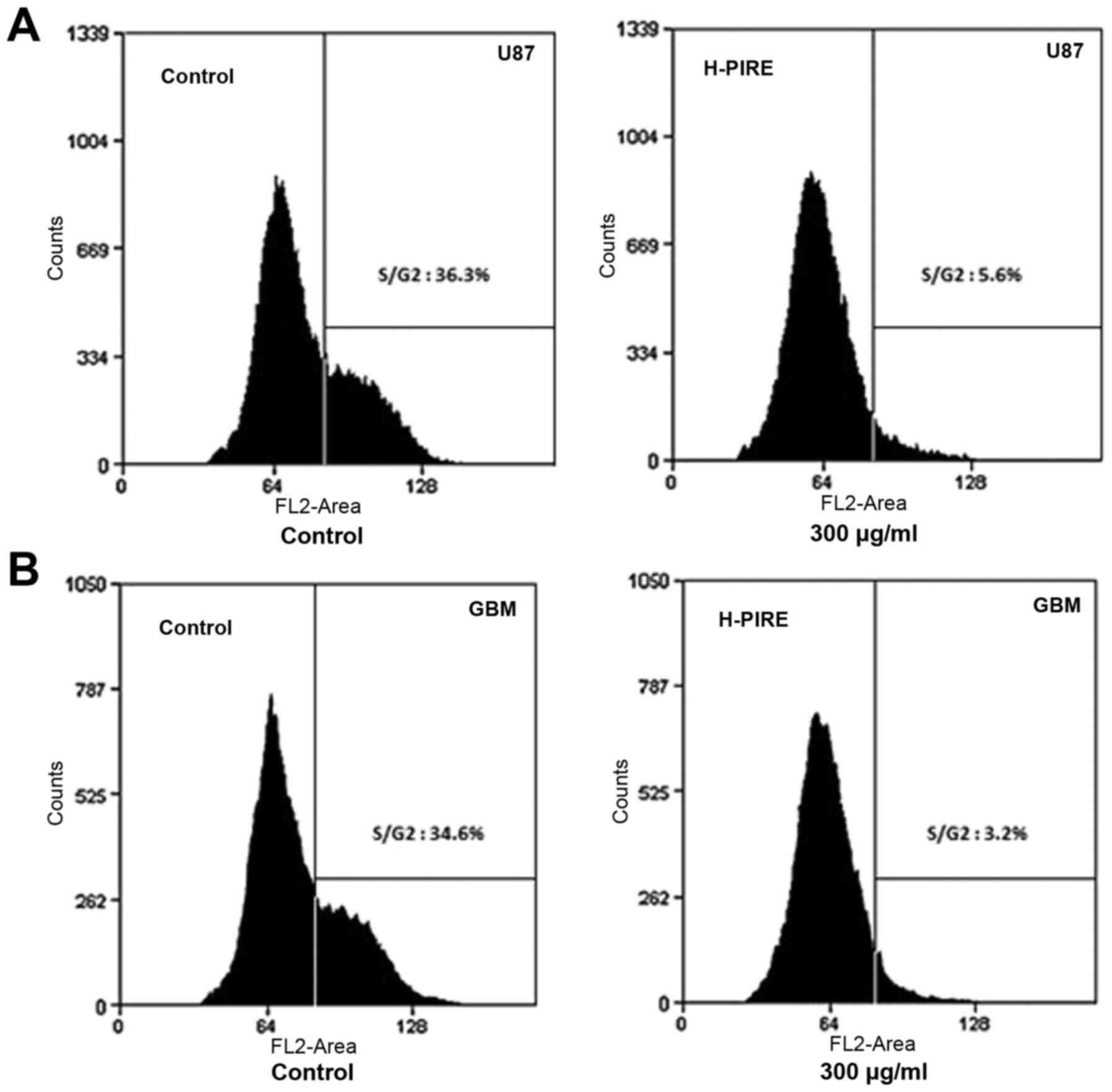
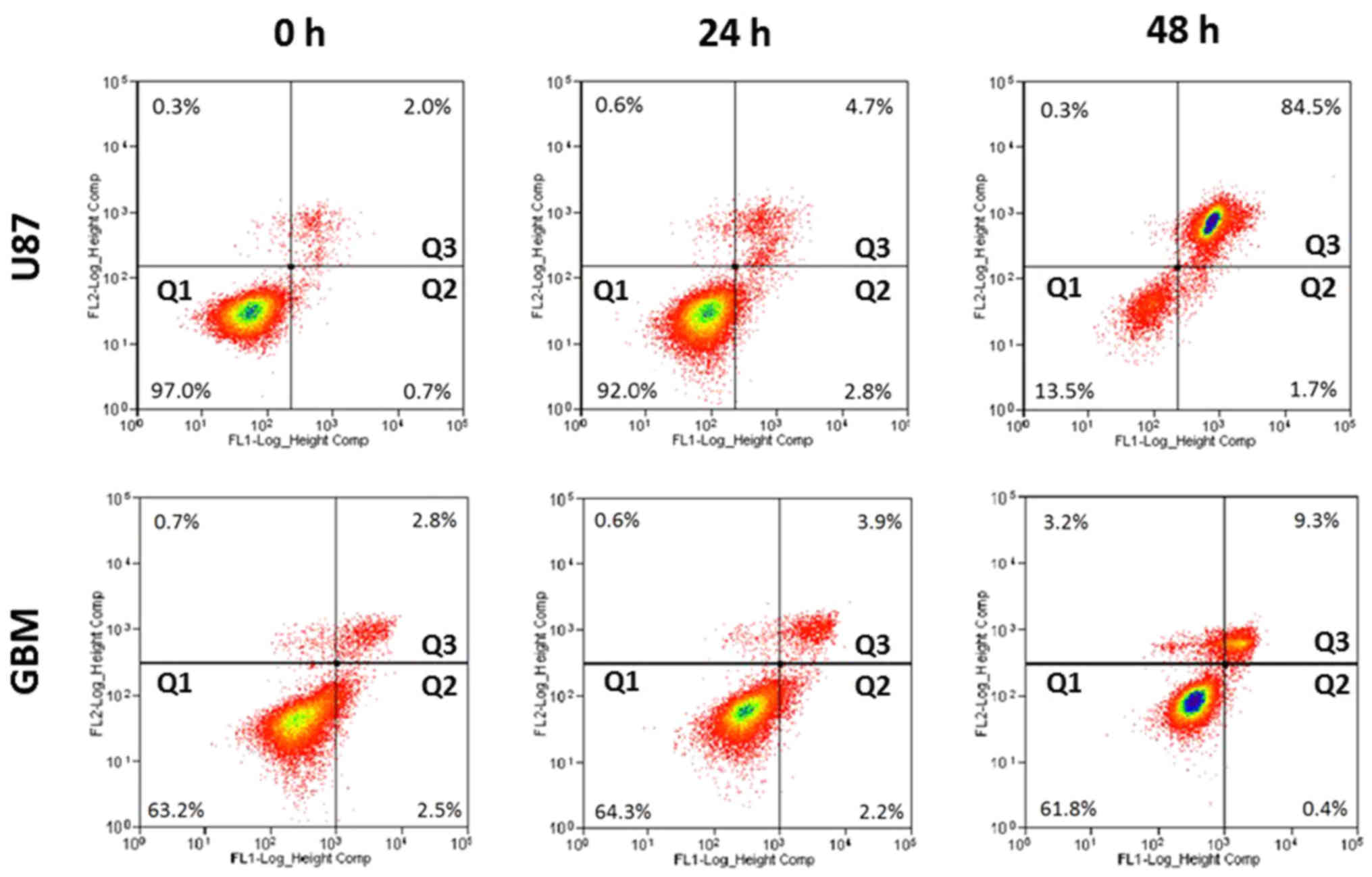
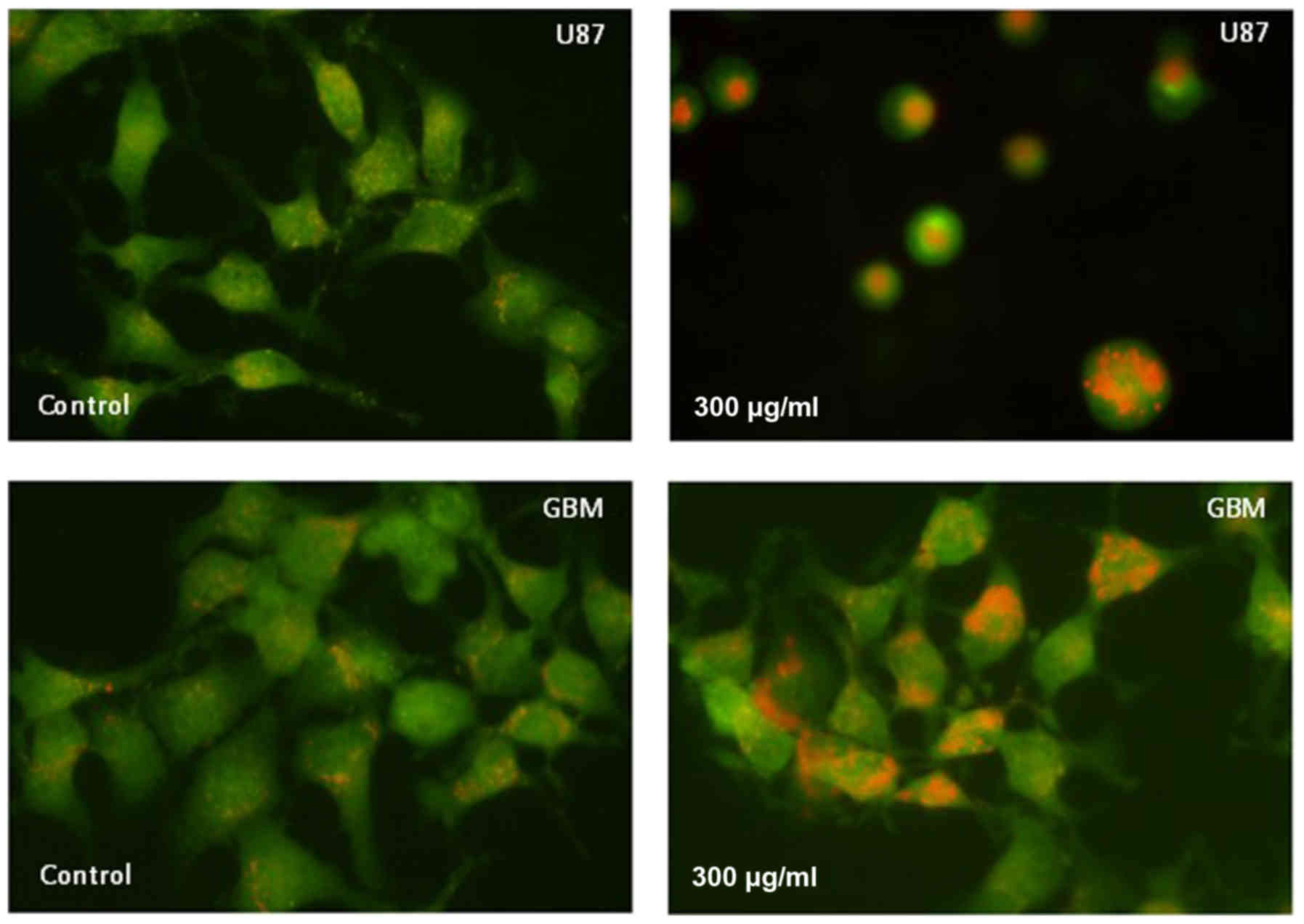
|
1
|
Bleeker FE, Molenaar RJ and Leenstra S:
Recent advances in the molecular understanding of glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 108:11–27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bleeker FE, Lamba S, Zanon C, Molenaar RJ,
Hulsebos TJM, Troost D, van Tilborg AA, Vandertop WP, Leenstra S,
van Noorden CJF, et al: Mutational profiling of kinases in
glioblastoma. BMC Cancer. 14:7182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crawford JR, Santi MR, Thorarinsdottir HK,
Cornelison R, Rushing EJ, Zhang H, Yao K, Jacobson S and Macdonald
TJ: Detection of human herpesvirus-6 variants in pediatric brain
tumors: Association of viral antigen in low grade gliomas. J Clin
Virol. 46:37–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baglietto L, Giles GG, English DR,
Karahalios A, Hopper JL and Severi G: Alcohol consumption and risk
of glioblastoma; evidence from the Melbourne Collaborative Cohort
Study. Int J Cancer. 128:1929–1934. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Braganza MZ, Kitahara CM, de González
Berrington A, Inskip PD, Johnson KJ and Rajaraman P: Ionizing
radiation and the risk of brain and central nervous system tumors:
A systematic review. Neuro-oncol. 14:1316–1324. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ellis HP, Greenslade M, Powell B, Spiteri
I, Sottoriva A and Kurian KM: Current challenges in glioblastoma:
Intratumour heterogeneity, residual disease and models to predict
disease recurrence. Front Oncol. 5:2512015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnson DR and O'Neill BP: Glioblastoma
survival in the United States before and during the temozolomide
era. J Neurooncol. 107:359–364. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wrensch M, Minn Y, Chew T, Bondy M and
Berger MS: Epidemiology of primary brain tumors: Current concepts
and review of the literature. Neuro Oncol. 4:278–299. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Emsen B, Aslan A, Togar B and Turkez H: In
vitro antitumor activities of the lichen compounds olivetoric,
physodic and psoromic acid in rat neuron and glioblastoma cells.
Pharm Biol. 54:1748–1762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mulpur BH, Nabors LB, Thompson RC, Olson
JJ, LaRocca RV, Thompson Z and Egan KM: Complementary therapy and
survival in glioblastoma. Neurooncol Pract. 2:122–126.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sen T, Dhara AK, Bhattacharjee S, Pal S
and Chaudhuri Nag AK: Antioxidant activity of the methanol fraction
of Pluchea indica root extract. Phytother Res. 16:331–335.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rahman Ab MR, Razak Abdul F and Bakri Mohd
M: Evaluation of wound closure activity of Nigella sativa,
Melastoma malabathricum, Pluchea indica and Piper
sarmentosum extracts on scratched monolayer of human gingival
fibroblasts. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:1903422014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arsiningtyas IS, Gunawan-Puteri MD, Kato E
and Kawabata J: Identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors from the
leaves of Pluchea indica (L.) Less., a traditional
Indonesian herb: Promotion of natural product use. Nat Prod Res.
28:1350–1353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gomes A, Saha A, Chatterjee I and
Chakravarty AK: Viper and cobra venom neutralization by
β-sitosterol and stigmasterol isolated from the root extract of
Pluchea indica Less. (Asteraceae). Phytomedicine.
14:637–643. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Biswas R, Dutta PK, Achari B,
Bandyopadhyay D, Mishra M, Pramanik KC and Chatterjee TK: Isolation
of pure compound R/J/3 from Pluchea indica (L.) Less. and
its anti-amoebic activities against Entamoeba histolytica.
Phytomedicine. 14:534–537. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sen T, Ghosh TK and Chaudhuri AK: Studies
on the mechanism of anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer activity of
Pluchea indica-probable involvement of 5-lipooxygenase
pathway. Life Sci. 52:737–743. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mohamad S, Zin NM, Wahab HA, Ibrahim P,
Sulaiman SF, Zahariluddin ASM and Noor SSM: Antituberculosis
potential of some ethnobotanically selected Malaysian plants. J
Ethnopharmacol. 133:1021–1026. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Locher CP, Witvrouw M, De Béthune MP,
Burch MT, Mower HF, Davis H, Lasure A, Pauwels R, De Clercq E and
Vlietinck AJ: Antiviral activity of Hawaiian medicinal plants
against human immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1). Phytomedicine.
2:259–264. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohtsuki T, Yokosawa E, Koyano T, Preeprame
S, Kowithayakorn T, Sakai S, Toida T and Ishibashi M: Quinic acid
esters from Pluchea indica with collagenase, MMP-2 and −9
inhibitory activities. Phytother Res. 22:264–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho JJ, Cho CL, Kao CL, Chen CM, Tseng CN,
Lee YZ, Liao LJ and Hong YR: Crude aqueous extracts of Pluchea
indica (L.) Less. inhibit proliferation and migration of cancer
cells through induction of p53-dependent cell death. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 12:2652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kao CL, Cho J, Lee YZ, Cheng YB, Chien CY,
Hwang CF, Hong YR, Tseng CN and Cho CL: Ethanolic extracts of
Pluchea indica induce apoptosis and antiproliferation
effects in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Molecules.
20:11508–11523. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harborne JB: Phytochemical methods: a
guide to modern techniques of plant analysis. 3rd. Chapman and
Hall; London, UK: 1998, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Butler LG, Price ML and Brotherton JE:
Vanillin assay for proanthocyanidins (condensed tannins):
Modification of the solvent for estimation of the degree of
polymerization. J Agric Food Chem. 30:1087–1089. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pavon LF, Marti LC, Sibov TT, Malheiros
SM, Brandt RA, Cavalheiro S and Gamarra LF: In vitro analysis of
neurospheres derived from gioblastoma primary culture: A novel
methodology paradigm. Front Neurol. 4:2142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wink M, Ashour ML and El-Readi MZ:
Secondary metabolites from plants inhibiting ABC transporters and
reversing resistance of cancer cells and microbes to cytotoxic and
antimicrobial agents. Front Microbiol. 3:1302012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tabrez S, Priyadarshini M, Urooj M, Shakil
S, Ashraf GM, Khan MS, Kamal MA, Alam Q, Jabir NR, Abuzenadah AM,
et al: Cancer chemoprevention by polyphenols and their potential
application as nanomedicine. J Environ Sci Health C Environ
Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 31:67–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hansen TE and Johansen T: Following
autophagy step by step. BMC Biol. 9:392011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takeuchi H, Kondo Y, Fujiwara K, Kanzawa
T, Aoki H, Mills GB and Kondo S: Synergistic augmentation of
rapamycin-induced autophagy in malignant glioma cells by
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B inhibitors. Cancer
Res. 65:3336–3346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berger Z, Ravikumar B, Menzies FM, Oroz
LG, Underwood BR, Pangalos MN, Schmitt I, Wullner U, Evert BO,
O'Kane CJ, et al: Rapamycin alleviates toxicity of different
aggregate-prone proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 15:433–442. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cuadrado A and Nebreda AR: Mechanisms and
functions of p38 MAPK signalling. Biochem J. 429:403–417. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun T, Li D, Wang L, Xia L, Ma J, Guan Z,
Feng G and Zhu X: c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation is essential
for up-regulation of LC3 during ceramide-induced autophagy in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. J Transl Med. 9:1612011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou C, Zhou J, Sheng F, Zhu H, Deng X,
Xia B and Lin J: The heme oxygenase-1 inhibitor ZnPPIX induces
non-canonical, Beclin 1-independent, autophagy through p38 MAPK
pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 44:815–822. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sui X, Kong N, Ye L, Han W, Zhou J, Zhang
Q, He C and Pan H: p38 and JNK MAPK pathways control the balance of
apoptosis and autophagy in response to chemotherapeutic agents.
Cancer Lett. 344:174–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tanida I: Autophagosome formation and
molecular mechanism of autophagy. Antioxid Redox Signal.
14:2201–2214. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shimizu S, Yoshida T, Tsujioka M and
Arakawa S: Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
15:3145–3153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koukourakis MI, Mitrakas AG and
Giatromanolaki A: Therapeutic interactions of autophagy with
radiation and temozolomide in glioblastoma: Evidence and issues to
resolve. Br J Cancer. 114:485–496. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yan Y, Xu Z, Dai S, Qian L, Sun L and Gong
Z: Targeting autophagy to sensitive glioma to temozolomide
treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nicholson KM and Anderson NG: The protein
kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal.
14:381–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Morgensztern D and McLeod HL:
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a target for cancer therapy. Anticancer
Drugs. 16:797–803. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|