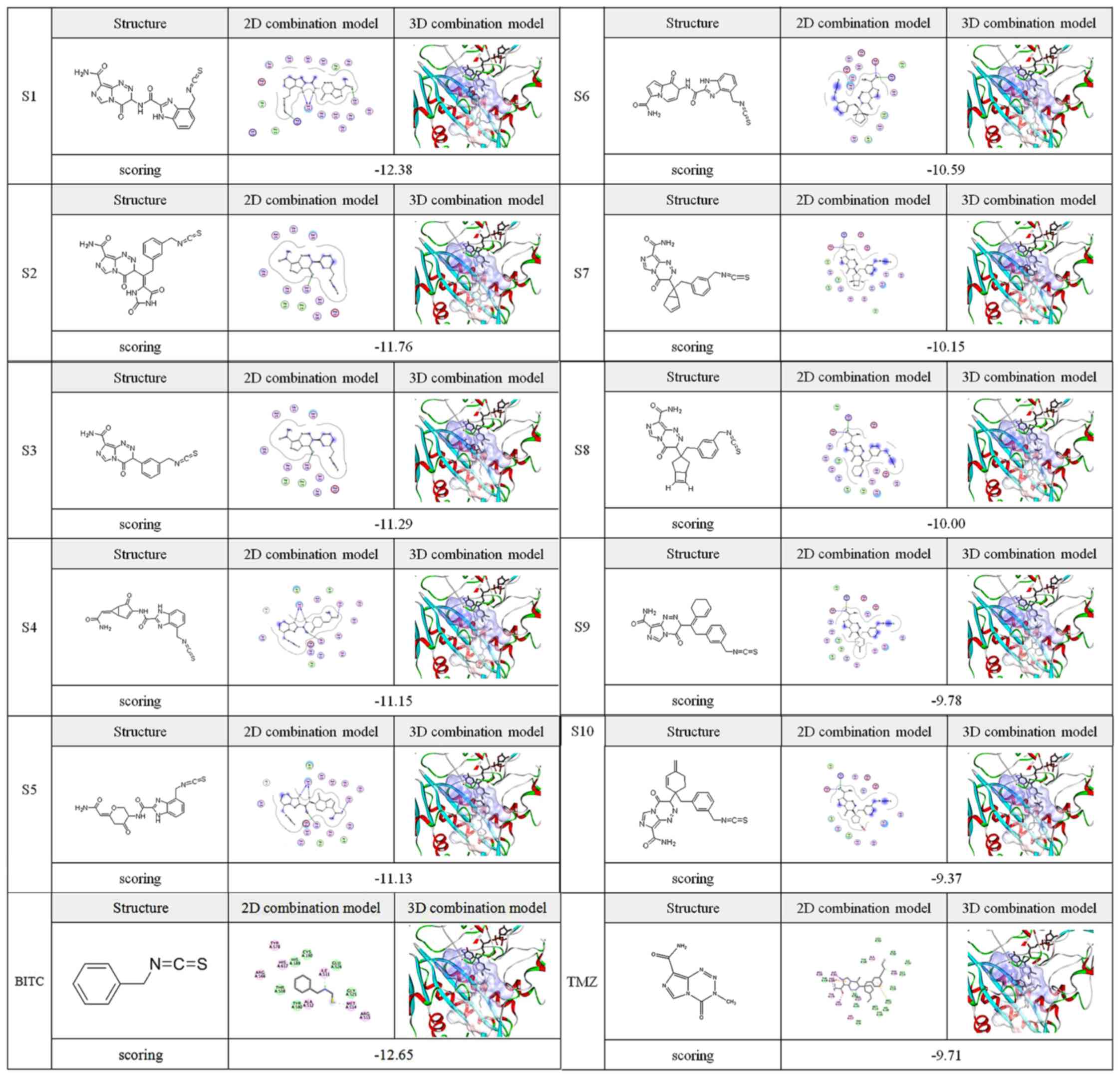
|
1
|
Zhang H, Nie W, Zhang X, Zhang G, Li Z, Wu
H, Shi Q, Chen Y, Ding Z, Zhou X, et al: NEDD4-1 regulates
migration and invasion of glioma cells through CNrasGEF
ubiquitination in vitro. PLoS One. 8:e827892013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kahlert UD, Nikkhah G and Maciaczyk J:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular
event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 331:131–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organization
Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhu Y, Yang P, Wang Q, Hu J, Xue J, Li G,
Zhang G, Li X, Li W, Zhou C, et al: The effect of CXCR4 silencing
on epithelial-mesenchymal transition related genes in glioma U87
cells. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 296:1850–1856. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gai XJ, Wei YM, Tao HM, An DZ, Sun JT and
Li BS: Comparison of long-term survival between temozolomide-based
chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy alone for patients with
low-grade gliomas after surgical resection. Onco Targets Ther.
9:5117–5121. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ashby LS, Smith KA and Stea B: Gliadel
wafer implantation combined with standard radiotherapy and
concurrent followed by adjuvant temozolomide for treatment of newly
diagnosed high-grade glioma: A systematic literature review. World
J Surg Oncol. 14:2252016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Коbylinska LI, Klyuchivska OY, Grytsyna
II, Finiuk N, Panchuk RR, Starykovych MO, Lehka L, Lesyk RB,
Zіmenkovsky BS and Stoika RS: Differential pro-apoptotic effects of
synthetic 4-thiazolidinone derivative Les-3288, doxorubicin and
temozolomide in human glioma U251 cells. Croat Med J. 58:150–159.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen TC, Cho HY, Wang W, Wetzel SJ, Singh
A, Nguyen J, Hofman FM and Schönthal AH: Chemotherapeutic effect of
a novel temozolomide analog on nasopharyngeal carcinoma in vitro
and in vivo. J Biomed Sci. 22:712015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Piano V, Benjamin DI, Valente S, Nenci S,
Marrocco B, Mai A, Aliverti A, Nomura DK and Mattevi A: Discovery
of Inhibitors for the Ether Lipid-Generating Enzyme AGPS as
Anti-Cancer Agents. ACS Chem Biol. 10:2589–2597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Liu XJ, Yang P, Zhao M, Lv LX,
Zhang GD, Wang Q and Zhang L: Alkylglyceronephosphate synthase
(AGPS) alters lipid signaling pathways and supports chemotherapy
resistance of glioma and hepatic carcinoma cell lines. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:3219–3226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cai Z, Zhang G, Zhang X, Liu Y and Fu X:
Current insights into computer-aided immunotherapeutic design
strategies. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 28:278–285. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Scotti L and Scotti MT: Computer Aided
Drug Design Studies in the Discovery of Secondary Metabolites
Targeted Against Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. Curr Top
Med Chem. 15:2239–2252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Baig MH, Ahmad K, Rabbani G, Danishuddin
and Choi I: Danishuddin and Choi I: Computer aided drug design and
its application to the development of potential drugs for
neurodegenerative disorders. Curr Neuropharmacol. Oct 16–2017.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhu Y, Liu A, Zhang X, Qi L, Zhang L, Xue
J, Liu Y and Yang P: The effect of benzyl isothiocyanate and its
computer-aided design derivants targeting alkylglycerone phosphate
synthase on the inhibition of human glioma U87MG cell line. Tumour
Biol. 36:3499–3509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hvizdos KM and Goa KL: Temozolomide. CNS
Drugs. 12:237–243. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Hao QQ, Liu X, Jing Z, Jia WQ,
Wang SQ, Xu WR, Cheng XC and Wang RL: Molecular docking, 3D-QSAR
and structural optimization on imidazo-pyridine derivatives dually
targeting AT1 and PPARg. Oncotarget. 8:25612–25627. 2017.
|
|
17
|
Ma Y, Jin YY, Wang YL, Wang RL, Lu XH,
Kong DX and Xu WR: The discovery of a novel and selective inhibitor
of PTP1B over TCPTP: 3D QSAR pharmacophore modeling, virtual
screening, synthesis, and biological evaluation. Chem Biol Drug
Des. 83:697–709. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Allen M, Bjerke M, Edlund H, Nelander S
and Westermark B: Origin of the U87MG glioma cell line: Good news
and bad news. Sci Transl Med. 8:354re32016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Seyfried TN: Cancer as a mitochondrial
metabolic disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 3:432015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liegel RP, Ronchetti A and Sidjanin DJ:
Alkylglycerone phosphate synthase (AGPS) deficient mice: Models for
rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctate type 3 (RCDP3) malformation
syndrome. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 1:299–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhu Y, Li WM, Zhang L, Xue J, Zhao M and
Yang P: Inhibitory effect of isothiocyanate derivant targeting AGPS
by computer-aid drug design on proliferation of glioma and hepatic
carcinoma cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:812–817. 2015.
|
|
22
|
Turku A, Borrel A, Leino TO, Karhu L,
Kukkonen JP and Xhaard H: A pharmacophore model to discover OX1 and
OX2 orexin receptor ligands. J Med Chem. 59:8263–8275. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Medeiros Turra K, Pineda Rivelli D,
Berlanga de Moraes Barros S and Mesquita Pasqualoto KF:
Constructing and Validating 3D-pharmacophore Models to a Set of
MMP-9 Inhibitors for Designing Novel Anti-melanoma Agents. Mol
Inform. 35:238–252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Battu MB, Chandra AM, Sriram D and
Yogeeswari P: Pharmacophore-based 3DQSAR and molecular docking
studies to identify new non-peptidic inhibitors of cathepsin S.
Curr Med Chem. 21:1910–1921. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chakrabarti S and Michor F:
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Interactions Determine Optimum
Combination Strategies in Computational Models of Cancer Evolution.
Cancer Res. 77:3908–3921. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Valasani KR, Chaney MO, Day VW and Shidu
Yan S: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: Structure based design,
synthesis, pharmacophore modeling, and virtual screening. J Chem
Inf Model. 53:2033–2046. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|