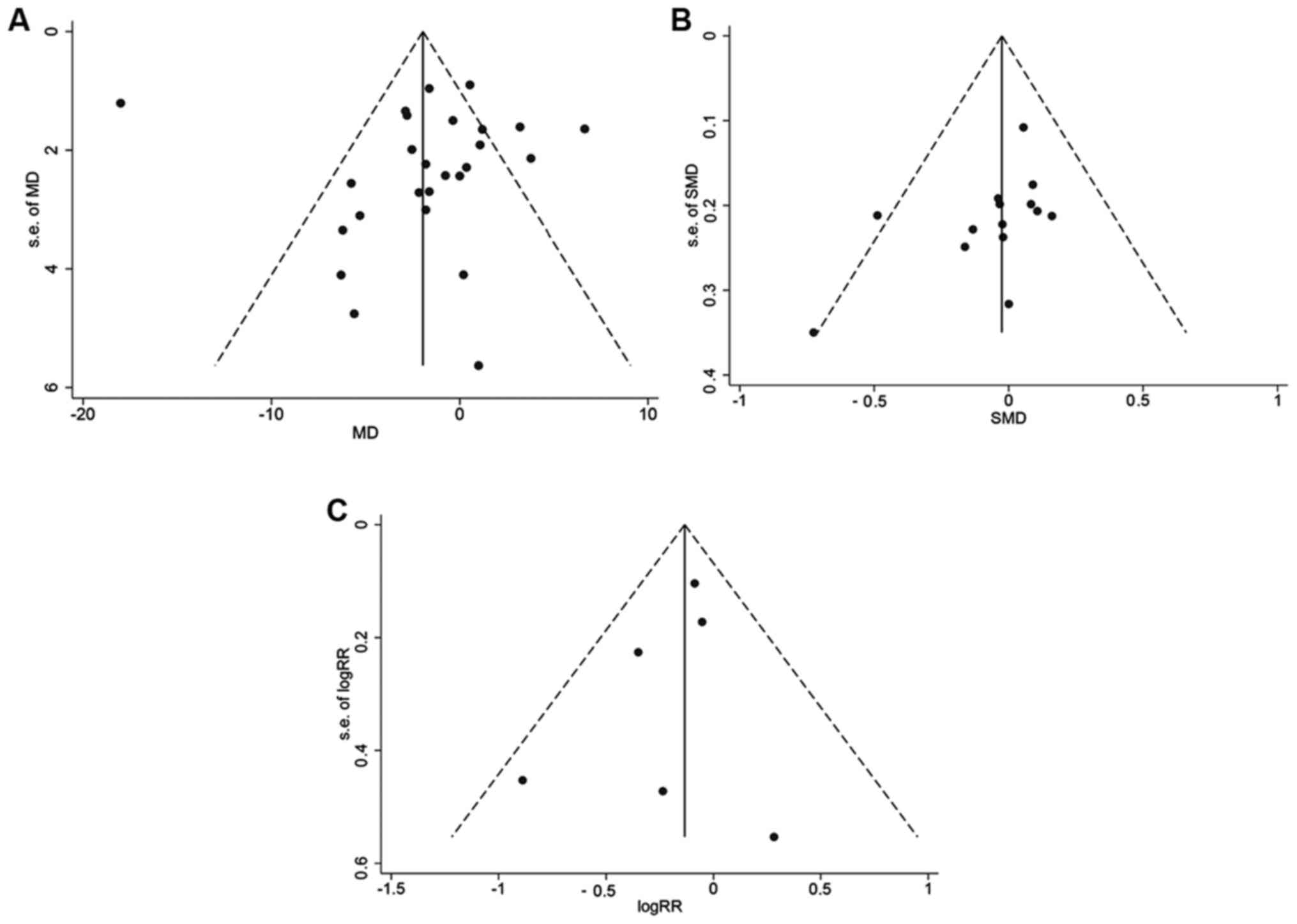
|
1
|
van Driel M and van Leeuwen JPTM: Vitamin
D endocrinology of bone mineralization. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
453:46–51. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bikle DD: Extraskeletal actions of vitamin
D. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1376:29–52. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Autier P, Boniol M, Pizot C and Mullie P:
Vitamin D status and ill health: A systematic review. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:76–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang H, Chen W, Li D, Yin X, Zhang X,
Olsen N and Zheng SG: Vitamin D and chronic diseases. Aging Dis.
8:346–353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pannu PK, Piers LS, Soares MJ, Zhao Y and
Ansari Z: Vitamin D status is inversely associated with markers of
risk for type 2 diabetes: A population based study in Victoria,
Australia. PLoS One. 12:e01788252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lucato P, Solmi M, Maggi S, Bertocco A,
Bano G, Trevisan C, Manzato E, Sergi G, Schofield P, Kouidrat Y, et
al: Low vitamin D levels increase the risk of type 2 diabetes in
older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas.
100:8–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Berridge MJ: Vitamin D deficiency and
diabetes. Biochem J. 474:1321–1332. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Belenchia AM, Tosh AK, Hillman LS and
Peterson CA: Correcting vitamin D insufficiency improves insulin
sensitivity in obese adolescents: A randomized controlled trial. Am
J Clin Nutr. 97:774–781. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagpal J, Pande JN and Bhartia A: A
double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of the
short-term effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on
insulin sensitivity in apparently healthy, middle-aged, centrally
obese men. Diabet Med. 26:19–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pittas AG, Harris SS, Stark PC and
Dawson-Hughes B: The effects of calcium and vitamin D
supplementation on blood glucose and markers of inflammation in
nondiabetic adults. Diabetes Care. 30:980–986. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuchay MS, Laway BA, Bashir MI, Wani AI,
Misgar RA and Shah ZA: Effect of vitamin D supplementation on
glycemic parameters and progression of prediabetes to diabetes: A
1-year, open-label randomized study. Indian J Endocrinol Metab.
19:387–392. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iraj B, Aminorroaya A and Amini M: Does
the intramuscular injection of vitamin D increase insulin
resistance? J Res Pharm Pract. 1:60–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davidson MB, Duran P, Lee ML and Friedman
TC: High-dose vitamin D supplementation in people with prediabetes
and hypovitaminosis D. Diabetes Care. 36:260–266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grimnes G, Figenschau Y, Almås B and Jorde
R: Vitamin D, insulin secretion, sensitivity, and lipids: Results
from a case-control study and a randomized controlled trial using
hyperglycemic clamp technique. Diabetes. 60:2748–2757. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jorde R, Sneve M, Torjesen P and
Figenschau Y: No improvement in cardiovascular risk factors in
overweight and obese subjects after supplementation with vitamin D3
for 1 year. J Intern Med. 267:462–472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moreira-Lucas TS, Duncan AM, Rabasa-Lhoret
R, Vieth R, Gibbs AL, Badawi A and Wolever TM: Effect of vitamin D
supplementation on oral glucose tolerance in individuals with low
vitamin D status and increased risk for developing type 2 diabetes
(EVIDENCE): A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Diabetes Obes Metab. 19:133–141. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dutta D, Mondal SA, Choudhuri S, Maisnam
I, Reza Hasanoor AH, Bhattacharya B, Chowdhury S and Mukhopadhyay
S: Vitamin-D supplementation in prediabetes reduced progression to
type 2 diabetes and was associated with decreased insulin
resistance and systemic inflammation: An open label randomized
prospective study from Eastern India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
103:e18–e23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
de Boer IH, Tinker LF, Connelly S, Curb
JD, Howard BV, Kestenbaum B, Larson JC, Manson JE, Margolis KL,
Siscovick DS and Weiss NS: Women's Health Initiative Investigators:
Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and the risk of incident
diabetes in the Women's Health Initiative. Diabetes Care.
31:701–707. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jorde R, Sollid ST, Svartberg J, Schirmer
H, Joakimsen RM, Njølstad I, Fuskevåg OM, Figenschau Y and
Hutchinson MY: Vitamin D 20,000 IU per week for five years does not
prevent progression from prediabetes to diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 101:1647–1655. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu C, Qiu S, Zhu X and Li L: Vitamin D
supplementation and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism. 73:67–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee CJ, Iyer G, Liu Y, Kalyani RR, Bamba
N, Ligon CB, Varma S and Mathioudakis N: The effect of vitamin D
supplementation on glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention studies. J
Diabetes Complications. 31:1115–1126. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akbari M, Moosazadeh M, Lankarani KB,
Tabrizi R, Samimi M, Karamali M, Jamilian M, Kolahdooz F and Asemi
Z: Correction: The effects of vitamin D supplementation on glucose
metabolism and lipid profiles in patients with gestational
diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Horm Metab Res. Aug 2–2017.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
23
|
Jamka M, Woźniewicz M, Jeszka J, Mardas M,
Bogdański P and Stelmach-Mardas M: The effect of vitamin D
supplementation on insulin and glucose metabolism in overweight and
obese individuals: Systematic review with meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
5:161422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kresevic DM, Denton JE, Burant CJ and
Pallaki M: Racial difference in response to vitamin D
supplementation. J Natl Med Assoc. 107:18–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dasarathy J, Varghese R, Feldman A,
Khiyami A, McCullough AJ and Dasarathy S: Patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease have a low response rate to
vitamin D supplementation. J Nutr. 147:1938–1946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis
and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 33 Suppl
1:S62–S69. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Higgins and Green JPT S: Cochrane Handbook
for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, version 5.1.0. The
Cochrane Collaboration. 2282011.
|
|
28
|
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson
C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ and McQuay HJ: Assessing the quality of
reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?
Control Clin Trials. 17:1–12.. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Follmann D, Elliott P, Suh I and Cutler J:
Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with
continuous response. J Clin Epidemiol. 45:769–773. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Flegal KM, Kit BK, Orpana H and Graubard
BI: Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity
using standard body mass index categories: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. JAMA. 309:71–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gallagher JC and Sai AJ: Vitamin D
insufficiency, deficiency, and bone health. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 95:2630–2633. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin ZC, Zhou XH and He J: Statistical
methods for dealing with publication bias in meta-analysis. Stat
Med. 34:343–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Salehpour A, Shidfar F, Hosseinpanah F,
Vafa M, Razaghi M and Amiri F: Does vitamin D3
supplementation improve glucose homeostasis in overweight or obese
women? A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Diabet Med. 30:1477–1481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oosterwerff MM, Eekhoff EM, Van Schoor NM,
Boeke AJ, Nanayakkara P, Meijnen R, Knol DL, Kramer MH and Lips P:
Effect of moderate-dose vitamin D supplementation on insulin
sensitivity in vitamin D-deficient non-Western immigrants in the
Netherlands: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr.
100:152–160. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qi M, Song Y, Li J, Tian L, Wang L, Xie Y,
Gup Y and Bao Y: Effect of vitamin D supplementation on
postprandial glucose in the elder with vitamin D deficiency and
impaired glucose tolerance. Chin J Mod Drug Appl. 10:196–197.
2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Mitri J, Dawson-Hughes B, Hu FB and Pittas
AG: Effects of vitamin D and calcium supplementation on pancreatic
β cell function, insulin sensitivity, and glycemia in adults at
high risk of diabetes: The calcium and vitamin D for diabetes
mellitus (CaDDM) randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr.
94:486–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tuomainen TP, Virtanen JK, Voutilainen S,
Nurmi T, Mursu J, de Mello VD, Schwab U, Hakumäki M, Pulkki K and
Uusitupa M: Glucose metabolism effects of vitamin D in prediabetes:
The VitDmet randomized placebo-controlled supplementation study. J
Diabetes Res. 2015:6726532015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sollid ST, Hutchinson MY, Fuskevåg OM,
Figenschau Y, Joakimsen RM, Schirmer H, Njølstad I, Svartberg J,
Kamycheva E and Jorde R: No effect of high-dose vitamin D
supplementation on glycemic status or cardiovascular risk factors
in subjects with prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 37:2123–2131. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Harris SS, Pittas AG and Palermo NJ: A
randomized, placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D supplementation
to improve glycaemia in overweight and obese African Americans.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 14:789–794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Major GC, Alarie F, Doré J, Phouttama S
and Tremblay A: Supplementation with calcium + vitamin D enhances
the beneficial effect of weight loss on plasma lipid and
lipoprotein concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:54–59.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wood AD, Secombes KR, Thies F, Aucott L,
Black AJ, Mavroeidi A, Simpson WG, Fraser WD, Reid DM and Macdonald
HM: Vitamin D3 supplementation has no effect on conventional
cardiovascular risk factors: A parallel-group, double-blind,
placebo-controlled RCT. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:3557–3568.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zittermann A, Frisch S, Berthold HK,
Götting C, Kuhn J, Kleesiek K, Stehle P, Koertke H and Koerfer R:
Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight
loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am J Clin Nutr.
89:1321–1327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun X, Cao ZB, Tanisawa K, Ito T, Oshima S
and Higuchi M: Vitamin D supplementation reduces insulin resistance
in Japanese adults: A secondary analysis of a double-blind,
randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr Res. 36:1121–1129. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vimaleswaran KS, Berry DJ, Lu C, Tikkanen
E, Pilz S, Hiraki LT, Cooper JD, Dastani Z, Li R, Houston DK, et
al: Genetic Investigation of Anthropometric Traits-GIANT
Consortium: Causal relationship between obesity and vitamin D
status: Bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis of multiple
cohorts. PLoS Med. 10:e10013832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gowda U, Ruwanpathirana T, Fong DP, Kaur A
and Renzaho AM: Efficacy of high dose vitamin D supplementation in
improving serum 25(OH)D among migrant and non migrant population: A
retrospective study. BMC Health Serv Res. 16:5792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yang Y, Li Z, Yan G, Jie Q and Rui C:
Effect of different dose of vitamin D supplementation on preterm
infants- an updated meta-analysis. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. Oct
5–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pittas AG, Dawson-Hughes B, Li T, Van Dam
RM, Willett WC, Manson JE and Hu FB: Vitamin D and calcium intake
in relation to type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care. 29:650–656.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|