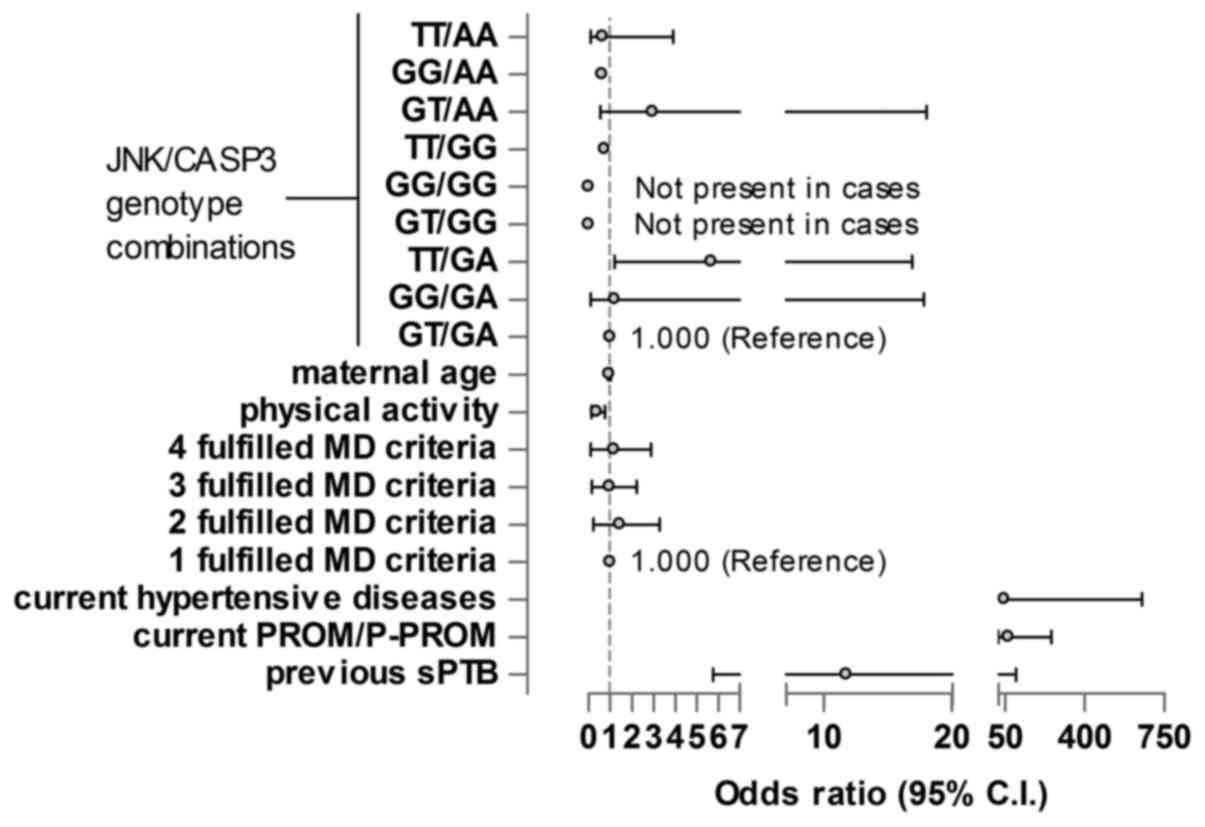
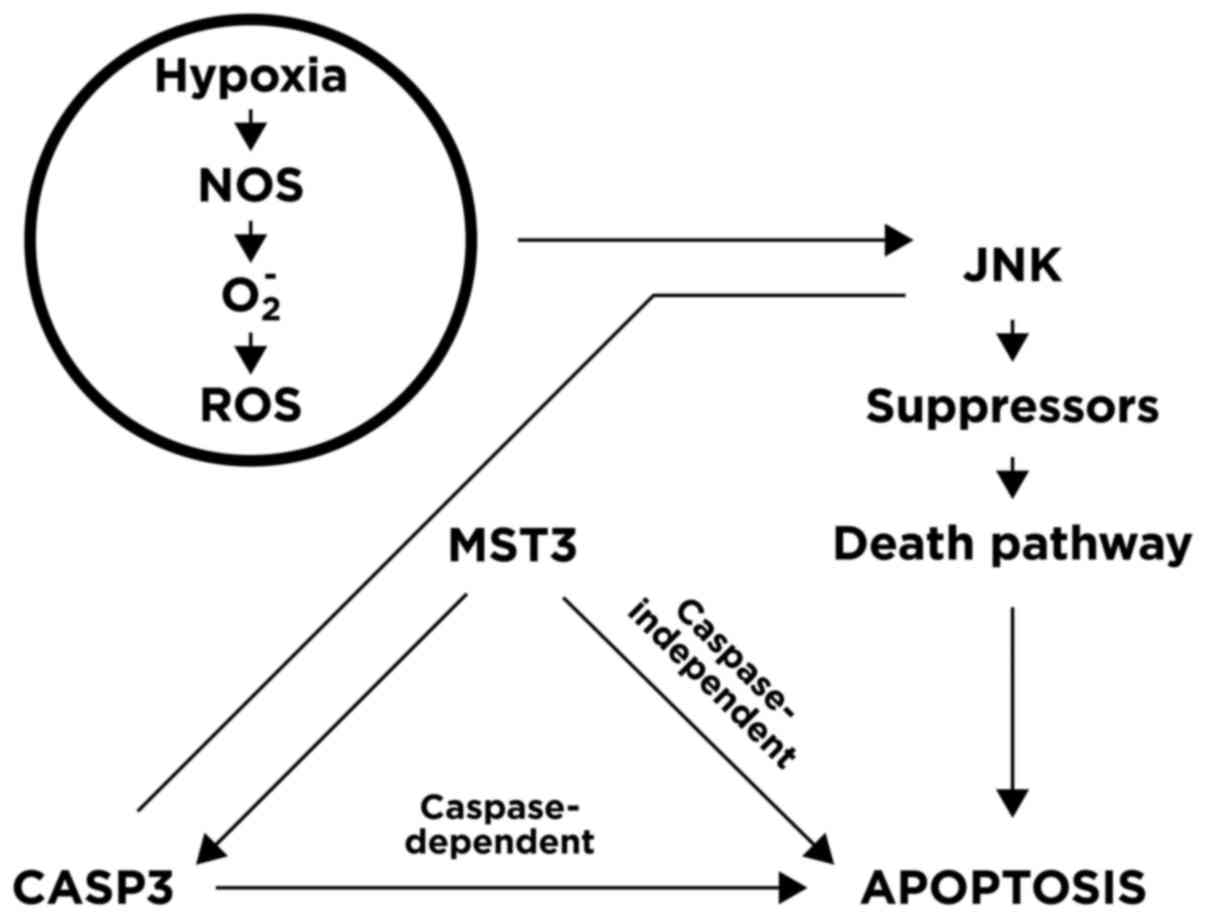
|
1
|
Ferrero DM, Larson J, Jacobsson B, Di
Renzo GC, Norman JE, Martin JN Jr, D'Alton M, Castelazo E, Howson
CP, Sengpiel V, et al: Cross-country individual participant
analysis of 4.1 million singleton births in 5 countries with very
high human development index confirms known associations but
provides no biologic explanation for 2/3 of all preterm births.
PLoS One. 11:e01625062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McLean M, Bisits A, Davies J, Woods R,
Lowry P and Smith R: A placental clock controlling the length of
human pregnancy. Nat Med. 1:460–463. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levy RR, Cordonier H, Czyba JC and Guerin
JF: Apoptosis in preimplantation mammalian embryo and genetics.
Ital J Anat Embryol. 106(Suppl 2): 101–108. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu HY, Lin CY, Lin TY, Chen TC and Yuan
CJ: Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3 mediates trophoblast
apoptosis in spontaneous delivery. Apoptosis. 13:283–294. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu HY, Lin CY, Chen TC, Pan ST, Yuan CJ
and Wu HY1: Mammalian Ste20-like protein kinase 3 plays a role in
hypoxia-induced apoptosis of trophoblast cell line 3A-sub-E. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 43:742–750. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen M, Meisser A, Haenggeli L and
Bischof P: Involvement of MAPK pathway in TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9
expression in human trophoblastic cells. Mol Hum Reprod.
12:225–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dutta EH, Behnia F, Boldogh I, Saade GR,
Taylor BD, Kacerovský M and Menon R: Oxidative stress
damage-associated molecular signaling pathways differentiate
spontaneous preterm birth and preterm premature rupture of the
membranes. Mol Hum Reprod. 22:143–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ruiz RJ, Jallo N, Murphey C, Marti CN,
Godbold E and Pickler RH: Second trimester maternal plasma levels
of cytokines IL-1Ra, Il-6 and IL-10 and preterm birth. J Perinatol.
32:483–490. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nold C, Anton L, Brown A and Elovitz M:
Inflammation promotes a cytokine response and disrupts the cervical
epithelial barrier: A possible mechanism of premature cervical
remodeling and preterm birth. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
206:208.e201–e207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Goepfert AR, Jeffcoat MK, Andrews WW,
Faye-Petersen O, Cliver SP, Goldenberg RL and Hauth JC: Periodontal
disease and upper genital tract inflammation in early spontaneous
preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol. 104:777–783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Yang X, Zheng Y, Wu ZH, Zhang XA,
Li QP, He XY, Wang CZ and Feng ZC: The SEPS1 G-105A polymorphism is
associated with risk of spontaneous preterm birth in a Chinese
population. PLoS One. 8:e656572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang G, Feenstra B, Bacelis J, Liu X,
Muglia LM, Juodakis J, Miller DE, Litterman N, Jiang PP, Russell L,
et al: Genetic associations with gestational length and spontaneous
preterm birth. N Engl J Med. 377:1156–1167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Capra L, Tezza G, Mazzei F and Boner AL:
The origins of health and disease: The influence of maternal
diseases and lifestyle during gestation. Ital J Pediatr. 39:72013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smith LK, Draper ES, Evans TA, Field DJ,
Johnson SJ, Manktelow BN, Seaton SE, Marlow N, Petrou S and Boyle
EM: Associations between late and moderately preterm birth and
smoking, alcohol, drug use and diet: A population-based case-cohort
study. Arch Dis Child Foetal Neonatal Ed. 100:F486–491. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ehrenberg HM, Iams JD, Goldenberg RL,
Newman RB, Weiner SJ, Sibai BM, Caritis SN, Miodovnik M and
Dombrowski MP; Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child
Health and Human Development (NICHD) Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units
Network (MFMU): Maternal obesity, uterine activity, and the risk of
spontaneous preterm birth. Obstet Gynecol. 113:48–52. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meltzer HM, Brantsæter AL, Nilsen RM,
Magnus P, Alexander J and Haugen M: Effect of dietary factors in
pregnancy on risk of pregnancy complications: Results from the
Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Am J Clin Nutr.
94:(Suppl):. 1970S–1974S. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ziebarth JD, Bhattacharya A, Chen A and
Cui Y: PolymiRTS Database 2.0: Linking polymorphisms in microRNA
target sites with human diseases and complex traits. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40(D1): D216–D221. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heilig R, Eckenberg R, Petit JL,
Fonknechten N, Da Silva C, Cattolico L, Levy M, Barbe V, de
Berardinis V, Ureta-Vidal A, et al: The DNA sequence and analysis
of human chromosome 14. Nature. 421:601–607. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yashin AI, Wu D, Arbeev KG and Ukraintseva
SV: Joint influence of small-effect genetic variants on human
longevity. Aging (Albany NY). 2:612–620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuersten S and Goodwin EB: The power of
the 3′ UTR: Translational control and development. Nat Rev Genet.
4:626–637. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Romero R, Dey SK and Fisher SJ: Preterm
labor: One syndrome, many causes. Science. 345:760–765. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Domingues MR, Matijasevich A and Barros
AJ: Physical activity and preterm birth: A literature review.
Sports Med. 39:961–975. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Srinivas SK, Ma Y, Sammel MD, Chou D,
McGrath C, Parry S and Elovitz MA: Placental inflammation and viral
infection are implicated in second trimester pregnancy loss. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 195:797–802. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harper M, Zheng SL, Thom E, Klebanoff MA,
Thorp J Jr, Sorokin Y, Varner MW, Iams JD, Dinsmoor M, Mercer BM,
et al: Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health
and Human Development (NICHD) Maternal-Fetal Medicine Units Network
(MFMU): Cytokine gene polymorphisms and length of gestation. Obstet
Gynecol. 117:125–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Romero RI, Velez Edwards DR, Kusanovic JP,
Hassan SS, Mazaki-Tovi S, Vaisbuch E, Kim CJ, Chaiworapongsa T,
Pearce BD, Friel LA, Bartlett J, et al: Identification of fetal and
maternal single nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes that
predispose to spontaneous preterm labor with intact membranes. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 202:431.e1–34. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ota S, Miyamura H, Nishizawa H, Inagaki H,
Inagaki A, Inuzuka H, Suzuki M, Miyazaki J, Sekiya T, Udagawa Y, et
al: Contribution of fetal ANXA5 gene promoter polymorphisms to the
onset of pre-eclampsia. Placenta. 34:1202–1210. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Roberts JM and Cooper DW: Pathogenesis and
genetics of pre-eclampsia. Lancet. 357:53–56. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dunlop AL, Kramer MR, Hogue CJ, Menon R
and Ramakrishan U: Racial disparities in preterm birth: An overview
of the potential role of nutrient deficiencies. Acta Obstet
Gyunecol Scand. 90:1332–1341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|