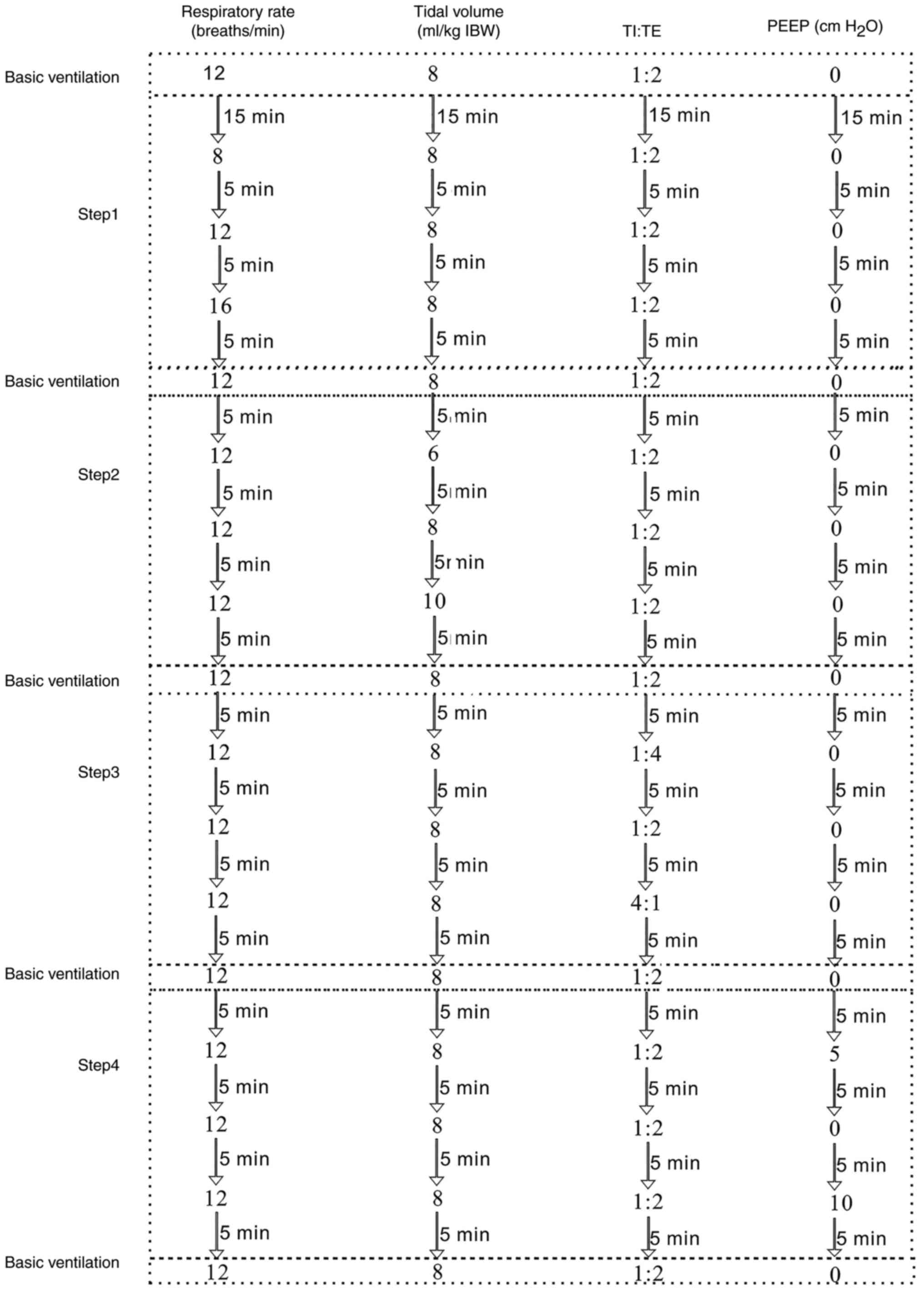
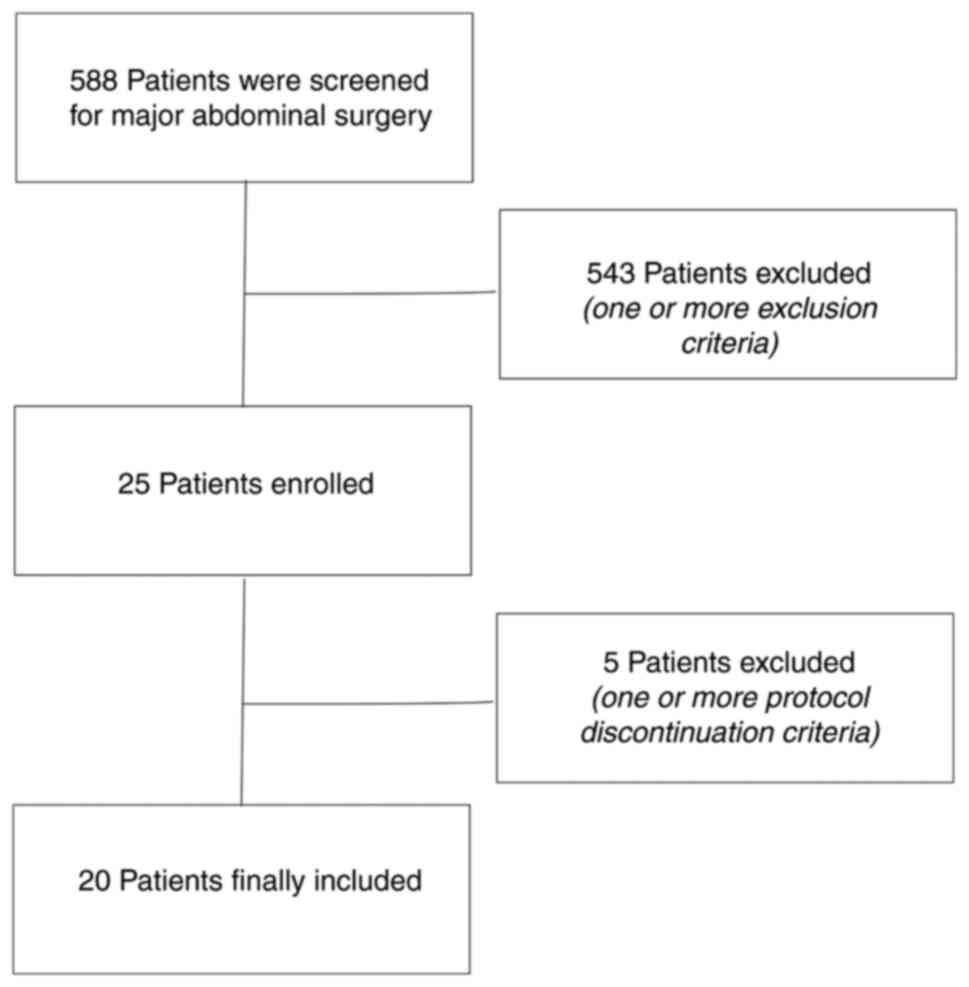
|
1
|
Frank SM, Beattie C, Christopherson R,
Norris EJ, Rock P, Parker S and Kimball AW Jr: Epidural versus
general anesthesia, ambient operating room temperature, and patient
age as predictors of inadvertent hypothermia. Anesthesiology.
77:252–257. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Morettini E, Turchini F, Tofani L, Villa
G, Ricci Z and Romagnoli S: Intraoperative core temperature
monitoring: Accuracy and precision of zero-heat flux heated
controlled servo sensor compared with esophageal temperature during
major surgery; the ESOSPOT study. J Clin Monit Comput.
34:1111–1119. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hymczak H, Gołąb A, Mendrala K, Plicner D,
Darocha T, Podsiadło P, Hudziak D, Gocoł R and Kosiński S: Core
temperature measurement-principles of correct measurement,
problems, and complications. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
18(10606)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lenhardt R and Sessler DI: Estimation of
mean body temperature from mean skin and core temperature.
Anesthesiology. 105:1117–1121. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sessler DI: Temperature monitoring and
perioperative thermoregulation. Anesthesiology. 109:318–338.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Krizanac D, Stratil P, Hoerburger D,
Testori C, Wallmueller C, Schober A, Haugk M, Haller M, Behringer
W, Herkner H, et al: Femoro-iliacal artery versus pulmonaryartery
core temperature measurement during therapeutic hypothermia: An
observational study. Resuscitation. 84:805–809. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Uleberg O, Eidstuen SC, Vangberg G and
Skogvoll E: Temperature measurements in trauma patients: Is the ear
the key to the core? Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med.
23(101)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Launey Y, Larmet R, Nesseler N, Malledant
Y, Palpacuer C and Seguin P: The accuracy of temperature
measurements provided by the edwards lifesciences pulmonary artery
catheter. Anesth Analg. 122:1480–1483. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Verheyden C, Neyrinck A, Laenen A, Rex S
and Van Gerven E: Clinical evaluation of a cutaneous zero-heat-flux
thermometer during cardiac surgery. J Clin Monit Comput.
36:1279–1287. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Iden T, Horn EP, Bein B, Böhm R, Beese J
and Höcker J: Intraoperative temperature monitoring with zero heat
flux technology (3M SpotOn sensor) in comparison with sublingual
and nasopharyngeal temperature: An observational study. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 32:387–391. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wagner M, Lim-Hing K, Bautista MA, Blaber
B, Ryder T, Haymore J and Badjatia N: Comparison of a continuous
noninvasive temperature to monitor core temperature measures during
targeted temperature management. Neurocrit Care. 34:449–455.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cereda M and Maccioli GA: Intraoperative
temperature monitoring. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 42:41–54.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fox RH, Solman AJ, Isaacs R, Fry AJ and
MacDonald IC: A new method for monitoring deep body temperature
from the skin surface. Clin Sci. 44:81–86. 1973.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Atallah L, Ciuhu C, Paulussen I, Bongers
E, Blom AHM, Idrissi A and Noordergraaf G: Perioperative
measurement of core body temperature using an unobtrusive passive
heat flow sensor. J Clin Monit Comput. 34:1351–1359.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Flouris AD and Cheung SS: The validity of
tympanic and exhaled breath temperatures for core temperature
measurement. Physiol Meas. 31:N35–N42. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Logie KM, Kusel MM, Sly PD and Hall GL:
Exhaled breath temperature in healthy children is influenced by
room temperature and lung volume. Pediatr Pulmonol. 46:1062–1068.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Caraballo C, Desai NR, Mulder H, Alhanti
B, Wilson FP, Fiuzat M, Felker GM, Piña IL, O'Connor CM, Lindenfeld
J, et al: Clinical Implications of the New York Heart Association
Classification. J Am Heart Assoc. 8(e014240)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Parsons PE, Eisner MD, Thompson BT,
Matthay MA, Ancukiewicz M, Bernard GR and Wheeler AP: NHLBI Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Clinical Trials Network. Lower tidal
volume ventilation and plasma cytokine markers of inflammation in
patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med. 33:1–6; discussion
230-2. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Lim H, Son KG and Ko S: Optimal
nasopharyngeal temperature probe placement. Anesth Analg.
119:875–879. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ellinas H and Albrecht MA: Malignant
hyperthermia update. Anesthesiol Clin. 38:165–181. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bindu B, Bindra A and Rath G: Temperature
management under general anesthesia: Compulsion or option. J
Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 33:306–316. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tufvesson E, Nilsson E, Popov TA,
Hesselstrand R and Bjermer L: Fractional exhaled breath temperature
in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or
systemic sclerosis compared to healthy controls. Eur Clin Respir J.
7(1747014)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sol IS, Kim YH, Kim SY, Choi SH, Kim HR,
Kim KW and Sohn MH: Exhaled breath temperature as a tool for
monitoring asthma control after an attack in children. Pediatr
Pulmonol. 54:230–236. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Crespo Lessmann A, Giner J, Torrego A,
Mateus E, Torrejón M, Belda A and Plaza V: Usefulness of the
exhaled breath temperature plateau in asthma patients. Respiration.
90:111–117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Melo RE, Popov TA and Sole D: Exhaled
breath temperature, a new biomarker in asthma control: A pilot
study. J Bras Pneumol. 36:693–699. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
26
|
Piacentini GL, Peroni DG, Bodini A,
Corradi M and Boner AL: Exhaled breath temperature as a marker of
airway remodelling in asthma: A preliminary study. Allergy.
63:484–485. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
de Castro J Jr, Bolfi F, de Carvalho LR
and Braz JR: The temperature and humidity in alow-flow anesthesia
workstation with and without a heat and moisture exchanger. Anesth
Analg. 113:534–538. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Piacentini GL, Bodini A, Peroni D, Ress M,
Costella S and Boner AL: Exhaled air temperature and eosinophil
airway inflammation in allergic asthmatic children. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 114:202–204. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Paredi P, Kharitonov SA and Barnes PJ:
Correlation of exhaled breath temperature with bronchial blood flow
in asthma. Respir Res. 6(15)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Piacentini GL, Peroni D, Crestani E,
Zardini F, Bodini A, Costella S and Boner AL: Exhaled air
temperature in asthma: Methods and relationship with markers of
disease. Clin Exp Allergy. 37:415–419. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pifferi M, Ragazzo V, Previti A, Pioggia
G, Ferro M, Macchia P, Piacentini GL and Boner AL: Exhaled air
temperature in asthmatic children: A mathematical evaluation.
Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 20:164–171. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
García G, Bergna M, Uribe E, Yañez A and
Soriano JB: Increased exhaled breath temperature in subjects with
uncontrolled asthma. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 17:969–972.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Svensson H, Nilsson D, Bjermer L and
Tufvesson E: Exhaled breath temperature increases after exercise in
asthmatics and controls. Respiration. 84:283–290. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Carpagnano GE, Lacedonia D, Spanevello A,
Martinelli D, Saliani V, Ruggieri C and Foschino-Barbaro MP:
Exhaled breath temperature in NSCLC: Could be a new non-invasive
marker? Med Oncol. 31(952)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lázár Z, Bikov A, Martinovszky F, Gálffy
G, Losonczy G and Horváth I: Exhaled breath temperature in patients
with stable and exacerbated COPD. J Breath Res.
8(046002)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|