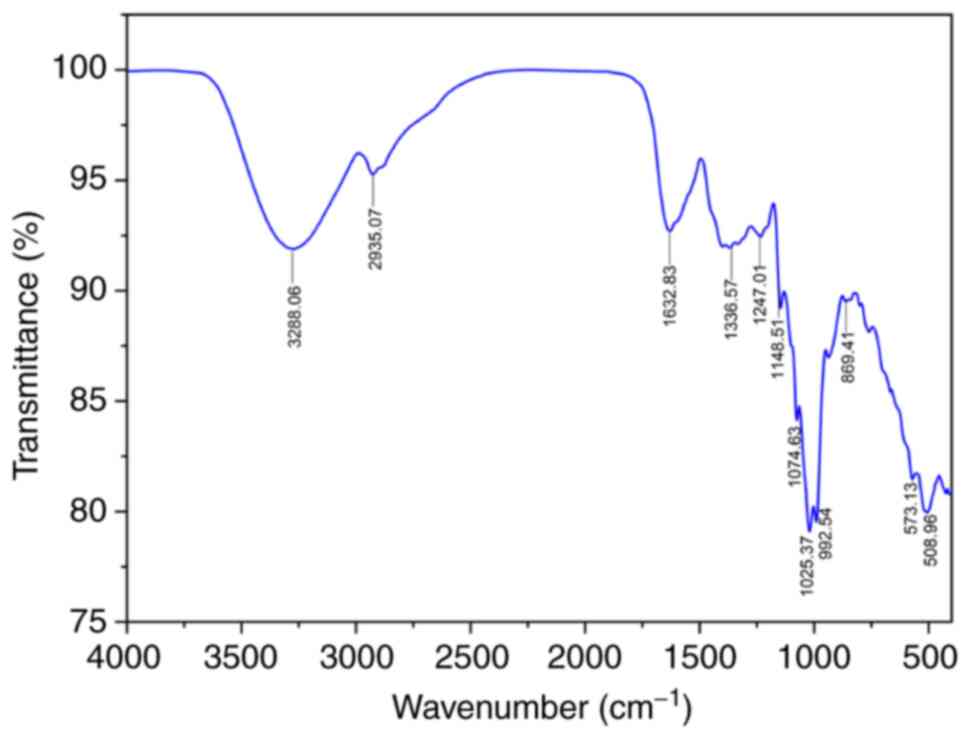
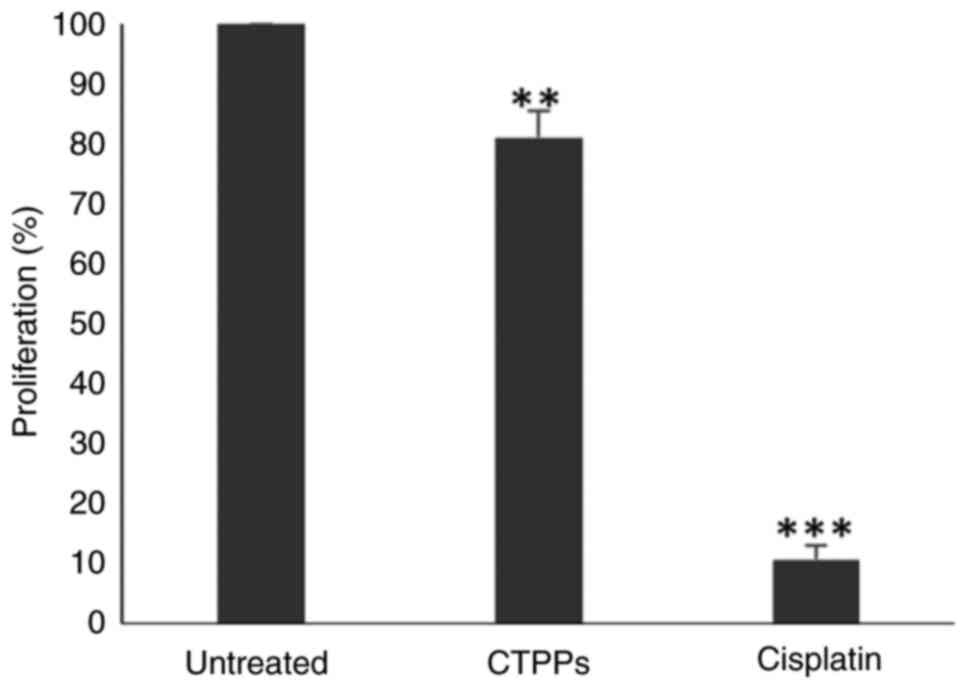
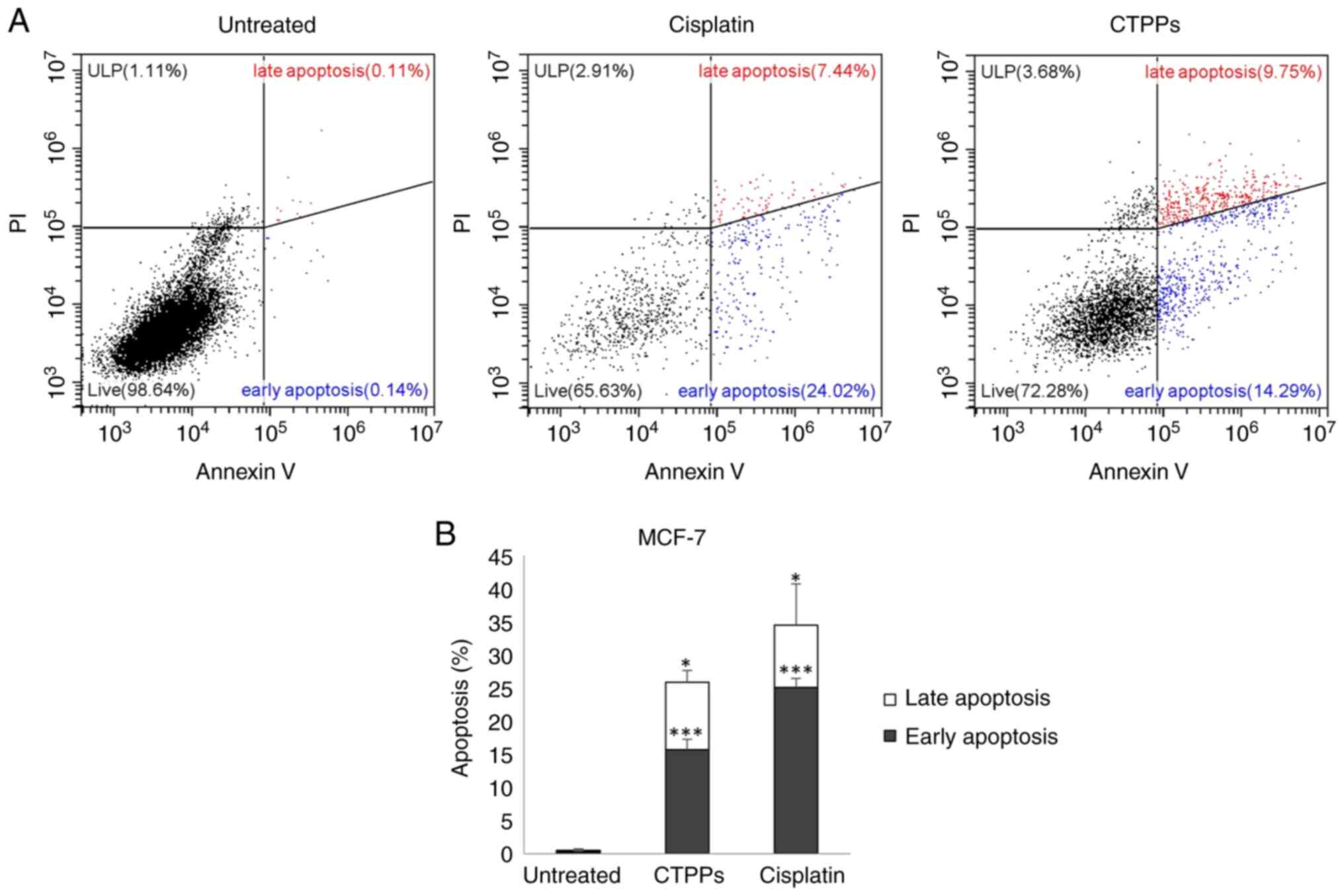
|
1
|
García MA, Fueyo R and Martínez-Balbás MA:
Chapter 10-lysine demethylases: Structure, function, and
disfunction. In: Chromatin Signaling and Diseases. Binda O and
Fernandez-Zapico ME (eds). Academic Press, Boston, pp179-194,
2016.
|
|
2
|
Ramírez K, Acevedo F, Herrera ME, Ibáñez C
and Sánchez C: Physical activity and breast cancer. Rev Med Chil.
145:75–84. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Spanish).
|
|
3
|
Prihantono and Faruk M: Breast cancer
resistance to chemotherapy: When should we suspect it and how can
we prevent it? Ann Med Surg (Lond). 70(102793)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ko EY and Moon A: Natural products for
chemoprevention of breast cancer. J Cancer Prev. 20:223–231.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Noel B, Singh SK, Lillard JW Jr and Singh
R: Role of natural compounds in preventing and treating breast
cancer. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 12:137–160. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang Z, Zhang Q, Yu L, Zhu J, Cao Y and
Gao X: The signaling pathways and targets of traditional Chinese
medicine and natural medicine in triple-negative breast cancer. J
Ethnopharmacol. 264(113249)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lin SR, Chang CH, Hsu CF, Tsai MJ, Cheng
H, Leong MK, Sung PJ, Chen JC and Weng CF: Natural compounds as
potential adjuvants to cancer therapy: Preclinical evidence. Br J
Pharmacol. 177:1409–1423. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
He N, Tian L, Zhai X, Zhang X and Zhao Y:
Composition characterization, antioxidant capacities and
anti-proliferative effects of the polysaccharides isolated from
Trametes lactinea (Berk.) Pat. Int J Biol Macromol. 115:114–123.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wan JMF: Chapter 27-polysaccaride krestin
(PSK) and polysaccharopeptide PSP. In: Handbook of Biologically
Active Peptides (Second Edition). Kastin AJ (ed). Academic Press,
Boston, pp180-184, 2013.
|
|
10
|
Zhang M, Yan M, Yang J, Li F, Wang Y, Feng
K, Wang S, Lin N, Wang Y and Yang B: Structural characterization of
a polysaccharide from Trametes sanguinea Lloyd with
immune-enhancing activity via activation of TLR4. Int J Biol
Macromol. 206:1026–1038. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jędrzejewski T, Pawlikowska M, Piotrowski
J and Kozak W: Protein-bound polysaccharides from Coriolus
versicolor attenuate LPS-induced synthesis of pro-inflammatory
cytokines and stimulate PBMCs proliferation. Immunol Lett.
178:140–147. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dou H, Chang Y and Zhang L: Chapter
Fifteen-coriolus versicolor polysaccharopeptide as an
immunotherapeutic in China. In: Progress in Molecular Biology and
Translational Science. Vol. 163. Zhang L (ed). Academic Press,
pp361-381, 2019.
|
|
13
|
Maehara Y, Tsujitani S, Saeki H, Oki E,
Yoshinaga K, Emi Y, Morita M, Kohnoe S, Kakeji Y, Yano T and Baba
H: Biological mechanism and clinical effect of protein-bound
polysaccharide K (KRESTIN(®)): Review of development and
future perspectives. Surg Today. 42:8–28. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kowalczewska M, Piotrowski J, Jędrzejewski
T and Kozak W: Polysaccharide peptides from Coriolus versicolor
exert differential immunomodulatory effects on blood lymphocytes
and breast cancer cell line MCF-7 in vitro. Immunol Lett.
174:37–44. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wan JMF, Sit WH and Louie JC:
Polysaccharopeptide enhances the anticancer activity of doxorubicin
and etoposide on human breast cancer cells ZR-75-30. Int J Oncol.
32:689–699. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kijpornyongpan T, Schwartz A, Yaguchi A
and Salvachúa D: Systems biology-guided understanding of white-rot
fungi for biotechnological applications: A review. iScience.
25(104640)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lueangjaroenkit P, Teerapatsakul C, Sakka
K, Sakka M, Kimura T, Kunitake E and Chitradon L: Two manganese
peroxidases and a laccase of Trametes polyzona KU-RNW027
with novel properties for dye and pharmaceutical product
degradation in redox mediator-free system. Mycobiology. 47:217–229.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wulandari R, Lotrakul P, Punnapayak H,
Amirta R, Kim SW and Prasongsuk S: Toxicity evaluation and
biodegradation of phenanthrene by laccase from Trametes
polyzona PBURU 12. 3 Biotech. 11(32)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Adongbede EM, Jaiswal YS, Davis SS,
Randolph PD, Huo LN and Williams LL: Antioxidant and antibacterial
activity of Trametes polyzona (Pers.) Justo. Food Sci
Biotechnol. 29:27–33. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Leyva A, Quintana A, Sánchez M, Rodriguez
EN, Cremata J and Sánchez JC: Rapid and sensitive anthrone-sulfuric
acid assay in microplate format to quantify carbohydrate in
biopharmaceutical products: Method development and validation.
Biologicals. 36:134–141. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tantray JA, Mansoor S, Wani RFC and Nissa
NU: Chapter 16-protein estimation by Lowry's method. In: Basic Life
Science Methods. Tantray JA, Mansoor S, Wani RFC and Nissa NU
(eds). Academic Press, pp65-67, 2023.
|
|
22
|
Ramos-Andrés M, Aguilera-Torre B and
García-Serna J: Hydrothermal production of high-molecular weight
hemicellulose-pectin, free sugars and residual cellulose pulp from
discarded carrots. J Clean Prod. 290(125179)2021.
|
|
23
|
Wu J, Kaewnarin K, Nie X, Li Q, He N,
Huang J and Geng A: Biological activities of a polysaccharide from
the coculture of Ganoderma lucidum and Flammulina velutipes mycelia
in submerged fermentation. Process Biochem. 109:10–18. 2021.
|
|
24
|
Sridhar K and Charles AL: In vitro
antioxidant activity of Kyoho grape extracts in DPPH and ABTS
assays: Estimation methods for EC50 using advanced
statistical programs. Food Chem. 275:41–49. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hanyu X, Lanyue L, Miao D, Wentao F,
Cangran C and Hui S: Effect of Ganoderma applanatum polysaccharides
on MAPK/ERK pathway affecting autophagy in breast cancer MCF-7
cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 146:353–362. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Meng Q, Li Y, Xiao T, Zhang L and Xu D:
Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of polysaccharides
isolated and purified from Diaphragma juglandis fructus. Int J Biol
Macromol. 105:431–437. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang S, He B, Ge J, Li H, Luo X, Zhang H,
Li Y, Zhai C, Liu P, Liu X and Fei X: Extraction, chemical analysis
of Angelica sinensis polysaccharides and antioxidant activity of
the polysaccharides in ischemia-reperfusion rats. Int J Biol
Macromol. 47:546–550. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li F, Wei Y, Liang L, Huang L, Yu G and Li
Q: A novel low-molecular-mass pumpkin polysaccharide: Structural
characterization, antioxidant activity, and hypoglycemic potential.
Carbohydr Polym. 251(117090)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li F, Yuan Q and Rashid F: Isolation,
purification and immunobiological activity of a new water-soluble
bee pollen polysaccharide from Crataegus pinnatifida Bge. Carbohydr
Polym. 78:80–88. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Luo QL, Tang ZH, Zhang XF, Zhong YH, Yao
SZ, Wang LS, Lin CW and Luo X: Chemical properties and antioxidant
activity of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Dendrobium
officinale. Int J Biol Macromol. 89:219–227. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mecozzi M, Pietroletti M, Scarpiniti M,
Acquistucci R and Conti ME: Monitoring of marine mucilage formation
in Italian seas investigated by infrared spectroscopy and
independent component analysis. Environ Monit Assess.
184:6025–6036. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pavia DL, Lampman GM, Kriz GS and Vyvyan
JR: Introduction to Spectroscopy. Brooks/Cole, 2009.
|
|
33
|
Sitkoff A: 90-Medicinal mushrooms. In:
Textbook of Natural Medicine (Fifth Edition). Pizzorno JE and
Murray MT (eds). Churchill Livingstone, St. Louis (MO),
pp679-692.e676, 2020.
|
|
34
|
Wang H, Liu YM, Qi ZM, Wang SY, Liu SX, Li
X, Wang HJ and Xia XC: An overview on natural polysaccharides with
antioxidant properties. Curr Med Chem. 20:2899–2913.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ajisaka K, Agawa S, Nagumo S, Kurato K,
Yokoyama T, Arai K and Miyazaki T: Evaluation and comparison of the
antioxidative potency of various carbohydrates using different
methods. J Agric Food Chem. 57:3102–3107. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen Y, Lin Q, Wang J, Mu J and Liang Y:
Proteins, polysaccharides and their derivatives as macromolecular
antioxidant supplements: A review of in vitro screening methods and
strategies. International Int J Biol Macromol. 224:958–971.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li X and Wang L: Effect of extraction
method on structure and antioxidant activity of Hohenbuehelia
serotina polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. 83:270–276.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang KF, Sui KY, Guo C and Liu CZ: Quorum
sensing molecule-farnesol increased the production and biological
activities of extracellular polysaccharide from Trametes
versicolor. Int J Biol Macromol. 104:377–383. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Knežević A, Stajić M, Sofrenić I,
Stanojković T, Milovanović I, Tešević V and Vukojević J:
Antioxidative, antifungal, cytotoxic and antineurodegenerative
activity of selected Trametes species from Serbia. PLoS One.
13(e0203064)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Amaral I, Silva C, Correia-Branco A and
Martel F: Effect of metformin on estrogen and progesterone
receptor-positive (MCF-7) and triple-negative (MDA-MB-231) breast
cancer cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 102:94–101. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Luo Z, Hu X, Xiong H, Qiu H, Yuan X, Zhu
F, Wang Y and Zou Y: A polysaccharide from Huaier induced apoptosis
in MCF-7 breast cancer cells via down-regulation of MTDH protein.
Carbohydr Polym. 151:1027–1033. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, Ye ZW, Tew KD and Townsend DM:
Cisplatin chemotherapy and renal function. Adv Cancer Res.
152:305–327. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Vaikundamoorthy R, Krishnamoorthy V,
Vilwanathan R and Rajendran R: Structural characterization and
anticancer activity (MCF7 and MDA-MB-231) of polysaccharides
fractionated from brown seaweed Sargassum wightii. Int J Biol
Macromol. 111:1229–1237. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xie Y, Jiang Z, Yang R, Ye Y, Pei L, Xiong
S, Wang S, Wang L and Liu S: Polysaccharide-rich extract from
Polygonatum sibiricum protects hematopoiesis in bone marrow
suppressed by triple negative breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
137(111338)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu H, Zou S and Xu X: The β-glucan from
Lentinus edodes suppresses cell proliferation and promotes
apoptosis in estrogen receptor positive breast cancers. Oncotarget.
8:86693–86709. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xu X, Zhu R, Ying J, Zhao M, Wu X, Cao G
and Wang K: Nephrotoxicity of herbal medicine and its prevention.
Front Pharmacol. 11(569551)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sivapatham S and Selvaraj L: Currently
available molecular analyses for personalized tumor therapy
(Review). Biomed Rep. 17(95)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Feitelson MA, Arzumanyan A, Kulathinal RJ,
Blain SW, Holcombe RF, Mahajna J, Marino M, Martinez-Chantar ML,
Nawroth R, Sanchez-Garcia I, et al: Sustained proliferation in
cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets. Semin Cancer
Biol. 35 (Suppl):S25–S54. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Peng Y, Li J and Zhu L: Chapter 8-cancer
and non-coding RNAs. In: Nutritional Epigenomics. Vol. 14. Ferguson
BS (ed). Academic Press, pp119-132, 2019.
|
|
50
|
Zhu YS and Zhu J: Molecular and cellular
functions of long non-coding RNAs in prostate and breast cancer.
Adv Clin Chem. 106:91–179. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Liu W, Jin W, Zhu S, Chen Y and Liu B:
Targeting regulated cell death (RCD) with small-molecule compounds
in cancer therapy: A revisited review of apoptosis,
autophagy-dependent cell death and necroptosis. Drug Discov Today.
27:612–625. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014(150845)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wan X, Jin X, Xie M, Liu J, Gontcharov AA,
Wang H, Lv R, Liu D, Wang Q and Li Y: Characterization of a
polysaccharide from Sanghuangporus vaninii and its antitumor
regulation via activation of the p53 signaling pathway in breast
cancer MCF-7 cells. Int J Biol Macromol. 163:865–877.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Jian L, Zhicheng H and Shubai L:
Polysaccharide peptide induced colorectal cancer cells apoptosis by
down-regulating EGFR and PD-L1 expression. Iran J Pharm Res.
21(e123909)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Di Nardo P, Lisanti C, Garutti M, Buriolla
S, Alberti M, Mazzeo R and Puglisi F: Chemotherapy in patients with
early breast cancer: Clinical overview and management of long-term
side effects. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 21:1341–1355. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|